Understanding the Importance of Cloud Backup Strategies
In today’s digital era, data has become a vital asset for businesses and individuals alike. With the increasing dependence on cloud storage services, it is essential to have a robust and reliable backup strategy in place. This comprehensive guide will explore various backup strategies for cloud storage, helping you make informed decisions to safeguard your invaluable data.
The Role of Cloud Backup in Data Protection
Cloud backup plays a significant role in safeguarding data against accidental deletion, hardware failures, and cyber threats. A dependable backup strategy is crucial to minimize data loss and downtime, ensuring business continuity and data availability. By storing copies of critical data in a secure and remote location, organizations can quickly recover from unexpected data disasters and maintain their operations.
Key Components of a Reliable Cloud Backup Strategy: Data Selection and Prioritization
In a robust cloud backup strategy, data selection and prioritization play a crucial role in ensuring the protection of essential data. Identifying and categorizing critical data that requires backup is the first step in creating an effective backup plan. This process involves evaluating data based on its value, sensitivity, and frequency of change. By prioritizing data, organizations can allocate resources more efficiently and minimize the risk of data loss.
Valuable data often includes customer information, financial records, and intellectual property. Sensitive data, on the other hand, may consist of confidential communications, personal identifiable information (PII), or protected health information (PHI). Frequently changing data, such as databases or transactional records, require more frequent backups to ensure data integrity and consistency. By categorizing data based on these factors, organizations can create a tiered backup approach that prioritizes critical data and optimizes resource usage.
Data selection and prioritization also help organizations comply with various regulations and industry standards. For instance, healthcare organizations must adhere to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), while financial institutions must comply with the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA). By identifying and protecting sensitive data, organizations can maintain compliance and avoid potential fines or legal issues.
In summary, data selection and prioritization are essential components of a reliable cloud backup strategy. By evaluating data based on its value, sensitivity, and frequency of change, organizations can create a tiered backup approach that prioritizes critical data and optimizes resource usage. This process not only helps minimize the risk of data loss but also ensures compliance with various regulations and industry standards.
Frequency and Schedule of Backups: Reliable Backup Strategies for Cloud Storage
When designing a reliable cloud backup strategy, determining the ideal frequency and schedule for backups is essential. Factors such as data change rate, recovery time objectives (RTOs), and resource availability should be considered to ensure data protection while minimizing the impact on system performance and storage costs. In this article, we will discuss the importance of backup frequency and scheduling and provide recommendations for optimizing your cloud backup strategy.
Data change rate is a critical factor in determining backup frequency. Frequently changing data, such as databases or transactional records, require more frequent backups to ensure data integrity and consistency. On the other hand, static data, such as archived documents or media files, may only require periodic backups. By aligning backup frequency with data change rate, organizations can strike a balance between data protection and resource utilization.
Recovery time objectives (RTOs) are another essential factor to consider when scheduling backups. RTOs represent the maximum acceptable length of time for recovering data after a disruption or failure. Organizations should consider their RTOs when scheduling backups to ensure that they can meet their recovery objectives in the event of a disaster. For instance, organizations with short RTOs may require more frequent backups, while those with longer RTOs may be able to schedule backups less frequently.
Resource availability is also a critical consideration when scheduling backups. Backups can consume significant system resources, such as CPU, memory, and network bandwidth. Organizations should schedule backups during periods of low system usage to minimize the impact on system performance and user experience. For instance, scheduling backups during off-peak hours or during maintenance windows can help ensure that backups do not interfere with critical business operations.
Based on these factors, organizations should consider the following recommendations for scheduling backups:
- Schedule full backups weekly or monthly, depending on data change rate and RTOs.
- Schedule incremental or differential backups daily or weekly, depending on data change rate and RTOs.
- Schedule backups during periods of low system usage to minimize the impact on system performance and user experience.
- Monitor backup performance and adjust the schedule as needed to ensure that backups are completed within acceptable timeframes.
- Implement backup verification and validation processes to ensure that backups are complete and consistent.
In conclusion, determining the ideal frequency and schedule for backups is a critical component of a reliable cloud backup strategy. By aligning backup frequency with data change rate, RTOs, and resource availability, organizations can ensure data protection while minimizing the impact on system performance and storage costs. By following the recommendations outlined in this article, organizations can optimize their backup schedules and ensure the long-term security and availability of their data in the cloud.
Backup Types and Methods
When creating a reliable cloud backup strategy, it is essential to understand the different backup types and methods available. This knowledge will help you make informed decisions and choose the most suitable options based on your needs and constraints.
Full Backups
A full backup is a complete copy of all selected data at a given point in time. Full backups are resource-intensive, as they require significant storage space and time to complete. However, they offer the advantage of quick and straightforward data restoration, as only one backup file is needed to restore the entire dataset.
Incremental Backups
Incremental backups capture only the changes made to the data since the last backup, whether it was a full, incremental, or differential backup. These backups are more efficient in terms of storage space and time compared to full backups. However, restoring data from incremental backups can be more complex, as multiple backup files may be required to restore the entire dataset.
Differential Backups
Differential backups capture all changes made to the data since the last full backup. These backups are more resource-intensive than incremental backups but less intensive than full backups. Restoring data from differential backups is faster than incremental backups, as only two backup files are needed: the last full backup and the most recent differential backup.
Backup Methods
In addition to backup types, it is crucial to consider the backup methods that best suit your needs:
Image-based Backups
Image-based backups create an exact replica of a system, including the operating system, applications, and data. These backups are particularly useful for disaster recovery scenarios, as they enable quick and easy system restores.
File-level Backups
File-level backups focus on specific files and folders, allowing for more granular data protection. This method is ideal for protecting individual documents, databases, or application data.
Application-aware Backups
Application-aware backups are designed to capture the data and application-specific metadata required for a successful restore. These backups ensure that applications function correctly after a restore, minimizing the risk of data loss or corruption.
By understanding the various backup types and methods, you can create a reliable cloud backup strategy that meets your needs and protects your valuable data from potential threats and losses.
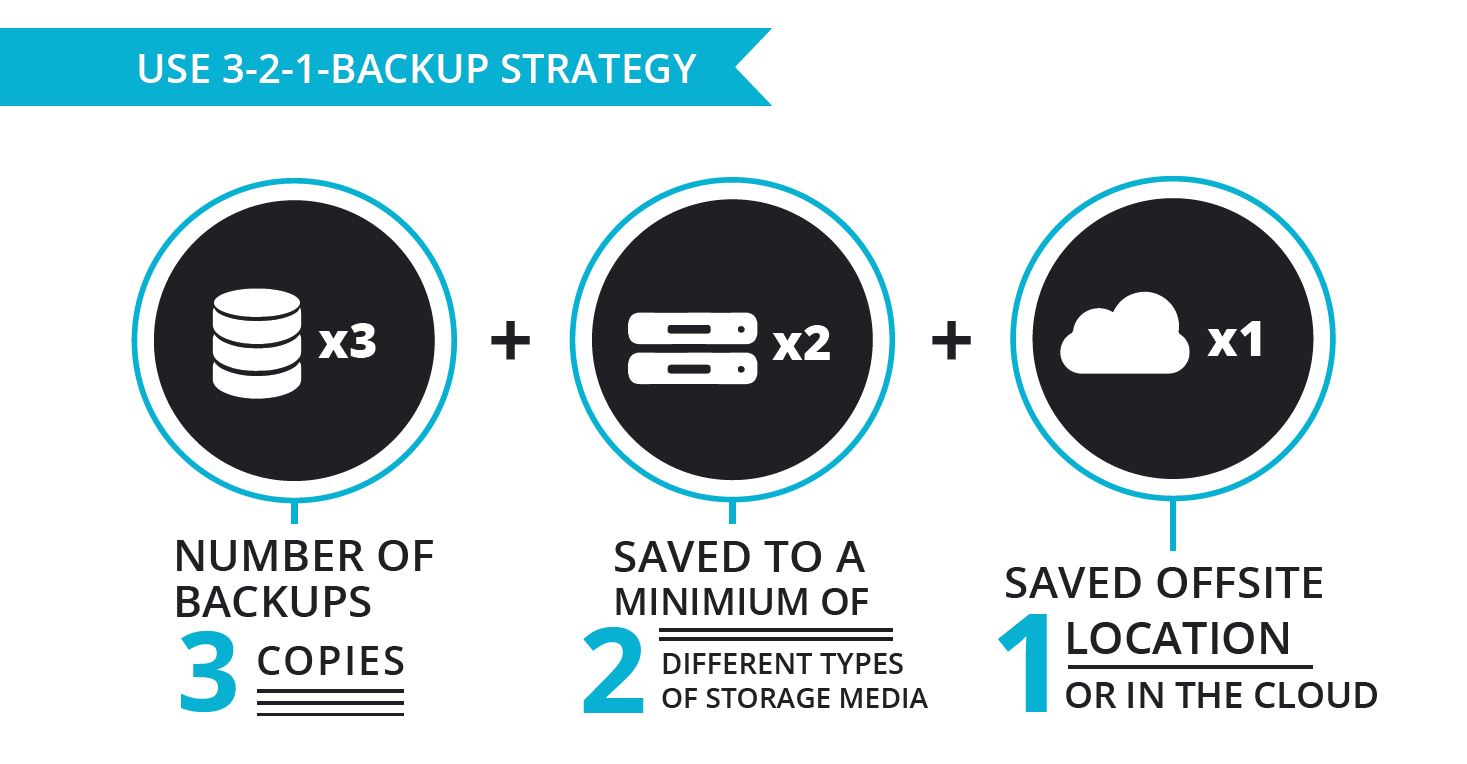
Redundancy and Data Distribution
A critical aspect of a reliable cloud backup strategy is ensuring data redundancy and distribution. Redundancy refers to storing multiple copies of data across different locations or cloud storage providers, while data distribution involves spreading the data across various regions or availability zones. Both techniques aim to minimize the risk of data loss due to provider outages, regional disasters, or other unforeseen circumstances.
Benefits of Redundancy and Data Distribution
Implementing redundancy and data distribution in your cloud backup strategy offers several benefits:
- Increased data availability: By storing multiple copies of data in different locations, you can ensure that your data remains accessible even if one storage provider or region experiences an outage.
- Improved disaster recovery: In the event of a regional disaster, having data distributed across various regions can help minimize data loss and expedite recovery efforts.
- Enhanced security: Storing data with multiple providers or in different regions can reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Strategies for Implementing Redundancy and Data Distribution
To effectively implement redundancy and data distribution in your cloud backup strategy, consider the following strategies:
- Use multiple cloud storage providers: By storing data with more than one provider, you can minimize the risk of data loss due to provider-specific issues or outages.
- Distribute data across regions: Store data in different regions or availability zones to reduce the risk of data loss due to regional disasters or outages.
- Implement data replication: Use cloud storage services that offer built-in data replication features to automatically create and maintain multiple copies of your data.
- Regularly test data recovery: Regularly test data recovery processes to ensure that data can be successfully restored from multiple locations or providers.
By incorporating redundancy and data distribution into your cloud backup strategy, you can significantly reduce the risk of data loss and ensure the long-term security and availability of your valuable data.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Backup and Restore
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Backup and Restore is a fully-managed service designed to centralize and automate data protection across AWS services. With its pay-as-you-go pricing model, AWS Backup offers a cost-effective solution for organizations looking to implement reliable backup strategies for cloud storage. This service supports various AWS resources, including Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) volumes, Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) databases, Amazon DynamoDB tables, Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) file systems, and AWS Storage Gateway volumes.
Key Features and Benefits
AWS Backup offers several features and benefits that make it an attractive option for cloud backup:
- Centralized management: AWS Backup enables users to manage backups for multiple AWS services from a single console, simplifying administration and reducing operational overhead.
- Automated backups: The service allows users to create backup plans that automate the backup process, ensuring consistent and timely backups without manual intervention.
- Policy-based backup rules: AWS Backup enables users to define backup policies based on specific rules, such as frequency, retention period, and resource tags, ensuring that data protection aligns with organizational requirements.
- Secure data transfer and storage: AWS Backup encrypts data in transit and at rest, using AWS Key Management Service (KMS) keys, ensuring the security and confidentiality of your data.
- Cost-effective: With its pay-as-you-go pricing model, AWS Backup allows users to pay only for the resources they consume, reducing the overall cost of data protection.
Real-World Use Cases and Customer Reviews
AWS Backup has been successfully implemented across various industries, with users praising its ease of use, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. For instance, a healthcare provider leveraged AWS Backup to centralize and automate backups for their AWS-based applications, ensuring compliance with stringent data protection regulations. A media company, on the other hand, used AWS Backup to reduce their data protection costs by 40% while maintaining a robust and reliable backup strategy.
Limitations
While AWS Backup offers numerous benefits, it does have some limitations. For example, it does not support backup and restore for Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) objects, requiring users to rely on native S3 features for data protection. Additionally, AWS Backup may not be the best option for organizations with stringent compliance requirements, as it does not offer the same level of granular control as some third-party backup solutions.
Conclusion
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Backup and Restore is a powerful and cost-effective solution for organizations looking to implement reliable backup strategies for cloud storage. By offering centralized management, automated backups, and policy-based backup rules, AWS Backup simplifies data protection and ensures the long-term security and availability of your valuable data.

Microsoft Azure Backup: A Reliable Cloud Backup Solution
Microsoft Azure Backup is a robust and secure cloud-based backup solution that offers organizations a reliable disaster recovery and data protection strategy. This service is designed to protect data across various workloads, including servers, applications, and client computers, by providing automated backups and flexible recovery options. This article will explore the unique selling points of Microsoft Azure Backup, its potential drawbacks, and how it compares with other popular cloud backup solutions.
One of the key advantages of Microsoft Azure Backup is its seamless integration with existing Microsoft environments. Organizations using Microsoft Windows Server, SQL Server, Exchange, and SharePoint can leverage Azure Backup to protect their data without needing to invest in additional infrastructure or third-party tools. This integration simplifies management and reduces the total cost of ownership for businesses looking to implement a reliable cloud backup strategy.
Azure Backup offers several features that make it an attractive choice for businesses. These features include centralized management, unlimited data storage, and long-term retention options. The centralized management console allows administrators to monitor and control backups for multiple servers and clients from a single interface, making it easy to manage even large-scale deployments. Unlimited data storage ensures that businesses never have to worry about running out of space for their backups, while long-term retention options enable organizations to maintain compliance with data retention policies and regulations.
However, Microsoft Azure Backup does have some limitations. For instance, it may not be the best choice for businesses that rely heavily on non-Microsoft platforms, as its integration capabilities are primarily focused on Microsoft environments. Additionally, while Azure Backup offers robust data protection features, it may not be as feature-rich as some dedicated third-party backup solutions. Businesses should carefully evaluate their specific needs and requirements before deciding whether Azure Backup is the right choice for their cloud backup strategy.
When comparing Microsoft Azure Backup with Amazon Web Services (AWS) Backup and Restore, several key differences emerge. While both services offer automated backups and flexible recovery options, Azure Backup’s seamless integration with Microsoft environments may give it an edge for businesses already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem. However, AWS Backup and Restore may be more appealing to organizations that use a mix of Microsoft and non-Microsoft platforms, as it supports a wider range of operating systems and applications. Ultimately, the choice between these two services will depend on an organization’s specific needs, existing infrastructure, and budget.
In conclusion, Microsoft Azure Backup is a reliable and secure cloud-based backup solution that offers organizations a robust disaster recovery and data protection strategy. Its seamless integration with Microsoft environments, centralized management, unlimited data storage, and long-term retention options make it an attractive choice for businesses looking to implement a reliable cloud backup strategy. However, organizations should carefully evaluate their specific needs and requirements before deciding whether Azure Backup is the right choice for them. By understanding the unique selling points and potential drawbacks of Microsoft Azure Backup, businesses can make informed decisions about their cloud backup strategies and ensure the long-term security and availability of their data.
Google Cloud Backup and Disaster Recovery
Google Cloud Backup and Disaster Recovery is a robust and flexible solution for businesses looking to protect their data and minimize downtime in the event of a disaster. This service offers a variety of features and benefits that make it an attractive choice for organizations of all sizes. In this article, we will explore Google Cloud Backup and Disaster Recovery’s capabilities, pricing, and user experience, and offer insights into its suitability for different use cases and industries.
Google Cloud Backup and Disaster Recovery offers several unique features that set it apart from other cloud backup solutions. For instance, it provides automated backups and flexible recovery options, allowing businesses to restore data at the file, application, or system level. This flexibility ensures that organizations can quickly recover from data loss events, minimizing downtime and reducing the impact on business operations.
One of the key advantages of Google Cloud Backup and Disaster Recovery is its pricing model. The service operates on a pay-as-you-go basis, meaning businesses only pay for the storage and resources they use. This pricing model provides businesses with greater flexibility and control over their cloud backup costs, allowing them to scale their backup strategy as their data volumes grow.
Google Cloud Backup and Disaster Recovery also offers robust data protection features, including encryption, access controls, and activity tracking. These features ensure that businesses can protect their data from unauthorized access, cyber threats, and data breaches. Additionally, Google Cloud Backup and Disaster Recovery provides businesses with the ability to distribute their data across multiple regions, reducing the risk of data loss due to provider outages or regional disasters.
However, Google Cloud Backup and Disaster Recovery does have some limitations. For instance, it may not be as feature-rich as some dedicated third-party backup solutions, and it may require more technical expertise to set up and manage. Additionally, while Google Cloud Backup and Disaster Recovery offers robust data protection features, it may not be as well-suited for businesses with highly regulated data or complex compliance requirements.
When comparing Google Cloud Backup and Disaster Recovery with other cloud backup solutions, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) Backup and Restore and Microsoft Azure Backup, businesses should carefully evaluate their specific needs and requirements. While all three services offer automated backups and flexible recovery options, Google Cloud Backup and Disaster Recovery’s pay-as-you-go pricing model and data distribution capabilities may make it a more attractive choice for businesses with fluctuating data volumes or those operating in multiple regions.
In conclusion, Google Cloud Backup and Disaster Recovery is a reliable and flexible cloud backup solution that offers businesses a robust disaster recovery and data protection strategy. Its pay-as-you-go pricing model, data protection features, and data distribution capabilities make it an attractive choice for organizations looking to protect their data and minimize downtime. However, businesses should carefully evaluate their specific needs and requirements before deciding whether Google Cloud Backup and Disaster Recovery is the right choice for their cloud backup strategy.

Regular Audits and Test Restores
Regular audits and test restores are essential components of a robust cloud backup strategy. These practices help ensure that your backup solution remains effective and reliable over time, minimizing the risk of data loss and downtime. By conducting regular audits, you can validate that your backup strategy is functioning as intended, identify potential issues, and address them proactively. Test restores, on the other hand, allow you to verify that your backup data can be successfully restored, ensuring that you can recover your data when needed.
To streamline the process of conducting regular audits and test restores, consider implementing the following best practices:
- Schedule recurring audits: Set up a regular schedule for auditing your backup solution, such as monthly or quarterly. This will help ensure that you consistently monitor your backup strategy and address any issues in a timely manner.
- Automate the audit process: Use backup management tools and software to automate the audit process, reducing the manual effort required and increasing the accuracy of the audit results.
- Document your findings: Keep a record of your audit results and any issues identified, along with the steps taken to address them. This documentation can help you track the effectiveness of your backup strategy over time and provide valuable insights for continuous improvement.
- Test restore frequently: Regularly test the restore process to ensure that your backup data can be successfully recovered. This will help you identify and address any issues with the restore process before they become critical.
- Simulate disaster scenarios: Test your backup strategy in simulated disaster scenarios, such as a complete system failure or a ransomware attack. This will help you ensure that your backup solution can effectively handle real-world data loss events and minimize downtime.
By incorporating regular audits and test restores into your cloud backup strategy, you can maintain a reliable and effective solution for protecting your valuable data. Remember to continuously monitor and optimize your backup strategy to ensure its long-term success.
Continuous Improvement and Optimization
As your business evolves and grows, so do your data protection needs. A reliable cloud backup strategy should be continuously improved and optimized to address changing data volumes, new threats, and evolving business requirements. Regularly review your backup strategy and consider the following best practices to ensure its ongoing effectiveness:
- Monitor data growth: Keep track of your data growth and adjust your backup strategy accordingly. As your data volumes increase, you may need to scale your backup resources or refine your data selection and prioritization process.
- Stay informed about emerging threats: Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and new vulnerabilities are discovered regularly. Stay up-to-date with the latest threat intelligence and adjust your backup strategy to address emerging risks, such as new ransomware variants or sophisticated phishing attacks.
- Evaluate new technologies: New backup technologies and services are regularly introduced to the market. Regularly evaluate these innovations and consider how they can be integrated into your backup strategy to improve its efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Review resource allocation: Periodically review your resource allocation to ensure that your backup strategy remains cost-effective and efficient. This includes assessing your storage capacity, network bandwidth, and computing resources, as well as optimizing your backup schedules and frequencies.
- Test and validate: Regularly test and validate your backup strategy to ensure that it remains effective and reliable. This includes conducting test restores, simulating disaster scenarios, and validating your backup data’s integrity and completeness.
By continuously improving and optimizing your cloud backup strategy, you can ensure that it remains a valuable and effective component of your overall data protection plan. Remember to stay proactive, informed, and adaptable to maintain the long-term security and availability of your valuable data in the cloud.
