What are Containers in the Cloud Computing World?
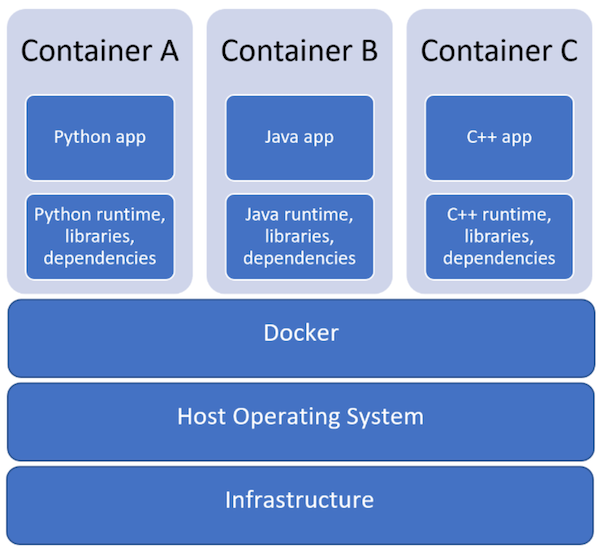
Imagine shipping containers at a port. Each container holds goods, neatly packaged and ready for transport. Cloud containers work similarly. They package software applications and all their dependencies – libraries, system tools, and runtime environments – into one unit. This makes applications portable and easy to move between different computing environments. Understanding what is container in cloud computing is key to efficient development and deployment. This self-contained nature simplifies the process of deploying and running applications. The key benefits include increased portability, ensuring consistent performance across various platforms, and improved efficiency in resource utilization. What is container in cloud? It’s a standardized unit for software distribution and deployment.
Containers isolate applications from the underlying infrastructure. This means an application running in a container won’t be affected by changes in the host operating system. This isolation improves consistency and reduces conflicts. A containerized application runs reliably across different machines, whether it’s a developer’s laptop, a testing server, or a production cloud environment. This solves many challenges that hinder traditional application deployments. What is container in cloud? It is a solution for consistent, reliable application delivery.
The portability of containers is a significant advantage. Developers can create an application once and deploy it to any environment supporting containers. This eliminates the compatibility issues often encountered with traditional deployments. They streamline the development lifecycle and facilitate collaboration among teams. What is container in cloud? It is a key component in achieving greater agility and efficiency in modern software development. Containers efficiently use resources, needing less overhead compared to virtual machines, thereby saving costs and improving performance. Understanding what is container in cloud is essential for anyone involved in modern software development and deployment.
How Containers Simplify Application Deployment
Deploying applications traditionally involves complex configurations and dependencies. Each environment (development, testing, production) might require different setups, leading to inconsistencies and deployment challenges. Understanding what is a container in cloud helps solve this. Containers, however, package the application and all its necessary components – libraries, dependencies, runtime environment – into a single unit. This ensures consistency across different environments. The same container image runs identically on a developer’s laptop, a testing server, and in production, simplifying the deployment process significantly. This consistency is a key advantage of understanding what is container in cloud and how it is used.
With containers, deployment becomes a matter of copying the container image to the target environment and running it. This contrasts sharply with traditional methods that often involve manual configuration, dependency management, and environment-specific adjustments. Containers streamline this process, reducing deployment time and minimizing errors. They provide a level of abstraction that isolates the application from the underlying infrastructure, making it highly portable. What is a container in cloud? It is a self-contained unit, encapsulating everything needed to run the application successfully. This simplifies troubleshooting, as issues are confined within the container itself. This dramatically reduces the risk of conflicts between applications or inconsistencies between environments.
Consider a scenario where an application requires specific versions of libraries or system tools. In a traditional deployment, ensuring these versions are consistent across environments can be a major headache. Containers eliminate this problem. The container image includes all necessary components, ensuring the application runs consistently regardless of the underlying infrastructure. This portability and consistency are paramount to understanding what is a container in cloud and how it improves operational efficiency. Containers, therefore, provide a reliable and efficient approach to application deployment, offering significant advantages over traditional methods. They simplify the process, reduce errors, and improve consistency across different environments. What is a container in cloud? It’s the answer to simplified and consistent application deployment.
Key Components of a Containerized Application
Understanding what is container in cloud computing requires examining its core components. A container packages everything an application needs to run: the application code itself, the necessary runtime environment (like a specific version of Python or Java), system tools, and libraries. These elements are bundled together, ensuring consistency across different environments. This is unlike traditional deployments where inconsistencies in dependencies can lead to deployment problems. The container isolates the application and its dependencies from the underlying infrastructure, promoting portability and enhancing reliability. What is container in cloud essentially boils down to this self-contained package.
Dockerfiles play a crucial role in creating container images. A Dockerfile is a text file that contains a set of instructions that Docker uses to build a container image. It specifies the base image, copies the application code, installs dependencies, sets environment variables, and defines the commands to run the application. This ensures repeatability and consistency across different deployments. Once built, this image becomes a template for creating new containers. It can be distributed and deployed efficiently across various platforms, further emphasizing the portability benefits of using containers. What is container in cloud, when examined closely, becomes a picture of efficient, repeatable deployment.
Docker images, created from Dockerfiles, are essentially read-only templates. They act as blueprints for creating containers. When you run a container, Docker creates a writable layer on top of the read-only image. This layer allows the container to make changes, but these changes only exist within the container’s lifetime. When the container is stopped, this writable layer is discarded. This feature ensures the container’s integrity and reduces the risk of unintended changes. The image itself, which acts as a base, remains unchanged. This approach provides stability and consistency, further explaining what is container in cloud and its value proposition. The process of creating and deploying images is a fundamental aspect of containerization. Efficient image management is key to successful container deployments in the cloud. Understanding how Docker images work is essential to grasping what is container in cloud.
Exploring Popular Container Orchestration Platforms
Container orchestration platforms automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Understanding what is container in cloud is crucial for leveraging these platforms effectively. These platforms address the complexities of managing numerous containers across multiple hosts. They handle tasks like scheduling, resource allocation, and health monitoring, significantly simplifying operations. Two leading examples are Kubernetes and Docker Swarm. Kubernetes, known for its scalability and robustness, is widely adopted for managing complex deployments. It excels in automating deployments across various cloud providers and on-premise infrastructure, offering features like self-healing and automated rollouts. Docker Swarm, a simpler solution integrated with Docker, is ideal for smaller-scale deployments or those seeking a more streamlined approach. It provides a good starting point for learning container orchestration, particularly when learning what is container in cloud.
The choice between Kubernetes and Docker Swarm depends largely on the specific needs of the application. For instance, applications requiring high availability and automatic scaling would benefit from Kubernetes’ advanced features. Its extensive community support and broad ecosystem make it a strong choice for larger, more complex projects. In contrast, Docker Swarm’s ease of use and integration with the Docker ecosystem make it an attractive option for developers who want a quicker and simpler way to manage a smaller number of containers. Understanding the fundamental aspects of what is container in cloud is vital for making an informed decision. Both platforms offer significant advantages over manually managing containers. They alleviate the overhead associated with resource management, ensuring efficient utilization of computing resources. Choosing the right platform ensures the application scales effectively and efficiently as user demands change.
Container orchestration platforms significantly enhance the efficiency and scalability of containerized applications. Understanding what is container in cloud and how orchestration platforms work is essential for building robust and scalable cloud-native applications. These platforms are crucial for organizations seeking to modernize their infrastructure and deploy applications more efficiently. The ability to automate deployment, scaling, and management of containers simplifies operations and allows developers to focus on application development rather than infrastructure management. The proper utilization of these tools is critical for harnessing the full potential of container technology in cloud environments and understanding what is container in cloud.
Choosing the Right Containerization Strategy for Your Needs
Understanding when to utilize containers is crucial for maximizing their benefits. What is container in cloud computing? It’s a powerful tool, but not always the optimal solution. Containerization shines when dealing with microservices architectures. These are applications broken down into small, independent units. Containers excel at managing and deploying these units efficiently. This modular approach improves scalability and simplifies updates. The portability aspect also becomes invaluable for developers testing across different environments before production.
Conversely, monolithic applications – those built as a single, large unit – might not see as much benefit from containerization. The overhead of managing containers might outweigh the advantages in such cases. Factors to consider include the application’s complexity, its scaling requirements, and the existing infrastructure. A simple application with minimal scaling needs might be better served by traditional deployment methods. However, if the application anticipates significant growth or requires frequent updates, containers offer a robust and flexible solution. What is container in cloud? Essentially, it’s a way to package an application and its dependencies for easy deployment and scaling in cloud environments. Careful consideration of these factors ensures that the chosen containerization strategy aligns with the specific needs of the application.
Another important factor to consider is the team’s expertise. Implementing and managing containerized applications requires familiarity with tools like Docker and Kubernetes. If the team lacks this experience, adopting containers might introduce unnecessary complexity and delays. Therefore, a realistic assessment of the team’s skills and the available resources is essential before committing to a containerization strategy. What is container in cloud? Simply put, it’s a method for packaging, deploying, and managing applications efficiently. But choosing the right approach demands a thorough understanding of the application’s characteristics and the team’s capabilities. A well-informed decision ensures that containerization enhances efficiency and scalability without adding undue complexity.
How to Get Started with Cloud Containers: A Practical Guide
Understanding what is a container in cloud computing is the first step. This practical guide demonstrates setting up a simple containerized application using Docker and a cloud provider. The example focuses on a “Hello World” application, illustrating the core principles. This process helps clarify what is container in cloud and its advantages. First, install Docker Desktop on your local machine. This software simplifies the process of building and running containers. Next, create a simple application—a text file containing “Hello, World!”—and a Dockerfile to define the container image. The Dockerfile specifies the base image (a lightweight Linux distribution), copies the application file, and sets the command to execute. Build the Docker image using the `docker build` command. This creates a container image containing your application and all its dependencies. After building, test the image locally using `docker run`. This ensures the application runs correctly before deployment. This local testing is crucial before moving to a cloud environment, helping you understand what is a container in cloud.
To deploy to a cloud provider, choose a service like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure. Each offers managed container services, simplifying deployment and management. For this example, let’s consider Google Cloud Run. This serverless platform handles scaling and infrastructure automatically. Push your Docker image to a container registry like Google Container Registry (GCR). You’ll need to authenticate your local Docker client to push the image. After pushing, deploy the image to Cloud Run using the Google Cloud console or command-line tools. Cloud Run will create and manage the container instances, automatically scaling them based on demand. Observe your application running on Cloud Run—access it through the URL provided by Google Cloud. This process introduces the practical aspects of what is a container in cloud. The deployment method varies slightly depending on the cloud provider, but the core concepts—building the image and deploying it to a managed service—remain consistent. This reinforces the portability aspect of containers, a key benefit of understanding what is a container in cloud.
This example provides a basic understanding of deploying a containerized application. It highlights the simplicity and efficiency of containerization, particularly when compared to traditional methods. While simple, it demonstrates the key steps involved in answering what is a container in cloud and how it simplifies deployment. More complex applications will require additional configuration and considerations, but this foundational knowledge is essential for working with cloud containers. Remember, security best practices, covered elsewhere in this guide, should be implemented at every stage of development and deployment for a robust and secure cloud containerized application. To better grasp what is a container in cloud, experiment with different aspects like scaling your application or adding more features.
Security Best Practices for Cloud Containers
Securing containerized applications is crucial for maintaining data integrity and system stability. Understanding what is container in cloud and its inherent security implications is the first step. Containers, while offering numerous advantages, also introduce new security challenges. A robust security strategy involves multiple layers of protection, starting with secure image creation. Employing automated image scanning tools helps identify vulnerabilities before deployment. Regular vulnerability assessments are essential to detect and address emerging threats. These processes ensure that what is container in cloud remains a secure and efficient method for application deployment.
Network security plays a vital role in protecting containerized environments. Implementing strong network segmentation isolates containers from each other and external networks. This reduces the impact of potential breaches. Utilizing firewalls and intrusion detection systems further enhances the security posture. Access control mechanisms, including role-based access control (RBAC), limit who can access and manage containers and their underlying infrastructure. Careful management of credentials and secrets is also critical to prevent unauthorized access. What is container in cloud security? It requires a multi-faceted approach.
Beyond technical measures, robust security practices are essential. Regular security audits and penetration testing uncover weaknesses in the system. Keeping software up-to-date, especially container runtimes and libraries, is critical for patching known vulnerabilities. Adopting a DevOps security model, integrating security into the software development lifecycle, significantly improves overall security. Continuous monitoring and logging of container activity enable rapid detection and response to security incidents. Understanding what is container in cloud security and how to implement these measures is paramount for maintaining a safe and reliable cloud infrastructure. These practices, along with a strong focus on secure development practices, form a complete security framework, ensuring the long-term security of your cloud container environment. What is container in cloud security? It requires attention to detail, and multiple layers of security.
Comparing Container Services from Major Cloud Providers
Understanding what is a container in cloud computing is crucial before exploring the services offered by major providers. Each major cloud platform—Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure—provides managed container services. These services simplify the deployment, management, and scaling of containerized applications. AWS offers Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) and Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS). ECS provides a managed container orchestration service, while EKS is a managed Kubernetes service. Both offer different approaches to managing containers, catering to varying needs and expertise levels. Choosing between them often depends on the level of control required and existing infrastructure.
Google Cloud Platform’s Kubernetes Engine (GKE) is a highly popular and robust managed Kubernetes service. GKE offers auto-scaling, automatic upgrades, and integrates well with other GCP services. It’s a strong contender for organizations already invested in the Google ecosystem or seeking a feature-rich Kubernetes solution. Understanding what is a container in cloud computing, and subsequently how GKE manages them, is essential for leveraging its capabilities effectively. This service simplifies many operational tasks, allowing developers to focus on application development rather than infrastructure management. The pricing models for GKE are based on resource consumption, with various options available for optimizing costs.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) is Microsoft’s managed Kubernetes offering. Similar to GKE and EKS, AKS simplifies the deployment and management of Kubernetes clusters. AKS integrates seamlessly with other Azure services, making it a compelling choice for organizations using the Azure cloud. When considering what is a container in cloud computing and the various platforms for managing them, AKS presents a robust and well-integrated solution. Azure offers various pricing tiers, allowing for flexible cost management based on resource usage. Each provider’s service offers similar core functionalities, but the specific features, integration options, and pricing models vary. The best choice depends on the specific requirements of the application and the overall cloud strategy.