Understanding the Basics: Power BI and Tableau Overview
Power BI and Tableau are two of the most popular data visualization tools in the business intelligence industry. They enable organizations to transform raw data into interactive and visually appealing reports and dashboards, facilitating informed decision-making. Power BI, developed by Microsoft, primarily focuses on integrating with other Microsoft products and services, while Tableau, owned by Salesforce, is known for its user-friendly interface and extensive data manipulation capabilities.
When comparing Power BI and Tableau, it is essential to consider various factors, including licensing models, user types, and additional features. These factors significantly impact the overall cost and value of each tool, making it crucial to perform a comprehensive analysis before making a decision.
Key Factors to Consider When Comparing Power BI and Tableau Cost
When evaluating the cost of Power BI and Tableau, consider several essential aspects to ensure a well-informed decision. These factors include licensing models, user types, and additional features.
Licensing models play a significant role in determining the overall cost. Both Power BI and Tableau offer various licensing options tailored to different user needs and organizational requirements. Understanding these models and their associated costs is crucial for a fair comparison.
User types are another critical factor to consider. Power BI and Tableau categorize users into different groups, such as creators, explorers, and viewers, with varying costs and permissions. Assessing the number and type of users in your organization will help you estimate the total cost more accurately.
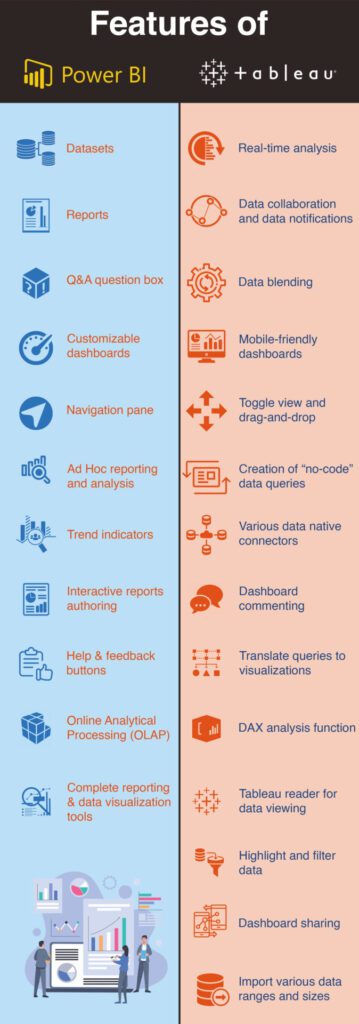
Lastly, consider the additional features offered by both tools. Power BI and Tableau provide various features, such as data connectors, data preparation tools, and AI capabilities. Evaluating the value of these features in the context of your business intelligence project will help you determine which tool offers the best cost-to-value ratio.
Power BI Pricing: Overview of Licensing Models and Costs
Power BI offers three primary licensing models, each catering to different user needs and organizational requirements. These models include Power BI Free, Power BI Pro, and Power BI Premium.
Power BI Free is a free version of the software that provides limited features, such as access to Power BI service, basic data refresh, and the ability to share content with others. However, it lacks advanced features like data connectors, collaboration tools, and increased data capacity.
Power BI Pro, priced at $9.99 per user per month (as of March 2023), offers advanced features such as data connectors, collaboration tools, and increased data capacity. It also includes features like AI capabilities, custom visuals, and the ability to publish reports to the web.
Power BI Premium, designed for large organizations, offers dedicated cloud computing resources for hosting and managing Power BI content. Priced at a minimum of $4,995 per month, it provides features like automatic data refresh, paginated reports, and the ability to embed Power BI content into custom applications.
Tableau Pricing: Overview of Licensing Models and Costs
Tableau offers several licensing models, each catering to different user needs and organizational requirements. These models include Tableau Public, Tableau Desktop, Tableau Prep, Tableau Server, and Tableau Online.
Tableau Public is a free version of the software that allows users to create and publish interactive data visualizations on the web. However, it lacks advanced features like data security, data governance, and the ability to connect to local data sources.
Tableau Desktop, priced at $70 per user per month (as of March 2023), offers advanced features such as data blending, data transformation, and advanced analytics. It also includes features like custom visuals, AI capabilities, and the ability to create offline visualizations.
Tableau Prep, priced at $35 per user per month, is a data preparation tool that allows users to clean, transform, and prepare data for analysis. It includes features like data profiling, data cleansing, and the ability to automate data preparation tasks.
Tableau Server, priced at $35 per user per month, is a server-based solution that allows organizations to host, manage, and share Tableau visualizations. It includes features like data governance, data security, and the ability to integrate with other business applications.
Tableau Online, priced at $42 per user per month, is a cloud-based solution that offers the same features as Tableau Server, without the need for on-premises infrastructure. It includes features like automatic software updates, automatic backups, and the ability to scale resources on demand.
Comparing Power BI and Tableau Cost: A Feature-by-Feature Analysis
When comparing Power BI and Tableau costs, consider the features offered in each licensing model and their respective values. This analysis will help you make an informed decision based on your organization’s needs and budget.
Power BI Free offers limited features, making it less suitable for large-scale business intelligence projects. However, it can be a good starting point for small organizations or individuals looking to explore data visualization.
Power BI Pro, priced at $9.99 per user per month, offers advanced features like data connectors, collaboration tools, and increased data capacity. It also includes features like AI capabilities, custom visuals, and the ability to publish reports to the web. This model is suitable for small to medium-sized organizations with a limited number of users.
Power BI Premium, priced at a minimum of $4,995 per month, offers dedicated cloud computing resources for hosting and managing Power BI content. It provides features like automatic data refresh, paginated reports, and the ability to embed Power BI content into custom applications. This model is suitable for large organizations with a high volume of data and a large number of users.
Tableau Public is a free version of the software that allows users to create and publish interactive data visualizations on the web. However, it lacks advanced features like data security, data governance, and the ability to connect to local data sources.
Tableau Desktop, priced at $70 per user per month, offers advanced features such as data blending, data transformation, and advanced analytics. It also includes features like custom visuals, AI capabilities, and the ability to create offline visualizations. This model is suitable for small to medium-sized organizations with a limited number of users.
Tableau Prep, priced at $35 per user per month, is a data preparation tool that allows users to clean, transform, and prepare data for analysis. It includes features like data profiling, data cleansing, and the ability to automate data preparation tasks. This model is suitable for organizations with a high volume of data and a need for data preparation.
Tableau Server, priced at $35 per user per month, is a server-based solution that allows organizations to host, manage, and share Tableau visualizations. It includes features like data governance, data security, and the ability to integrate with other business applications. This model is suitable for large organizations with a high volume of data and a large number of users.
Tableau Online, priced at $42 per user per month, is a cloud-based solution that offers the same features as Tableau Server, without the need for on-premises infrastructure. It includes features like automatic software updates, automatic backups, and the ability to scale resources on demand. This model is suitable for organizations with a need for cloud-based solutions and a large number of users.
How to Choose Between Power BI and Tableau Based on Cost and Value
When deciding between Power BI and Tableau based on cost and value, consider the following factors:
- Size of the organization: Power BI is a more cost-effective solution for small to medium-sized organizations, while Tableau is more suitable for large organizations with a high volume of data and a large number of users.
- Number of users: Power BI Pro and Tableau Desktop are priced per user per month, making them more suitable for organizations with a limited number of users. Power BI Premium and Tableau Server/Online are priced per user per month but also require a minimum number of users, making them more suitable for organizations with a larger number of users.
- Specific needs of the business intelligence project: Consider the features and capabilities required for your specific business intelligence project. Power BI offers a more integrated solution with other Microsoft products, while Tableau offers a more flexible and customizable solution.
- Data volume and complexity: Power BI is better suited for smaller data volumes and simpler data models, while Tableau is better suited for larger data volumes and more complex data models.
- Data security and governance: Tableau offers more advanced data security and governance features, making it more suitable for organizations with strict data security requirements.
- Integration with existing infrastructure: Consider the existing infrastructure and technology stack of your organization. Power BI offers better integration with other Microsoft products, while Tableau offers better integration with other third-party tools and platforms.
Ultimately, the decision between Power BI and Tableau should be based on a careful evaluation of the cost and value of their features, as well as the specific needs and requirements of your organization and business intelligence project.
Real-World Scenarios: Comparing Power BI and Tableau Cost in Practice
To better understand the practical implications of choosing between Power BI and Tableau based on cost and value, let’s look at some real-world examples and case studies.
Case Study 1: Small Non-Profit Organization
A small non-profit organization was looking for a cost-effective data visualization tool to analyze and report on their fundraising and program data. They chose Power BI Pro due to its lower cost per user and integration with other Microsoft products they were already using. The organization was able to create interactive reports and dashboards, share them with stakeholders, and make data-driven decisions without incurring significant costs.
Case Study 2: Medium-Sized Manufacturing Company
A medium-sized manufacturing company was looking for a data visualization tool to analyze and report on their production and sales data. They chose Tableau Desktop due to its advanced data manipulation and visualization capabilities. Although the cost per user was higher than Power BI Pro, the company found that the additional features and flexibility provided by Tableau were worth the investment.
Case Study 3: Large Financial Institution
A large financial institution was looking for a data visualization tool to analyze and report on their financial data. They chose Power BI Premium due to its ability to handle large data volumes and its integration with other Microsoft products they were already using. Although the cost was higher than Tableau Server or Online, the institution found that the cost was justified by the improved performance and integration with their existing infrastructure.
These case studies demonstrate that the decision between Power BI and Tableau based on cost and value depends on the specific needs and requirements of the organization and business intelligence project. By carefully evaluating the features and capabilities of each tool, organizations can make informed decisions that balance cost and value.
Making an Informed Decision: Balancing Cost and Value in Power BI and Tableau
When selecting a data visualization tool for business intelligence projects, it’s essential to balance cost and value. Both Power BI and Tableau offer robust features and capabilities, but the right choice depends on the specific needs and requirements of the organization and business intelligence project.
Here are some key takeaways from our comparative analysis of Power BI and Tableau costs:
- Power BI offers a more cost-effective solution for small to medium-sized organizations, while Tableau is more suitable for large organizations with a high volume of data and a large number of users.
- Power BI Pro and Tableau Desktop are priced per user per month, making them more suitable for organizations with a limited number of users. Power BI Premium and Tableau Server/Online are priced per user per month but also require a minimum number of users, making them more suitable for organizations with a larger number of users.
- Power BI offers a more integrated solution with other Microsoft products, while Tableau offers a more flexible and customizable solution.
- Power BI is better suited for smaller data volumes and simpler data models, while Tableau is better suited for larger data volumes and more complex data models.
- Tableau offers more advanced data security and governance features, making it more suitable for organizations with strict data security requirements.
- Consider the existing infrastructure and technology stack of your organization. Power BI offers better integration with other Microsoft products, while Tableau offers better integration with other third-party tools and platforms.
By carefully evaluating the features and capabilities of each tool and considering the specific needs and requirements of your organization and business intelligence project, you can make an informed decision that balances cost and value.