Blue Green: A Dichotomy Explained
The term “blue green” often refers to a duality or a combination of two distinct elements. This concept has found its way into various fields, including technology, environmental science, and design. The unique interplay between these two entities offers a fresh perspective and valuable insights in each of these domains.
When exploring the question “what is blue green,” one can find a myriad of applications and interpretations. In technology, for instance, blue green represents a deployment strategy that minimizes downtime and reduces risk during system updates. Meanwhile, in environmental science, blue green alludes to the symbiotic relationship between aquatic ecosystems and blue-green algae, as well as the breathtaking phenomenon of blue green galaxies and bioluminescent bays.
Moreover, in design, blue green serves as a striking color combination that can evoke specific emotions and reactions in users and customers. By understanding the significance of blue green in these diverse contexts, one can appreciate the versatility and depth of this intriguing concept.
Blue Green in Technology: Infrastructure and Deployment Methods
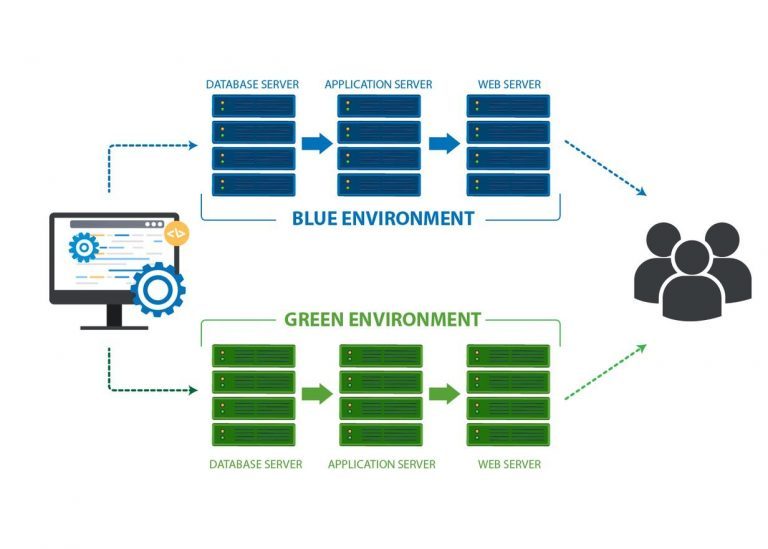
The concept of blue green in technology revolves around a sophisticated deployment strategy that minimizes downtime and risk during system updates. This approach involves running two identical production environments, known as Blue and Green, with one environment serving as the live production environment, while the other undergoes maintenance and updates.
At its core, the blue green method ensures a seamless transition between environments, allowing for quick rollbacks in case of issues during updates. By maintaining a stable and functional environment at all times, businesses can minimize disruptions and maintain high levels of customer satisfaction.
When examining the question “what is blue green” in the context of technology, it’s essential to understand the benefits of this deployment strategy. Blue green methods significantly reduce downtime, as the switch between environments typically takes only a few seconds. Additionally, this approach minimizes risk during system updates, as the updated environment remains isolated from the live production environment until it’s thoroughly tested and deemed stable.
Moreover, blue green technology enables efficient rollbacks in case of issues during updates. By simply switching back to the previous environment, businesses can quickly resolve any problems without affecting the user experience. This flexibility and adaptability are crucial in today’s fast-paced digital landscape, where downtime and system instability can lead to significant losses in revenue and customer trust.
Blue Green in Environmental Science: Algae and Natural Phenomena
The environmental aspect of blue green encompasses two primary areas: blue-green algae in aquatic ecosystems and the natural phenomenon of blue green galaxies and bioluminescent bays. Both of these elements showcase the unique interplay between blue and green, highlighting the importance of this dichotomy in the natural world.
Blue-Green Algae in Aquatic Ecosystems
Blue-green algae, also known as cyanobacteria, play a crucial role in aquatic ecosystems. These microorganisms are responsible for producing oxygen through photosynthesis, contributing significantly to the Earth’s atmosphere. Furthermore, blue-green algae serve as a vital food source for various aquatic creatures, supporting complex food webs and maintaining ecological balance.
Blue Green Galaxies and Bioluminescent Bays
In the cosmos, blue green galaxies and bioluminescent bays display the captivating beauty of this dichotomy. Blue green galaxies are rare celestial objects characterized by their unique color combination, resulting from the presence of young, hot stars and vast clouds of interstellar gas. Similarly, bioluminescent bays exhibit a mesmerizing blue green glow, created by the interaction between single-celled organisms called dinoflagellates and chemical reactions in the water.
When considering the question “what is blue green” in the context of environmental science, it’s evident that this dichotomy represents a delicate balance between two distinct elements. By understanding the role of blue green in nature, we can appreciate the intricate relationships that exist between various ecosystems and the universe at large.
Blue Green in Design: Color Theory and Aesthetics
The combination of blue and green in design offers a unique and versatile color palette that can evoke various emotions and reactions in users and customers. By understanding the psychological impact of these colors and their harmonious relationship, designers can create captivating visual experiences that resonate with their target audience.
Color Theory: The Basics
Color theory is a fundamental concept in design, encompassing the relationships between colors and the visual effects they create. Blue and green, when combined, form a soothing and balanced palette that can convey feelings of tranquility, growth, and stability. Designers can manipulate the intensity, saturation, and hue of these colors to achieve the desired visual impact.
Aesthetics and Emotional Responses
In design, blue is often associated with trust, loyalty, and wisdom, while green symbolizes nature, harmony, and growth. When used together, these colors can create a powerful visual narrative that appeals to users’ emotional and psychological needs. For instance, a blue green color scheme in a corporate setting can convey a sense of reliability and environmental responsibility, while in a wellness context, it can evoke feelings of relaxation and rejuvenation.
When exploring the question “what is blue green” in the context of design, it’s crucial to consider the various applications and creative possibilities this color combination offers. By harnessing the unique qualities of blue and green, designers can craft compelling visual stories that engage and inspire their audience.
How to Incorporate Blue Green in Your Life: Practical Applications
The concept of blue green offers a wealth of opportunities for incorporation into daily life, whether through technology, environmental efforts, or design choices. By understanding the unique qualities of this dichotomy, individuals can make informed decisions that positively impact their personal and professional lives.
Technology: Adopting Blue Green Deployment Methods
Businesses and organizations can adopt blue green deployment methods to minimize downtime and risk during system updates. By maintaining two identical production environments and seamlessly transitioning between them, companies can ensure a stable and functional environment at all times, ultimately leading to increased customer satisfaction and productivity.
Environment: Supporting Blue Green Algae Research and Conservation
Individuals can contribute to blue green environmental efforts by supporting research and conservation initiatives focused on blue-green algae. By understanding the critical role these microorganisms play in aquatic ecosystems, we can help protect and preserve our planet’s delicate balance and promote sustainable practices.
Design: Incorporating Blue Green Color Schemes
Incorporating blue green color schemes into personal and professional spaces can create a calming and harmonious atmosphere. Designers and individuals alike can experiment with various shades and intensities of blue and green to achieve the desired visual impact, whether it’s for a corporate office, a wellness center, or a cozy home environment.
By exploring the question “what is blue green” in the context of practical applications, individuals can discover innovative ways to harness the power of this dichotomy and enrich their lives in meaningful and impactful ways.
The Future of Blue Green: Trends and Predictions
As the concept of blue green continues to evolve and gain traction in various fields, it’s essential to explore emerging trends and future predictions that could shape the way we understand and utilize this dichotomy.
Technology: Automation and Machine Learning
In the realm of technology, the future of blue green is likely to involve increased automation and machine learning capabilities. By harnessing the power of artificial intelligence, businesses can optimize their blue green deployment strategies, further reducing downtime and minimizing risk during system updates.
Environment: Climate Change and Adaptation
In environmental science, blue green research and conservation efforts will likely focus on climate change adaptation and mitigation strategies. As our planet’s ecosystems face unprecedented challenges, understanding the role of blue-green algae in aquatic environments will be crucial in promoting resilience and sustainability.
Design: Virtual and Augmented Reality
In the world of design, virtual and augmented reality technologies will play a significant role in shaping the future of blue green aesthetics. Designers can experiment with immersive, interactive experiences that leverage the unique emotional and psychological impact of this color combination, creating captivating visual stories that resonate with users and customers.
By examining the question “what is blue green” in the context of future trends and predictions, we can better understand the potential of this dichotomy and anticipate the exciting possibilities that lie ahead.
Blue Green: Balancing Act or Cohesive Whole?
In exploring the concept of blue green, one cannot overlook the intriguing relationship between its dual elements and the potential for unity they present. By examining the various applications of blue green in technology, environment, and design, we can begin to understand the delicate balance between these two colors and the powerful impact they can have when combined.
A Balancing Act
In many contexts, blue and green serve as complementary forces, each bringing their unique qualities to the table. In technology, for instance, blue green deployment methods balance the need for stability and innovation, ensuring seamless system updates with minimal disruption. Similarly, in environmental science, blue-green algae strike a balance in aquatic ecosystems, contributing to both oxygen production and nutrient cycling.
A Cohesive Whole
Despite their distinct identities, blue and green can also merge to create a cohesive whole, as seen in the world of design. When used together in color schemes, these colors can evoke a sense of harmony, tranquility, and growth, appealing to users and customers on both an emotional and psychological level. This unity showcases the potential for blue and green to transcend their individual boundaries and create something truly unique and powerful.
Ultimately, the dichotomy of blue green offers a fascinating exploration into the world of duality and the potential for balance or unity in various applications. By understanding the complex relationship between these two elements, we can better appreciate the versatility and impact of this intriguing concept.