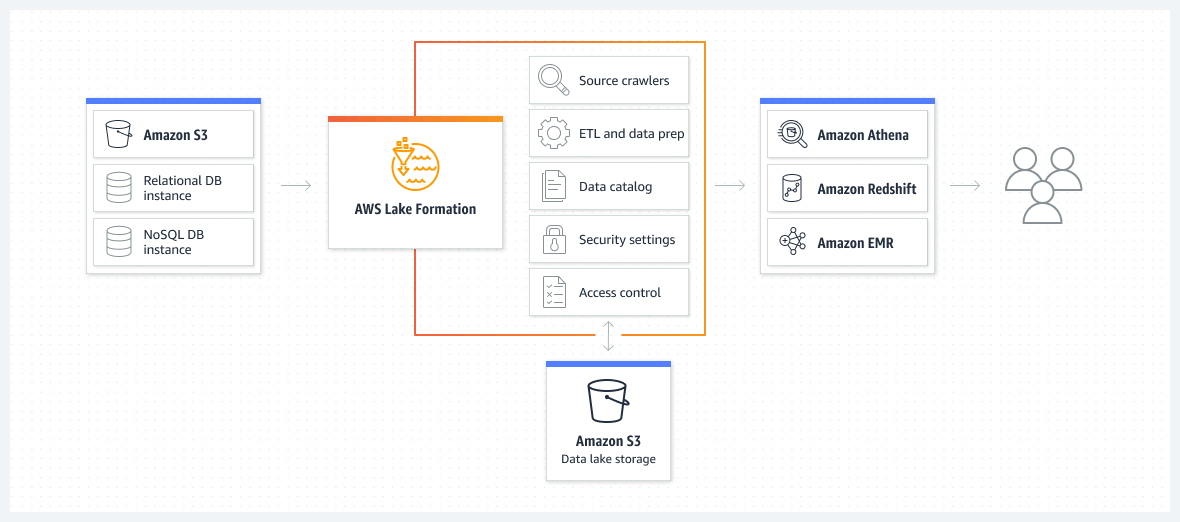
Understanding the Benefits of S3 Data Lakes
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) provides a powerful and cost-effective foundation for building a scalable s3 datalake. Its inherent scalability allows organizations to effortlessly handle massive datasets and diverse data types. The cost-effectiveness of S3 storage significantly reduces the expenses associated with traditional data warehousing solutions. Easy access to data in the s3 datalake empowers data scientists and analysts to quickly and efficiently retrieve and process information, enabling faster insights and decision-making. The robust architecture of S3 makes it an ideal platform to manage data growth and evolving data complexities. S3’s flexible storage capacity and fault tolerance provide a secure and dependable solution.
A well-structured s3 datalake offers significant advantages. Its scalability allows it to accommodate substantial data growth without performance issues. The high availability and durability features of S3 ensure data integrity, even in challenging circumstances. The cost-effectiveness of S3 results in reduced storage costs compared to other solutions. This makes it an attractive option for organizations of all sizes. Employing S3 to build a s3 datalake proves highly beneficial, providing a versatile and resilient environment for data management.
The flexible storage options in S3 excel in accommodating various data types and formats, thereby offering a comprehensive data management solution. This versatility makes S3 a suitable platform for different business domains and use cases. S3’s adaptability to evolving data storage needs underscores its value as a dependable solution. The s3 datalake model fosters a scalable and robust environment for data analysis and insights. The design principles of S3 are engineered to be adaptable and flexible, thereby handling diverse data requirements.
Choosing the Right Tools for Data Ingestion
Selecting appropriate tools for ingesting data into an S3 data lake is crucial for a successful data strategy. The right tools will ensure data quality and facilitate seamless integration with the S3 architecture. Various methods exist, from traditional ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) techniques to more modern streaming pipelines and APIs. Careful consideration of these options is essential for a scalable and flexible data ingestion process. A well-designed ingestion strategy within the S3 data lake is a key to future-proofing the data pipeline.
Different ingestion methods suit various data volumes and velocities. ETL tools are excellent for batch data loads, while streaming pipelines are ideal for real-time data streams. APIs offer a versatile option for integrating data from diverse sources. Critically, data validation and quality checks are paramount during the ingestion phase. Ensuring high-quality data flowing into the S3 datalake is essential for reliable insights. This ensures that the analysis on the data stored within the S3 data lake is accurate. Flexible data sources, such as web applications, IoT sensors, or databases, can be incorporated into the ingestion process.
Considering the scalability and flexibility of the S3 platform is vital when choosing ingestion methods. The ability to handle varied data types and volumes is critical. The key takeaway here is that selecting the optimal tools for data ingestion directly impacts the effectiveness of the entire S3 data lake project, supporting the overall data strategy. Tools must also be compatible with the chosen infrastructure and architecture of the S3 data lake.
Data Organization and Management in S3 Data Lakes
Effective organization is paramount for a successful S3 data lake. A well-structured S3 data lake enables efficient data retrieval and analysis. Logical folder structures are crucial for navigating the data landscape. Creating a hierarchical directory system mirrors the organization of your data sources, which improves searchability. This promotes ease of discovery and facilitates efficient data exploration. Implementing consistent object naming conventions enhances discoverability and ensures data integrity. Metadata tagging is another valuable technique. Adding relevant metadata tags to your data objects allows filtering and searching based on specific criteria. Employing descriptive tags enhances the accessibility and usability of the data stored in the S3 datalake. Utilizing standardized tagging structures simplifies future analysis and reporting. For example, tag files with project, date, and type of data. By employing these strategies, a well-organized S3 datalake architecture ensures seamless exploration and analysis of massive datasets.
Robust data management strategies are essential components of any successful S3 datalake. Proper folder structures are vital to ensure that data is readily accessible and organized logically. Implementing metadata tagging improves data discovery and querying by allowing users to filter data based on characteristics. Metadata acts as a crucial identifier for data within the S3 data lake. For example, tagging files with keywords allows quick retrieval of specific data sets. Object naming conventions are critical to maintain uniformity and consistency within the system. Consistent naming protocols improve the searchability of data in the S3 data lake, streamlining the analysis process. Adopting these best practices guarantees effective data management for your S3 datalake environment. This streamlined approach enables data analysts to efficiently navigate and analyze large volumes of data, accelerating insights and decision-making processes.
Applying these strategies fosters a robust and scalable S3 data lake architecture. Robust organization enhances discoverability, simplifying data retrieval and analysis. A clear strategy for organizing and managing data within an S3 datalake helps extract valuable insights. Adopting these strategies leads to a streamlined S3 datalake environment. A well-structured S3 datalake supports effective data exploration. Implementing these data organization practices promotes efficient data retrieval and analysis. Employing these strategies ensures effective management and accessibility of the S3 datalake. This approach enhances data exploration in the S3 datalake.
Security and Access Control for S3 Data Lakes
Robust security is paramount for any S3 data lake. Protecting sensitive data is crucial for maintaining compliance with industry regulations and preventing unauthorized access. Implementing strong access control mechanisms is vital for safeguarding the integrity of the data stored within the s3 datalake. Effective data protection measures are essential to maintain confidentiality and prevent data breaches. Employing various access control methods and robust encryption options will ensure data safety.
Access control lists (ACLs) and Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies are key to restricting access to specific resources within the S3 datalake. Define granular permissions to control who can view, modify, or delete data in the s3 environment. Implement server-side encryption (SSE) to encrypt data at rest, protecting it even if an unauthorized party gains access to the storage hardware. The use of SSE ensures the privacy and confidentiality of sensitive information within the s3 datalake. Integrate data encryption during transit to secure data transferred to and from the s3 storage layer. By adhering to these security protocols, organizations can effectively mitigate risks and protect their sensitive data within the s3 datalake.
Consider employing data loss prevention (DLP) tools to identify and prevent sensitive data from leaving the s3 datalake. Data masking techniques are useful in protecting sensitive data without altering the integrity of the data. Adhering to industry regulations and compliance standards, like HIPAA or GDPR, is vital for organizations handling sensitive data in the s3 datalake. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are necessary to identify and address any potential weaknesses in the s3 datalake security framework. This proactive approach ensures that the s3 datalake is protected from malicious threats and data breaches, maintaining the integrity of the data.
Analyzing Data Stored in an S3 Data Lake
Extracting valuable insights from data stored within an S3 data lake is a critical aspect of its effectiveness. Various tools empower users to query and analyze the data residing in this robust storage solution. The key is understanding how these tools interact with the S3 infrastructure for optimal performance.
Powerful tools such as Apache Spark, Presto, and Amazon Athena offer a range of functionalities for querying and analyzing data. These services allow users to interact with the S3 datalake directly, enabling them to manipulate the vast amounts of data stored there. Efficient querying and analysis are crucial for deriving meaningful information from large datasets. Apache Spark excels at complex data transformations, allowing for advanced analyses. Presto, another popular choice, facilitates fast query execution against S3 data. Amazon Athena, a query service, offers a straightforward and interactive way to extract valuable data from the S3 datalake.
These tools interact seamlessly with the S3 infrastructure. The data stored in S3 buckets is directly accessible to these analytical platforms, enabling faster query processing. Data retrieval and manipulation processes are optimized through this direct integration, contributing to enhanced productivity and allowing for rapid insight generation. This efficiency in accessing and analyzing information within the s3 datalake is vital for extracting maximum value from the data stored.
How to Design an Efficient S3 Data Lake Architecture
Designing a robust and scalable S3 data lake requires a methodical approach. Initial planning is crucial. Start by defining the scope of the data lake project, identifying the specific data sources, and determining the volume and velocity of incoming data. This preliminary stage establishes a clear foundation for subsequent steps.
A critical component of any s3 datalake architecture is storage. Choose the appropriate storage class within Amazon S3 to optimize costs based on access patterns. Archival storage might suit infrequently accessed data. Hot storage offers fast access for frequently queried data. This strategy optimizes storage costs while ensuring rapid data retrieval when needed. Processing capabilities also demand careful consideration. Implementing a scalable data processing framework, like Apache Spark or Presto, for querying and transforming data within the s3 datalake is crucial. Leveraging these tools allows seamless integration with the S3 infrastructure, facilitating efficient data manipulation. Proper security measures are paramount. Implement robust access control mechanisms to restrict data access based on roles and permissions. Utilize server-side encryption to protect sensitive data at rest. Regular audits and monitoring of security policies ensure compliance and data integrity.
Finally, ensure ongoing maintenance of the s3 datalake. Implementing data lifecycle management strategies allows for the efficient transition of data between storage classes, reducing storage costs and improving overall performance. Automated processes for data cleanup and regular monitoring for potential issues are critical. By proactively managing data retention policies, organizations can minimize storage costs and avoid performance degradation within the s3 datalake architecture. This comprehensive approach to maintenance will guarantee efficient and sustained performance for years to come.
Maintaining a Healthy S3 Data Lake
A well-maintained S3 data lake is crucial for efficient data access and analysis. Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance and prevents storage costs from escalating. Effective data lifecycle management is key. Identify and remove outdated data. Employ automated systems for data deletion and archiving. Proper data cleanup prevents unnecessary storage consumption, reducing costs associated with the S3 datalake.
Regular monitoring of S3 datalake performance is essential. Track storage usage and identify potential bottlenecks. Proactive monitoring allows for timely adjustments to storage and processing configurations. Continuous optimization is vital for achieving optimal performance. Monitor query performance, and adjust resource allocation accordingly. Implement strategies for dealing with data growth and storage needs. By proactively addressing these issues, organizations can prevent performance degradation and maintain the integrity of their S3 data lake.
Implementing robust data governance policies is a cornerstone of an efficient S3 data lake. Establishing clear data retention policies ensures compliance with regulations and industry standards. Regularly auditing data access and usage patterns provides insights for improving data management processes. Implementing data quality checks and validation processes early in the data ingestion pipeline will contribute to preventing issues in downstream data analysis. This proactive approach strengthens the reliability and usability of the S3 data lake, ensuring long-term success for data-driven decisions.
Future Trends in S3 Data Lakes
The S3 data lake landscape is constantly evolving, driven by innovation in cloud computing. Serverless computing is poised to significantly impact S3 data lake architectures. By leveraging serverless functions, organizations can automate tasks and reduce operational overhead. This trend offers cost-effectiveness and optimized scalability for the s3 datalake.
Edge computing integrations are another emerging trend gaining traction. This allows for processing data closer to its source, potentially improving data latency and enabling real-time analytics on s3 datalake. This capability is essential for applications requiring near real-time insights, such as IoT data processing or financial transactions. By bringing compute closer to the data source, companies can significantly reduce the latency associated with accessing and analyzing data stored in the s3 datalake.
Data security and governance remain paramount. Robust encryption, access control, and data governance policies are crucial for protecting sensitive data within the s3 datalake. Staying updated on advancements in security protocols and industry best practices is essential for safeguarding s3 datalake data. Furthermore, ongoing investments in sophisticated data cataloging and metadata management tools enhance data discovery and usability in s3 datalake environments.