Scrum Master vs Project Manager: Key Differences
A Scrum Master and a Project Manager play distinct roles in project management, despite sharing some similarities. Traditional Project Managers often focus on controlling and organizing resources, schedules, and processes to ensure project completion within specified constraints. In contrast, a Scrum Master facilitates communication, collaboration, and continuous improvement within the Scrum framework. This role emphasizes servant leadership, fostering an environment that enables high-performing teams to deliver valuable outcomes iteratively and incrementally.
The Scrum Framework: An Overview
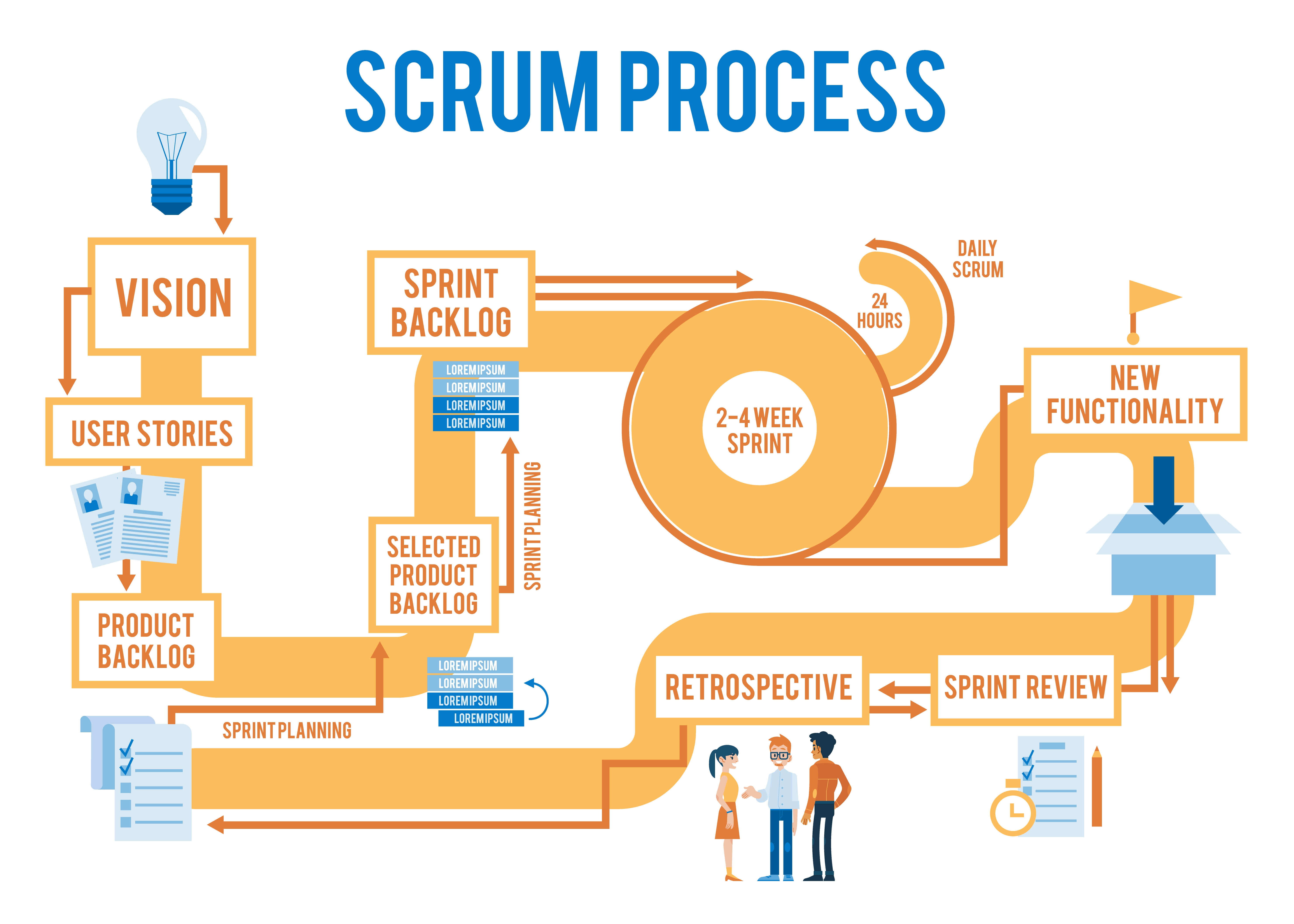
Scrum is an iterative and incremental Agile software development methodology that originated from a set of principles and practices developed by Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherland in the early 1990s. The Scrum framework is designed to promote efficient team collaboration, adaptability, and continuous improvement. It consists of three roles: the Product Owner, the Development Team, and the Scrum Master. The Scrum Master, as one of the key roles, facilitates communication, collaboration, and ensures the team adheres to Scrum principles and practices.
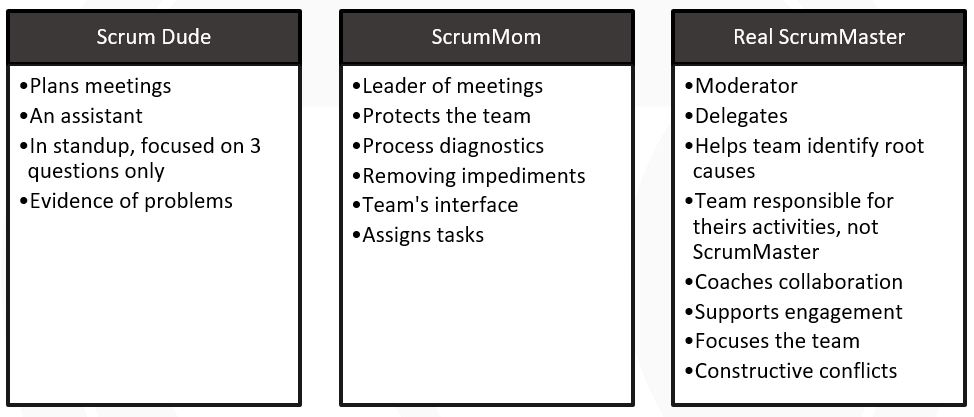
The Scrum Master: Primary Responsibilities
A Scrum Master’s primary responsibilities include facilitating daily Scrums, Sprint Planning, Sprint Reviews, and Sprint Retrospectives. These ceremonies ensure the team remains aligned with the project’s goals and maintains a consistent rhythm of work. By fostering a collaborative environment, the Scrum Master helps the Development Team self-organize and make decisions that lead to high-quality, incremental deliveries.
Moreover, Scrum Masters emphasize servant leadership, focusing on the needs of the team and removing any obstacles that hinder progress. By creating an environment that encourages continuous improvement, Scrum Masters empower teams to reach their full potential and deliver value to stakeholders more efficiently.
What is One Responsibility of the Scrum Master: Ensuring a Clear Product Vision
A crucial responsibility of the Scrum Master is to ensure the Product Owner communicates a clear product vision and backlog to the Development Team. The Scrum Master facilitates discussions between the Product Owner and the Development Team to clarify any ambiguities or misalignments in the product backlog items. By doing so, the Scrum Master helps maintain transparency and alignment between stakeholders and the Development Team, fostering a shared understanding of project goals and objectives.
The Scrum Master also encourages the Product Owner to continuously refine the product backlog, ensuring it remains up-to-date and accurately reflects the evolving needs of the project. This process helps the Development Team plan and execute sprints more effectively, delivering valuable increments that contribute to the overall product vision.
How to Excel as a Scrum Master: Building Trust and Collaboration
Building trust and collaboration within the Scrum Team is essential for a Scrum Master’s success. By employing strategies such as active listening, empathy, and fostering a culture of continuous learning and improvement, Scrum Masters can create an environment that encourages open communication and collaboration.
Active listening involves giving your undivided attention to team members during conversations, acknowledging their ideas and concerns, and providing thoughtful responses. This approach helps build trust and rapport, ensuring team members feel valued and heard.
Empathy is another crucial skill for Scrum Masters. By understanding and sharing the emotions, perspectives, and challenges of team members, Scrum Masters can create a supportive environment that fosters trust and collaboration. Empathy also helps Scrum Masters address conflicts and misunderstandings more effectively, maintaining a positive and productive team atmosphere.
Lastly, promoting a culture of continuous learning and improvement enables Scrum Masters to create high-performing teams. By encouraging experimentation, knowledge sharing, and constructive feedback, Scrum Masters can help teams identify areas for improvement, adapt to changing requirements, and stay up-to-date with industry trends and best practices.
Scrum Master Certification: Enhancing Credibility and Expertise
Scrum Master certifications, such as Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) and Professional Scrum Master (PSM), can significantly enhance a Scrum Master’s credibility and expertise in the field. These certifications demonstrate a solid understanding of Scrum principles and practices, as well as a commitment to continuous learning and improvement.
The CSM certification, offered by the Scrum Alliance, covers the fundamentals of Scrum, including its roles, artifacts, and ceremonies. It also emphasizes the importance of servant leadership and empirical process control in Scrum. The PSM certification, offered by Scrum.org, focuses on understanding and applying Scrum’s principles and practices in real-world situations.
Both certifications involve passing an exam that tests one’s knowledge of Scrum. Obtaining these certifications can lead to various benefits, such as improved job prospects, higher salaries, and increased confidence in facilitating Scrum events and coaching teams.
However, it is essential to remember that certifications are just one aspect of becoming an effective Scrum Master. Continuous learning, staying up-to-date with industry trends, and gaining hands-on experience are equally important for long-term success in the role.
Scaling Scrum: Scrum Master Challenges and Best Practices
Scaling Scrum in large organizations can present unique challenges for Scrum Masters. However, by applying best practices and adopting a flexible mindset, Scrum Masters can help their teams navigate these challenges and achieve success.
One of the primary challenges in scaling Scrum is coordinating multiple teams working on large-scale projects. To address this issue, Scrum Masters can implement techniques such as Scrum of Scrums, where representatives from each team meet regularly to discuss progress, dependencies, and potential risks. This approach helps maintain transparency and alignment across teams, fostering a collaborative environment that supports efficient problem-solving and decision-making.
Another challenge in scaling Scrum is ensuring consistency in practices and processes across teams. Scrum Masters can establish shared guidelines and standards, promote knowledge sharing and continuous learning, and provide training and coaching to help teams adopt Scrum best practices. This approach helps create a unified organizational culture that supports agility, innovation, and continuous improvement.
Success stories from organizations that have successfully scaled Scrum demonstrate the value of strong leadership, effective communication, and a commitment to continuous learning and improvement. By adopting these best practices, Scrum Masters can help their organizations achieve the benefits of Scrum at scale, including increased productivity, faster time-to-market, and higher levels of customer satisfaction.
Scrum Master Career Path: Opportunities and Growth
Scrum Masters can explore various career paths that build upon their foundational skills and experience in Agile project management. By continuously learning and staying up-to-date with industry trends and best practices, Scrum Masters can expand their expertise and pursue new opportunities for growth and development.
One potential career path for Scrum Masters is becoming an Agile Coach. In this role, Scrum Masters can leverage their expertise to help organizations adopt Agile methodologies more broadly, guiding multiple teams and stakeholders through the transition. Agile Coaches also focus on fostering a culture of continuous learning and improvement at the organizational level, driving long-term success and sustainability.
Another career path for Scrum Masters is transitioning to Director of Agile or similar leadership roles. In these positions, Scrum Masters can apply their experience and knowledge to oversee Agile practices and initiatives across the organization, driving strategic alignment and ensuring that Agile principles are consistently applied throughout the project lifecycle.
Scrum Masters can also consider transitioning to Product Owner or Developer roles. As Product Owners, Scrum Masters can leverage their understanding of customer needs, product vision, and Agile practices to prioritize and manage the product backlog, driving value creation and product innovation. As Developers, Scrum Masters can apply their technical expertise and Agile skills to contribute directly to the development of high-quality software products.
Regardless of the specific career path chosen, Scrum Masters should prioritize continuous learning and development to stay competitive and relevant in the ever-evolving field of Agile project management. By attending workshops, conferences, and networking events, Scrum Masters can expand their knowledge, build new skills, and connect with like-minded professionals, opening up new opportunities for growth and advancement.