The Advantages of Cloud Integration: A Modern Approach
Cloud adoption has become a popular trend among businesses seeking to leverage the numerous benefits it offers, such as cost savings, scalability, and flexibility. Organizations can significantly reduce their capital and operational expenses by utilizing cloud services, as they no longer need to invest in expensive hardware, maintain on-premises data centers, or manage physical servers. Moreover, cloud solutions enable businesses to scale their resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and resource allocation.
Selecting the most suitable migration strategies for cloud adoption is crucial to ensure a seamless transition to the cloud. A well-planned and executed migration strategy can help organizations minimize downtime, reduce risks, and maintain business continuity throughout the process. In this article, we will explore various migration strategies and discuss best practices for implementing them effectively.
Assessing Your IT Infrastructure: A Crucial First Step
Before selecting a migration strategy for cloud adoption, it is essential to evaluate the existing IT infrastructure. A thorough assessment helps organizations identify the types of applications, data, and workloads to be migrated and understand the compatibility of their current infrastructure with cloud environments. By conducting a comprehensive review, businesses can ensure a smooth transition to the cloud and minimize potential risks and disruptions.
Here are some factors to consider when evaluating your IT infrastructure:
- Application compatibility: Assess the compatibility of your applications with cloud environments. Some legacy applications may require modifications or replacements to function correctly in the cloud. Identifying these applications early in the process can help you plan and allocate resources accordingly.
- Data migration: Determine the volume and type of data to be migrated. Large data sets may require specific migration tools and techniques to ensure a smooth transfer. Additionally, consider the security and privacy requirements for your data during and after the migration process.
- Workload analysis: Analyze the workloads of your applications and services to determine the appropriate cloud deployment model (public, private, or hybrid). For instance, applications with variable workloads may benefit from the scalability offered by public cloud environments, while sensitive data may require the additional security of a private cloud.
- Network infrastructure: Evaluate your network infrastructure to ensure it can support the increased traffic and connectivity required for cloud services. This may involve upgrading your network equipment or redesigning your network architecture to optimize performance and security.
- Skill gaps: Identify any skill gaps within your organization that may hinder a successful migration. Training and upskilling your team or hiring external experts can help bridge these gaps and ensure a smooth transition to the cloud.
By carefully assessing your IT infrastructure, you can choose the most suitable migration strategy for your organization’s goals and objectives, ensuring a seamless transition to the cloud.

Selecting the Optimal Migration Path: Expert Recommendations
When considering cloud adoption, choosing the right migration strategy is crucial for a seamless transition. Various migration strategies are available, each with its benefits and drawbacks. Understanding these factors can help organizations select the most suitable approach based on their goals and objectives.
Here are some common migration strategies for cloud adoption:
- Lift-and-shift: Also known as rehosting, this strategy involves moving applications and data from on-premises infrastructure to the cloud without significant modifications. Lift-and-shift is a quick and cost-effective approach, but it may not fully leverage the cloud’s capabilities. Organizations may face compatibility issues, and performance may be suboptimal due to the lack of architectural optimization.
- Replatforming: This method involves making minor updates to applications and data before migrating them to the cloud. Replatforming can help organizations take advantage of cloud-native features, such as automation and scaling, while minimizing the need for extensive redevelopment. However, this approach may still leave some performance and compatibility issues unresolved.
- Refactoring: Refactoring involves rearchitecting applications and data to optimize them for the cloud. This strategy allows organizations to fully leverage cloud capabilities, such as automation, scalability, and resilience. However, refactoring can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, requiring significant development efforts and testing.
- Rearchitecting: In some cases, organizations may choose to rebuild their applications and data from scratch using cloud-native technologies. This approach, known as rearchitecting, enables businesses to take full advantage of the cloud’s benefits, including flexibility, scalability, and resilience. However, rearchitecting is the most complex and time-consuming migration strategy, requiring substantial development resources and expertise.
When selecting a migration strategy for cloud adoption, consider the following:
- Organizational goals: Align your migration strategy with your organization’s objectives, such as cost savings, scalability, or agility.
- Application and data compatibility: Assess the compatibility of your applications and data with cloud environments and choose a strategy that addresses any potential issues.
- Resource availability: Evaluate your team’s skills, expertise, and bandwidth to determine the most feasible migration strategy.
- Timeline: Establish a realistic timeline for migration, considering the complexity and resource requirements of each strategy.
By carefully considering these factors, organizations can choose the optimal migration path for their cloud adoption journey, ensuring a successful transition to a more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective IT infrastructure.

Devising a Robust Migration Strategy: Best Practices
Migration strategies for cloud adoption play a critical role in ensuring a seamless transition to a more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective IT infrastructure. Proper planning is essential for a successful migration, and organizations should follow best practices when creating a detailed migration plan.
Here are some tips for devising a robust migration strategy:
- Set clear objectives: Define your organization’s goals and objectives for cloud adoption, such as cost savings, scalability, or agility. This will help guide your migration strategy and ensure alignment with your business needs.
- Establish timelines: Create a realistic timeline for migration, considering the complexity and resource requirements of each strategy. Break down the migration process into manageable phases, allowing for regular checkpoints and progress assessments.
- Allocate resources: Determine the necessary resources, including personnel, budget, and technology, to support the migration. Ensure that your team has the required skills and expertise to execute the migration strategy effectively.
- Assess compatibility: Evaluate the compatibility of your applications, data, and workloads with cloud environments. Identify potential issues and choose a migration strategy that addresses these challenges.
- Plan for data transfer: Develop a plan for transferring data to the cloud, considering factors such as data volume, transfer speed, and security. Utilize tools and techniques to optimize data transfer and minimize downtime.
- Modernize applications: Assess your applications’ suitability for the cloud and consider modernization efforts, such as refactoring or rearchitecting, to leverage cloud-native features and improve performance.
- Monitor and test: Continuously monitor and test the migration process to ensure a smooth transition. Address any issues or discrepancies promptly to minimize disruptions and maintain business continuity.
By following these best practices, organizations can devise a robust migration strategy for cloud adoption, ensuring a seamless transition to a more efficient and agile IT infrastructure. Remember that careful planning and execution are crucial for a successful migration, and continuous monitoring and testing are essential throughout the process.
Implementing the Migration Strategy: Step-by-Step Guide
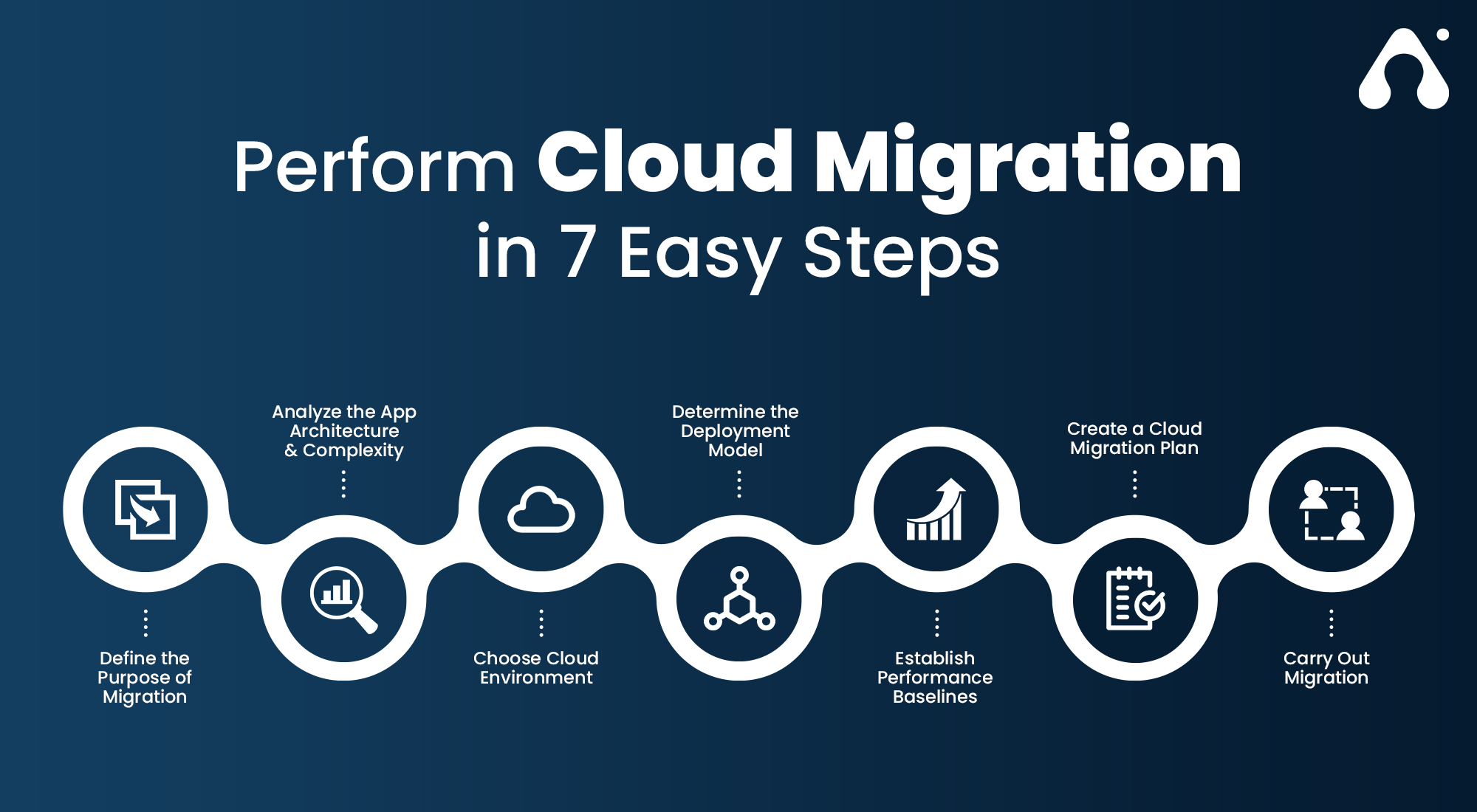
Migration strategies for cloud adoption require careful planning and execution to ensure a seamless transition to a more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective IT infrastructure. This step-by-step guide covers essential aspects of implementing the selected migration strategy, including data transfer, application modernization, and infrastructure setup.
Here are the key steps for implementing the migration strategy:
- Prepare the data: Before transferring data to the cloud, ensure it is properly cleaned, organized, and formatted. Remove any redundant, obsolete, or trivial (ROT) data to reduce costs and improve migration efficiency. Utilize tools and techniques to optimize data transfer and minimize downtime.
- Modernize applications: Assess your applications’ suitability for the cloud and consider modernization efforts, such as refactoring or rearchitecting, to leverage cloud-native features and improve performance. This may involve redesigning the application architecture, adopting microservices, or integrating with cloud-based services.
- Configure infrastructure: Set up the cloud infrastructure according to your organization’s requirements and the chosen migration strategy. This includes provisioning virtual machines, configuring storage, and establishing networking and security settings. Ensure compatibility with your applications and data.
- Test and validate: Continuously monitor and test the migration process to ensure a smooth transition. Validate the functionality and performance of applications and data in the cloud environment. Address any issues or discrepancies promptly to minimize disruptions and maintain business continuity.
- Transfer data: Initiate the data transfer process, ensuring minimal downtime and disruption. Utilize tools and techniques to optimize data transfer and maintain data integrity throughout the process.
- Monitor and optimize: Continuously monitor the cloud environment post-migration to ensure optimal performance, security, and cost management. Leverage cloud-native tools and third-party solutions to identify and address potential issues, fine-tune configurations, and optimize resource utilization.
By following these steps, organizations can effectively implement their chosen migration strategy for cloud adoption, ensuring a seamless transition to a more efficient and agile IT infrastructure. Remember that continuous monitoring and testing are essential throughout the migration process, and post-migration optimization is crucial for long-term success in the cloud.
Optimizing Your Cloud Environment: Post-Migration Best Practices
Migration strategies for cloud adoption involve careful planning and execution, but the journey doesn’t end with a successful transition to the cloud. To maximize the benefits of cloud adoption, organizations must focus on managing and optimizing their cloud environment post-migration. This includes addressing topics such as cost management, security, and performance enhancement.
- Cost management: Cloud environments offer scalability and flexibility, but they can also lead to unexpected costs if not managed properly. Implement cost optimization strategies, such as reserving instances, utilizing spot instances, and monitoring usage patterns. Leverage cloud-native tools and third-party solutions to track and manage costs effectively.
- Security: Security remains a top concern for organizations adopting cloud technologies. Implement robust security measures, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and access controls. Regularly review and update security policies to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities. Leverage cloud-native security tools and services to enhance protection and maintain compliance.
- Performance enhancement: Cloud environments offer numerous opportunities to improve application performance and user experience. Utilize cloud-native services, such as load balancers, auto-scaling groups, and content delivery networks (CDNs), to optimize resource allocation and ensure high availability. Monitor performance metrics and fine-tune configurations to maintain optimal performance levels.
By following these best practices, organizations can effectively manage and optimize their cloud environment post-migration, ensuring long-term success and realizing the full potential of their cloud investment. Remember that continuous monitoring, testing, and adaptation are essential in the ever-evolving cloud landscape. Stay informed about new tools, techniques, and best practices to maintain a competitive edge and maximize the benefits of cloud adoption.
Overcoming Barriers in Cloud Adoption: Expert Solutions
Migration strategies for cloud adoption offer numerous benefits, but organizations may face various challenges during the transition process. Addressing these barriers effectively is crucial for a smooth and successful cloud journey. In this section, we will discuss common obstacles and provide practical solutions to help organizations overcome them.
- Data security concerns: Data security is a primary concern for organizations moving to the cloud. To address these concerns, implement robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Leverage cloud-native security tools and services to enhance protection and maintain compliance. Educate employees about best practices for handling sensitive data and maintaining security.
- Skill gaps: Cloud adoption often requires new skills and expertise. Organizations can bridge the skill gap by investing in employee training and certification programs. Additionally, consider partnering with a managed service provider (MSP) to leverage their expertise and resources. This can help ensure a successful migration and ongoing management of the cloud environment.
- Vendor lock-in: Vendor lock-in can limit an organization’s flexibility and increase costs. To avoid vendor lock-in, consider using open standards and multi-cloud strategies. This allows organizations to distribute workloads across multiple cloud providers, reducing dependence on a single vendor and increasing negotiation power.
By addressing these common barriers, organizations can ensure a smooth transition to the cloud and maximize the benefits of their cloud investment. Remember that continuous learning and adaptation are essential in the ever-evolving cloud landscape. Stay informed about new tools, techniques, and best practices to maintain a competitive edge and overcome any future challenges in cloud adoption.

Achieving Success in Your Cloud Journey: Expert Insights
Migration strategies for cloud adoption are a critical aspect of modern business success. Organizations that effectively leverage the cloud can achieve significant benefits, including cost savings, scalability, and flexibility. However, a successful cloud journey requires careful planning, execution, and ongoing management. In this section, we will summarize the key aspects of a successful cloud migration and emphasize the importance of continuous learning and adaptation in the ever-evolving cloud landscape.
- Assess your IT infrastructure: Before choosing a migration strategy, evaluate your existing IT infrastructure. Consider the types of applications, data, and workloads to be migrated, as well as the compatibility of the current infrastructure with cloud environments. This assessment will help you select the most suitable migration strategy and ensure a seamless transition to the cloud.
- Select the optimal migration path: There are various migration strategies, such as lift-and-shift, replatforming, refactoring, and rearchitecting. Each method has its benefits and drawbacks, and the most suitable strategy depends on an organization’s goals and objectives. Carefully weigh the pros and cons of each approach to make an informed decision.
- Plan meticulously: Careful planning is essential for a successful migration. Create a detailed migration plan, including clear objectives, established timelines, and allocated resources. Continuous monitoring and testing throughout the migration process will help ensure a smooth transition.
- Optimize your cloud environment: Post-migration, focus on managing and optimizing the cloud environment. Implement best practices for cost management, security, and performance enhancement. Leverage tools and techniques to help achieve these goals and maintain a competitive edge.
- Overcome barriers: Address potential challenges, such as data security concerns, skill gaps, and vendor lock-in, with practical solutions and strategies. Continuous learning and adaptation are crucial for overcoming any future challenges in cloud adoption.
Migration strategies for cloud adoption are a vital component of modern business success. By following best practices and remaining adaptable, organizations can unlock the full potential of the cloud and maintain a competitive edge in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
