What is an Azure Service Level Agreement?
In the realm of cloud computing, a Service Level Agreement, or SLA, serves as a cornerstone of trust between a service provider and its customers. Essentially, an SLA represents a formal commitment, a promise of performance that outlines the specific expectations for a service. This commitment encompasses crucial factors such as uptime, availability, and responsiveness. When discussing cloud platforms, understanding the nuances of an SLA becomes paramount. Specifically, a Microsoft Azure service level agreement details the guarantees that Microsoft provides to its users regarding the availability and performance of its various Azure services. These agreements are not just legal documents; they’re a vital tool for planning, managing, and ensuring the reliability of your cloud-based applications and infrastructure. The foundation of an effective cloud strategy lies in a solid grasp of these agreements, allowing organizations to make informed decisions about their cloud architecture. With a Microsoft Azure service level agreement, clients can ascertain the expected performance levels, aligning their business needs with Azure’s capabilities. It’s important to recognize that the SLA is designed to protect both the provider and the customer, setting clear boundaries and defining what is considered acceptable performance for each service.
A Microsoft Azure service level agreement is much more than a simple guarantee; it’s an articulation of the reliability you can expect when leveraging Azure’s broad range of services. This agreement is particularly important for any business considering a full or partial migration to the cloud. Understanding the terms within an SLA will empower you to select the right Azure services and configurations for your specific needs, impacting your ability to deliver dependable products and services to your own customers. The specific terms of the Microsoft Azure service level agreement can vary significantly from one service to another, depending on the complexity, criticality, and the infrastructure behind it. The agreement dictates the availability percentages, for example, 99.9% or 99.99%, the redress mechanism for failing to meet those standards, and the conditions under which certain outcomes may apply. A deep understanding of these aspects is crucial to making informed decisions about which Azure services will best meet the needs of your applications, operations and, ultimately, your business objectives. Therefore, reviewing the Microsoft Azure service level agreement for each service you use is a vital step toward ensuring stability and continuous operations of your cloud environment.
How to Navigate Microsoft Azure’s Uptime Promises
The structure of a Microsoft Azure Service Level Agreement is not uniform; instead, it is tailored to each specific service offered within the Azure ecosystem. It’s crucial to understand that a single, overarching microsoft azure service level agreement does not exist. Instead, each service, be it a virtual machine, a database, or a storage solution, has its own individual SLA document detailing the performance guarantees you can expect. These agreements outline the specific performance metrics that Microsoft commits to, which can significantly vary based on the nature and complexity of the service in question. For example, a basic virtual machine will likely have a different microsoft azure service level agreement than a highly available, multi-node database cluster. Understanding this variation is key to effectively designing resilient applications. These SLAs are not a one-size-fits-all guarantee; rather, they are nuanced and specific to the individual service being utilized. A lack of awareness in this area might lead to over or underestimating the reliability you are entitled to, based on the services you choose for your implementation.
Navigating the specific metrics outlined in a microsoft azure service level agreement requires a keen eye for detail. Common metrics to consider include uptime percentage, the amount of service credits offered in case of a breach of the SLA, and the deployment of resources across availability zones. Uptime percentages, often expressed with multiple nines, indicate the guaranteed availability of the service. Service credits are a form of compensation for failing to meet the defined uptime. Availability zones, which offer geographically isolated locations within a region, can be a factor in a service’s overall resilience. Each service will have a unique document outlining these specifics, so it is critical for users to review and understand these individual microsoft azure service level agreement documents thoroughly. Failing to do so might lead to architectural designs that are not aligned with the expected availability or to a misinterpretation of the performance promises that you should expect and rely on. Always consider the availability zones to improve your uptime percentage and align with your microsoft azure service level agreement.
The variance in SLAs based on service underscores the need for careful planning when architecting cloud-based solutions. It is also vital to understand that services that have redundancy and multiple availability zones will offer a higher uptime percentage than basic services with a single instance. Therefore, planning the architecture of your application and aligning it with the individual service SLAs can result in a highly available application that fits your needs. Remember, the microsoft azure service level agreement is a foundational document, not a generic promise, and users must proactively familiarize themselves with the documentation for each service they are using.
Key Components of an Azure SLA: Decoding the Fine Print
Understanding the core elements of a Microsoft Azure Service Level Agreement is crucial for any organization relying on Azure services. An Azure SLA fundamentally revolves around the concept of “availability,” which is the percentage of time a service is operational and accessible. Downtime, conversely, is defined as any period where the service is unavailable, often categorized into planned maintenance and unplanned outages. It is important to recognize that the microsoft azure service level agreement is not a single entity; instead, each service within Azure has its own specific SLA, with varying terms and guarantees. A primary distinction lies between single-instance SLAs and multi-instance SLAs. A single-instance SLA pertains to scenarios where only one virtual machine or service instance is running, typically offering lower availability guarantees compared to multi-instance setups. Multi-instance SLAs, where multiple instances of a service are deployed, provide greater resilience as the failure of one instance does not necessarily impact the overall service availability. This is commonly achieved through the implementation of redundant infrastructure, ensuring that in case of a component failure, another instance can quickly take over.
Delving deeper into the specifics of a microsoft azure service level agreement reveals the importance of understanding the metrics used to quantify availability. The uptime percentage, often expressed as “99.9%” or “99.99%,” signifies the proportion of time a service is expected to be operational. The more “nines” there are, the higher the guarantee, though even small percentage differences can equate to significant downtime in a year. For example, 99.9% availability permits up to 8.76 hours of downtime per year, while 99.99% allows for just under an hour. Redundant infrastructure plays a key role in achieving the higher end of availability targets specified by the microsoft azure service level agreement. Moreover, the SLA document will detail the scope of the agreement, specify the geographic regions and the circumstances under which the availability commitment applies. A clear understanding of the terms and conditions within the document enables users to manage expectations and allows for appropriate architectural choices when building their cloud applications. Understanding the implications of various component failures and the recovery process is integral to adhering to the overall microsoft azure service level agreement.
It’s crucial to emphasize that thorough comprehension of these elements is paramount, and it is not recommended to treat them as standardized. The microsoft azure service level agreement components such as ‘availability’ and ‘downtime’ can have different meanings and implications based on the specific service being used. Organizations should carefully scrutinize the SLA details for each Azure service that they depend on, acknowledging the critical nuances in service specifics. It is necessary to understand how the specific SLA defines downtime, how it relates to the chosen redundancy approach, and the availability zones that it operates within. This critical analysis is required to ensure proper service implementation aligned to the business expectations. Therefore, a thorough study of these core elements within a Microsoft Azure Service Level Agreement can avoid surprises and ensure appropriate system architecture is achieved.
Availability Zones and Their Impact on Azure Guarantees
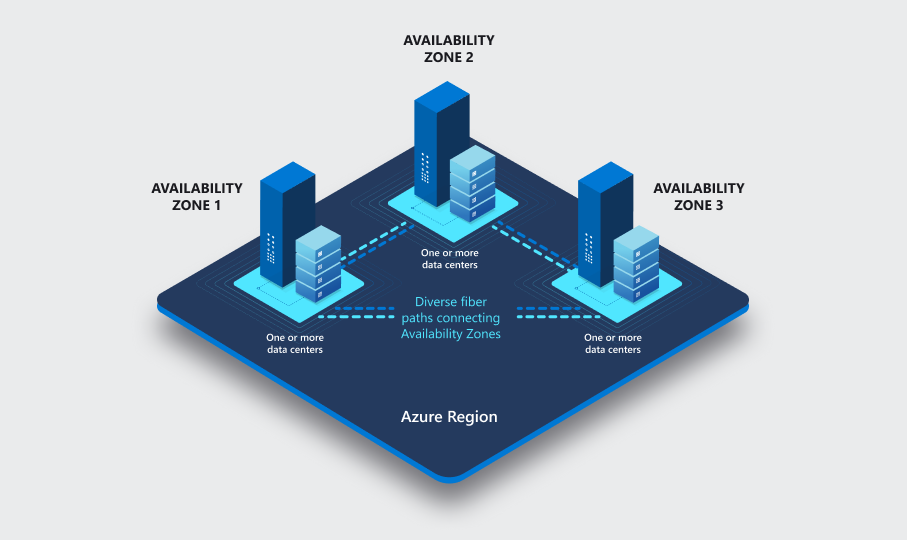
Availability Zones are a critical component of Microsoft Azure’s infrastructure, designed to enhance the resilience and availability of your applications. These zones are physically separate locations within an Azure region, each with independent power, networking, and cooling. The strategic separation between these zones ensures that a failure in one zone is unlikely to impact the others. When designing for high availability with Microsoft Azure service level agreement, distributing your resources across multiple Availability Zones is crucial. This means deploying your virtual machines, databases, and other services in different zones within the same region. In the event of a localized failure, such as a power outage or network issue, the resources in other zones remain operational, ensuring your application remains available. This is why understanding Availability Zones is key to understanding the core of a microsoft azure service level agreement.
Choosing to leverage Availability Zones in your architectural design is a proactive step toward achieving robust availability guarantees. Without utilizing this capability, a Microsoft Azure service level agreement may be harder to achieve. By spreading your resources across multiple zones, you mitigate the risk of single points of failure impacting your services. For example, if you have a web application hosted on virtual machines and one Availability Zone experiences downtime, the virtual machines in the other zones will continue to serve traffic, and end-users will see minimal service interruption. This architectural design not only helps meet, but can help exceed the targets specified in the Microsoft Azure service level agreement. It’s also important to note that while Availability Zones provide a robust foundation, a thorough understanding of the SLA for each individual service is still necessary.
The selection of Availability Zones isn’t merely about geographic separation. It also involves considering latency, as all Availability Zones within the same region are interconnected through low-latency networking. This ensures that applications can operate efficiently while being distributed for resilience. The concept of an Availability Zone is not something to be ignored, it is a core component of how Microsoft maintains a microsoft azure service level agreement. By choosing to implement this architectural design, you are actively enhancing the resilience and availability of your cloud applications, optimizing for both uptime and performance. Understanding the nuances of these zones is imperative to make sure you understand fully what your microsoft azure service level agreement encompasses.
Azure Service Credits: What Happens When the SLA is Breached
When a Microsoft Azure service fails to meet the uptime commitments outlined in its specific Microsoft Azure Service Level Agreement (SLA), customers are typically eligible for service credits. These credits represent a percentage of the monthly service fees, and are calculated based on the degree of deviation from the promised uptime. It is essential to understand that each Azure service has its distinct SLA, detailing specific uptime targets, and the corresponding credit percentages that will be applied in case of a breach. These service credits are not a form of compensation for any business losses incurred during downtime, but are rather a form of partial refund for the affected service. The calculations are meticulously detailed within each specific Microsoft Azure Service Level Agreement, specifying the exact credit amount a customer can expect if a breach happens. For example, an SLA might state that a 99.9% uptime guarantee offers a 10% service credit if uptime drops to 99%, while it would offer 25% if uptime drops to 95% or lower. These credit tiers incentivize the company to maintain its promised service levels, and offer the customer a degree of financial protection. It’s crucial for users of Microsoft Azure services to familiarize themselves with the SLA of each service they use, particularly regarding the uptime targets and the service credit structure.
Understanding how service credits are calculated is fundamental to managing expectations. Typically, the calculation process begins by assessing the total minutes the service was unavailable during a specific billing period. This downtime is then compared against the SLA’s defined uptime commitment. Depending on the service, the outage definition may vary, highlighting the need to carefully examine the specifics of each Microsoft Azure Service Level Agreement. The credits are usually applied to the customer’s next bill. Service credits are meant to serve as a form of acknowledgement that Microsoft has not met its contractual promise, and they are not intended to act as a compensation for the impact of the outage itself. As a partial refund, service credits do not fully offset the potential loss of productivity, revenue, or any associated damages resulting from a service disruption. Therefore, businesses should consider implementing their own redundancy measures, disaster recovery plans and monitoring solutions. Moreover, it is important to note that there are specific requirements and processes in place to request credits, usually requiring a claim within a specific timeframe.
The process for obtaining these credits usually involves submitting a claim through the Azure portal within a specified timeframe after the incident occurred. Customers should carefully adhere to these procedures to ensure their claims are processed correctly. It is also worth mentioning that Microsoft has a robust service health dashboard that keeps customers informed on the current status of services, as well as any incidents. The documentation for each Microsoft Azure Service Level Agreement is freely available online and should be routinely reviewed. Although the mechanism is in place to address shortcomings in service delivery, the primary focus for any user of Microsoft Azure should always be on proactive planning and configuration to reduce the likelihood of an outage rather than just relying on service credits as a recourse. It is imperative that customers use their Microsoft Azure Service Level Agreement documents to have a clear understanding of the processes in place to handle breaches of service level agreements.
Choosing the Right Azure Services Based on Your Availability Needs
Selecting the appropriate Microsoft Azure services is crucial for meeting specific availability requirements and aligning with overarching business objectives. It’s important to recognize that not all Azure services are created equal in terms of inherent availability guarantees. Some services are naturally designed for higher uptime and resilience compared to others. For instance, core infrastructure services like virtual machines might have different Microsoft Azure service level agreement targets compared to newer platform-as-a-service offerings. The key lies in understanding the nuances of each service’s SLA and how it corresponds to the desired levels of business continuity. Understanding your business objectives, whether it’s a mission-critical application requiring 99.99% uptime or a less critical service, should drive your choice of Azure services and their configurations. Further customization and proper planning can ensure that even services with lower base availability can be made more resilient, enhancing the overall compliance with your Microsoft Azure service level agreement.
Achieving the desired level of availability is not solely about picking a single service with the highest SLA. It also involves designing your architecture with this concept in mind. For example, using multiple instances of a service across availability zones will improve the probability of achieving a better Microsoft Azure service level agreement performance for your application. Properly configuring services by implementing load balancing, redundancy, and failover mechanisms greatly influences the availability metrics. In addition, it’s critical to consider the dependencies between various Azure services, as one weak link could impact the entire application’s availability, so a clear dependency map will help to make informed decisions. Understanding the SLA’s associated with these services and planning for any possible outages should be the main focus. For example, choosing between single instance VMs with lower SLA and VMs in an availability set with a higher SLA is a key design decision, each one with its own benefit.
Careful consideration of your organization’s recovery point objective (RPO) and recovery time objective (RTO) is essential when choosing your Azure services. RPO and RTO will define the business requirements around how much data you can afford to lose in a disaster scenario and how long it will take to recover. If, for instance, there is a need to minimize data loss or system downtime, the right configurations must be made to make sure these objectives are reached. Choosing services that offer backups and replication capabilities, is a basic best practice to start with. It is important to carefully review the specific Microsoft Azure service level agreement for each service and ensure that it aligns with your needs and that you are implementing your services in a way that they complement the SLA you are expecting to achieve. Aligning your business expectations with the appropriate service is the most crucial step to avoid costly outages and downtime.
Practical Tips for Maximizing Uptime and Meeting Your Azure SLA
Achieving and maintaining the uptime promises defined in a Microsoft Azure service level agreement requires a proactive and strategic approach. It is essential to move beyond simply understanding the terms of the agreement and implement practices that actively support high availability. Proper configuration is paramount; users must carefully choose and set up Azure resources to align with the specific service level agreement (SLA) requirements. This involves selecting appropriate instance sizes, storage options, and networking configurations, ensuring redundancy is built into the system. Leveraging tools provided by Microsoft Azure, such as Azure Monitor, helps in proactively identifying potential issues and resolving them before they escalate into major disruptions. Implementing robust logging and alerting systems facilitates quicker response times, minimizing the impact of any unforeseen problems and aiding in meeting the Microsoft Azure service level agreement objectives. Furthermore, adhering to Microsoft’s recommended architectures and best practice guidelines is a crucial step in maximizing uptime, users should consult the documentation regularly and make the necessary adjustments as needed.
Disaster recovery planning forms another critical component of achieving high availability and compliance with a Microsoft Azure service level agreement. This involves designing robust backup and recovery procedures that ensure minimal downtime in the event of a significant failure. Regular testing of these procedures helps to validate their effectiveness and address any potential shortcomings. Implementing strategies like failover mechanisms across different availability zones further enhances resilience, ensuring continuity of operations. Employing load balancers to distribute traffic and prevent overloads, and using content delivery networks (CDNs) to improve user experience while reducing load on the primary servers. Microsoft Azure also provides several services that can aid in creating a more resilient architecture, including Azure Site Recovery, which allows replication and orchestration of failover between different data centers. These techniques together, ensures that if one part of the infrastructure is affected, your application can continue running with minimal interruption. These practical steps are essential for users who want to make sure that they are aligned with the service level agreement.
Staying Updated on Azure Service Level Changes
The landscape of cloud services is ever-evolving, and with it, the specifics of a Microsoft Azure service level agreement (SLA) can also change. It is paramount to understand that these agreements are not static documents. Microsoft continuously updates its services and, consequently, the terms and conditions of their respective SLAs. Therefore, a proactive approach to staying informed is essential to ensure your applications and services remain within the guaranteed performance parameters. Accessing the most current information about your specific Microsoft Azure service level agreement is simple. All the necessary documentation resides within the official Microsoft Azure documentation portal. It is advisable to bookmark this location to quickly access the latest revisions. Each service has its own dedicated SLA document, and by searching for the specific Azure service, you will find the most current version of its service level agreement. Reviewing these updated documents regularly helps to confirm that your deployed architecture is aligned with the current agreement and that you are aware of any adjustments in uptime guarantees or credit policies. Moreover, changes can sometimes be subtle but significant, impacting your operations, so the need to remain informed is crucial.
In addition to the formal documentation, Microsoft also provides notification services that can alert users about changes to the Microsoft Azure service level agreement and other relevant updates. Subscribing to these notifications ensures that you receive immediate information about adjustments to SLAs, upcoming changes, or any planned maintenances that may affect your services. These notifications often contain specific details about the upcoming modifications, the expected impact, and the actions, if any, that you should take to ensure continuous compliance with the SLA. It’s important to also acknowledge the concept of service previews, or services still in development. Services in preview often do not offer a formal Microsoft Azure service level agreement or may only offer a limited version, which should be taken into consideration when designing your infrastructure. Understanding the differences between production-ready services and preview services is essential for planning and long-term stability. Prioritize reading every detail in the terms of service to know exactly what to expect from the Microsoft Azure service level agreement.