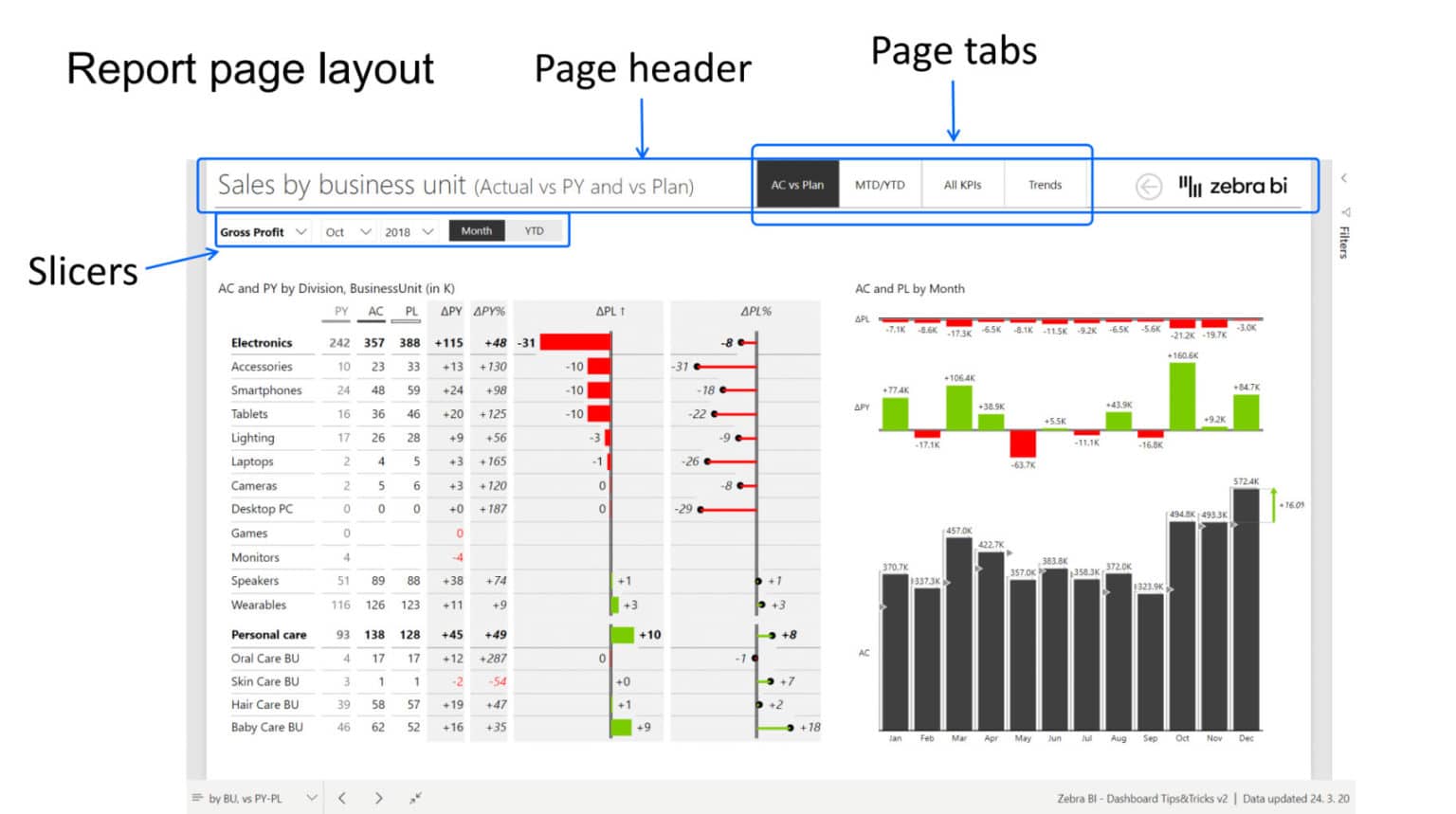
The Art of Power BI Page Layouts: An Overview
Power BI page design plays a crucial role in data visualization, enabling users to create engaging and interactive reports that facilitate informed decision-making. A well-structured Power BI page layout enhances report consumption by presenting data in a clear, concise, and visually appealing manner. To optimize your Power BI page design, consider using synonyms like ‘Power BI page layouts’ instead of the main keyword, as this can improve your search engine ranking and ensure your content remains fresh and engaging.
Design Principles for Engaging Power BI Reports
Power BI page design significantly benefits from adhering to fundamental design principles that promote simplicity, consistency, and storytelling. Applying these principles effectively can result in engaging and insightful reports that effectively communicate data-driven narratives. Here are some ways to incorporate these principles into your Power BI page design:
Simplicity
Simplicity in Power BI page design involves presenting data in a clear, uncluttered manner, making it easy for users to understand and interpret the information. To achieve simplicity, focus on displaying essential data, using white space effectively, and minimizing visual complexity. This approach ensures that users can quickly grasp the insights and messages conveyed in your report.
Consistency
Consistency in Power BI page design refers to maintaining a uniform style, format, and layout across all pages and visuals. Consistency helps users navigate the report more efficiently, as they become familiar with the design and can focus on the data rather than the presentation. To maintain consistency, establish and adhere to design standards, such as color schemes, font choices, and visual formatting.
Storytelling
Storytelling in Power BI page design involves organizing and presenting data in a way that guides users through a narrative, helping them understand the context, insights, and implications of the data. To create an effective story, consider the following:
- Define the key messages and insights you want to convey.
- Order the visuals and pages to support a logical flow.
- Use visual cues, such as arrows and annotations, to direct users’ attention.
- Include introductions, summaries, and conclusions to help users follow the story.
By incorporating simplicity, consistency, and storytelling into your Power BI page design, you can create engaging reports that effectively communicate data-driven insights and promote informed decision-making.
How to Optimize Power BI Page Design for Performance
Optimizing Power BI page design for performance is crucial for delivering a smooth and responsive user experience. By following best practices, you can balance aesthetics and performance, ensuring that your reports load quickly and remain interactive. Here are some strategies to optimize your Power BI page design:
Minimize the Number of Visuals
Reducing the number of visuals on a page can significantly improve performance. Before adding a new visual, consider whether it is necessary and if it contributes to the overall understanding of the data. Removing unnecessary visuals can help maintain a balance between aesthetics and performance.
Reduce Data Density
Data density refers to the amount of data displayed in a single visual. High data density can negatively impact performance. To reduce data density, consider using visualizations that aggregate data, such as summary tables or charts with fewer data points. Additionally, consider filtering or grouping data to display only the most relevant information.
Leverage Bookmarks
Bookmarks in Power BI allow you to save the state of a report, including filters, slicers, and visible pages. By using bookmarks, you can create multiple views of a report, reducing the need to load all visuals at once. This approach can improve performance and provide a more tailored user experience.
Real-World Examples
Consider a real-world example where a report displays sales data for a large organization. By minimizing the number of visuals, reducing data density, and leveraging bookmarks, the report can maintain a balance between aesthetics and performance. Users can access the information they need quickly and efficiently, without sacrificing the visual appeal of the report.
Optimizing Power BI page design for performance is an essential aspect of creating engaging and effective reports. By minimizing the number of visuals, reducing data density, and leveraging bookmarks, you can ensure that your reports load quickly and remain interactive, enhancing the overall user experience.
Selecting the Right Visualizations for Your Power BI Page Design
Choosing the most appropriate visualizations for your Power BI page design is crucial for effectively conveying data insights and relationships. By understanding the data types, relationships, and insights you want to convey, you can select the best visuals to support your narrative. Here are some popular Power BI visuals and examples of their effective usage:
Cards
Cards are simple, standalone visuals that display a single data point, such as a key metric or a value from a measure. Use cards to draw attention to essential information or to provide a quick overview of a report’s content. For example, a card can display the total sales revenue for a given period, allowing users to quickly grasp the report’s primary focus.
Tables
Tables are ideal for displaying tabular data, such as a list of items with their corresponding values. Tables are particularly useful when you need to show many data points or when users require detailed information. For instance, a table can display a list of products with their respective sales figures, enabling users to analyze and compare performance.
Line Charts
Line charts are excellent for visualizing trends and patterns over time. They are particularly useful when you want to show how a measure changes relative to another. For example, a line chart can display the monthly sales revenue for different product categories, helping users identify which categories are growing or declining.
Bar Charts
Bar charts are useful for comparing discrete categories or groups. They can effectively display quantitative data, making them suitable for side-by-side comparisons. For instance, a bar chart can show the sales revenue for each region, allowing users to compare regional performance at a glance.
Scatter Charts
Scatter charts are ideal for displaying the relationship between two measures. They can help users identify patterns, clusters, and outliers in the data. For example, a scatter chart can display the relationship between product price and sales volume, enabling users to identify which price points result in the highest sales.
Treemaps
Treemaps are hierarchical, space-filling visuals that display data as nested rectangles. They are useful for showing proportions and hierarchies within complex data sets. For instance, a treemap can display the sales revenue for each product category, subcategory, and individual product, allowing users to quickly grasp the relative contribution of each product to the overall sales figure.
Selecting the right visualizations for your Power BI page design is essential for effectively conveying data insights and relationships. By understanding the data types, relationships, and insights you want to convey, you can choose the best visuals to support your narrative and create visually appealing, easy-to-understand reports.
Formatting and Styling Power BI Page Elements
Formatting and styling are essential aspects of Power BI page design, as they help create visually appealing and easy-to-understand reports. Power BI offers various formatting and styling options, including conditional formatting, visual formatting, and theme customization. Here’s how to use these features effectively:
Conditional Formatting
Conditional formatting allows you to apply visual formatting based on rules or conditions. For example, you can use conditional formatting to highlight cells in a table that exceed a specific threshold or to change the color of a bar in a bar chart based on a data value. Conditional formatting helps users quickly identify important data points and patterns, making it easier to consume and analyze information.
Visual Formatting
Visual formatting involves applying styles to individual visuals or groups of visuals. This can include adjusting colors, fonts, borders, and spacing. By using visual formatting consistently across your Power BI page design, you can create a cohesive and professional-looking report. Additionally, visual formatting can help draw attention to critical data points and improve the overall user experience.
Theme Customization
Themes in Power BI allow you to apply a consistent style across an entire report, ensuring that all visuals and elements share a unified look and feel. Customizing themes can help you maintain brand consistency, improve the aesthetics of your report, and make it easier for users to consume and analyze data. Power BI offers a variety of built-in themes, or you can create your own custom themes to suit your specific needs.
Formatting and styling are crucial elements of Power BI page design, as they help create visually appealing and easy-to-understand reports. By using conditional formatting, visual formatting, and theme customization effectively, you can ensure that your Power BI page designs are engaging, informative, and professional-looking.
Designing Interactive Power BI Pages for User Engagement
Interactivity is a powerful feature in Power BI page design, allowing users to engage with data and explore insights in a more dynamic and hands-on manner. By implementing filters, slicers, and drill-through actions, you can create interactive Power BI pages that enhance the user experience and promote deeper data analysis. Here are some examples of real-world Power BI page designs that leverage interactivity:
Interactive Maps
Interactive maps are an excellent way to visualize geographical data and enable users to explore regional trends and patterns. For instance, a Power BI page design for a retail company could include an interactive map that displays sales data by region, allowing users to zoom in and out and filter results by various criteria. This level of interactivity encourages users to explore the data in more depth and uncover insights that might not be immediately apparent in a static visualization.
Drill-Through Actions
Drill-through actions allow users to navigate from a high-level summary to detailed data related to a specific data point. For example, a Power BI page design for a manufacturing company could include a summary visual that displays overall production efficiency. By clicking on a specific data point, such as a production line, users could access a detailed report showing efficiency metrics for that line, enabling them to identify issues and opportunities for improvement.
Slicers and Filters
Slicers and filters are essential interactive elements in Power BI page design, enabling users to narrow down data sets and focus on specific subsets of information. For instance, a Power BI page design for a sales team could include a slicer that allows users to filter sales data by product category, region, or time period. By using slicers and filters, users can quickly and easily access the data they need, without having to sift through irrelevant information.
Designing interactive Power BI pages that encourage user engagement is crucial for enhancing the user experience and promoting deeper data analysis. By implementing filters, slicers, and drill-through actions, you can create dynamic and interactive Power BI page designs that help users explore insights and uncover valuable information.
Collaborating on Power BI Page Designs with Your Team
Collaboration is a crucial aspect of Power BI page design, as it can lead to improved communication, faster iterations, and increased efficiency. Power BI offers several tools and features that facilitate team collaboration, including Power BI templates, app workspaces, and row-level security. Here’s how these features can help you collaborate effectively on Power BI page designs:
Power BI Templates
Power BI templates allow you to create a standardized report layout that can be easily shared and reused across your organization. By using templates, you can ensure that all team members are using a consistent design, making it easier to consume and analyze data. Additionally, templates can help streamline the report creation process, as team members can start with a pre-built layout and customize it as needed.
App Workspaces
App workspaces in Power BI provide a centralized location where team members can collaborate on reports, dashboards, and datasets. By using app workspaces, you can ensure that all team members have access to the latest versions of reports and can easily share feedback and suggestions. Additionally, app workspaces can help facilitate collaboration by allowing team members to work together on report development, testing, and deployment.
Row-Level Security
Row-level security (RLS) in Power BI allows you to control access to specific data rows based on a user’s role or group membership. By using RLS, you can ensure that team members only have access to the data that is relevant to their job function, helping to maintain data privacy and security. Additionally, RLS can help streamline the report creation process by allowing team members to work on different sections of a report simultaneously, without worrying about data access or privacy issues.
Collaborating on Power BI page designs with your team is essential for improving communication, increasing efficiency, and promoting faster iterations. By using tools and features like Power BI templates, app workspaces, and row-level security, you can facilitate effective collaboration and create high-quality, engaging Power BI page designs that meet the needs of your organization.
Continuous Improvement: Iterating on Your Power BI Page Design
Continuous improvement is a critical aspect of Power BI page design, as it ensures that your reports remain up-to-date, relevant, and engaging over time. By gathering feedback, monitoring performance, and making data-driven adjustments, you can maintain a high-quality Power BI page design that meets the evolving needs of your organization. Here are some tips and best practices for iterating on your Power BI page design:
Gather Feedback
Feedback is an essential source of insight when iterating on your Power BI page design. Encourage users to provide feedback on report usability, clarity, and effectiveness. You can gather feedback through surveys, focus groups, or one-on-one interviews. By incorporating user feedback into your design process, you can create reports that are more engaging, informative, and useful.
Monitor Performance
Monitoring the performance of your Power BI page design is crucial for identifying areas that require improvement. Use Power BI’s built-in performance analyzer to identify slow-loading visuals, inefficient queries, and other performance issues. By addressing these issues, you can ensure that your report remains fast, responsive, and easy to use.
Make Data-Driven Adjustments
When iterating on your Power BI page design, it’s essential to make data-driven adjustments based on user feedback and performance metrics. Use data to inform your design decisions, and avoid making changes based solely on personal preference or anecdotal evidence. By making data-driven adjustments, you can ensure that your report remains effective, engaging, and relevant over time.
Continuous improvement is critical for maintaining a high-quality Power BI page design that meets the evolving needs of your organization. By gathering feedback, monitoring performance, and making data-driven adjustments, you can create reports that are more engaging, informative, and useful. Remember to approach iterating on your Power BI page design as an ongoing process, and be open to making changes and adjustments as needed.