Key Capabilities of Microsoft Defender for Cloud
Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a robust and comprehensive cloud-based security management tool that offers a wide range of functionalities to help organizations protect their cloud resources. The key capabilities of Microsoft Defender for Cloud include:
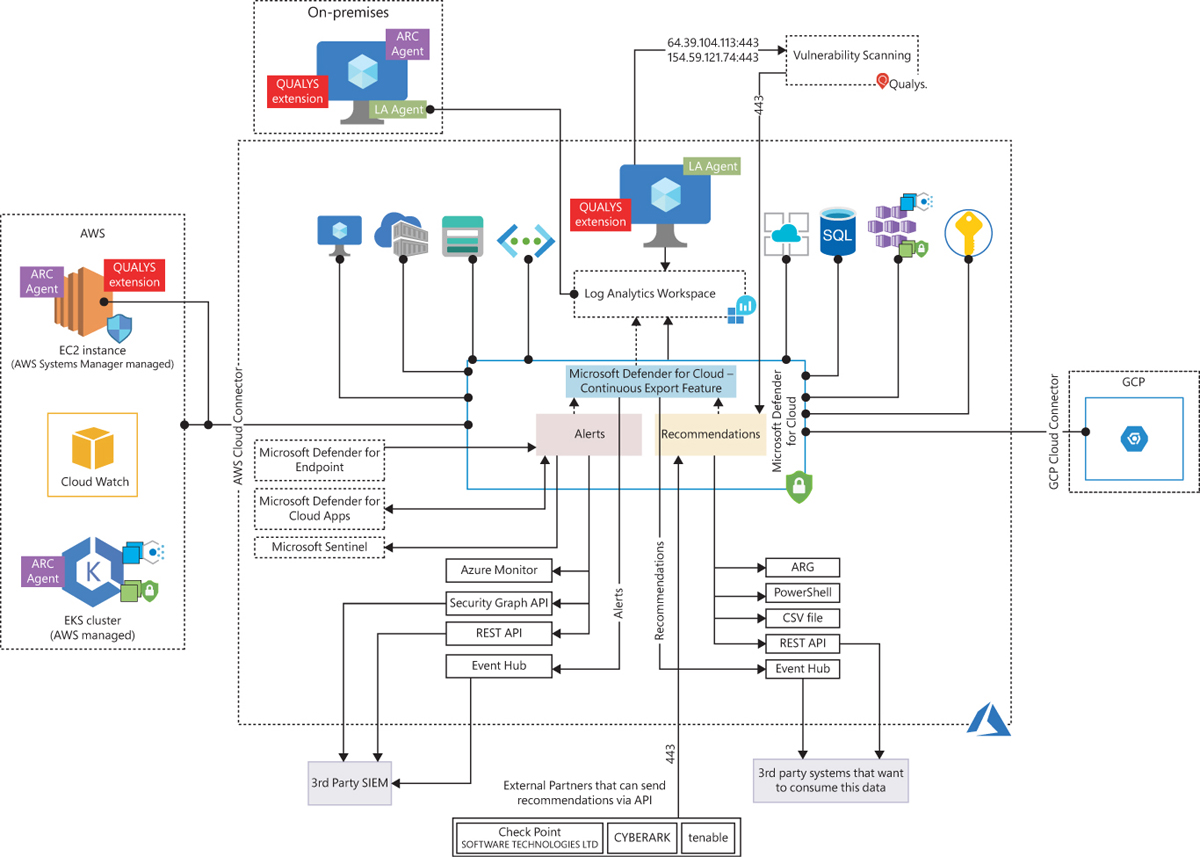
- Unified security management across multiple clouds: Microsoft Defender for Cloud supports multi-cloud environments, enabling organizations to manage and secure resources across Azure, AWS, and GCP using a single solution. This unified approach simplifies security management and reduces the complexity of managing multiple security tools.
- Threat detection and response: Microsoft Defender for Cloud uses advanced analytics and machine learning to detect threats and respond to security incidents in real-time. The tool continuously monitors cloud resources for suspicious activities and sends alerts to security teams when potential threats are detected. This enables organizations to respond quickly to security incidents and minimize the impact of cyber attacks.
- Security policy management: Microsoft Defender for Cloud allows organizations to define and enforce security policies across their cloud environments. This ensures that all cloud resources comply with the organization’s security standards and regulatory requirements. The tool also provides recommendations for improving security posture, enabling organizations to proactively address potential vulnerabilities.
- Regulatory compliance assessment: Microsoft Defender for Cloud includes built-in compliance assessment tools that help organizations comply with various regulatory standards, such as PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR. The tool provides a compliance score for each cloud resource, enabling organizations to identify and address compliance issues quickly.
- Integration with other Microsoft security tools: Microsoft Defender for Cloud integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft security tools, such as Microsoft Defender for Endpoint and Microsoft 365 Defender. This enables organizations to leverage the full range of Microsoft’s security capabilities and provides a holistic view of their security posture.
In summary, Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a powerful cloud-based security management tool that offers unified security management, threat detection and response, security policy management, regulatory compliance assessment, and integration with other Microsoft security tools. These capabilities make Microsoft Defender for Cloud a valuable asset for organizations looking to improve their cloud security posture and comply with regulatory requirements.
How to Set Up and Configure Microsoft Defender for Cloud
Setting up and configuring Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a straightforward process that can be completed in a few simple steps. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
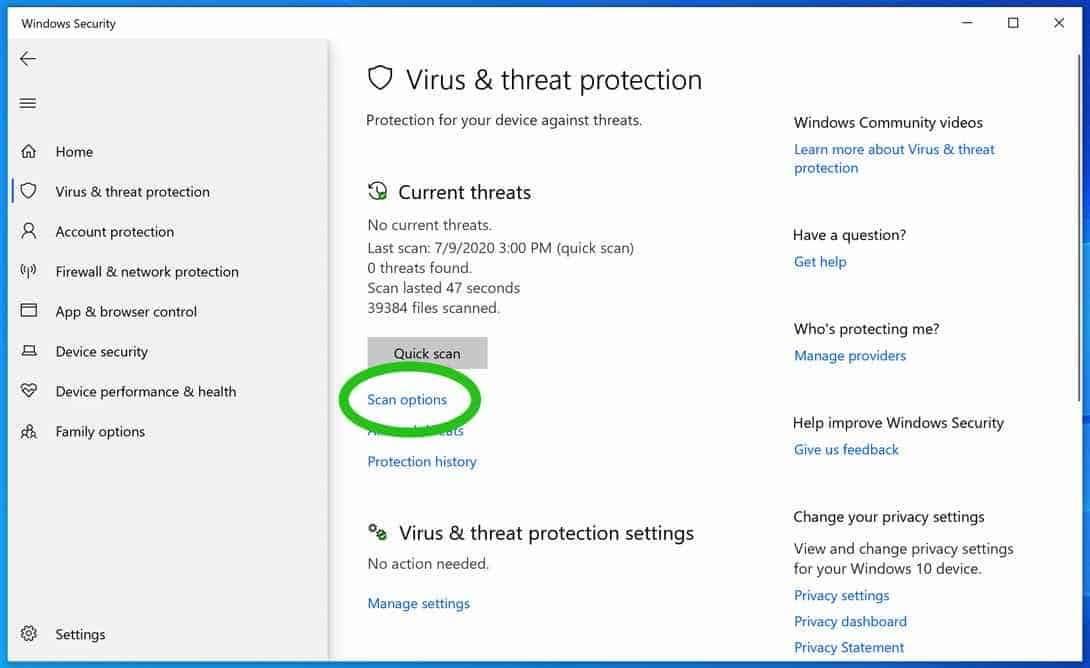
- Create a Microsoft Defender for Cloud account: To use Microsoft Defender for Cloud, you need to have a Microsoft Azure account. If you don’t have one, you can create a free account on the Microsoft Azure website. Once you have an account, navigate to the Microsoft Defender for Cloud dashboard and click on the “Get Started” button to create a new account.
- Connect cloud resources to the service: Microsoft Defender for Cloud supports multiple cloud platforms, including Azure, AWS, and GCP. To connect your cloud resources to the service, navigate to the “Subscriptions” page and click on the “Connect” button next to the cloud platform you want to connect. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the connection process.
- Set up security policies: Security policies are a set of rules and configurations that define how Microsoft Defender for Cloud should protect your cloud resources. To set up security policies, navigate to the “Security policies” page and click on the “Create policy” button. Follow the on-screen instructions to define the policy rules and configurations. You can also use pre-built policies provided by Microsoft or create custom policies that meet your specific security requirements.
- Configure notifications and alerts: Notifications and alerts are an essential part of Microsoft Defender for Cloud’s threat detection and response capabilities. To configure notifications and alerts, navigate to the “Settings” page and click on the “Notifications” tab. Here, you can define the notification channels, such as email or SMS, and the alert rules based on the severity and type of security events. You can also customize the alert thresholds and frequency to suit your needs.
By following these steps, you can set up and configure Microsoft Defender for Cloud to protect and monitor your cloud resources. Regularly reviewing security policies, monitoring alerts, and responding to threats promptly are essential best practices to make the most of Microsoft Defender for Cloud’s capabilities.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud Pricing and Plans
Microsoft Defender for Cloud offers flexible pricing plans to meet the needs of organizations of all sizes. Here are the available plans and their pricing details:
- Free plan: The free plan includes basic security features, such as vulnerability assessments, security recommendations, and threat detection for up to 50 assets. This plan is ideal for small organizations or those looking to test Microsoft Defender for Cloud’s capabilities before committing to a paid plan.
- Standard plan: The standard plan includes advanced security features, such as just-in-time access control, adaptive network hardening, and regulatory compliance assessment. This plan starts at $15 per node per month and is suitable for organizations with moderate security requirements.
- Premium plan: The premium plan includes all the features of the standard plan, plus additional capabilities, such as Microsoft Defender for SQL, Microsoft Defender for Container Registries, and Microsoft Defender for Key Vault. This plan starts at $25 per node per month and is ideal for organizations with complex security requirements and multiple cloud platforms.
It’s important to note that the pricing is based on the number of nodes protected, where a node can be a virtual machine, a Kubernetes cluster, or a SQL database. Microsoft Defender for Cloud also offers custom pricing for large-scale deployments and enterprise customers. To learn more about the pricing and plans, visit the Microsoft Defender for Cloud pricing page.
When choosing a plan, consider your organization’s security requirements, compliance needs, and budget. It’s also essential to regularly review your security policies and adjust your plan accordingly to ensure maximum protection and value for your investment.
Real-World Examples of Microsoft Defender for Cloud in Action
Microsoft Defender for Cloud has helped numerous organizations improve their cloud security posture and protect their cloud resources. Here are some examples of how Microsoft Defender for Cloud has been successfully implemented in real-world scenarios:
- Healthcare provider: A healthcare provider implemented Microsoft Defender for Cloud to secure their patient data and comply with regulatory requirements, such as HIPAA. By using Microsoft Defender for Cloud’s regulatory compliance assessment capabilities, the healthcare provider was able to identify and remediate vulnerabilities in their cloud environment, reducing their risk of a data breach and ensuring compliance with HIPAA regulations.
- Financial services firm: A financial services firm used Microsoft Defender for Cloud to secure their cloud-based applications and protect against cyber threats. By using Microsoft Defender for Cloud’s threat detection and response capabilities, the financial services firm was able to detect and respond to security incidents in real-time, reducing their risk of a data breach and protecting their customers’ sensitive information.
- Manufacturing company: A manufacturing company implemented Microsoft Defender for Cloud to secure their cloud-based infrastructure and protect against cyber threats. By using Microsoft Defender for Cloud’s unified security management capabilities, the manufacturing company was able to manage and monitor their cloud resources across multiple cloud platforms, reducing their risk of a security incident and improving their overall security posture.
These examples demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of Microsoft Defender for Cloud in securing cloud environments and protecting against cyber threats. By implementing Microsoft Defender for Cloud, organizations can improve their cloud security posture, comply with regulatory requirements, and protect their cloud resources from cyber threats.
Comparing Microsoft Defender for Cloud with Alternative Cloud Security Solutions
When it comes to cloud security, there are several tools and solutions available in the market. Here, we will compare Microsoft Defender for Cloud with alternative cloud security solutions, such as AWS Security Hub, Google Cloud Security Command Center, and third-party cloud security solutions.
- AWS Security Hub: AWS Security Hub is a cloud security posture management service that provides a comprehensive view of an organization’s security posture across their AWS environment. While AWS Security Hub offers similar threat detection and response capabilities as Microsoft Defender for Cloud, it is limited to the AWS platform. Therefore, organizations with a multi-cloud strategy may find it challenging to manage and monitor their cloud resources using AWS Security Hub alone.
- Google Cloud Security Command Center: Google Cloud Security Command Center is a security management and monitoring tool for Google Cloud Platform (GCP) resources. Similar to AWS Security Hub, Google Cloud Security Command Center is limited to the GCP platform and may not be suitable for organizations with a multi-cloud strategy. However, it offers robust security monitoring and threat detection capabilities, making it an ideal solution for organizations that primarily use GCP for their cloud infrastructure.
- Third-party cloud security solutions: Third-party cloud security solutions, such as CrowdStrike, McAfee, and Trend Micro, offer similar capabilities as Microsoft Defender for Cloud, including unified security management, threat detection and response, and regulatory compliance assessment. However, these solutions may require additional configuration and management efforts, and they may come with a higher price tag compared to Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
When choosing a cloud security solution, consider your organization’s cloud strategy, security requirements, and budget. Microsoft Defender for Cloud offers a cost-effective and comprehensive solution for securing and monitoring cloud resources across multiple cloud platforms. However, if your organization primarily uses a single cloud platform, such as AWS or GCP, you may want to consider the native security management and monitoring tools offered by these platforms.
Best Practices for Using Microsoft Defender for Cloud
Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a powerful tool for securing cloud environments, but it’s essential to follow best practices to make the most of its capabilities. Here are some recommendations and best practices for using Microsoft Defender for Cloud:
- Regularly review security policies: Security policies are the foundation of a strong cloud security posture. Regularly review and update your security policies to ensure they align with your organization’s security requirements and industry best practices. Microsoft Defender for Cloud provides built-in security policies that you can customize to meet your specific needs.
- Monitor alerts and respond to threats promptly: Microsoft Defender for Cloud provides real-time threat detection and response capabilities. Monitor alerts regularly and respond to threats promptly to minimize potential damage. Configure notifications and alerts to ensure you receive timely alerts for critical security events.
- Utilize built-in compliance assessment tools: Microsoft Defender for Cloud includes built-in compliance assessment tools that help you assess your cloud resources’ compliance with various regulatory standards, such as PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR. Utilize these tools to ensure your cloud resources comply with relevant regulatory standards and industry best practices.
- Integrate Microsoft Defender for Cloud with other security tools: Microsoft Defender for Cloud integrates with other Microsoft security tools, such as Microsoft Defender for Endpoint and Microsoft 365 Defender. Integrating these tools can provide a more comprehensive view of your organization’s security posture and enable more effective threat detection and response.
- Configure network security rules: Configure network security rules to control traffic flow and restrict access to your cloud resources. Microsoft Defender for Cloud provides network security recommendations and best practices to help you configure secure network security rules.
- Implement just-in-time access control: Just-in-time access control allows you to grant access to cloud resources only when necessary, reducing the attack surface and minimizing the risk of unauthorized access. Microsoft Defender for Cloud provides just-in-time access control capabilities for virtual machines and other cloud resources.
- Regularly backup and restore data: Regularly backup and restore data to ensure business continuity and data availability in case of a security incident or data loss. Microsoft Defender for Cloud provides backup and restore recommendations and best practices to help you implement effective backup and restore strategies.
By following these best practices, you can make the most of Microsoft Defender for Cloud’s capabilities and improve your cloud security posture. Regularly review and update your security policies, monitor alerts and respond to threats promptly, utilize built-in compliance assessment tools, integrate Microsoft Defender for Cloud with other security tools, and configure network security rules and just-in-time access control to ensure a strong cloud security posture.
Addressing Common Challenges and Limitations of Microsoft Defender for Cloud
While Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a powerful tool for cloud security management, it has some limitations and challenges that organizations should be aware of. Here are some common challenges and limitations of Microsoft Defender for Cloud and potential solutions:
- Managing false positives and false negatives: Microsoft Defender for Cloud may generate false positives or false negatives, which can lead to unnecessary alerts or missed security threats. To manage false positives and false negatives, regularly review and update your security policies, configure alert rules and thresholds, and investigate alerts to determine their legitimacy.
- Integrating with non-Microsoft cloud platforms: Microsoft Defender for Cloud primarily focuses on Azure, AWS, and GCP, but it may not fully support other cloud platforms. To integrate non-Microsoft cloud platforms with Microsoft Defender for Cloud, consider using third-party cloud security solutions that support multiple cloud platforms or using native security tools provided by the non-Microsoft cloud platforms.
- Addressing potential data privacy concerns: Microsoft Defender for Cloud collects and processes data from cloud resources, which may raise potential data privacy concerns. To address data privacy concerns, ensure you have a clear understanding of Microsoft Defender for Cloud’s data collection and processing practices, configure data collection and processing settings according to your organization’s data privacy policies, and use encryption and access controls to protect sensitive data.
- Limited customization options: Microsoft Defender for Cloud provides built-in security policies and recommendations, but it may not offer enough customization options for some organizations. To address this limitation, consider using custom security policies and rules, integrating Microsoft Defender for Cloud with other security tools, or using third-party cloud security solutions that offer more customization options.
- Limited visibility into on-premises environments: Microsoft Defender for Cloud primarily focuses on cloud environments, but it may not provide enough visibility into on-premises environments. To address this limitation, consider integrating Microsoft Defender for Cloud with other security tools that provide visibility into on-premises environments or using third-party cloud security solutions that support both cloud and on-premises environments.
By understanding and addressing these challenges and limitations, organizations can make the most of Microsoft Defender for Cloud’s capabilities and improve their cloud security posture. Regularly review and update security policies, manage false positives and false negatives, integrate Microsoft Defender for Cloud with other security tools, and use custom security policies and rules to ensure a strong cloud security posture.
The Future of Microsoft Defender for Cloud
Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a powerful and comprehensive cloud security management tool that has already proven its value in protecting and monitoring cloud resources across multiple platforms. As cloud computing continues to evolve and grow, so too will the need for robust and adaptable cloud security solutions. Here are some potential future developments and improvements for Microsoft Defender for Cloud:
- Potential new features and improvements: Microsoft Defender for Cloud is constantly evolving and improving, with new features and updates released regularly. Future developments may include enhanced threat intelligence, improved automation and orchestration capabilities, and expanded support for emerging technologies such as containerization and serverless computing.
- Integration with emerging technologies: As cloud computing continues to evolve, new technologies and architectures will emerge that require innovative security solutions. Microsoft Defender for Cloud is well-positioned to integrate with these emerging technologies, providing comprehensive security management and protection for cloud-native applications and infrastructure.
- The role of Microsoft Defender for Cloud in the evolving cybersecurity landscape: The cybersecurity landscape is constantly changing, with new threats and challenges emerging all the time. Microsoft Defender for Cloud is well-positioned to play a critical role in helping organizations navigate this evolving landscape, providing advanced threat protection, security management, and compliance features to help organizations safeguard their cloud environments.
By staying up-to-date with the latest developments and trends in cloud computing and cybersecurity, Microsoft Defender for Cloud can continue to provide organizations with the advanced threat protection, security management, and compliance features they need to safeguard their cloud environments. Whether you’re just getting started with cloud security or looking to enhance your existing security posture, Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a powerful and comprehensive tool that can help you achieve your goals.