Exploring the Essence of Data Tables
A data table is fundamentally an organized arrangement of information. It uses rows and columns to present data in a structured format. The primary purpose of a data table is to facilitate clarity and analysis. This structure is essential for organizing and presenting data across diverse fields. Fields include science, business, and technology. Data tables make it easier to understand complex information. They allow for efficient data manipulation and interpretation.
In essence, a data table, also known as a what is matrix table, provides a framework for organizing related pieces of information. Each row represents a single record, observation, or instance. Each column represents a specific attribute or characteristic of that record. This grid-like structure enables users to quickly locate, compare, and analyze data points. The organized format helps to identify patterns and trends, making data tables invaluable tools for decision-making. The concept of what is matrix table extends beyond simple spreadsheets. It encompasses various forms of structured data representation.
Furthermore, the use of data tables promotes consistency and accuracy in data handling. Standardized formats reduce the risk of misinterpretation and errors. The structure allows for easy integration with analytical tools and software. This makes it possible to perform complex calculations and visualizations. Understanding what is matrix table, is crucial in today’s data-driven world, where the ability to efficiently manage and analyze information is paramount. Data tables remain a cornerstone of effective data management, regardless of the specific application or industry.
Deciphering the Structure of Data Tables
Data tables are organized arrangements of information. They are built upon fundamental components that facilitate understanding and analysis. Rows and columns are the core building blocks. Rows are horizontal lines of data. Each row represents a single record or observation. This could be a customer, a product, or an experimental trial. Columns, on the other hand, are vertical lines of data. They represent specific attributes or variables associated with each record. For example, a column might contain names, ages, prices, or temperatures.
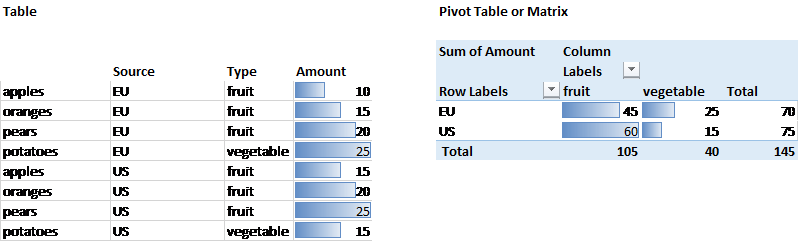
Headers play a crucial role in clarifying the contents of each column. A header is a label at the top of each column. It clearly describes the variable or attribute that the column contains. Without headers, it would be difficult to interpret the data within the table. Consider a “what is matrix table” scenario. A matrix table, a specific type of data table, also relies heavily on well-defined headers to accurately represent the relationships between variables.
Understanding the structure of data tables is essential for effective data management and analysis. Each component, from rows and columns to headers, contributes to the overall clarity and usability of the data. Properly structured tables allow for easy sorting, filtering, and analysis, providing valuable insights. Recognizing “what is matrix table” and how it fits within this broader context is critical for making informed decisions based on data. Consistent structure and clear labeling are key to avoiding misinterpretations and ensuring accurate data-driven outcomes. This systematic organization promotes a deeper comprehension of the relationships and trends within the data, ultimately improving decision-making processes.
How to Effectively Build Tables Using Spreadsheets
Creating data tables using spreadsheet software like Google Sheets or Microsoft Excel is a fundamental skill for data organization and analysis. This section provides a practical guide to building effective tables, ensuring data integrity, and maximizing usability. A matrix table is a specific type of data table often used for displaying relationships between two or more variables. Understanding how to construct general data tables is crucial before delving into more specialized forms like a matrix table.
Begin by opening a new spreadsheet in your chosen software. The first step involves inputting your data systematically. Each row should represent a single record or observation, while each column represents a specific attribute or variable. For example, in a sales dataset, each row might represent a single transaction, and columns could include date, product, quantity, and price. Ensuring accurate and consistent data entry is paramount. Utilize data validation features within the spreadsheet software to restrict the type of data that can be entered into specific cells. This helps prevent errors and maintains data consistency. For instance, you can set a column for dates to only accept valid date formats or a column for quantities to only accept numerical values. This contributes to what is matrix table, a data table organized for relationships and analysis.
Formatting your table is equally important for readability and comprehension. Start by adding headers to each column. Headers should clearly and concisely describe the data contained within each column. Use formatting options like bold text, different fonts, or background colors to distinguish headers from the rest of the data. Adjust column widths to accommodate the data without excessive whitespace. Consider using features like “Wrap Text” to display long text strings within a cell without overflowing into adjacent cells. These elements contribute to a well-structured table, whether a general data table or a specialized matrix table, for effective data exploration. Further enhance your table by applying borders to cells for better visual separation. Finally, remember to regularly save your work and back up your data to prevent data loss. This ensures that your efforts in creating an organized and informative table, including defining what is matrix table and its relationships within your dataset, are preserved for future analysis and reference.
Different Types of Tabular Data Structures
Data tables come in various forms, each suited to specific purposes and data management needs. One common type is the flat file, typically a simple text file where data is stored in rows and columns, often separated by delimiters like commas (CSV files) or tabs. Flat files are easy to create and transport, but they can be less efficient for complex queries and relationships compared to other data structures.
Relational database tables represent another significant type. These tables, found in systems like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or SQL Server, are structured to maintain relationships between different sets of data. Relational tables use primary and foreign keys to link related information across multiple tables, ensuring data integrity and enabling complex queries. The structure allows for efficient data retrieval and manipulation, making them ideal for applications requiring robust data management. A specific type worth exploring in detail is “what is matrix table” which shares qualities with the above but normally representing specifically mathematical data with more focus on rows and columns that can then be used to perform matrix operations. In general, the distinction from other data structures, such as graphs, lies in the explicit tabular format, where relationships are defined through keys rather than direct connections between nodes.
Pivot tables offer a dynamic way to summarize and analyze data. Often used in spreadsheet software, pivot tables allow users to rearrange and aggregate data based on different criteria, creating summaries and reports quickly. They are particularly useful for exploring trends and patterns within large datasets. Choosing the right type of data table depends on the specific application and the complexity of the data involved. Each type offers unique advantages and disadvantages in terms of storage, retrieval, and analysis capabilities. Understanding “what is matrix table” means grasping a more rigid structure focused on numerical relationships. Furthermore, a key consideration is also data volume. Flat files work well for smaller datasets while relational databases are designed to handle significantly larger amounts of structured information effectively.
Advantages of Using Organized Tables
Data tables offer substantial advantages, primarily by improving data organization. A well-structured table transforms raw data into an easily navigable format. This structured approach enhances readability and comprehension, making it simpler to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies. The enhanced clarity stems from the clear separation of data into rows (records) and columns (attributes), which facilitates quick information retrieval.
Moreover, data tables significantly facilitate data analysis. Sorting and filtering capabilities, inherent in most spreadsheet software, enable users to isolate specific data subsets for detailed examination. Calculations, ranging from simple sums and averages to complex statistical analyses, can be readily applied to the data within the table. This analytical power empowers users to derive meaningful insights and informed decisions from the information presented. Considering what is matrix table data representation, tables greatly contribute to simplifying complex data sets.
Efficiency gains in information retrieval are another major benefit. When data is organized into tables, specific information can be located quickly using search functions or by navigating through rows and columns. This contrasts sharply with unstructured data formats, where locating particular pieces of information can be time-consuming and arduous. Furthermore, the standardized format of data tables promotes consistency and reduces the likelihood of errors or misinterpretations. Considering what is matrix table, benefits can range from easy processing of information to allowing users to quickly draw conclusions and make decisions.
Applications Across Industries and Fields
Data tables are indispensable tools across a multitude of industries and fields, showcasing their adaptability and crucial role in organizing and interpreting information. Consider the realm of business, where sales data analysis relies heavily on tables to track performance, identify trends, and forecast future revenue. A well-structured table can reveal key insights into customer behavior, product popularity, and regional sales variations, enabling informed decision-making. The concept of what is matrix table might not be directly applicable here, but the underlying principles of data organization and analysis are shared.
In the sphere of scientific research, data tables are essential for recording and analyzing experimental results. Scientists use tables to document observations, measurements, and statistical findings. These tables facilitate the comparison of different experimental conditions, the identification of significant patterns, and the validation of hypotheses. What is matrix table becomes relevant in specific scientific applications, such as analyzing genetic data or representing complex relationships between variables in a matrix format. The organization of data in tabular form ensures accuracy and reproducibility of research findings.
Logistics and supply chain management also benefit significantly from the use of data tables. Inventory management systems rely on tables to track stock levels, monitor shipments, and optimize warehouse operations. These tables provide a real-time view of inventory status, enabling businesses to minimize storage costs, prevent stockouts, and improve order fulfillment efficiency. Furthermore, in healthcare, patient records, treatment plans, and medical research data are often organized in tables for easy access and analysis. Understanding what is matrix table can be helpful when dealing with complex data sets involving multiple variables and relationships in healthcare research. The widespread use of data tables across these diverse sectors underscores their fundamental importance in managing and interpreting information for enhanced productivity and informed decision-making.
Common Challenges and Potential Pitfalls
Working with data tables, while generally efficient, presents several challenges. Data inconsistencies represent a significant hurdle. These inconsistencies arise from various sources, including human error during data entry and flawed data collection processes. Addressing these inconsistencies is crucial for maintaining data integrity and ensuring accurate analysis. Errors in data entry are another common pitfall. Typos, incorrect formatting, and misinterpretations of data can all lead to inaccuracies. Careful data validation techniques, such as implementing data type constraints and range checks, can help minimize these errors. A what is matrix table, if poorly constructed or maintained, becomes susceptible to these errors.
Handling large datasets poses further challenges. As the volume of data increases, performance can degrade, and it becomes more difficult to identify and correct errors. Efficient data management practices, including data compression, indexing, and the use of specialized database systems, become essential. Outdated or redundant data contributes to inefficiencies and can skew analysis results. Regular data cleaning and archiving are necessary to maintain a streamlined and relevant dataset. The principles behind what is matrix table usage extend to dealing with large datasets, but the scale amplifies the potential problems.
To mitigate these risks, several best practices should be adopted. Data validation should be implemented at the point of entry to prevent errors from propagating through the dataset. Standardized data formats and naming conventions enhance consistency and facilitate data integration. Data cleaning procedures should be established to identify and correct inconsistencies, handle missing values, and remove duplicate records. Regular backups are essential to protect against data loss. Employing these strategies contributes to the creation of reliable and usable data tables. A well-managed what is matrix table, free from errors and inconsistencies, forms the basis for sound decision-making and insightful analysis.
Leveraging Tools for Analyzing Information in Tables
Analyzing data within tables often requires specialized tools beyond basic spreadsheet functionalities. A variety of software and programming languages are available to extract meaningful insights. Selecting the appropriate tool depends on the complexity of the data and the specific analytical goals. Understanding what is matrix table structures and their inherent data relationships is also crucial for effective analysis.
Statistical software packages, such as SPSS, SAS, and R, provide advanced analytical capabilities. These tools enable users to perform complex statistical tests, regression analysis, and hypothesis testing. They are particularly useful for researchers and data scientists who need to validate findings and build predictive models. Data visualization tools, like Tableau and Power BI, transform raw data into interactive dashboards and reports. These platforms facilitate the exploration of trends, patterns, and outliers, making it easier to communicate insights to a broader audience. A key consideration with these tools is understanding what is matrix table formatting and how they can be transformed into effective visualizations.
Programming languages like Python, with libraries like Pandas and NumPy, offer a flexible and powerful environment for data manipulation and analysis. Pandas provides data structures for efficiently storing and processing tabular data, while NumPy offers mathematical functions for performing complex calculations. These languages are ideal for automating data cleaning, transformation, and analysis tasks. Moreover, they can be integrated with machine learning libraries like Scikit-learn, enabling the development of predictive models. Deciding when to use each tool depends on factors such as the size and complexity of the data, the required level of analytical depth, and the user’s technical expertise. Effective utilization of these tools enhances the ability to understand what is matrix table data and extract actionable insights.