What are RBAC Policies and Why are They Important?
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) policies are a type of access control model that restricts or grants user access to digital resources based on their roles within an organization. RBAC policies are crucial in managing user permissions and ensuring that individuals only have access to the resources they need to perform their job functions. By implementing RBAC policies, organizations can improve security, reduce administrative overhead, and increase operational efficiency.
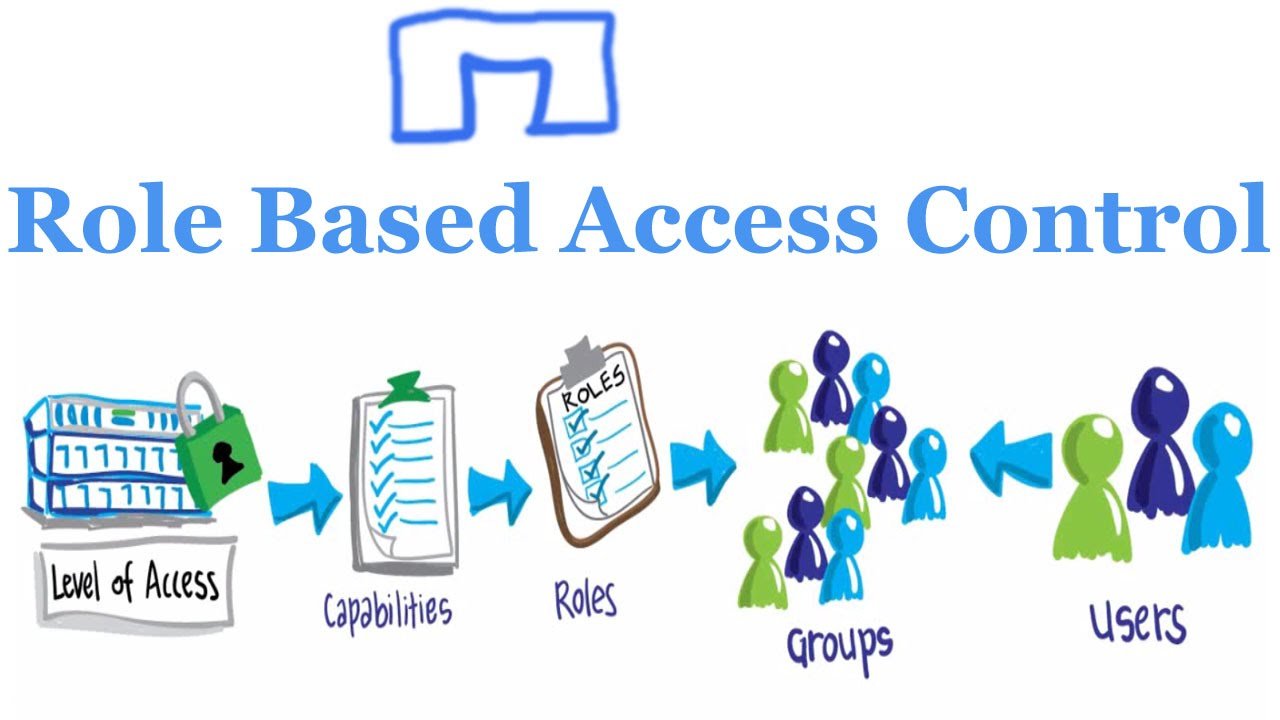
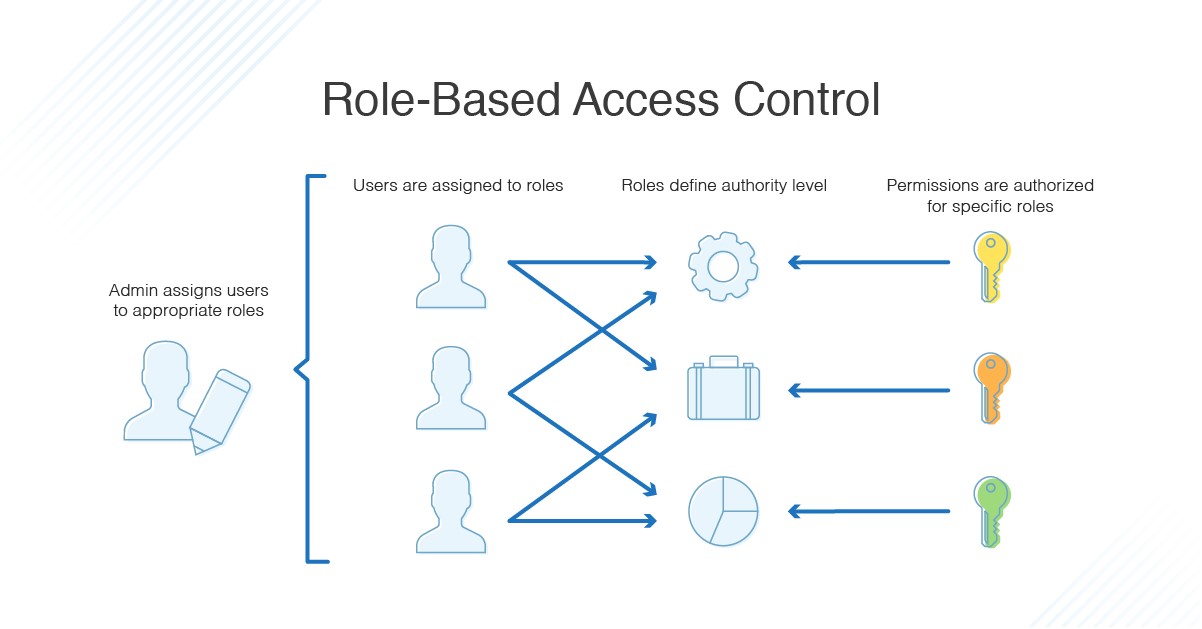
At the heart of RBAC policies are three essential components: roles, permissions, and users. Roles define the level of access and privileges that a user has, while permissions specify the actions that a user can perform on a particular resource. Users are assigned to one or more roles based on their job functions and responsibilities. By assigning users to roles and defining permissions for each role, organizations can ensure that users only have access to the resources they need to perform their job functions.
One of the primary benefits of RBAC policies is improved security. By restricting user access to only the resources they need, organizations can reduce the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats. Additionally, RBAC policies can help organizations meet compliance requirements for data privacy and security. By defining and enforcing access controls, organizations can demonstrate that they are taking appropriate measures to protect sensitive data.
Another benefit of RBAC policies is reduced administrative overhead. By defining roles and permissions once and assigning users to those roles, organizations can save time and resources compared to managing access controls on a per-user basis. This approach also ensures consistency in access controls and reduces the risk of errors or oversights. Furthermore, RBAC policies can help organizations manage user access as employees join, leave, or change roles within the organization.
Finally, RBAC policies can increase operational efficiency by ensuring that users have the access they need to perform their job functions. By defining roles and permissions based on job functions, organizations can ensure that users have the appropriate level of access to complete their tasks. This approach can also help organizations identify and address gaps in access controls that may be hindering productivity or efficiency.
Key Components of an Effective RBAC Policy
An effective RBAC policy includes three essential components: roles, permissions, and users. These components interact to ensure that users have the appropriate level of access to digital resources based on their job functions. By defining and managing these components, organizations can improve security, reduce administrative overhead, and increase operational efficiency.
Roles
Roles define the level of access and privileges that a user has within an organization. Roles can be based on job functions, such as administrator, manager, or employee. By defining roles, organizations can ensure that users have the appropriate level of access to complete their tasks and responsibilities. Roles can also help organizations manage user access as employees join, leave, or change roles within the organization.
Permissions
Permissions specify the actions that a user can perform on a particular resource. Permissions can include read, write, modify, or delete access. By defining permissions for each role, organizations can ensure that users only have the access they need to perform their job functions. Permissions can also help organizations manage security risks by limiting access to sensitive data and resources.
Users
Users are assigned to one or more roles based on their job functions and responsibilities. By assigning users to roles, organizations can ensure that users have the appropriate level of access to complete their tasks. Users can also be assigned to multiple roles, providing them with the access they need to perform cross-functional tasks. By managing user access, organizations can improve security, reduce administrative overhead, and increase operational efficiency.
RBAC policies can also include other components, such as groups and organizational units (OUs). Groups are collections of users who share common characteristics or job functions. OUs are hierarchical containers that organize users and resources within an organization. By using groups and OUs, organizations can further refine access controls and improve security.
In summary, an effective RBAC policy includes roles, permissions, and users as essential components. By defining and managing these components, organizations can improve security, reduce administrative overhead, and increase operational efficiency. By incorporating other components, such as groups and OUs, organizations can further refine access controls and improve security.
How to Implement RBAC Policies: Best Practices and Strategies
Implementing RBAC policies can be a complex process, but by following best practices and strategies, organizations can ensure a successful implementation. Here are some steps to consider when implementing RBAC policies:
Step 1: Define Roles
The first step in implementing RBAC policies is to define roles based on job functions and responsibilities. Roles should be clearly defined and aligned with the organization’s security policies and goals. It’s essential to involve stakeholders in this process to ensure that all job functions and responsibilities are considered.
Step 2: Assign Permissions
Once roles are defined, the next step is to assign permissions to each role. Permissions should be based on the principle of least privilege, meaning that users should only have the access they need to perform their job functions. It’s essential to regularly review and update permissions to ensure that they are still relevant and necessary.
Step 3: Assign Users to Roles
After defining roles and assigning permissions, the next step is to assign users to roles. Users should be assigned to the role that best matches their job functions and responsibilities. It’s essential to regularly review and update user assignments to ensure that they are still relevant and necessary.
Step 4: Monitor and Audit User Activity
Once RBAC policies are implemented, it’s essential to monitor and audit user activity to ensure that the policies are effective and that there are no security breaches. Regular audits can help identify potential security risks and provide data for making data-driven decisions for policy updates and changes.
Step 5: Maintain and Manage RBAC Policies
RBAC policies should be regularly maintained and managed to ensure that they are still relevant and effective. This includes regularly reviewing and updating roles, permissions, and user assignments, as well as monitoring and auditing user activity. It’s also essential to keep up with emerging trends and best practices in RBAC policies to ensure that the organization’s policies are up-to-date and effective.
When implementing RBAC policies, it’s essential to consider common challenges and how to overcome them. These challenges can include resistance to change, lack of user understanding, and difficulty in defining roles and permissions. To overcome these challenges, it’s essential to communicate the benefits of RBAC policies, provide training and support to users, and involve stakeholders in the implementation process.
In summary, implementing RBAC policies requires careful planning, definition of roles and permissions, assignment of users to roles, monitoring and auditing user activity, and ongoing maintenance and management. By following best practices and strategies, organizations can ensure a successful implementation and reap the benefits of improved security, reduced administrative overhead, and increased operational efficiency.
Comparing RBAC Policies to Other Access Control Models
RBAC policies are just one type of access control model used to manage user permissions and access to digital resources. Two other common access control models are discretionary access control (DAC) and mandatory access control (MAC). Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each model, as well as when to use them, is essential for effective access control.
Discretionary Access Control (DAC)
DAC is a type of access control model that allows the owner of a resource to grant or deny access to other users. This model is often used in file systems, where the owner of a file can set permissions for other users to read, write, or execute the file. DAC is flexible and allows for fine-grained access control, but it can also be complex and difficult to manage, especially in large organizations with many resources and users.
Mandatory Access Control (MAC)
MAC is a type of access control model that enforces access control based on a set of predefined rules. This model is often used in high-security environments, such as government or military organizations, where access to resources must be strictly controlled. MAC is less flexible than DAC but more secure, as access is based on predefined rules rather than the discretion of the resource owner.
When to Use RBAC, DAC, or MAC
The choice of access control model depends on the organization’s security requirements and the type of resources being accessed. RBAC is best suited for organizations with many users and resources, where access control needs to be scalable and manageable. DAC is best suited for environments where fine-grained access control is necessary, such as file systems or databases. MAC is best suited for high-security environments where access to resources must be strictly controlled.
It’s important to note that access control models are not mutually exclusive and can be used together to provide a layered approach to access control. For example, an organization may use RBAC to manage access to resources at a high level, while using DAC or MAC to provide fine-grained access control for specific resources.
In summary, RBAC, DAC, and MAC are three common access control models used to manage user permissions and access to digital resources. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each model, as well as when to use them, is essential for effective access control. By using a layered approach to access control, organizations can provide scalable, manageable, and secure access to digital resources.
Real-World Examples of Successful RBAC Policy Implementation
RBAC policies have been successfully implemented in a variety of organizations and systems, providing improved security, reduced administrative overhead, and increased operational efficiency. Here are some real-world examples of successful RBAC policy implementation:
Example 1: Healthcare Organization
A large healthcare organization implemented RBAC policies to manage access to patient records. The organization defined roles based on job functions, such as doctors, nurses, and administrative staff. Each role was assigned specific permissions to access patient records based on the principle of least privilege. The implementation resulted in improved security, reduced administrative overhead, and increased operational efficiency.
Example 2: Financial Institution
A financial institution implemented RBAC policies to manage access to financial data. The institution defined roles based on job functions, such as accountants, auditors, and financial analysts. Each role was assigned specific permissions to access financial data based on the principle of least privilege. The implementation resulted in improved security, reduced administrative overhead, and increased operational efficiency.
Example 3: E-commerce Platform
An e-commerce platform implemented RBAC policies to manage access to customer data. The platform defined roles based on job functions, such as customer service representatives, marketing specialists, and sales representatives. Each role was assigned specific permissions to access customer data based on the principle of least privilege. The implementation resulted in improved security, reduced administrative overhead, and increased operational efficiency.
Challenges and Lessons Learned
While implementing RBAC policies can provide significant benefits, it’s important to be aware of potential challenges and lessons learned from real-world examples. Some common challenges include resistance to change, lack of user understanding, and difficulty in defining roles and permissions. To overcome these challenges, it’s essential to communicate the benefits of RBAC policies, provide training and support to users, and involve stakeholders in the implementation process.
Lessons learned from real-world examples include the importance of ongoing maintenance and management of RBAC policies. Regular reviews and updates of roles, permissions, and user assignments can help ensure that the policies remain effective and relevant. It’s also essential to monitor and audit user activity to identify potential security risks and make data-driven decisions for policy updates and changes.
In summary, RBAC policies have been successfully implemented in a variety of organizations and systems, providing improved security, reduced administrative overhead, and increased operational efficiency. By learning from real-world examples and addressing potential challenges, organizations can successfully implement RBAC policies and reap the benefits they provide.
How to Evaluate and Improve Your RBAC Policy
Implementing an RBAC policy is an ongoing process that requires regular evaluation and improvement. Here are some tips for evaluating and improving your RBAC policy:
Monitor and Audit User Activity
Monitoring and auditing user activity is essential for identifying potential security risks and ensuring that the RBAC policy is effective. Regularly review user activity logs to identify any unusual or unauthorized access attempts. Use analytics tools to identify trends and patterns in user activity, such as frequent access to sensitive resources or high levels of activity during off-hours.
Identify Potential Security Risks
Identifying potential security risks is essential for improving your RBAC policy. Regularly review roles, permissions, and user assignments to identify any potential security risks. Look for roles with excessive permissions, users with unnecessary access, or permissions that are no longer needed.
Make Data-Driven Decisions
Making data-driven decisions is essential for improving your RBAC policy. Use analytics tools to identify trends and patterns in user activity, and use this data to make informed decisions about policy updates and changes. Consider implementing role-based analytics tools that provide insights into role-based access and usage patterns.
Implement a Role Review Process
Implementing a role review process is essential for ensuring that roles remain effective and relevant. Regularly review roles to identify any that are no longer needed or that have excessive permissions. Consider implementing an automated role review process that alerts administrators to roles that have not been used in a certain period of time or that have excessive permissions.
Provide Training and Support
Providing training and support is essential for ensuring that users understand and comply with the RBAC policy. Regularly provide training and resources to users on the importance of access control and the specific RBAC policy. Consider implementing a user support system that provides users with assistance in understanding and complying with the RBAC policy.
Continuously Improve
Continuously improving the RBAC policy is essential for ensuring that it remains effective and relevant. Regularly review and update the RBAC policy based on data-driven decisions, user feedback, and changes in the organization or system. Consider implementing an agile access control approach that allows for continuous improvement and adaptation to changing needs.
In summary, evaluating and improving your RBAC policy is an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring and auditing of user activity, identification of potential security risks, data-driven decision making, implementation of a role review process, provision of training and support, and continuous improvement. By following these tips, organizations can ensure that their RBAC policy remains effective and relevant, providing improved security, reduced administrative overhead, and increased operational efficiency.
The Future of RBAC Policies: Trends and Predictions
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) policies have been a critical component of access control for many organizations, providing improved security, reduced administrative overhead, and increased operational efficiency. As technology continues to evolve, so too will RBAC policies, with new trends and predictions emerging for the future of access control models.
Emerging Trends
One emerging trend in RBAC policies is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms to automate access control decisions. By using AI and ML algorithms to analyze user behavior and access patterns, organizations can make more informed access control decisions, reducing the risk of security breaches and improving operational efficiency.
Another trend is the integration of RBAC policies with cloud-based access control solutions. As more organizations move their digital resources to the cloud, there is a growing need for cloud-based access control solutions that can provide the same level of security and efficiency as on-premises solutions. Cloud-based RBAC policies can provide organizations with the flexibility and scalability they need to manage access to cloud-based resources.
Predictions for the Future
In the future, we can expect to see RBAC policies become more dynamic and adaptive, with real-time access control decisions based on user behavior and context. This will require the integration of advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to provide real-time insights into user behavior and access patterns.
We can also expect to see the continued integration of RBAC policies with other access control models, such as attribute-based access control (ABAC) and policy-based access control (PBAC). By combining different access control models, organizations can provide more granular and flexible access control, tailored to the specific needs of their users and resources.
Preparing for the Future
To prepare for the future of RBAC policies, organizations should consider the following best practices:
- Stay up-to-date with emerging trends and technologies in access control.
- Invest in advanced analytics and machine learning tools to provide real-time insights into user behavior and access patterns.
- Consider integrating RBAC policies with other access control models to provide more granular and flexible access control.
- Regularly review and update RBAC policies to ensure they remain effective and relevant.
- Provide training and support to users to ensure they understand and comply with RBAC policies.
In summary, the future of RBAC policies is promising, with emerging trends and predictions for the evolution of access control models. By staying up-to-date with these trends and best practices, organizations can prepare for the future of access control and ensure the security and efficiency of their digital resources.
Conclusion: The Importance of Effective RBAC Policies
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) policies are a critical component of access control for organizations of all sizes and industries. By defining roles, permissions, and users, RBAC policies provide a framework for managing user permissions and access to digital resources, improving security, reducing administrative overhead, and increasing operational efficiency.
Effective RBAC policies require careful planning, implementation, and maintenance. By following best practices and strategies for success, organizations can ensure that their RBAC policies are effective and relevant. Regular monitoring and auditing of user activity, identification of potential security risks, and data-driven decisions for policy updates and changes can help organizations continuously improve their RBAC policies and stay ahead of emerging trends and predictions in access control models.
As technology continues to evolve, so too will RBAC policies. By staying up-to-date with emerging trends and best practices, organizations can prepare for the future of access control and ensure the security and efficiency of their digital resources. We encourage readers to consider implementing RBAC policies in their own systems and to explore additional resources for further learning and implementation.