Understanding the Cloud Migration Process: An Overview
Migration to cloud steps is a strategic approach to optimizing an organization’s IT infrastructure and operations. By transitioning from on-premises systems to cloud-based services, businesses can enhance flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency. Proper planning, execution, and monitoring are crucial elements for a successful migration to cloud process.
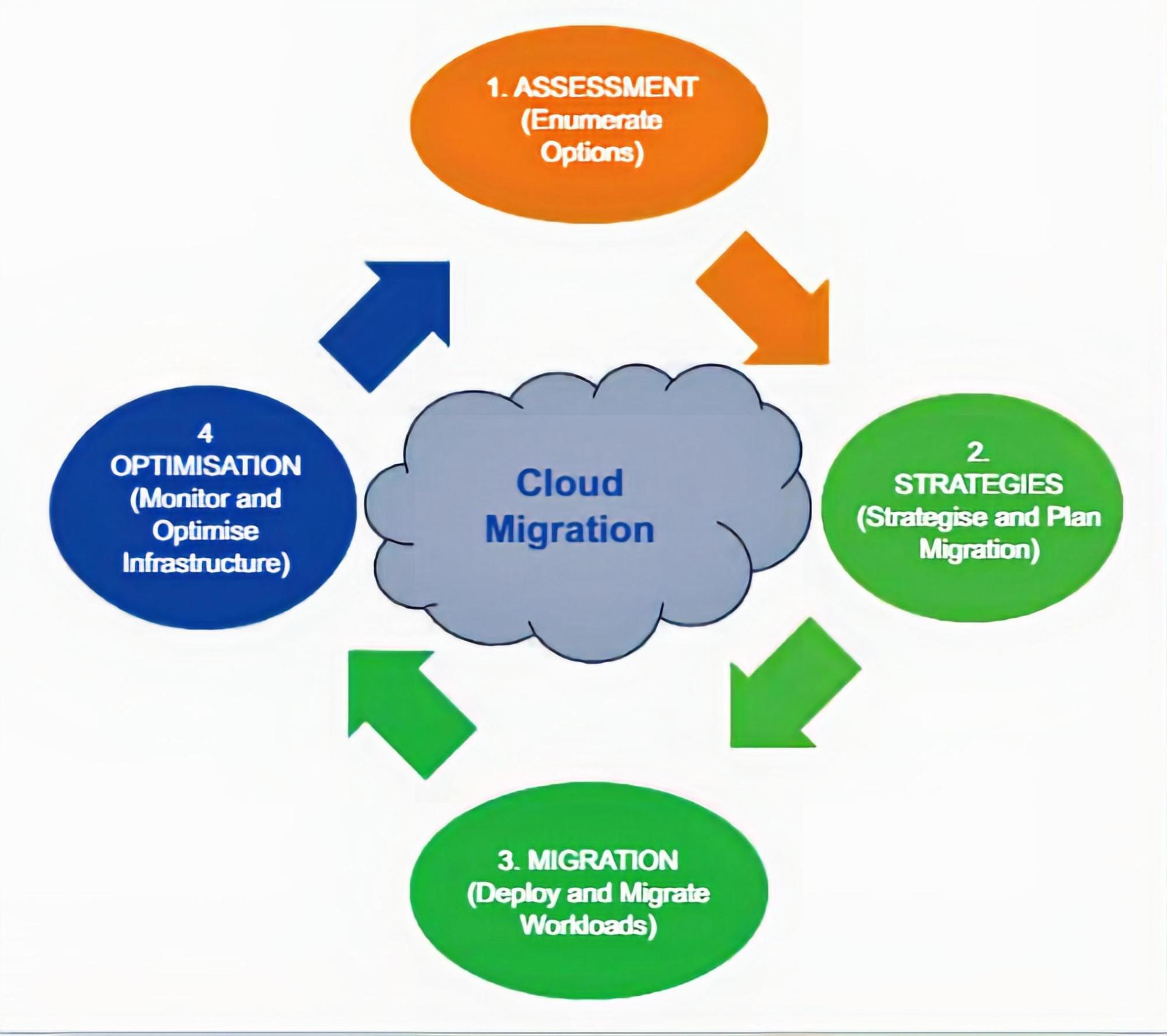
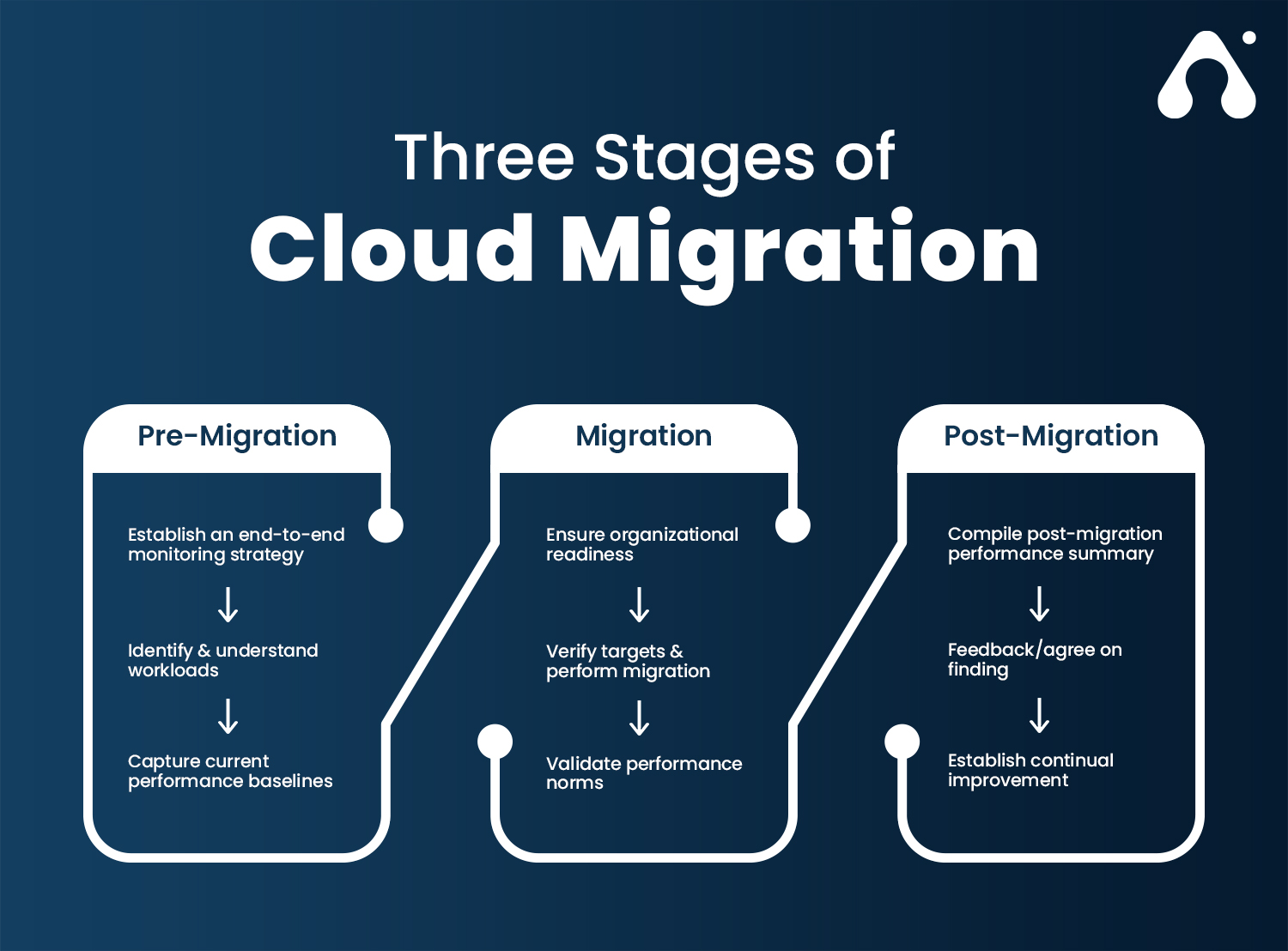
Cloud migration involves several stages, each requiring careful consideration and preparation. The process begins with a thorough assessment of the existing IT infrastructure, applications, and data. This evaluation helps organizations identify potential challenges, such as application compatibility issues, data privacy concerns, and resistance to change. Addressing these challenges early on ensures a smoother transition to the cloud.
Once the assessment is complete, organizations must select the most suitable cloud platform and migration strategy based on their unique needs and objectives. Various cloud migration strategies, such as lift-and-shift, re-hosting, re-platforming, and re-architecting, offer different advantages and disadvantages. By understanding these strategies, businesses can make informed decisions and maximize the benefits of their migration to cloud process.
A successful migration to cloud process relies on meticulous planning, rigorous testing, and seamless deployment. Organizations must prepare their data, configure the cloud environment, and ensure that applications and services function optimally in the new setting. Post-migration, continuous monitoring and optimization are essential to maintain cloud performance, security, and cost management. By adopting best practices and utilizing monitoring tools, businesses can proactively address potential issues and ensure ongoing cloud migration success.
Identifying the Ideal Cloud Solution: A Comparative Analysis
Migration to cloud steps is a strategic decision that requires careful consideration of various cloud platforms and services. Each provider offers unique features, costs, and scalability options, making it essential to compare and evaluate them based on an organization’s specific needs. Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are prominent examples of successful cloud migrations.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a mature and widely adopted cloud platform, offering a vast array of services and tools. AWS boasts an extensive ecosystem, making it an ideal choice for businesses seeking flexibility, scalability, and a wide range of integrations. Moreover, AWS provides robust security features, making it suitable for organizations handling sensitive data.
Microsoft Azure is another popular choice for migration to cloud steps, particularly among businesses already using Microsoft products. Azure integrates seamlessly with Microsoft’s suite of tools, including Office 365 and Dynamics 365. This integration enables organizations to leverage existing investments and streamline their operations by consolidating their IT infrastructure on a single platform.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a relative newcomer to the cloud services market but has quickly gained traction due to its innovative approach and competitive pricing. GCP excels in data analytics and machine learning capabilities, making it an attractive option for businesses prioritizing these areas. Furthermore, GCP offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which can result in significant cost savings for organizations with fluctuating resource requirements.
When selecting a cloud platform, organizations must consider factors such as compatibility with existing systems, security features, scalability, and cost. Conducting a thorough comparative analysis ensures that businesses choose the most suitable cloud solution for their unique needs, maximizing the benefits of their migration to cloud process.
Assessing Your Current IT Infrastructure: A Pre-Migration Checklist
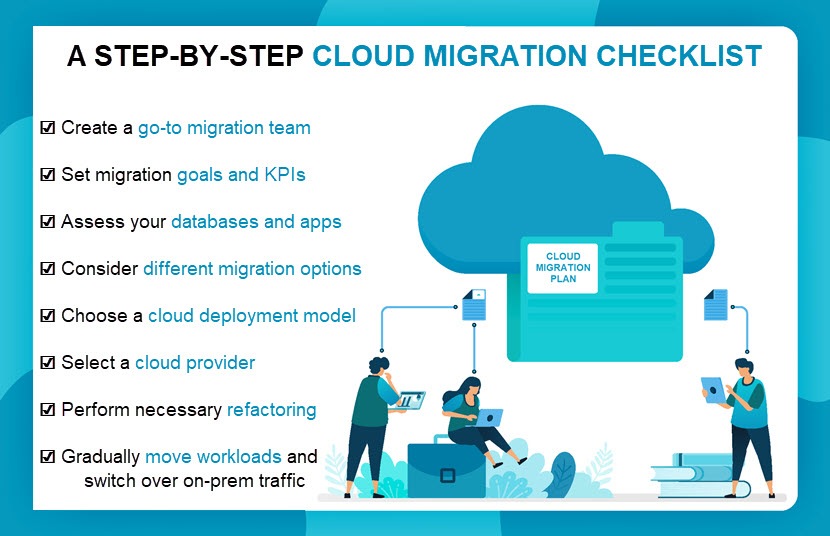
Migration to cloud steps necessitates a thorough evaluation of the existing IT infrastructure. Pre-migration planning ensures a smooth transition and helps organizations avoid potential issues. A pre-migration checklist should include the following assessments:
- Data security: Examine the current data security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and backup procedures. Identify any gaps and implement necessary improvements before migrating to the cloud.
- Application compatibility: Assess the compatibility of existing applications with the chosen cloud platform. Determine whether any adjustments or updates are required to ensure seamless operation in the cloud environment.
- Network readiness: Evaluate the organization’s network infrastructure, including bandwidth, latency, and connectivity. Ensure that the existing network can support the increased traffic and demands of a cloud-based system.
Additionally, organizations should consider the following best practices when evaluating their current IT infrastructure:
- Establish clear migration objectives and goals to guide the assessment process.
- Involve key stakeholders, such as IT personnel, management, and end-users, to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the existing infrastructure and its requirements.
- Document the current IT environment, including hardware, software, and network configurations, to facilitate a smooth migration process.
- Create a contingency plan to address potential issues during and after the migration.
By diligently assessing their current IT infrastructure and following a pre-migration checklist, organizations can minimize risks, ensure a smooth transition, and maximize the benefits of their migration to cloud process.
Planning the Migration: Strategies for a Smooth Transition
Migration to cloud steps involves selecting the most appropriate strategy for a seamless transition. Various approaches, such as lift-and-shift, re-hosting, re-platforming, and re-architecting, offer unique advantages and disadvantages. Organizations should carefully evaluate their needs and objectives to determine the best strategy.
- Lift-and-shift: This approach involves moving applications and data from on-premises systems to the cloud without significant modifications. Lift-and-shift is ideal for organizations seeking a quick and straightforward migration process, but it may not fully leverage cloud benefits, such as scalability and cost savings.
- Re-hosting: Similar to lift-and-shift, re-hosting moves applications and data to the cloud without significant changes. However, it often involves optimizing the applications for the cloud environment, resulting in improved performance and cost savings compared to lift-and-shift.
- Re-platforming: Re-platforming involves modifying applications to better suit the cloud environment, typically by integrating them with cloud-native services. This approach allows organizations to take full advantage of cloud benefits, such as scalability and automation, but requires more time and resources than lift-and-shift or re-hosting.
- Re-architecting: Re-architecting involves redesigning applications and data structures to optimize them for the cloud. This strategy is the most time-consuming and resource-intensive but offers the greatest potential benefits, including enhanced scalability, performance, and cost savings.
When selecting a migration strategy, organizations should consider factors such as application complexity, time constraints, and budget. By choosing the most suitable approach, businesses can ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits of their migration to cloud process.
How to Execute a Cloud Migration: Step-by-Step Guide
Migration to cloud steps requires careful planning and execution. By following a structured process, organizations can ensure a smooth transition and minimize potential issues. The step-by-step guide includes:
- Preparing data: Begin by assessing the data to be migrated, identifying any redundant, obsolete, or trivial (ROT) data, and removing it. Organize the remaining data into logical units, and ensure it is properly cleaned, formatted, and tagged for easy identification in the cloud environment.
- Configuring the cloud environment: Select the appropriate cloud platform and set up the necessary accounts, storage, and security measures. Carefully design the architecture to meet the organization’s needs, considering factors such as scalability, performance, and cost management.
- Testing: Before deploying the migrated data and applications, thoroughly test the cloud environment to ensure it functions as expected. This step includes verifying data integrity, application performance, and security measures.
- Deploying: Once testing is complete, begin migrating data and applications to the cloud environment. Monitor the process closely to identify and address any issues that may arise. Implement a rollback plan in case of unexpected problems or failures during deployment.
Throughout the migration process, it is essential to maintain open communication with all stakeholders, including IT personnel, management, and end-users. Provide regular updates on the migration’s progress, and address any concerns or questions promptly. By following a structured step-by-step guide, organizations can ensure a successful migration to cloud process.
Monitoring and Optimizing the Cloud Environment: Post-Migration Best Practices
Migration to cloud steps is not a one-time process; continuous monitoring and optimization are crucial for long-term success. Organizations should employ various tools and techniques to ensure optimal performance, security, and cost management. Best practices include:
- Performance monitoring: Regularly assess application performance, server uptime, and response times to identify potential issues and optimize the cloud environment. Utilize cloud-native monitoring tools, such as AWS CloudWatch or Azure Monitor, to automate this process.
- Security monitoring: Implement robust security measures, including intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and encryption, to protect sensitive data in the cloud. Regularly review security logs and implement security information and event management (SIEM) systems to identify and address potential threats.
- Cost management: Monitor cloud expenditures and implement cost optimization strategies, such as rightsizing instances, utilizing reserved instances, and scheduling automatic start and stop times for non-production workloads.
By regularly reviewing and optimizing the cloud environment, organizations can ensure ongoing success and address potential issues before they become major problems. Continuous monitoring and optimization are essential migration to cloud steps that contribute to long-term success.
Overcoming Common Cloud Migration Challenges: Real-Life Solutions
Migration to cloud steps can present several challenges, including data privacy concerns, application compatibility issues, and resistance to change. However, real-life examples and solutions can help organizations overcome these obstacles. Here are some common challenges and potential solutions:
- Data privacy concerns: Organizations may worry about data security and privacy when migrating to the cloud. To address these concerns, implement robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Additionally, choose a reputable cloud provider with strong data protection policies and certifications, such as ISO 27001 or SOC 2.
- Application compatibility issues: Some applications may not function optimally in the cloud environment. To overcome this challenge, assess application compatibility before migration and consider re-platforming or re-architecting applications as needed. Utilize cloud-native services and tools to ensure seamless integration and smooth operation.
- Resistance to change: Employees may resist the change due to fear of the unknown or lack of technical skills. To overcome this challenge, provide adequate training and support to help employees adapt to the new environment. Encourage open communication and address concerns promptly to ensure a smooth transition.
By understanding and addressing these common challenges, organizations can ensure a successful migration to cloud process and maximize the benefits of cloud computing.
Measuring the Success of Your Cloud Migration: Key Performance Indicators
Migration to cloud steps is not a one-time achievement; ongoing evaluation and optimization are crucial for long-term success. By tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), organizations can measure the success of their cloud migration and identify areas for improvement. Here are some essential KPIs to consider:
- Cost savings: Calculate the cost savings associated with the cloud migration by comparing the expenses of the on-premises infrastructure to the cloud costs. Include factors such as hardware, software, maintenance, and energy consumption.
- Application performance: Monitor the performance of applications in the cloud environment, including response times, uptime, and error rates. Utilize cloud-native monitoring tools, such as AWS CloudWatch or Azure Monitor, to automate this process.
- User experience: Assess the user experience by gathering feedback from employees and stakeholders. Measure factors such as system availability, ease of use, and overall satisfaction.
- Security and compliance: Evaluate the effectiveness of security measures and ensure compliance with industry regulations. Regularly review security logs and implement security information and event management (SIEM) systems to identify and address potential threats.
By regularly reviewing and adjusting these KPIs, organizations can ensure ongoing cloud migration success and maximize the benefits of their cloud investment.