Understanding the Basics: OPX and CAPX Defined
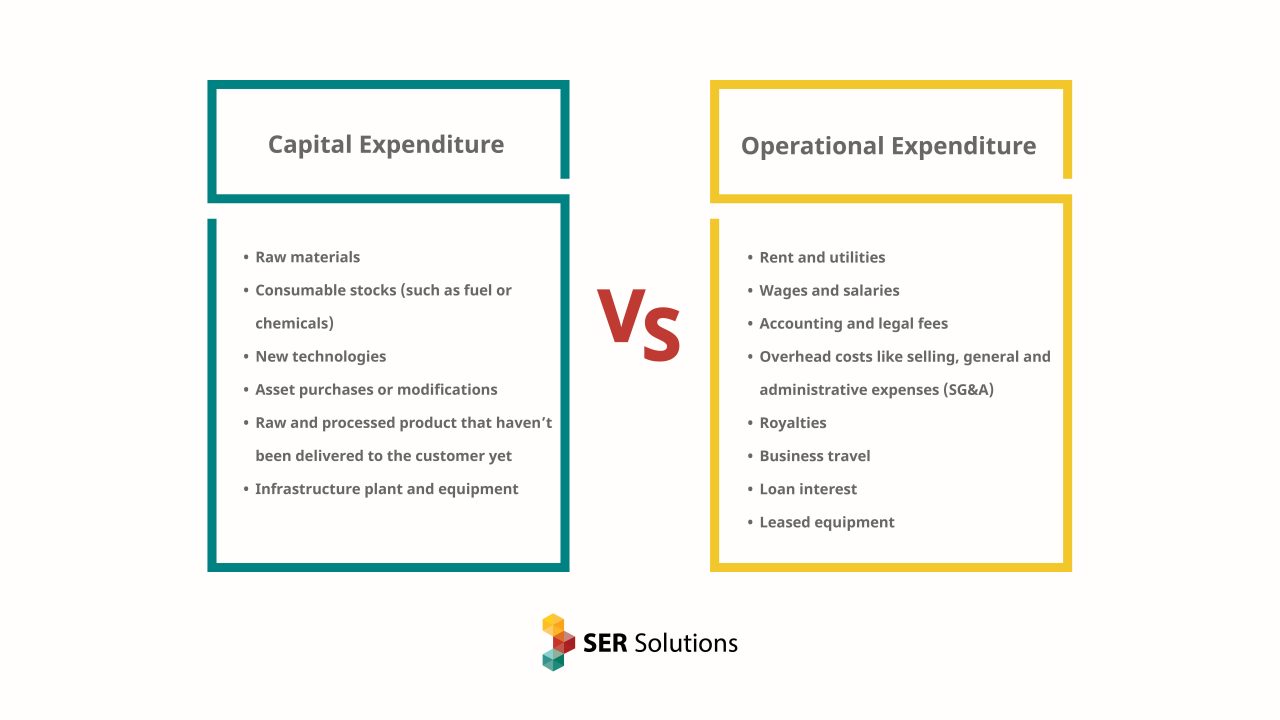
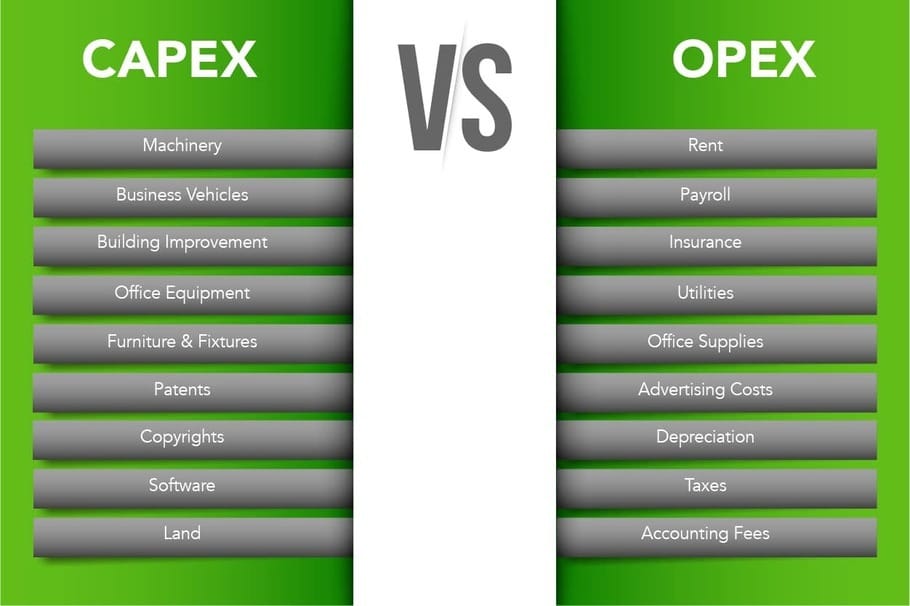
When discussing business investment decisions, two essential terms often arise: OPX and CAPX. Operating expenses, or OPX, represent the costs associated with a company’s day-to-day operations. These expenses typically include wages, rent, utilities, and maintenance. On the other hand, capital expenditures, or CAPX, refer to the funds invested in long-term assets, such as property, plant, equipment, or intellectual property. Both OPX and CAPX play crucial roles in a company’s financial health and operational efficiency, and understanding their differences is vital for making informed investment decisions.
Key Differences: OPX vs CAPX Contrasted
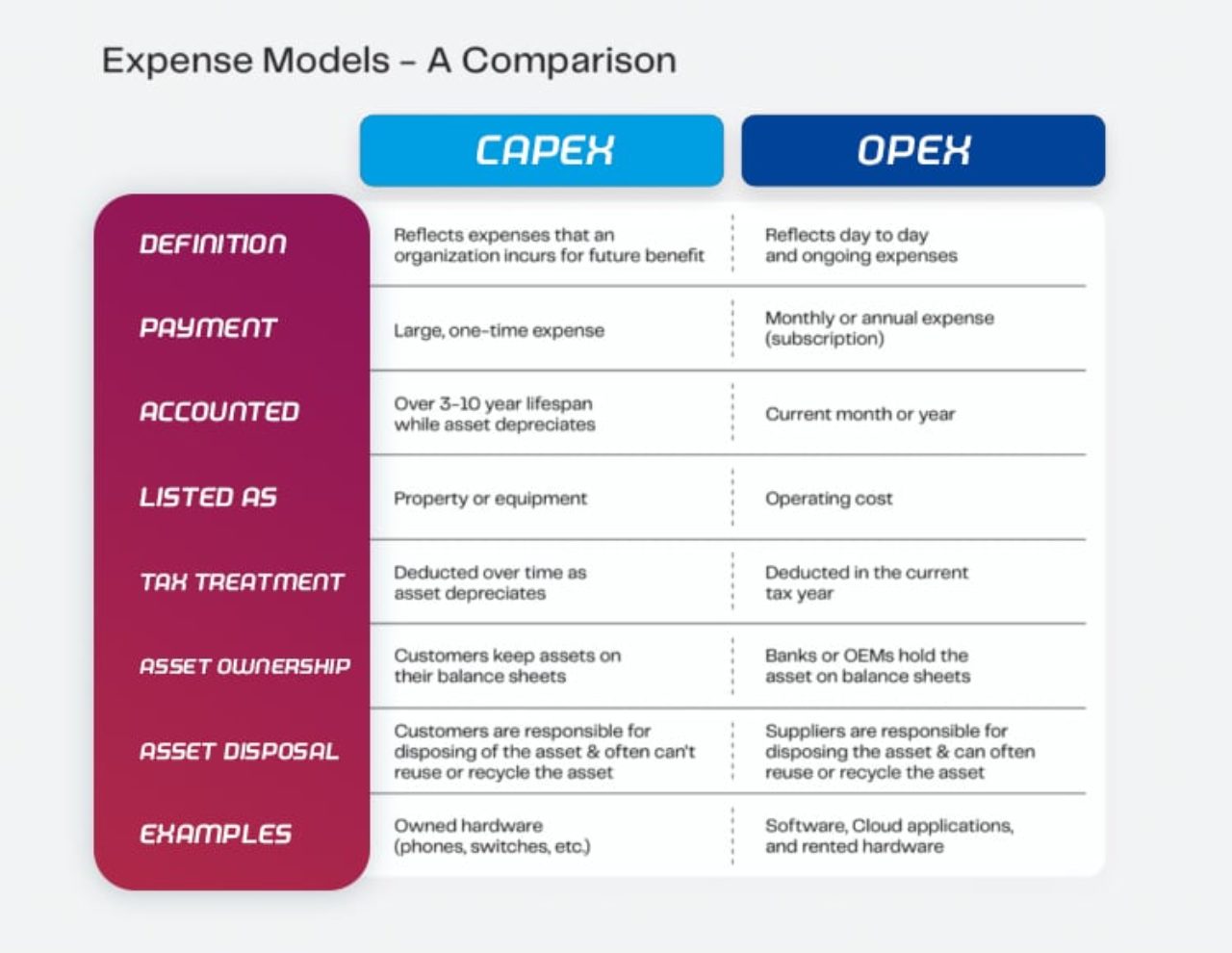
OPX and CAPX differ significantly in their impact on a company’s financial health and operational efficiency. Operating expenses (OPX) are the costs incurred in the day-to-day operations of a business, typically including wages, rent, utilities, and maintenance. These expenses are immediately expensed, reducing a company’s net income and affecting its profitability. In contrast, capital expenditures (CAPX) represent long-term investments in assets such as property, plant, equipment, or intellectual property. CAPX is capitalized, meaning the costs are spread over the asset’s useful life, and depreciation or amortization is expensed annually.
Understanding the differences between OPX and CAPX is essential when making investment decisions, as they impact a company’s financial statements and ratios differently. For instance, high OPX may signal inefficiencies or a low-margin business model, while substantial CAPX could indicate growth opportunities or a need for modernization. Comparing OPX and CAPX over time and against industry benchmarks can provide valuable insights into a company’s financial health and competitive position.
How to Analyze OPX and CAPX: A Practical Guide
Analyzing operating expenses (OPX) and capital expenditures (CAPX) is crucial for understanding a company’s financial health and investment strategies. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to analyze OPX and CAPX:
- Calculate OPX and CAPX: Start by determining a company’s OPX and CAPX for the desired time frame. OPX includes wages, rent, utilities, and maintenance, while CAPX consists of long-term investments in assets such as property, plant, equipment, or intellectual property.
- Determine Relevant Ratios: Identify essential financial ratios to assess a company’s performance, such as the OPX ratio (OPX as a percentage of revenue), the CAPX ratio (CAPX as a percentage of revenue), and the capital expenditure ratio (CAPX divided by depreciation).
- Compare Values Over Time: Analyze OPX and CAPX trends by comparing values over time. This comparison helps identify potential issues, such as increasing OPX or decreasing CAPX, which could signal inefficiencies or a lack of growth investments.
- Benchmark Against Industry Peers: Compare a company’s OPX and CAPX ratios against industry averages or competitors. This comparison provides insights into a company’s relative performance and competitive position.
- Assess Financial Statements: Review income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements to understand the impact of OPX and CAPX on a company’s financial health and operational efficiency.
Regularly analyzing OPX and CAPX is essential for making informed investment decisions and ensuring a company’s long-term financial sustainability. By comparing these values over time and against industry benchmarks, investors and managers can identify strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement.
OPX vs CAPX: Real-World Examples
Real-world examples can provide valuable insights into how companies successfully manage operating expenses (OPX) and capital expenditures (CAPX) to achieve growth and profitability. Here are two scenarios:
Example 1: Streamlining OPX in a Service-Based Business
A mid-sized marketing agency sought to optimize its OPX to improve profitability. By implementing a comprehensive performance management system, the agency closely monitored project costs, employee utilization rates, and client acquisition expenses. As a result, they identified inefficiencies and implemented process improvements, reducing OPX by 10% while maintaining the same level of service quality.
Example 2: Strategic CAPX Investments in a Manufacturing Company
A large manufacturing firm aimed to increase production capacity and efficiency. By investing in cutting-edge automation technology, they significantly improved their CAPX management. The new equipment not only increased output by 25% but also reduced maintenance costs and energy consumption, leading to long-term savings and improved financial performance.
These examples demonstrate the importance of effectively managing OPX and CAPX in various business contexts. By focusing on continuous improvement and strategic investments, companies can enhance operational efficiency, reduce financial risks, and boost profitability.
Strategies for Optimizing OPX and CAPX
Effectively managing operating expenses (OPX) and capital expenditures (CAPX) is crucial for businesses seeking to maximize returns and minimize financial risks. Here are several strategies to optimize OPX and CAPX:
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Develop detailed budgets and forecasts for OPX and CAPX, aligning them with a company’s strategic objectives. Regularly review and update these projections to ensure accuracy and relevance.
- Cost Containment: Implement cost-saving measures for OPX, such as negotiating better vendor contracts, optimizing resource utilization, and adopting energy-efficient technologies. For CAPX, consider leasing or sharing assets to reduce upfront costs and improve cash flow.
- Lifecycle Cost Analysis: Perform lifecycle cost analyses for CAPX investments, evaluating the total cost of ownership, including acquisition, operation, maintenance, and disposal costs. This approach helps identify the most cost-effective solutions and minimizes long-term financial risks.
- Performance Metrics: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor OPX and CAPX. Regularly track these metrics to identify trends, inefficiencies, or opportunities for improvement.
- Regular Reviews: Conduct periodic reviews of OPX and CAPX to ensure alignment with strategic objectives and to identify potential areas for optimization. Adjust spending as necessary to maintain financial health and support growth initiatives.
By implementing these strategies, businesses can optimize OPX and CAPX, maximizing returns and minimizing financial risks. Regular reviews, cost containment measures, and strategic investments can significantly enhance a company’s operational efficiency and long-term profitability.
The Role of OPX and CAPX in Financial Planning
Operating expenses (OPX) and capital expenditures (CAPX) play crucial roles in a company’s financial planning process. Understanding their impact on budgeting, forecasting, and long-term financial projections is essential for making informed investment decisions.
Budgeting
Incorporating OPX and CAPX into a company’s budget is vital for maintaining financial health and supporting growth initiatives. By allocating resources for day-to-day operations and long-term investments, businesses can ensure they have the necessary funds to achieve their strategic objectives.
Forecasting
Accurate forecasting of OPX and CAPX requires a thorough understanding of historical trends, industry benchmarks, and future growth prospects. Regularly reviewing and updating OPX and CAPX forecasts can help businesses anticipate cash flow needs, identify potential financial risks, and make proactive adjustments to their investment strategies.
Long-Term Financial Projections
OPX and CAPX significantly impact a company’s long-term financial projections, influencing revenue growth, profitability, and cash flow. By analyzing OPX and CAPX trends and making strategic investments, businesses can optimize their financial performance and ensure long-term sustainability.
Incorporating OPX and CAPX into a company’s financial planning process is essential for making informed investment decisions and achieving long-term success. By understanding the impact of these expenses on budgeting, forecasting, and financial projections, businesses can effectively manage their resources, minimize financial risks, and maximize returns.
Potential Pitfalls: Common Mistakes in Managing OPX and CAPX
Effective management of OPX and CAPX requires careful planning, execution, and monitoring. However, businesses often make common mistakes that can lead to suboptimal performance and financial risks. Here are some potential pitfalls to avoid:
- Ignoring Industry Benchmarks: Failing to compare OPX and CAPX against industry benchmarks can result in a company misinterpreting its financial performance. Benchmarking helps identify areas for improvement and ensures alignment with best practices.
- Inadequate Forecasting: Inaccurate forecasting of OPX and CAPX can lead to cash flow issues, unplanned expenses, and missed growth opportunities. Regularly reviewing and updating forecasts helps businesses stay agile and adapt to changing circumstances.
- Misaligned Strategic Objectives: Failing to align OPX and CAPX with a company’s strategic objectives can result in wasted resources and suboptimal performance. Ensure that all investments support long-term growth and profitability.
- Insufficient Cost Containment: Neglecting cost containment measures for OPX can result in unnecessary expenses and reduced profitability. Regularly review OPX and implement cost-saving measures where possible.
- Overlooking Lifecycle Costs: Failing to consider lifecycle costs for CAPX investments can lead to unexpected expenses and reduced long-term returns. Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including acquisition, operation, maintenance, and disposal costs, when making capital expenditure decisions.
By avoiding these common pitfalls, businesses can effectively manage OPX and CAPX, maximizing returns and minimizing financial risks. Proper planning, execution, and monitoring are essential for ensuring the alignment of OPX and CAPX with a company’s strategic objectives and maintaining long-term financial health.
The Future of OPX and CAPX: Trends and Predictions
As businesses continue to evolve and adapt to changing market conditions, understanding the future of operating expenses (OPX) and capital expenditures (CAPX) is essential for making informed investment decisions. Here are some emerging trends and future predictions for OPX and CAPX:
- Increased Digital Transformation: The ongoing shift towards digital technologies will continue to impact OPX and CAPX. Businesses can expect increased investments in cloud computing, data analytics, automation, and cybersecurity, while traditional OPX categories like travel and office supplies may decline.
- Sustainability and ESG Considerations: Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors will play an increasingly important role in OPX and CAPX decisions. Companies will prioritize investments in sustainable technologies, energy-efficient equipment, and ethical supply chains to meet growing ESG expectations from investors, customers, and regulators.
- Flexible Work Models: The rise of remote and hybrid work models may lead to changes in OPX and CAPX. Businesses may see reduced office space expenses and increased investments in remote collaboration tools, while CAPX may focus on technology infrastructure to support a distributed workforce.
- Continuous Monitoring and Optimization: Advanced analytics and real-time monitoring tools will enable businesses to optimize OPX and CAPX more effectively. By leveraging data-driven insights, companies can identify inefficiencies, streamline processes, and make more informed investment decisions.
Staying informed about the future of OPX and CAPX is crucial for businesses seeking to maintain a competitive edge and achieve long-term success. By understanding these trends and predictions, companies can adapt their investment strategies, optimize resources, and capitalize on emerging opportunities in the ever-evolving business landscape.