Unraveling the Concept: What is Defender?
Defender is a vital component in the realm of cybersecurity, specifically designed to protect systems and data from potential threats and attacks. Its primary function is to serve as a robust shield against malware, ransomware, and other malicious software, thereby maintaining the overall security and integrity of digital environments. In essence, Defender is a collection of security programs and tools that work in harmony to detect, prevent, and respond to cyber threats, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of critical data and systems.
The Role of Defender in Cybersecurity
Defender plays a pivotal role in the world of cybersecurity, safeguarding systems and data from an ever-evolving landscape of threats and attacks. As a critical line of defense, Defender serves as a robust shield against malware, ransomware, and other malicious software, ensuring the overall security and integrity of digital environments. By actively detecting, preventing, and responding to cyber threats, Defender helps maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of essential data and systems.
In today’s interconnected world, cybersecurity has become a top priority for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. With the increasing reliance on digital platforms and technologies, the risk of cyber threats has grown exponentially, making Defender an indispensable tool in the fight against cybercrime. By actively monitoring systems and networks, Defender helps identify potential vulnerabilities and threats, enabling users to take proactive measures to protect their digital assets.

How Defender Works: Understanding the Mechanism
Defender operates using a multi-layered approach to ensure comprehensive protection of systems and data. At its core, Defender focuses on three primary processes: detection, prevention, and response. By actively monitoring systems and networks, Defender is able to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities, preventing unauthorized access and mitigating the risk of data breaches.
Defender employs various advanced technologies, such as machine learning and behavior analysis, to detect and analyze potential threats. By continuously learning and adapting to new threats, Defender is able to stay one step ahead of cybercriminals, ensuring that systems and data remain secure. Additionally, Defender’s prevention mechanisms actively block known threats and suspicious activities, further reducing the risk of cyber attacks.
In the event of a security breach, Defender’s response capabilities enable users to quickly and effectively respond to the threat. By providing real-time alerts and detailed reports, Defender helps users take immediate action to contain and mitigate the impact of the breach, minimizing the potential damage and downtime.
Real-World Applications: Notable Products and Solutions
Defender has been integrated into various products and solutions, providing robust cybersecurity defenses for individuals, businesses, and organizations. Two of the most popular Defender-based solutions are Microsoft Defender and Defender for Endpoint.
Microsoft Defender
Microsoft Defender, formerly known as Windows Defender, is a built-in antivirus program for Windows operating systems. It offers real-time protection against various threats, including malware, ransomware, and spyware. Microsoft Defender also includes features such as automatic updates, cloud-delivered protection, and offline protection, ensuring comprehensive cybersecurity defenses for Windows users.
User reviews for Microsoft Defender have been generally positive, with many praising its ease of use, seamless integration with the Windows operating system, and reliable threat detection capabilities. However, some users have reported false positives and performance issues, highlighting the importance of proper configuration and maintenance.
Defender for Endpoint
Defender for Endpoint, formerly known as Windows Defender Advanced Threat Protection (ATP), is a cloud-based endpoint security solution designed for businesses and organizations. It provides advanced threat protection, automated investigation, and response capabilities, enabling security teams to quickly and effectively respond to cyber threats.
Defender for Endpoint has received positive reviews from users and industry experts, with many praising its comprehensive threat protection capabilities, user-friendly interface, and seamless integration with other Microsoft security solutions. However, some users have reported performance issues and compatibility problems with certain non-Microsoft applications and systems.

Implementing Defender: Best Practices and Recommendations
Implementing Defender in various settings requires careful planning, configuration, and maintenance. To ensure optimal performance and security, consider the following best practices and recommendations.
Proper Configuration
Properly configuring Defender is crucial for effective cybersecurity defense. This includes enabling real-time protection, configuring automatic updates, and setting up exclusions for trusted applications and folders. It is also important to regularly review and update Defender’s settings to ensure they are aligned with the latest security best practices and requirements.
Regular Maintenance
Regularly maintaining Defender is essential for ensuring its continued effectiveness and security. This includes regularly updating Defender’s definitions and software, performing system scans, and addressing any detected threats or vulnerabilities. It is also important to regularly review Defender’s logs and reports to identify any potential security issues or areas for improvement.
Monitoring and Alerts
Monitoring Defender and setting up alerts for potential security issues is crucial for proactive cybersecurity defense. This includes setting up email or SMS alerts for critical events, regularly reviewing Defender’s dashboard and reports, and integrating Defender with other security tools and systems for centralized monitoring and management.
Optimization for Specific Needs
Defender can be optimized for specific needs and requirements, such as performance, security, or compliance. This includes configuring Defender’s settings and policies for specific user groups, applications, or systems, and integrating Defender with other security solutions and tools for enhanced protection and visibility.

Comparing Defender with Other Security Solutions
Choosing the right cybersecurity solution is crucial for protecting systems and data from threats and attacks. While Defender is a powerful and effective solution, it may not always be the best fit for every organization or scenario. Here are some comparisons between Defender and other leading cybersecurity solutions, highlighting their similarities and differences, and discussing the advantages and disadvantages of each solution.
Defender vs. Antivirus Software
Defender is a built-in antivirus solution for Windows operating systems, but it can also be compared with third-party antivirus software. While Defender offers real-time protection, automatic updates, and cloud-delivered protection, third-party antivirus software may provide additional features, such as firewalls, email protection, and parental controls. However, third-party antivirus software may also come with a higher price tag and more complex configuration and maintenance requirements.
Defender vs. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Solutions
Defender for Endpoint is a cloud-based EDR solution designed for businesses and organizations. It provides advanced threat protection, automated investigation, and response capabilities, enabling security teams to quickly and effectively respond to cyber threats. However, it can also be compared with other EDR solutions, such as CrowdStrike or Carbon Black, which may offer additional features, such as threat hunting, sandboxing, and forensic analysis. While these solutions may provide more comprehensive protection, they may also require more technical expertise and higher costs.
Choosing the Right Solution
Choosing the right cybersecurity solution depends on specific needs, requirements, and budget constraints. When comparing Defender with other solutions, consider factors such as protection capabilities, performance, compatibility, ease of use, and cost. It is also important to consult with cybersecurity experts and conduct research, testing, and feedback to ensure the chosen solution meets the organization’s security and business objectives.
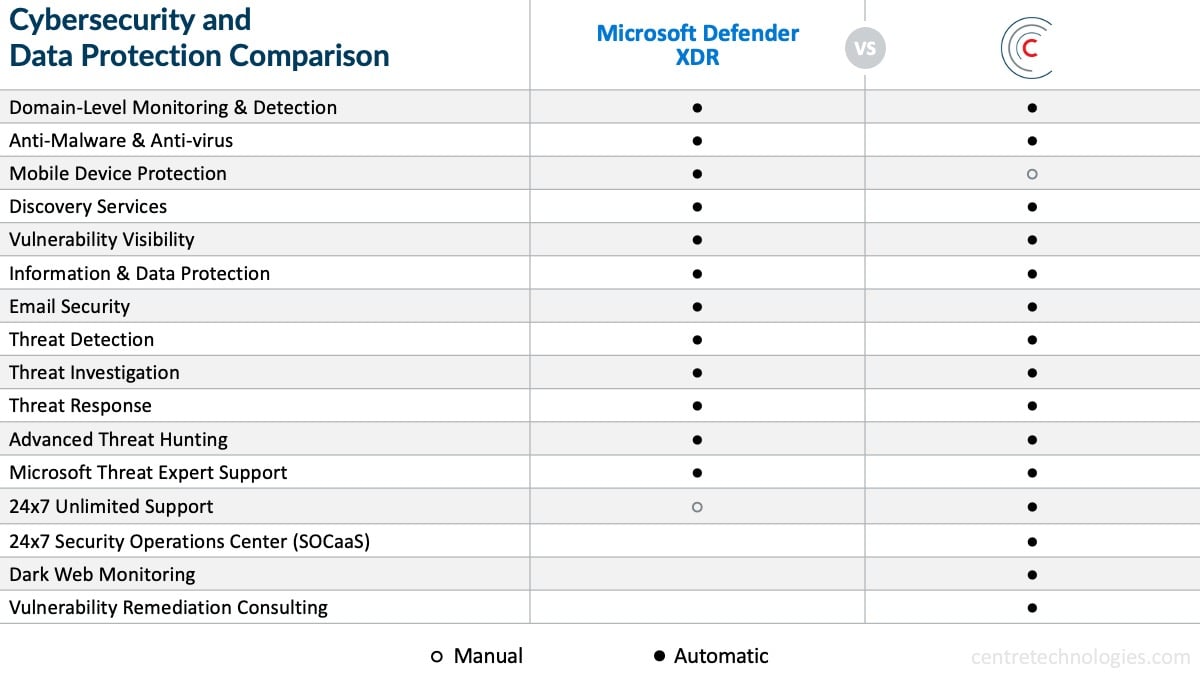
Staying Updated: Following the Evolution of Defender
Staying informed about the latest developments and updates in Defender is crucial for maintaining optimal cybersecurity defenses. Research, testing, and feedback play a vital role in improving Defender and keeping it up-to-date with the latest trends and best practices in cybersecurity.
Research
Researching Defender involves staying current with the latest cybersecurity threats, trends, and technologies. This includes reading industry publications, attending conferences, and participating in online forums and communities. By staying informed about the latest threats and trends, organizations can better understand how to configure and optimize Defender for their specific needs and requirements.
Testing
Testing Defender involves regularly conducting vulnerability assessments, penetration tests, and security audits. This helps identify potential weaknesses and vulnerabilities in Defender’s configuration, settings, and policies, and provides actionable insights for improving its performance and effectiveness. Testing should be conducted regularly, at least once a quarter, and should be integrated into the organization’s overall cybersecurity strategy and plan.
Feedback
Providing feedback on Defender is essential for improving its features, functionality, and performance. This includes reporting bugs, issues, and concerns to Microsoft, as well as sharing best practices, lessons learned, and success stories with the cybersecurity community. Feedback can be provided through various channels, such as Microsoft’s support forums, user groups, and social media platforms.
Staying Current
Staying current with the latest trends and best practices in cybersecurity involves regularly reviewing and updating Defender’s settings, policies, and configurations. This includes enabling automatic updates, regularly checking for new definitions and software updates, and integrating Defender with other security tools and solutions. By staying current with the latest trends and best practices, organizations can ensure that Defender remains an effective and reliable component of their cybersecurity strategy and plan.
Navigating Challenges: Addressing Common Issues and Concerns
Despite its many benefits and advantages, Defender may still encounter common issues and concerns, such as false positives, performance issues, and compatibility problems. Here are some practical solutions and workarounds to help readers navigate these challenges and optimize Defender for their specific needs and requirements.
False Positives
False positives occur when Defender incorrectly identifies a harmless file or application as a threat. To minimize false positives, it is important to regularly update Defender’s definitions and software, and to configure its settings and policies to suit the organization’s specific needs and requirements. It is also recommended to use exclusions for trusted files and applications, and to regularly review Defender’s logs and alerts to ensure accurate and reliable threat detection.
Performance Issues
Performance issues may arise when Defender consumes too many system resources, such as CPU, memory, and disk space. To optimize Defender’s performance, it is recommended to enable automatic updates, and to regularly check for new definitions and software updates. It is also advisable to configure Defender’s settings and policies to balance security and performance, and to use exclusions for resource-intensive files and applications. Regularly monitoring Defender’s performance metrics and logs can also help identify and address potential performance issues.
Compatibility Problems
Compatibility problems may occur when Defender conflicts with other security tools and solutions, or when it is not compatible with certain operating systems, applications, or hardware. To ensure compatibility, it is important to consult Defender’s system requirements and compatibility matrix, and to regularly check for updates and patches. It is also recommended to use Defender in conjunction with other compatible security tools and solutions, and to regularly review and update Defender’s settings and policies to ensure optimal compatibility and performance.
Seeking Professional Help and Support
For complex or persistent issues and concerns, it is advisable to seek professional help and support from Microsoft or a certified Defender partner. These experts can provide customized solutions and recommendations, as well as advanced diagnostic and troubleshooting tools and techniques. They can also help ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations, and provide ongoing maintenance and monitoring services to ensure optimal Defender performance and security.

