Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): The Foundation of Cloud Computing
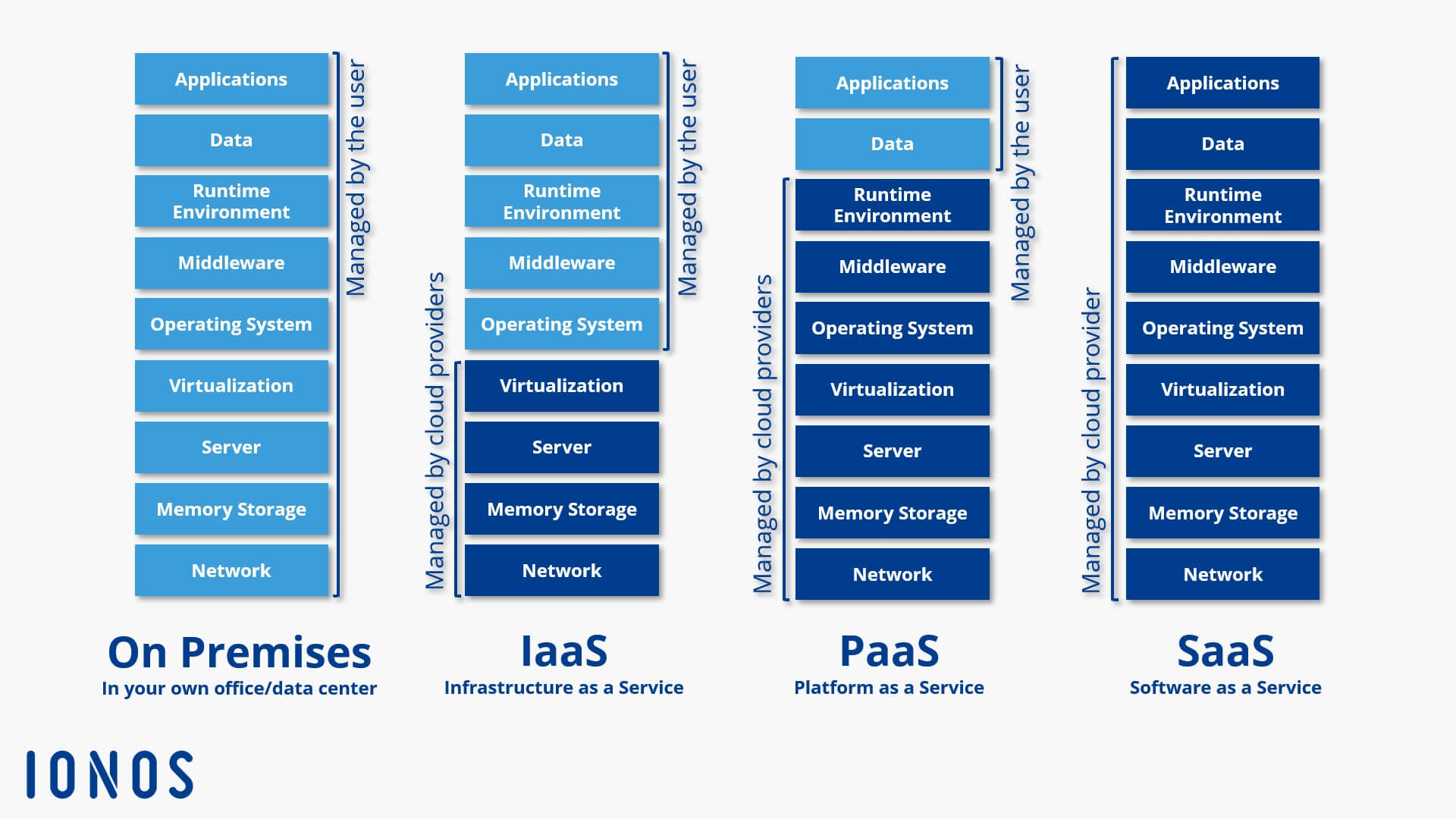
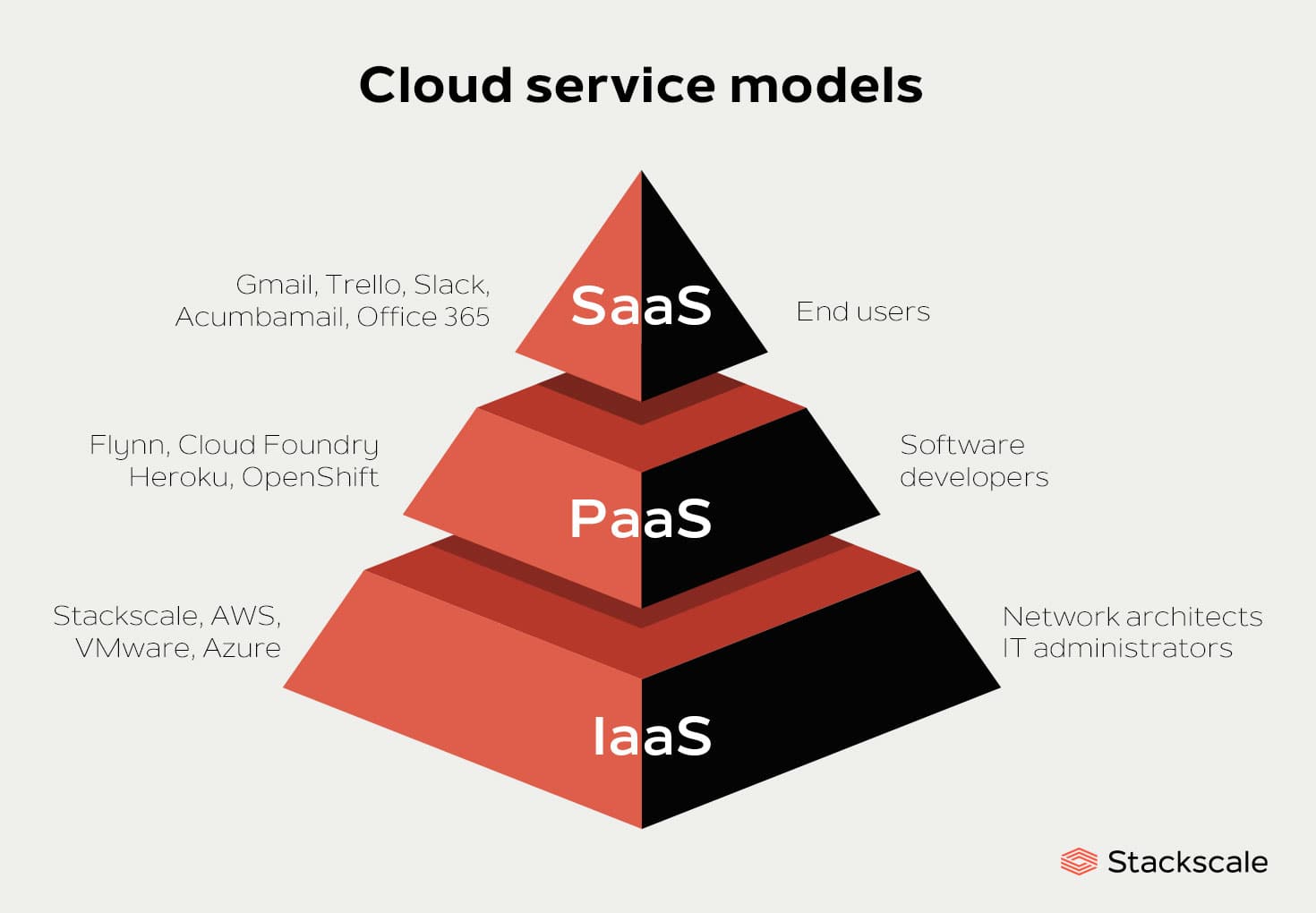
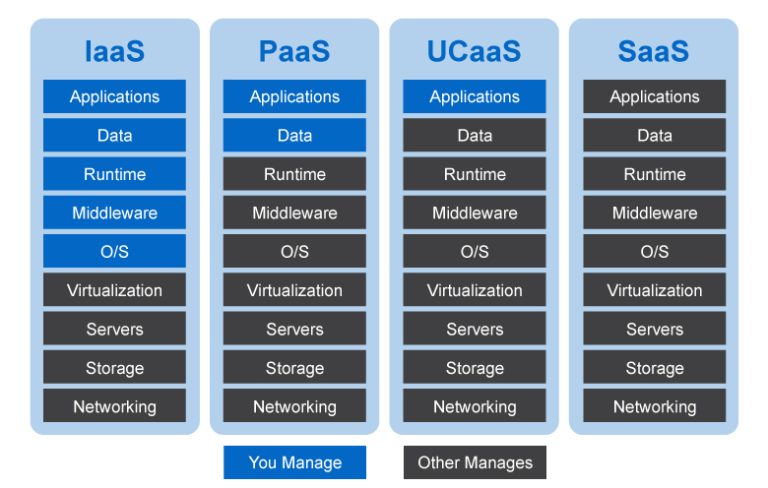
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) embodies the fundamental building blocks of cloud computing, offering users scalable and automated access to physical or virtual resources. These resources encompass virtualized servers, storage, networking components, and data center space, enabling organizations to construct and manage their IT infrastructure without the need for on-premises equipment.
IaaS provides numerous advantages, such as enhanced flexibility, cost savings, and streamlined IT management. By utilizing IaaS, businesses can swiftly scale their computing resources up or down in response to fluctuating demands, ensuring optimal performance and reducing waste. Moreover, IaaS alleviates the burden of maintaining and upgrading physical hardware, allowing IT teams to concentrate on higher-level tasks and strategic initiatives.
Prominent IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS) Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines, and Google Compute Engine. These platforms offer a wide array of features, tools, and pricing models, catering to diverse organizational needs and budgets. For instance, AWS EC2 enables users to launch and manage virtual servers, known as instances, in a matter of minutes, while Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines provides a robust and flexible platform for deploying and managing virtual machines across various operating systems and configurations.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): Streamlining Application Development and Deployment
Platform as a Service (PaaS) constitutes the middle layer of cloud computing, offering a complete development and deployment environment for applications. PaaS simplifies the application development process by providing a suite of tools, libraries, and pre-configured settings, enabling developers to focus on writing code and delivering functionality rather than managing infrastructure.
PaaS offerings typically include features such as version control, integrated development environments (IDEs), and drag-and-drop design tools, streamlining the development lifecycle and reducing time-to-market. Moreover, PaaS platforms often incorporate built-in support for databases, messaging systems, and other backend services, further simplifying application architecture and maintenance.
Popular PaaS platforms include Google App Engine, Heroku, and Microsoft Azure App Service. These platforms cater to diverse programming languages, frameworks, and use cases, allowing developers to choose the tools that best suit their needs. For instance, Google App Engine supports Python, Java, Go, and PHP, while Heroku offers support for Ruby, Node.js, Python, Java, and PHP, among others.
By adopting PaaS, organizations can reap numerous benefits, such as accelerated development cycles, reduced infrastructure costs, and simplified maintenance and scaling. PaaS also fosters collaboration and productivity among development teams, as developers can work concurrently on shared resources and leverage pre-built components to expedite the development process.
Software as a Service (SaaS): The Pinnacle of Cloud Computing
Software as a Service (SaaS) represents the highest layer of cloud computing, providing end-users with fully functional applications accessible through a web browser or a lightweight client. SaaS eliminates the need for local installations, maintenance, and updates, delivering a seamless and convenient user experience.
SaaS offerings encompass a wide array of applications, from productivity tools and collaboration platforms to customer relationship management (CRM) systems and enterprise resource planning (ERP) solutions. Popular SaaS products include Microsoft Office 365, Google Workspace, Salesforce, Dropbox, and Slack, among many others. These platforms cater to diverse industries, use cases, and user requirements, ensuring that businesses of all sizes can find suitable solutions for their needs.
By adopting SaaS, organizations can enjoy numerous benefits, such as reduced total cost of ownership (TCO), accelerated time-to-market, and increased agility. SaaS also enables organizations to scale their usage up or down on-demand, ensuring optimal resource utilization and minimizing waste. Furthermore, SaaS platforms often incorporate built-in support for mobile devices, enabling users to access applications and data from anywhere, at any time.
When selecting a SaaS solution, it is crucial to evaluate factors such as functionality, security, integration capabilities, and pricing models. Organizations should also consider the vendor’s reputation, track record, and commitment to innovation and continuous improvement. By carefully assessing these aspects, businesses can ensure that they choose a SaaS platform that aligns with their strategic objectives, enhances their operational efficiency, and delivers long-term value.
Selecting the Ideal Cloud Computing Model: A Comprehensive Guide
Having explored the three primary models of cloud computing, you may be wondering which one is best suited to your needs. To make an informed decision, consider the following step-by-step guide, which will help you evaluate your requirements, weigh the pros and cons of each model, and ultimately choose the solution that aligns with your strategic objectives and operational constraints.
Step 1: Define Your Business Objectives and Requirements
Begin by outlining your organization’s goals, priorities, and constraints. Identify the specific computing resources, applications, and services required to support your business operations and growth. Consider factors such as scalability, performance, security, and cost, as well as any regulatory or industry-specific requirements.
Step 2: Evaluate Your Technical Expertise and Resources
Assess your team’s technical capabilities and resources, including their proficiency in cloud computing technologies, development tools, and platforms. Determine whether you have the necessary in-house expertise to manage and maintain your chosen cloud computing model or whether you will require external support or assistance.
Step 3: Compare the Three Models of Cloud Computing
Next, compare the key features, advantages, and disadvantages of each cloud computing model, considering your business objectives, technical expertise, and resource constraints. Use the following table as a starting point for your evaluation:
| Model | Key Features | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| IaaS | Virtualized computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking components | Flexibility, scalability, cost-effectiveness, control over infrastructure | Requires technical expertise, responsibility for maintenance and updates |
| PaaS | Complete development and deployment environment for applications | Time-saving capabilities, ease of use, built-in support for databases and messaging systems | Limited control over infrastructure, potential vendor lock-in |
| SaaS | Fully functional applications accessible through a web browser or lightweight client | Convenience, cost-effectiveness, automatic updates, mobile access | Limited customization, potential data security concerns |
Step 4: Weigh the Pros and Cons
Based on your evaluation, weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each model, considering your unique business needs, technical capabilities, and resource constraints. Identify the model that offers the best balance of functionality, cost, and ease of use, while minimizing potential risks and challenges.
Step 5: Make an Informed Decision
Finally, make an informed decision about which cloud computing model best suits your organization’s needs. Implement the chosen model, continuously monitor its performance, and adjust your strategy as needed to ensure that you are maximizing its benefits and addressing any emerging challenges or opportunities.
Hybrid Cloud Computing: The Best of Both Worlds
Hybrid cloud computing offers a unique blend of flexibility, scalability, and security, making it an attractive option for organizations seeking to optimize their IT infrastructure. By combining the best features of public and private clouds, hybrid cloud computing enables businesses to create a tailored, seamless, and high-performance IT environment that caters to their specific needs and objectives.
What is Hybrid Cloud Computing?
Hybrid cloud computing refers to the integration of public and private cloud services, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. This approach enables organizations to leverage the benefits of both cloud computing models, such as the cost-effectiveness and scalability of public clouds and the security and control of private clouds. Hybrid cloud computing environments typically consist of the following components:
- Public cloud: A shared, multi-tenant environment managed by a third-party provider, offering computing resources, such as storage and processing power, on a pay-per-use basis.
- Private cloud: A dedicated, single-tenant environment managed by an organization’s internal IT team or a third-party provider, offering greater control and security over computing resources.
- Cloud bursting: A capability that enables organizations to automatically scale their computing resources from a private cloud to a public cloud during periods of high demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
- Hybrid cloud management: A set of tools and processes that enable organizations to manage, monitor, and orchestrate their hybrid cloud computing environment, ensuring seamless integration and operation.
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud Computing
Hybrid cloud computing offers several benefits to organizations, including:
- Flexibility: Organizations can choose the most appropriate cloud computing model for each application or workload, ensuring optimal performance, cost, and security.
- Scalability: Organizations can quickly and easily scale their computing resources up or down as needed, without the need for significant capital investments or lengthy procurement processes.
- Security: Organizations can maintain sensitive data and critical applications on a private cloud or on-premises infrastructure, while leveraging the public cloud for less sensitive workloads.
- Cost-effectiveness: Organizations can minimize their total cost of ownership (TCO) by using the public cloud for non-critical workloads and the private cloud for mission-critical applications.
Ideal Use Cases for Hybrid Cloud Computing
Hybrid cloud computing is particularly suitable for organizations with the following requirements:
- Fluctuating demand: Organizations with seasonal or unpredictable demand patterns can benefit from the scalability and flexibility of hybrid cloud computing, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency during peak periods.
- Data privacy and compliance: Organizations subject to data privacy regulations or compliance requirements can leverage hybrid cloud computing to maintain sensitive data on a private cloud or on-premises infrastructure, while using the public cloud for less sensitive workloads.
- Legacy application modernization: Organizations seeking to modernize their legacy applications can use hybrid cloud computing to gradually migrate their applications to the cloud, ensuring a smooth and seamless transition.
Navigating the Future of Cloud Computing: Trends and Predictions
As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, the cloud computing landscape is evolving to meet the changing needs of businesses and individuals alike. In this section, we will explore several emerging trends and predictions in cloud computing, focusing on topics such as edge computing, serverless architecture, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.
Edge Computing: Extending the Cloud to the Edge
Edge computing refers to the practice of processing data closer to the source, rather than transmitting it to a centralized data center or cloud. By reducing latency, improving bandwidth utilization, and enhancing data security, edge computing is becoming an increasingly popular solution for IoT, AI, and real-time applications. As the number of connected devices continues to grow, the demand for edge computing is expected to increase, driving innovation and investment in this area.
Serverless Architecture: A New Paradigm for Cloud Computing
Serverless architecture, also known as Function-as-a-Service (FaaS), is an emerging cloud computing model that enables developers to build and run applications without the need to manage servers or infrastructure. By automating the scaling, availability, and patching of resources, serverless architecture offers several benefits, such as reduced operational overhead, increased agility, and lower costs. As organizations seek to accelerate their digital transformation initiatives, the adoption of serverless architecture is expected to rise, leading to the creation of new tools, platforms, and best practices.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Unlocking the Power of Data
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are becoming increasingly important in cloud computing, as they enable organizations to unlock the value of their data and make more informed decisions. By leveraging AI and ML algorithms, businesses can automate complex processes, improve customer experiences, and gain a competitive advantage. As the amount of data generated continues to grow, the demand for AI and ML solutions is expected to increase, driving innovation and investment in this area.
Quantum Computing: A New Frontier in Cloud Computing
Quantum computing is an emerging field that promises to revolutionize cloud computing by enabling the processing of massive amounts of data at unprecedented speeds. By harnessing the power of quantum mechanics, organizations can solve complex problems, optimize their operations, and drive innovation. While still in its infancy, quantum computing is expected to become a major trend in cloud computing, as more businesses explore its potential and invest in this area.
Securing Your Cloud Computing Environment: Best Practices and Recommendations
As cloud computing continues to gain traction, ensuring the security and integrity of your cloud computing environment is of paramount importance. In this section, we will outline essential security measures, guidelines, and tools to protect your data, applications, and infrastructure from potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Implement Strong Access Control Policies
Establishing robust access control policies is crucial for securing your cloud computing environment. Implement strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), and enforce the principle of least privilege (PoLP), ensuring that users only have access to the resources necessary for their job functions. Regularly review and update access control policies to minimize the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Encrypt Data at Rest and in Transit
Encrypting data both at rest and in transit is essential for maintaining data confidentiality and integrity. Utilize encryption algorithms, such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and Transport Layer Security (TLS), to protect data from unauthorized access and eavesdropping. Implement key management practices, such as key rotation and storage, to ensure the secure handling and protection of encryption keys.
Monitor and Log Cloud Activities
Monitoring and logging cloud activities is crucial for detecting and responding to security incidents. Implement continuous monitoring solutions, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) tools, to track user activities, identify anomalies, and generate alerts for potential security threats. Regularly review and analyze logs to detect and respond to security incidents in a timely manner.
Implement Security Policies and Procedures
Developing and implementing comprehensive security policies and procedures is essential for maintaining a secure cloud computing environment. Establish guidelines for data classification, incident response, and disaster recovery, and ensure that all employees are aware of and adhere to these policies. Regularly review and update security policies and procedures to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Leverage Cloud Security Tools and Services
Cloud service providers (CSPs) offer a range of security tools and services to help organizations secure their cloud computing environments. Utilize these tools and services, such as virtual private clouds (VPCs), security groups, and network access control lists (NACLs), to enhance the security of your cloud infrastructure. Regularly review and update your security posture, and leverage the expertise of CSPs to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions: Demystifying Cloud Computing Models
To provide further clarity and address common misconceptions, concerns, and inquiries about cloud computing models, we have compiled a list of frequently asked questions. This section serves as a valuable resource for those seeking a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
What are the key differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS?
IaaS provides users with virtualized computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking components. PaaS offers a complete development and deployment environment for applications, while SaaS delivers fully functional applications to end-users through a web browser or a lightweight client. The main differences lie in the level of control, customization, and responsibility for managing infrastructure and applications.
How do I choose the right cloud computing model for my business needs?
To determine the ideal cloud computing model for your business, consider factors such as your technical requirements, in-house expertise, budget, and desired level of control. Evaluate the pros and cons of each model and consult with relevant stakeholders to make an informed decision.
Is it possible to migrate from one cloud computing model to another?
Yes, it is possible to migrate from one cloud computing model to another, although the process can be complex and time-consuming. Carefully assess the potential challenges and benefits of migrating and consult with cloud service providers to ensure a smooth transition.
How can I ensure the security of my cloud computing environment?
To ensure the security and integrity of your cloud computing environment, adhere to best practices and recommendations, such as implementing strong access control policies, encrypting data at rest and in transit, monitoring and logging cloud activities, and regularly reviewing and updating security policies and procedures.
What are the potential drawbacks of hybrid cloud computing?
Potential drawbacks of hybrid cloud computing include the complexity of managing multiple cloud environments, the risk of data inconsistencies, and the need for robust integration and orchestration solutions. Carefully assess these challenges and consult with cloud service providers to mitigate potential issues.