What are Smart Grid Solutions?
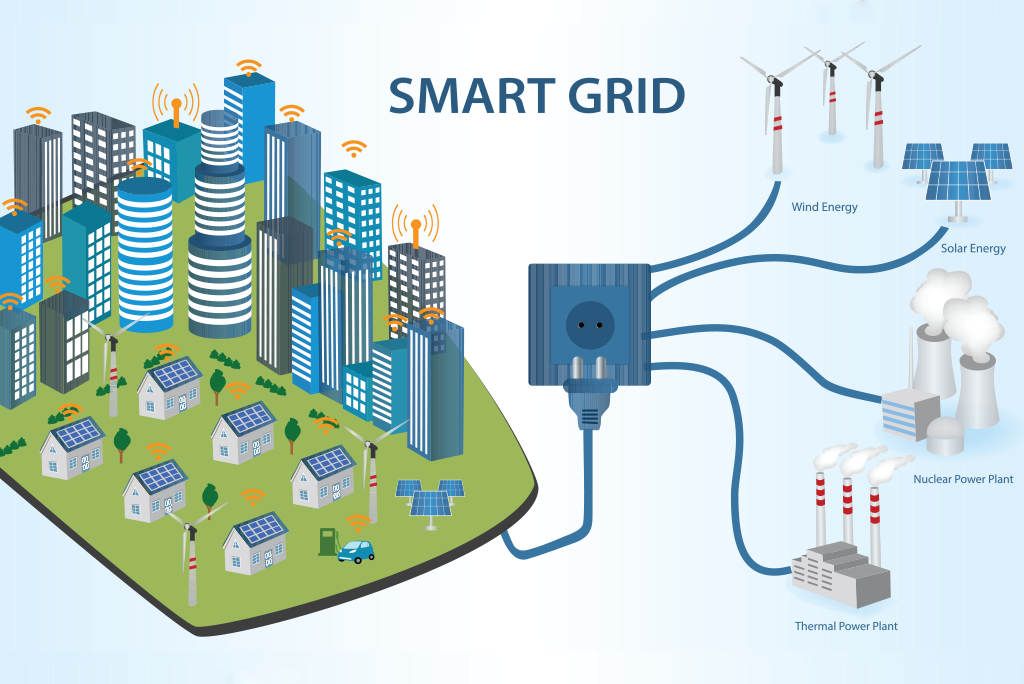
Smart grid solutions are advanced technologies designed to enhance the efficiency, sustainability, and customer-centricity of energy distribution systems. Unlike traditional grid systems, which are often one-way, centralized, and less responsive to real-time demand, smart grids leverage advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), advanced analytics, and renewable energy sources to create a more interactive, decentralized, and adaptive energy distribution network. These solutions aim to provide consumers with better control over their energy usage, while also allowing utility companies to manage energy distribution more efficiently and reduce operational costs. By adopting smart grid solutions, both consumers and utility companies can benefit from improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced sustainability.
How to Implement Smart Grid Solutions
Implementing smart grid solutions in existing infrastructure is a complex process that requires careful planning, strategic upgrades, and the integration of new technologies. The following steps provide a comprehensive guide on how to implement these solutions effectively:
1. Conduct a thorough assessment of the current infrastructure to identify areas that require upgrades or replacement. This includes evaluating the condition of transmission lines, distribution networks, and customer premises equipment.
2. Upgrade current systems to ensure compatibility with smart grid technologies. This may involve replacing traditional meters with smart meters, upgrading transformers, and enhancing communication networks.
3. Integrate IoT devices throughout the grid to collect real-time data on energy consumption, transmission, and distribution. These devices can include smart meters, sensors, and other monitoring equipment.
4. Implement advanced analytics to process the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices. This will enable utility companies to gain insights into energy usage patterns, identify potential issues before they occur, and optimize grid operations.
5. Enhance customer engagement by providing consumers with access to their energy usage data through mobile apps or web portals. This encourages consumers to make informed decisions about their energy consumption and helps reduce peak demand.
6. Invest in cybersecurity measures to protect the grid from potential cyber threats. This includes implementing robust security protocols, conducting regular vulnerability assessments, and training personnel on cybersecurity best practices.
7. Collaborate with stakeholders, including consumers, regulatory bodies, and technology providers, to ensure a smooth transition to smart grid solutions. Engaging with these stakeholders can help address concerns, gather feedback, and leverage expertise.
8. Continuously monitor and evaluate the performance of the smart grid solutions once implemented. This involves tracking key performance indicators, identifying areas for improvement, and making necessary adjustments to optimize operations.
By following these steps, utility companies can successfully implement smart grid solutions that enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. The integration of advanced technologies and innovative strategies will revolutionize the way energy is distributed and consumed, paving the way for a more sustainable and efficient energy future.
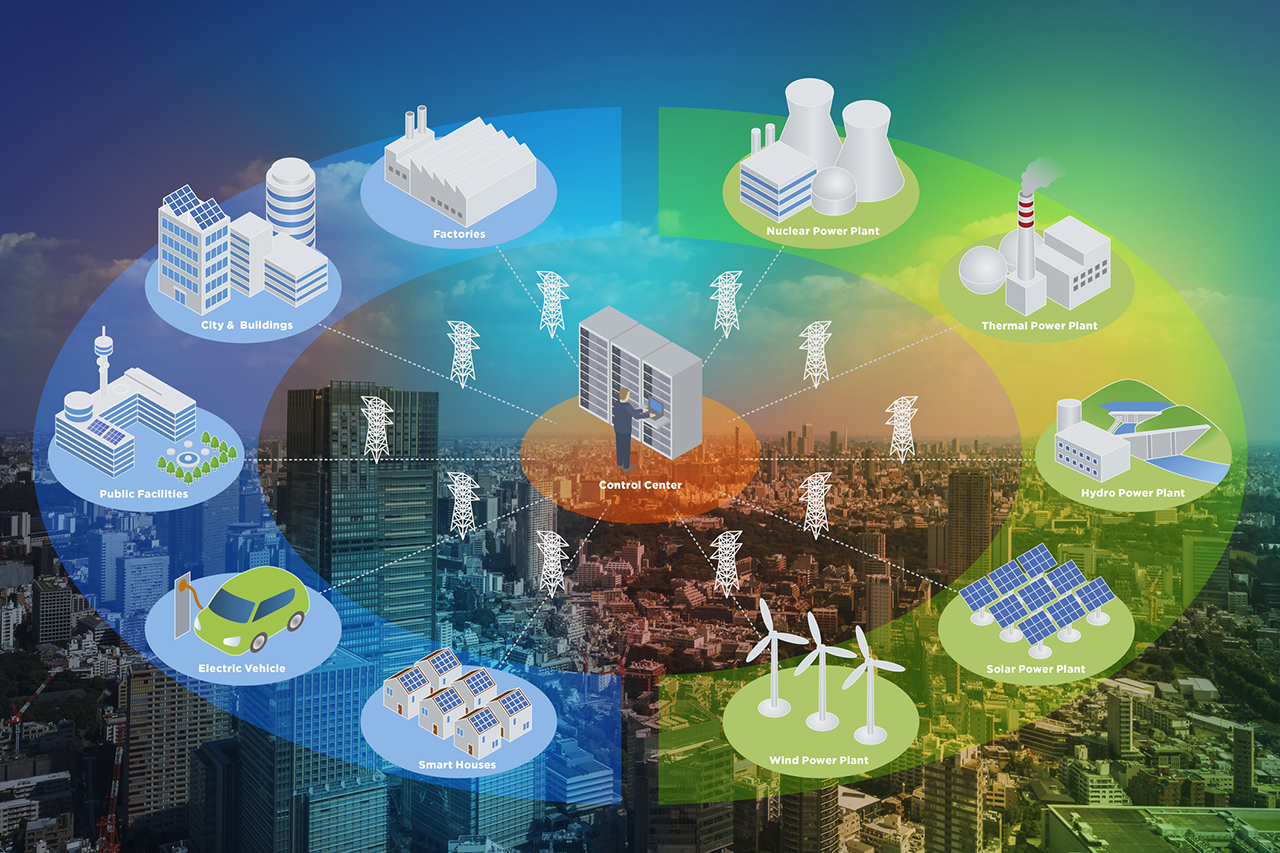

Real World Examples of Smart Grid Solutions
Smart grid solutions have been successfully implemented by various utility companies around the world, demonstrating their effectiveness in improving efficiency and reducing costs. One notable example is the smart grid project undertaken by Enel, an Italian multinational energy company. Enel’s smart grid solution, known as Open Meter, uses advanced technologies such as IoT devices and advanced analytics to manage energy distribution more efficiently. This project has resulted in significant improvements in customer satisfaction and operational efficiency, with reduced power outages and faster response times to faults.
Another example is the smart grid initiative by Duke Energy, a leading electric power holding company in the United States. Duke Energy’s smart grid solution focuses on integrating renewable energy sources into the grid, enhancing the sustainability and efficiency of energy distribution. This initiative has led to substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and improved customer satisfaction due to better management of peak demand periods.
These real-world examples showcase the potential of smart grid solutions to revolutionize the energy sector by providing more efficient, sustainable, and customer-centric services. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of smart grid solutions in the future.
The Role of Renewable Energy in Smart Grid Solutions
The integration of renewable energy sources into smart grid solutions is a pivotal step towards enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of energy distribution systems. Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power, offer an alternative to traditional fossil fuels, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and reliance on finite resources. In the context of smart grids, renewable energy can be integrated through various technologies and strategies.
One key strategy involves the use of distributed generation systems, where renewable energy sources are connected directly to the grid at various points. This decentralized approach allows for a more flexible and resilient energy distribution system, as it reduces reliance on a single, central power plant. Moreover, distributed generation systems can provide real-time data on energy production and consumption, enabling utilities to better manage energy distribution and optimize grid operations.
Another important aspect of integrating renewable energy into smart grids is the implementation of advanced technologies such as smart inverters and energy storage systems. Smart inverters enable the efficient integration of solar and wind power into the grid by providing real-time monitoring and control capabilities. Energy storage systems, on the other hand, help to mitigate the intermittency of renewable energy sources, ensuring a stable and reliable energy supply even when the sun is not shining or the wind is not blowing.
The integration of renewable energy sources into smart grids also presents opportunities for consumers to participate in the energy market. Through technologies such as rooftop solar and community solar programs, consumers can generate their own renewable energy and sell any excess back to the grid. This not only reduces energy costs for consumers but also increases the overall efficiency of the grid by providing additional sources of clean energy.
However, the integration of renewable energy into smart grids also poses challenges. One of the primary concerns is the variability of renewable energy sources, which can lead to fluctuations in energy supply. To address this issue, utilities must develop advanced forecasting and scheduling tools to predict energy demand and adjust energy production accordingly. Additionally, the integration of renewable energy requires significant investments in infrastructure upgrades and technology deployments, which can be costly and time-consuming.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of integrating renewable energy into smart grids far outweigh the drawbacks. By leveraging advanced technologies and innovative strategies, utilities can create a more efficient, sustainable, and customer-centric energy distribution system. As the global energy landscape continues to evolve, the role of renewable energy in smart grid solutions will become increasingly important, driving progress towards a cleaner, more resilient energy future.
Challenges and Opportunities in Smart Grid Solutions
While smart grid solutions offer numerous benefits for both consumers and utility companies, there are several challenges that must be addressed during implementation. One of the primary hurdles is regulatory hurdles. Existing laws and regulations often lag behind technological advancements, making it difficult for utility companies to fully adopt smart grid solutions. Additionally, the integration of advanced technologies into existing infrastructure can be costly, posing a significant financial burden on utility companies. Furthermore, consumer acceptance can also be a challenge as some individuals may be hesitant to adopt new technologies due to concerns about privacy, security, and reliability.
Despite these challenges, the opportunities that arise from adopting smart grid solutions far outweigh the difficulties. For instance, improved customer satisfaction is a significant opportunity for utility companies. By providing consumers with real-time data on their energy consumption and enabling them to make informed decisions about their energy usage, utility companies can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. Moreover, smart grid solutions can increase revenue for utility companies by optimizing energy distribution and reducing operational costs. The integration of renewable energy sources into smart grids also presents opportunities for utility companies to reduce their environmental footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Another opportunity arises from the creation of new jobs and industries related to the development, installation, and maintenance of smart grid technologies. As the demand for these solutions continues to grow, so does the need for skilled professionals who can design, implement, and manage these complex systems. This presents an opportunity for economic growth and development in regions where smart grid solutions are being implemented.
Finally, the adoption of smart grid solutions can lead to increased innovation in the energy sector. By leveraging advanced technologies such as IoT devices, blockchain, and artificial intelligence, utility companies can develop new products and services that cater to changing consumer needs and preferences. This innovation can drive further growth and development in the energy industry, leading to a more efficient, sustainable, and customer-centric energy distribution system.
Smart Grid Solutions and Cybersecurity
As the integration of advanced technologies into energy distribution systems continues to grow, so does the concern for cybersecurity. Smart grid solutions, which rely heavily on IoT devices, advanced analytics, and other digital technologies, are not immune to potential risks and vulnerabilities. In fact, the increased reliance on these technologies can create new entry points for cyber threats.
One of the primary concerns is the potential for hacking attacks on smart grid systems. Hackers could exploit vulnerabilities in IoT devices or other parts of the system to disrupt energy distribution, leading to power outages or even physical damage to infrastructure. Additionally, there is a risk of data breaches, where sensitive customer information could be compromised.
Another challenge is ensuring that the systems used in smart grids are secure and resilient. This requires ongoing monitoring and maintenance to identify and address potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Furthermore, the increasing use of third-party vendors and contractors in the development and implementation of smart grid solutions can introduce additional cybersecurity risks if not properly managed.
Despite these challenges, there are several strategies that utility companies can employ to mitigate these risks. One key approach is to implement robust security measures, such as encryption and firewalls, to protect against hacking attempts. Regular security audits and penetration testing can also help identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Another important strategy is to ensure that all IoT devices and other technologies used in smart grids are designed with security in mind. This includes implementing secure communication protocols and ensuring that devices are regularly updated with the latest security patches. Additionally, utility companies should establish clear guidelines and protocols for managing third-party vendors and contractors to minimize the risk of data breaches or other cybersecurity threats.
Finally, it is essential for utility companies to educate consumers about the importance of cybersecurity in smart grids. By raising awareness about the potential risks and encouraging consumers to take steps to protect their own devices and data, utility companies can help create a more secure and resilient energy distribution system.
Overall, while the integration of advanced technologies into energy distribution systems presents several cybersecurity challenges, there are numerous strategies that utility companies can employ to mitigate these risks. By prioritizing security, implementing robust measures, and educating consumers, it is possible to create a more efficient, sustainable, and customer-centric energy distribution system through smart grid solutions.
The Future of Smart Grid Solutions
As technology continues to advance, the future of smart grid solutions holds immense potential for growth and innovation. Emerging technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and 5G networks are set to revolutionize the energy distribution system, making it more efficient, sustainable, and customer-centric.
Blockchain technology, for instance, can enhance the security and transparency of smart grids by providing a decentralized platform for data exchange between consumers, utility companies, and other stakeholders. This will not only improve the reliability of the system but also enable peer-to-peer energy trading, allowing consumers to sell excess energy back to the grid.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is another key player in shaping the future of smart grid solutions. AI algorithms can analyze real-time data from various sources, including IoT devices, weather forecasts, and consumer behavior, to optimize energy distribution and consumption. This predictive analytics capability will enable utility companies to better manage peak demand, reduce energy waste, and improve overall efficiency.
The integration of 5G networks into smart grids will significantly enhance the speed and reliability of data transmission. With faster data processing times, utility companies can respond more quickly to changes in demand and outages, ensuring a more stable and efficient energy supply. Additionally, 5G networks will enable the widespread adoption of IoT devices, further expanding the capabilities of smart grids.
Moreover, advancements in renewable energy technologies will continue to play a crucial role in smart grid solutions. As consumers increasingly turn to solar, wind, and other renewable sources for their energy needs, smart grids must adapt to accommodate these changes. This includes integrating distributed energy resources, managing variable renewable energy output, and optimizing energy storage solutions.
Finally, the future of smart grid solutions also involves enhancing consumer engagement and participation. By providing consumers with real-time data on their energy usage and offering personalized recommendations for reducing consumption, utility companies can foster a more collaborative approach to energy management. This not only benefits consumers through lower bills but also helps utility companies manage peak demand and improve overall efficiency.
In conclusion, the future of smart grid solutions is marked by significant advancements in technology, consumer engagement, and sustainability. As these innovations continue to evolve, they will pave the way for a more efficient, sustainable, and customer-centric energy distribution system.
Smart grid solutions have revolutionized the way energy is distributed and consumed, offering a more efficient, sustainable, and customer-centric system. The integration of advanced technologies such as IoT devices, artificial intelligence, and blockchain has transformed the traditional grid system into a smart grid that can manage energy distribution in real-time. This article has explored the various aspects of smart grid solutions, from their implementation to their potential challenges and future trends.
Implementing smart grid solutions requires a comprehensive approach that involves upgrading current infrastructure and integrating new technologies. The process begins with assessing the existing grid system to identify areas for improvement and potential bottlenecks. Once identified, utility companies can start upgrading their infrastructure by installing smart meters, advanced sensors, and other IoT devices that enable real-time monitoring and control of energy distribution.
The integration of renewable energy sources is another crucial aspect of smart grid solutions. By incorporating solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources into the grid, utility companies can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and improve the sustainability of their operations. This not only benefits the environment but also helps to reduce costs associated with energy production and distribution.
However, implementing smart grid solutions also presents several challenges. One of the main hurdles is regulatory hurdles, as utility companies must comply with various laws and regulations that govern the energy sector. Technological limitations can also hinder the adoption of smart grid solutions, particularly in areas where the existing infrastructure is outdated or inadequate. Additionally, consumer acceptance can be a challenge, as some customers may be resistant to change or skeptical about the benefits of smart grid solutions.
Despite these challenges, the opportunities that arise from adopting smart grid solutions far outweigh the risks. For instance, smart grid solutions can improve customer satisfaction by providing real-time information on energy consumption and enabling consumers to make informed decisions about their energy usage. They can also increase revenue for utility companies by optimizing energy distribution and reducing waste.
Moreover, smart grid solutions offer a platform for innovation and growth in the energy sector. Emerging technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and 5G networks are set to shape the future of smart grid solutions, enabling even more efficient and sustainable energy distribution systems. These advancements will not only enhance the functionality of smart grids but also create new opportunities for businesses and consumers alike.
In conclusion, smart grid solutions are transforming the energy sector by providing a more efficient, sustainable, and customer-centric system for energy distribution. While there are challenges associated with implementing these solutions, the benefits they offer make them an attractive option for utility companies looking to improve their operations and enhance customer satisfaction. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative solutions emerge in the future.
