OCID: A Key Term in the Digital World
OCID, or Oracle Cloud Identifier, is a unique identifier assigned to every resource in the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. This alphanumeric string plays a crucial role in managing and accessing cloud-based resources securely and efficiently. Understanding the OCID meaning is essential for developers, administrators, and users working with Oracle’s cloud services.
The Role of OCID in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
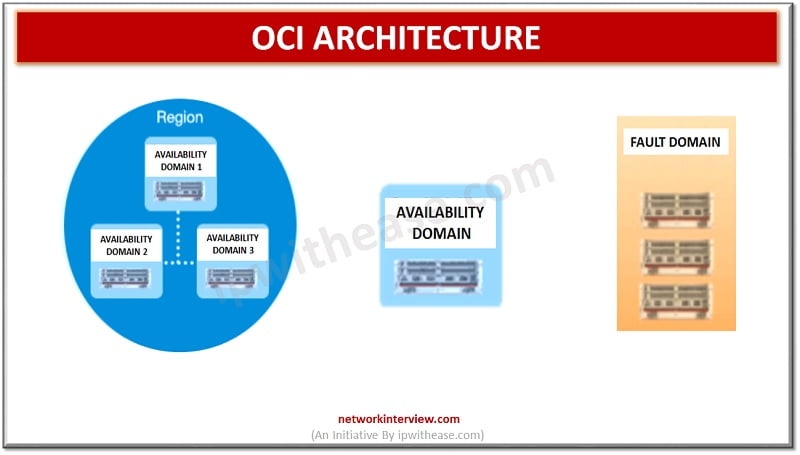
OCID, or Oracle Cloud Identifier, is a fundamental component of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, serving as a unique identifier for every resource within the platform. Its primary function is to facilitate seamless management and secure access to cloud-based resources.
In the context of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, OCID is essential for several reasons. First, it enables users to precisely identify and manage individual resources, such as compute instances, block volumes, and virtual cloud networks. By assigning a unique OCID to each resource, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure allows for granular control and monitoring, ensuring that users can efficiently manage their cloud environments.
Second, OCID plays a critical role in maintaining secure access to cloud resources. By using OCID in conjunction with Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies, administrators can define and enforce fine-grained access controls, restricting or granting permissions to specific users, groups, or compartments. This approach ensures that only authorized individuals can access and manage cloud resources, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
In summary, OCID is an integral part of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, providing a means to uniquely identify and manage cloud resources while ensuring secure access. Understanding the role of OCID is crucial for making the most of Oracle’s cloud services and effectively managing cloud-based resources.
How to Locate Your Oracle Cloud Identifier (OCID)
To find your Oracle Cloud Identifier (OCID) within the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure console, follow these straightforward steps:
- Log in to your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure account using your credentials.
- From the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure dashboard, navigate to the left-side menu and click on the “Governance & Administration” section.
- Under “Governance & Administration,” select “Tenancy Details.”
- In the “Tenancy Details” page, locate the “OCID” field. Your OCID will be displayed as a unique alphanumeric string.
- Copy the OCID and store it securely for future reference. It is essential to handle your OCID with care, as it provides access to your cloud resources.
By following these simple steps, you can quickly locate your OCID within the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure console. Having your OCID at hand will enable you to manage and monitor your cloud resources effectively.
Understanding OCID Components: A Detailed Breakdown
An Oracle Cloud Identifier (OCID) is a unique alphanumeric string that consists of several components, each serving a specific purpose. Understanding these components can provide valuable insights into the structure and functionality of an OCID.
- Tenancy ID: The tenancy ID is a unique identifier for your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure tenancy. It represents the top-level container for all your cloud resources and serves as the root for your cloud infrastructure hierarchy.
- Region: The region component of an OCID specifies the geographical location where your cloud resource is deployed. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure has multiple regions worldwide, enabling users to choose a location that best suits their needs in terms of data privacy, latency, and compliance requirements.
- Resource Type: The resource type indicates the specific Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resource associated with the OCID. This could be a compute instance, block volume, virtual cloud network, or any other resource type available within the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure ecosystem.
- Resource-Specific Details: Depending on the resource type, additional components may be included in the OCID to provide further details about the resource. For instance, a compute instance OCID might include the instance ID, availability domain, and compartment information.
By understanding the components of an OCID, you can better manage and monitor your cloud resources, ensuring that you maintain control over your cloud infrastructure and can effectively utilize Oracle Cloud Infrastructure’s powerful features and capabilities.
Security Best Practices for Handling OCID
An Oracle Cloud Identifier (OCID) is a critical piece of information that provides access to your cloud resources. As such, it is essential to implement robust security measures to protect your OCID and prevent unauthorized access. Here are some best practices for managing and safeguarding your OCID:
- Limit Access: Only provide OCID access to authorized personnel who require it for managing cloud resources. Implement strict access control policies using Identity and Access Management (IAM) to ensure that only the right individuals have access to your OCID.
- Store Securely: Store your OCID securely, using a password manager or other secure storage solutions. Avoid storing your OCID in publicly accessible locations, such as email, chat platforms, or version control systems.
- Regularly Review: Regularly review OCID access and usage to detect any unauthorized or suspicious activity. Monitoring tools and logs can help you identify potential security threats and take appropriate action.
- Rotate OCIDs: Periodically rotate your OCIDs to minimize the risk of unauthorized access. Rotating OCIDs reduces the attack surface and ensures that any compromised OCIDs are no longer valid.
- Use IAM Roles: Instead of sharing OCIDs directly, consider using IAM roles to delegate access to cloud resources. IAM roles allow you to grant specific permissions to users or groups without exposing sensitive OCID information.
By following these best practices, you can effectively manage and protect your OCID, ensuring the security and integrity of your cloud resources.
OCID Use Cases: Real-World Applications
Oracle Cloud Identifiers (OCIDs) play a crucial role in managing and monitoring cloud resources in various real-world scenarios. Here are some examples of how OCIDs are utilized in real-world applications:
- Resource Management: OCIDs enable users to manage and monitor individual cloud resources, such as compute instances, block volumes, and virtual cloud networks. By using OCIDs, administrators can efficiently control resource configurations, update policies, and track resource usage, ensuring optimal performance and security.
- Access Control: OCIDs are integral to Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. By associating OCIDs with IAM policies, administrators can define and enforce fine-grained access controls, restricting or granting permissions to specific users, groups, or compartments. This approach ensures that only authorized individuals can access and manage cloud resources, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
- Auditing and Compliance: OCIDs facilitate auditing and compliance by enabling users to track resource activities and monitor changes. By integrating OCIDs with logging and monitoring tools, organizations can maintain a detailed record of resource usage and access, ensuring adherence to internal policies and external regulations.
- Automation and Scripting: OCIDs are essential for automating cloud resource management tasks using scripts and APIs. By incorporating OCIDs into automation workflows, users can efficiently manage and scale cloud resources, reducing manual intervention and potential errors.
These real-world examples demonstrate the versatility and importance of OCIDs in managing and securing cloud resources in various industries and applications.
OCID vs. Other Identifiers: A Comparative Analysis
Oracle Cloud Identifier (OCID) is a unique identifier used within Oracle Cloud Infrastructure to manage and monitor cloud resources. While OCIDs serve a similar purpose to other identifiers in the industry, they have distinct features and advantages that set them apart. Here’s a comparative analysis of OCID and other identifiers:
- AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) Role ARNs: Amazon Web Services (AWS) uses IAM Role ARNs (Amazon Resource Names) to identify and manage resources within its cloud infrastructure. While both OCIDs and IAM Role ARNs serve similar purposes, OCIDs offer a more granular breakdown of components, such as tenancy ID, region, and resource type, providing a more detailed understanding of the resource hierarchy.
- Microsoft Azure Resource IDs: Microsoft Azure uses Resource IDs to identify resources within its cloud infrastructure. Similar to OCIDs, Azure Resource IDs consist of several components, including subscription ID, resource group, and resource type. However, OCIDs offer a more flexible and customizable structure, allowing users to define additional components, such as the compartment, to better organize and manage their cloud resources.
- Google Cloud Resource Names: Google Cloud Platform (GCP) uses Resource Names to identify resources within its cloud infrastructure. Resource Names in GCP are similar to OCIDs in that they consist of several components, including project ID, location, and resource type. Nevertheless, OCIDs provide a more comprehensive and fine-grained structure, enabling users to better manage and monitor their cloud resources.
In summary, while OCIDs share similarities with other identifiers in the industry, they offer unique features and advantages, such as a more granular breakdown of components and greater flexibility in defining additional components. These distinctions make OCIDs a powerful and valuable tool for managing and monitoring cloud resources within Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
Staying Updated: The Future of OCID
Oracle Cloud Identifier (OCID) has become an essential component of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, providing a robust and secure method for managing and monitoring cloud resources. As cloud technologies continue to evolve, OCID is expected to adapt and expand, offering new features and capabilities to meet the growing demands of users and organizations.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: As cloud infrastructure continues to support emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT), OCIDs will likely play a crucial role in managing and securing these resources. By integrating OCIDs with these advanced technologies, Oracle can ensure seamless management and secure access for users and organizations.
- Enhanced Security Features: Security remains a top priority for organizations leveraging cloud infrastructure. OCID is expected to introduce enhanced security features, such as advanced encryption and multi-factor authentication, to further strengthen the security and integrity of cloud resources.
- Improved Scalability and Flexibility: As cloud infrastructure scales to accommodate growing workloads and increasingly complex applications, OCIDs will need to adapt and offer improved scalability and flexibility. This may include support for additional resource types, expanded customization options, and more efficient methods for managing large-scale cloud environments.
- Integration with Third-Party Services: Oracle is likely to expand OCID’s compatibility with third-party services and platforms, enabling users to manage and monitor their cloud resources more effectively. By integrating OCIDs with popular tools and services, Oracle can provide users with a seamless and unified experience for managing their cloud infrastructure.
Staying informed about the evolution of OCID is crucial for organizations and users looking to maximize the potential of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. By understanding the future developments of OCID, you can ensure that your cloud management strategies remain up-to-date, efficient, and secure.