Understanding Docker Compose: A Developer’s Essential Tool
What is Docker Compose? It is a powerful tool designed to simplify the process of defining and managing multi-container Docker applications. Instead of wrestling with individual container configurations, Docker Compose allows developers to use a single YAML file to describe how all the different parts of an application fit together. This tool is particularly useful when your application is made up of multiple services, for instance, a web application might need a database and a caching server. Think of Docker Compose as a detailed blueprint. This blueprint outlines how these various pieces work and interact within your application ecosystem. It effectively eliminates the hassle of manually running and configuring multiple containers. Thus it gives you more time to focus on development itself. What is Docker Compose’s main advantage? It’s that it streamlines the management of complex applications. It lets you define your entire application stack in one easily manageable file.
This approach moves away from the tedious commands required to manage each container separately. Docker Compose promotes consistency, especially during the development process, meaning a developer can spin up their entire application environment using a single command. This capability provides predictability and efficiency. Imagine you are constructing a house, you don’t lay every brick individually without a plan. You rely on a blueprint to coordinate the placement of all elements. In a similar way, Docker Compose orchestrates your containers based on a single configuration file. It allows seamless interactions and dependencies between these containers. This tool makes it significantly easier to manage multi-container environments than traditional methods. It also facilitates easier scaling and testing.
By using Docker Compose, you are defining everything your application needs to run in a declarative manner. This includes the images, networking, and volume configurations. It ensures that your environment is replicated correctly on any machine that has Docker and Docker Compose installed. This makes sharing development environments with your team easier than ever before, and allows your application to consistently run during development, testing, and in production. Developers can spend less time on setup, and more time on enhancing features. This leads to better software and more efficient development cycles. This makes it easier to manage and understand complex applications. In essence, what is Docker Compose? It is a tool that makes container management for complex apps as easy as it should be.
How to Use Docker Compose: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a `docker-compose.yml` file is essential for using Docker Compose effectively. This file acts as the blueprint for your multi-container application. It defines the services, networks, and volumes needed. Begin by specifying the Compose file version. For example, use `version: ‘3.8’`. Next, define your services under the `services` key. Each service represents a container. Consider a simple web application with a database. The `services` section would include a web service and a database service. For the web service, you would specify an `image`, such as `nginx:latest`, or a `build` path if you’re building a custom image. Define port mappings with the `ports` key, like `ports: – “80:80″`. This maps the host’s port 80 to the container’s port 80. The database service might use an image such as `postgres:latest`. Environment variables can be configured using the `environment` key, providing values to your containers. For example, the database service needs a password. You would use the `environment` field to specify `POSTGRES_PASSWORD=mysecretpassword`. Volumes, declared using the `volumes` key, allow for data persistence. For example, the database data could be stored in a named volume to be persisted between container recreations.
A basic `docker-compose.yml` file structure would look like this:
version: '3.8'
services:
web:
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- "80:80"
db:
image: postgres:latest
environment:
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: mysecretpassword
volumes:
- db_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
volumes:
db_data:
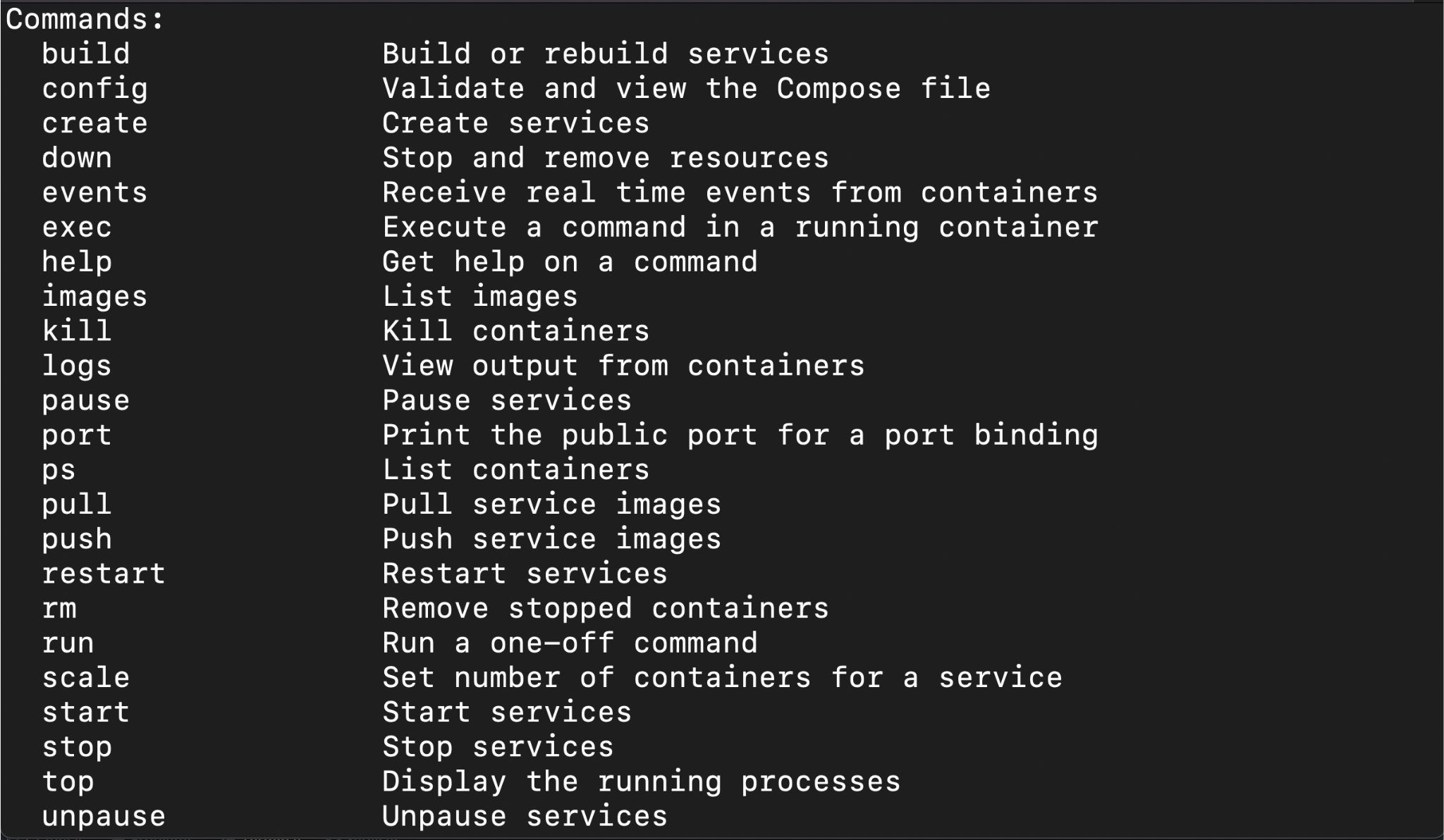
This is a basic example of a `docker-compose.yml` file. What is docker compose’s function here? It orchestrates these services. To start the application, use the command `docker-compose up -d`. This will build or pull the necessary images and start the services in detached mode. The `-d` flag runs the containers in the background. To stop and remove the containers, use the command `docker-compose down`. This process allows for quick and easy deployment of applications. The `docker-compose.yml` file can become complex as application requirements increase. This file is key to understanding how to use Docker Compose to its fullest potential. Keep it simple and organized. This approach makes maintenance and troubleshooting easier. By following these steps, you can effectively manage multi-container Docker applications.
Benefits of Utilizing Docker Compose in Your Workflow
Employing Docker Compose in your development workflow yields numerous advantages. The primary benefit is the simplified management of multi-container applications. Instead of wrestling with individual container commands, Docker Compose allows for defining the entire application stack in a single `docker-compose.yml` file. This file acts as a blueprint. It specifies how each service, such as web servers, databases, and message queues, should interact. This approach dramatically reduces complexity when handling multiple containers. With Docker Compose, developers can deploy complex applications with ease. Furthermore, what is docker compose? It promotes a consistent environment across various stages of software development. This consistency becomes essential when moving from development to testing, and then to production environments. Docker Compose ensures that the environment remains the same. This eliminates the common “it works on my machine” problem. It ensures all environments behave the same way.
Another considerable benefit stems from the easy replication of environments. Sharing the `docker-compose.yml` file with team members or across different machines enables the creation of identical application environments. This replication capability ensures that everyone works under the same conditions. Moreover, this speeds up onboarding of new developers. It also simplifies debugging and collaboration. Version control of your `docker-compose.yml` file is another key advantage. By managing your application’s definition file with a version control system, teams can track changes over time. This helps roll back to a previous working state if necessary. This greatly enhances stability. This way, it becomes easier to understand the history of your application’s architecture. This way, we can maintain a reliable build process. Ultimately, what is docker compose?, it saves significant time and effort when managing complex applications. It significantly speeds up development process and creates a robust system.
The time saved in setup and configuration allows developers to focus more on coding and features. Moreover, it also reduces the likelihood of errors related to environment misconfigurations. Docker Compose also ensures the software development lifecycle is more streamlined. This speeds up the overall time from concept to deployment. The ability to quickly deploy and manage multi-container applications is invaluable to modern development. What is docker compose?, is a tool that greatly simplifies the entire application lifecycle by providing automation and consistency in building, running and debugging. It allows teams to work more efficiently and reliably. This makes it an important tool for modern software development.
Docker Compose vs. Docker: Knowing the Key Differences
Understanding the distinction between Docker and what is docker compose is crucial for efficient container management. Docker, at its core, is a platform that allows you to build, run, and manage single containers. It uses the Docker CLI to execute commands for container creation, starting, stopping, and deletion. Think of Docker as the engine that powers individual containers, providing all the necessary tools to isolate and run your applications. It works well when dealing with applications that fit within a single container. Docker is very useful when deploying a simple application, such as a static web page, or a tool like a database. In contrast, Docker Compose is designed to manage multi-container applications. It provides a framework to define and run multiple containers that work together as a single unit. This is accomplished by using a YAML file to define a blueprint for the desired application setup. Docker compose leverages Docker API, allowing the orchestration of several containers at once. This allows you to set up the necessary networks, volumes, and dependencies for all your services in one simple file.
The key difference lies in their scope. Docker focuses on the lifecycle of individual containers. When you need to scale a complex application with numerous interconnected services, manually managing these through Docker CLI becomes tedious and error-prone. This is precisely where what is docker compose shines. Docker Compose simplifies the deployment of multi-container applications. It handles the creation, networking, and scaling of related services based on the specifications outlined in the `docker-compose.yml` file. For example, think about a web application that requires a database and a caching service. Docker alone would require you to manually run each container, configure their networks, and dependencies. However, using Docker Compose, the entire setup can be defined and launched with a single command. Docker compose is a tool that makes it easy to set up an environment and manage multiple containers with just one instruction.
To summarize, Docker is the fundamental technology for containerizing applications. It is used when working with individual containers. Docker compose orchestrates multiple containers using Docker API. It is preferred when your application needs several interlinked containers. Docker is essential for handling individual units, while what is docker compose streamlines the management of complex, multi-container applications. Therefore, the choice between them depends on the complexity of your application. Simple, single-container applications can just use Docker CLI. Complex, multi-service applications greatly benefit from using what is docker compose. Choosing the right tool will drastically simplify your development and deployment process.
Managing Application Dependencies with Docker Compose
Docker Compose significantly aids in handling application dependencies by enabling the definition of how different services interact within a multi-container application. Using the `depends_on` directive, one service can be set to start only after another service has been started and is running, ensuring that dependencies are properly initialized. For instance, a web application often relies on a database service; with Docker Compose, the web application service can be configured to depend on the database service. This ensures the database is fully operational before the web app attempts to connect, preventing common startup errors. This declarative approach to dependency management using a `docker-compose.yml` file is very beneficial and reduces the potential for errors.
Additionally, Docker Compose provides a network layer, allowing services to communicate with each other using their service names as hostnames. This means the web application can connect to the database using a consistent, simple network configuration that is abstracted away from low-level networking details. Instead of using IP addresses that may change, the web application simply connects to the database service using the database service name as its address. This greatly simplifies the networking complexity and promotes modular and scalable microservice architectures. This approach helps illustrate how what is docker compose helps to manage inter-service communication and dependencies effectively.
For example, consider a `docker-compose.yml` file where a web application service is named `web` and a database service is named `db`. The `web` service’s configuration would include a `depends_on: [db]` entry. This directive informs Docker Compose to start `db` before `web`. Furthermore, if the web application needs to connect to the database, it can refer to the database as just `db` because docker compose takes care of the networking part internally, so they can communicate easily, making the whole process very easy to manage and control. The whole process explains how what is docker compose plays an important role in simplifying the management of dependencies between microservices by providing a clear and concise way to define service relationships and dependencies.
Advanced Techniques in Docker Compose Configuration
Exploring beyond the basics, Docker Compose offers several advanced configuration options to optimize your multi-container application setups. Understanding build arguments allows for customization during the image building process, injecting specific values needed by the application. These arguments, defined in the `docker-compose.yml` file, can control variables like software versions or compilation flags. Environment variables are another powerful feature, enabling dynamic configuration without modifying the container image. This is particularly useful for managing database credentials, API keys, or other sensitive data. Environment variables can be defined directly in the compose file or loaded from an external `.env` file, enhancing security and flexibility. What is docker compose becomes even more powerful when leveraging these techniques.
Networks in Docker Compose permit isolated communication between services, ensuring that only necessary connections are allowed. You can define custom networks, specifying driver types and subnets, to match specific application needs. Docker volumes are essential for data persistence, allowing data to be shared across containers or preserved even when containers are restarted. They can be named for easy reference, facilitating better management of persistent data storage. The `extends` field is an often overlooked yet crucial functionality. It allows you to share common configurations between different compose files, fostering code reuse and simplifying complex setups. For instance, a base configuration with shared settings can be extended and modified for development or production, reducing redundancy. These advanced concepts enrich the understanding of what is docker compose capabilities and enable creation of efficient, maintainable, and adaptable applications.
Furthermore, integrating these advanced options judiciously can significantly enhance your docker compose workflow. Proper use of build arguments, ensures that images are built with necessary custom configurations based on your requirements. Strategic utilization of environment variables keeps configuration out of code and images. Employing networking correctly means that communication between containers is controlled and secure. Consistent use of volumes allows for data persistence. And finally, the `extends` option promotes modular configuration files. These advanced features make what is docker compose a robust tool for real-world deployment scenarios by providing a solid framework for building sophisticated, adaptable, and manageable applications.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Docker Compose
Encountering issues is part of the development process. When working with Docker Compose, several common problems can arise. One frequent issue is network configuration. Containers within a Docker Compose setup sometimes fail to communicate with each other. This often results from misconfigured network settings in the `docker-compose.yml` file. Check for correct network names and ensure services are in the same network. Port conflicts also present issues. If different services attempt to use the same port on the host machine, one will fail. It’s important to ensure each service uses unique host ports. Image building errors may also occur. When Docker Compose cannot build an image, it’s usually because of errors in the Dockerfile or problems accessing resources needed for the build. Always double-check the Dockerfile for syntax errors, missing files, and permissions issues. Syntax errors within the `docker-compose.yml` file are another common trouble. Errors in the structure, like missing colons, incorrect indentations, or unrecognized keys can prevent Docker Compose from interpreting the file correctly. It’s always recommended to validate the file with an online YAML parser, or by trying to execute it, where any syntax errors will be reported. What is docker compose is a complex tool with a lot of configurations, so these kind of problems are to be expected.
Debugging is key to solving Docker Compose issues. Start by examining the logs. Use the `docker-compose logs` command to view the logs of all services, or `docker-compose logs
Finally, practicing good code practices can prevent such problems. Ensure your `docker-compose.yml` file is clean and organized. Use version control for the `docker-compose.yml` file and the Dockerfile. Write clean docker files and avoid copying more code than necessary inside the images. Always review your configuration. If you keep a habit of using these methods, problems when using what is docker compose will be much less frequent. A well maintained and structured docker compose setup will reduce errors during development and production.
Optimizing Your Workflow: Integrating Docker Compose Best Practices
To fully leverage the power of what is docker compose, it’s crucial to adhere to best practices that ensure your configurations are not only functional but also maintainable and scalable. One of the most significant aspects is keeping your `docker-compose.yml` file clean and organized. This involves structuring your file logically, perhaps grouping services with similar functions or dependencies, and using consistent naming conventions. A well-structured compose file makes it easier for others to understand your setup, reduces the risk of errors, and simplifies future modifications. Furthermore, leverage the use of named volumes, which are essential for data persistence across container restarts. Named volumes also make it easier to back up and restore data, unlike bind mounts which are tied to your host system. Therefore, avoid relying on container storage for persistent data and always opt for named volumes for any kind of stateful service like a database.
Another critical best practice is effective management of secrets. Hardcoding sensitive data like API keys or passwords directly into your compose file or images is a major security risk. Instead, utilize Docker’s built-in secret management tools or third-party solutions to safely handle sensitive configuration. What is docker compose also integrates with environment variables seamlessly, allowing you to externalize sensitive data from your compose file by defining and loading them through an `.env` file or the system environment. This approach offers greater flexibility and security, especially when dealing with production environments. Ensure that your `.env` file, if used, is excluded from version control systems by adding it to your `.gitignore` file. By following these approaches you can ensure that your compose file doesn’t have any kind of private information exposed.
Finally, treat your `docker-compose.yml` file as any other piece of code by applying version control practices. Commit your compose file into a version control system, like Git, to keep a history of changes and enable collaborative development. This facilitates rollback capabilities in case of errors, allows teams to develop simultaneously, and promotes transparency and understanding in the project’s infrastructure. In addition, version control gives the possibility to revert changes easily and to have the chance to track what changes were made across the time and by which collaborators. By adopting these best practices, you will ensure that your use of what is docker compose is efficient, safe, and facilitates long-term project maintainability.