Unveiling Azure Active Directory: A Powerful Identity and Access Management Solution
Microsoft Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is a robust, cloud-based identity and access management solution that offers a wide range of features and capabilities. Organizations can leverage Azure AD to manage user and group identities, authenticate users, and provide single sign-on (SSO) services for various applications. By streamlining these processes, Azure AD enables businesses to enhance security, reduce administrative overhead, and improve user experiences.
Key Features and Capabilities of Azure Active Directory
Microsoft Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) offers a wide array of features and capabilities that cater to the diverse needs of organizations. Among these are conditional access, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and identity protection. These features significantly enhance security and simplify user management for businesses.
Conditional Access
Conditional access is a powerful security feature that enables organizations to control access to applications and services based on specific conditions, such as user location, device compliance, and risk level. By defining and enforcing granular access policies, businesses can minimize the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA is an authentication method that requires users to provide two or more verification factors to access their accounts. By implementing MFA, organizations can add an extra layer of security to their Azure AD environments, making it significantly more challenging for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
Identity Protection
Identity protection is a comprehensive solution that helps organizations detect, investigate, and respond to identity-related threats. By leveraging advanced machine learning algorithms and adaptive intelligence, Azure AD can automatically identify suspicious activities, alert administrators, and take appropriate action to protect user identities and data.
Azure AD’s Value Proposition
Microsoft Azure Active Directory’s key features and capabilities provide organizations with a robust, secure, and flexible identity and access management solution. By incorporating these innovative and creative concepts into their IT infrastructure, businesses can streamline user management, enhance security, and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements.
How to Implement Azure Active Directory: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing Microsoft Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) in an organization can significantly enhance security and simplify user management. By following this comprehensive, easy-to-understand guide, businesses can successfully integrate Azure AD into their IT infrastructure.
Step 1: Create a Tenant
A tenant is a dedicated instance of Azure AD that an organization uses to manage its identities and access to Microsoft cloud services. To create a tenant, sign up for a Microsoft Azure account and follow the onboarding process. Ensure that you use a business email address associated with your organization during sign-up.
Step 2: Configure User and Group Settings
After creating a tenant, configure user and group settings to align with your organization’s needs. This includes setting up user accounts, creating groups, and assigning appropriate permissions and roles. Utilize Azure AD’s intuitive interface to streamline these processes and maintain a clear organizational structure.
Step 3: Enable Single Sign-On (SSO)
SSO allows users to access multiple applications and services using a single set of credentials. To enable SSO, integrate Azure AD with your chosen applications and configure SSO settings. This will provide a seamless user experience and reduce the administrative burden of managing multiple accounts.
Step 4: Implement Conditional Access, MFA, and Identity Protection
Leverage Azure AD’s key features to enhance security and simplify user management. Implement conditional access policies, enable multi-factor authentication (MFA), and configure identity protection settings to safeguard your organization’s identities and data.
Azure AD’s Value Proposition
By following this step-by-step guide, organizations can successfully implement Microsoft Azure Active Directory and enjoy its robust features and capabilities. Azure AD offers a comprehensive, flexible, and secure identity and access management solution that can significantly improve user experiences and reduce administrative overhead.
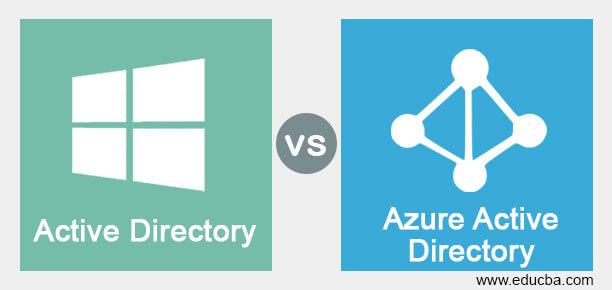
Azure Active Directory vs. On-Premises Active Directory: A Comparative Analysis
Microsoft Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) and On-Premises Active Directory (AD) are two distinct identity and access management solutions that cater to different organizational needs. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of both solutions can help businesses determine which one to use.
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD)
Azure AD is a cloud-based identity and access management solution that offers various features, including user and group management, authentication, and single sign-on (SSO) services. As a cloud-native service, Azure AD provides several benefits, such as automatic updates, scalability, and ease of access for remote and hybrid workforces.
On-Premises Active Directory (AD)
On-Premises AD is a traditional, on-site identity and access management solution that has been the cornerstone of many organizations’ IT infrastructures for years. On-Premises AD offers direct control over user identities, seamless integration with Windows-based systems, and compatibility with various third-party applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages
When comparing Azure AD and On-Premises AD, consider the following advantages and disadvantages:
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD)
- Advantages: Automatic updates, scalability, ease of access for remote and hybrid workforces, seamless integration with Microsoft cloud services, and support for various third-party applications.
- Disadvantages: Dependency on internet connectivity, potential data privacy concerns, and limited control over the underlying infrastructure.
On-Premises Active Directory (AD)
- Advantages: Direct control over user identities, seamless integration with Windows-based systems, and compatibility with various third-party applications.
- Disadvantages: Requires on-site hardware, manual updates and maintenance, limited access for remote and hybrid workforces, and potential scalability issues.
Choosing the Right Solution
The choice between Azure AD and On-Premises AD depends on an organization’s specific needs, priorities, and IT infrastructure. Businesses with a strong on-premises presence, Windows-based systems, and limited cloud adoption may prefer On-Premises AD. Meanwhile, organizations with a growing cloud footprint, remote or hybrid workforces, and a need for scalability may benefit from Azure AD.
Integrating Azure Active Directory with Other Microsoft Services
Microsoft Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) offers seamless integration with various Microsoft services, enabling organizations to streamline user management and enhance productivity. By integrating Azure AD with Office 365, Dynamics 365, and Power BI, businesses can leverage the full potential of these platforms while ensuring secure access for their users.
Azure AD and Office 365
Azure AD serves as the identity and access management solution for Office 365, allowing businesses to manage user access to productivity tools, such as Microsoft Teams, SharePoint, and Exchange Online. By integrating Azure AD with Office 365, organizations can:
- Implement single sign-on (SSO) for a seamless user experience.
- Centrally manage user identities and access rights.
- Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) and conditional access policies.
Azure AD and Dynamics 365
Azure AD also integrates with Dynamics 365, a suite of intelligent business applications that help organizations manage sales, marketing, customer service, and operations. By connecting Azure AD with Dynamics 365, businesses can:
- Simplify user management for Dynamics 365 applications.
- Implement SSO and MFA for secure access.
- Leverage Azure AD’s advanced security features, such as conditional access and identity protection.
Azure AD and Power BI
Azure AD integration with Power BI, Microsoft’s business analytics and data visualization service, enables organizations to:
- Centrally manage user access to Power BI reports and dashboards.
- Implement SSO and MFA for secure access.
- Assign appropriate permissions and roles to users and groups.
Benefits of Integration
Integrating Azure Active Directory with other Microsoft services offers several benefits, including:
- Simplified user management through centralized identity and access management.
- Enhanced security with features such as SSO, MFA, and conditional access.
- Improved productivity by enabling seamless access to Microsoft’s suite of business applications.
Azure AD’s Value Proposition
By integrating Azure Active Directory with other Microsoft services, organizations can create a cohesive, secure, and productive digital ecosystem. Azure AD’s robust features and seamless integration capabilities make it an invaluable tool for businesses looking to optimize their use of Microsoft’s cloud services.
Azure Active Directory Pricing and Licensing Options
Microsoft Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) offers various pricing and licensing options to cater to the diverse needs of organizations. Understanding the different tiers and their features can help businesses choose the best plan for their requirements and budget.
Free Tier
Azure AD’s free tier includes basic features, such as user and group management, directory objects, and self-service password reset. This tier is suitable for small businesses or organizations with limited requirements for identity and access management.
Basic Tier
The Basic tier, starting at $1 per user per month, adds premium features, such as group management, Azure AD Connect, and company branding. This tier is ideal for organizations that require more advanced identity and access management capabilities.
Premium P1 Tier
The Premium P1 tier, starting at $6 per user per month, offers advanced features, such as conditional access, Azure AD Identity Protection, and Microsoft Cloud App Security. This tier is designed for businesses that prioritize security and require comprehensive identity and access management solutions.
Premium P2 Tier
The Premium P2 tier, starting at $9 per user per month, includes all features from the Premium P1 tier, as well as additional capabilities, such as Identity Governance and Privileged Identity Management. This tier is recommended for large enterprises with complex identity and access management needs.
Choosing the Right Plan
When selecting an Azure AD pricing and licensing option, consider the following factors:
- Number of users and directory objects.
- Required features and capabilities, such as group management, conditional access, and Azure AD Connect.
- Budget constraints and cost considerations.
- Security and compliance requirements.
Azure AD’s Value Proposition
Microsoft Azure Active Directory offers flexible pricing and licensing options, enabling organizations to select the plan that best meets their needs and budget. By choosing the right Azure AD tier, businesses can leverage robust identity and access management features, enhance security, and maintain compliance.
Best Practices for Managing Microsoft Azure Active Directory
Effectively managing Microsoft Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is crucial for organizations seeking to maintain security, streamline user management, and ensure compliance. By following these best practices, businesses can optimize their Azure AD implementation and enhance overall identity and access management.
Regularly Review Access Rights
Periodically review user access rights to ensure that employees only have the necessary permissions to perform their job functions. This practice helps minimize the risk of unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Implementing MFA adds an extra layer of security to user accounts by requiring a second form of authentication, such as a phone call, text message, or authenticator app verification. Enabling MFA for all users reduces the likelihood of compromised accounts and data breaches.
Monitor Audit Logs
Regularly monitor Azure AD audit logs to track user activity, identify potential security threats, and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements. Azure AD’s audit logs provide valuable insights into user behavior and system changes.
Implement Conditional Access Policies
Conditional access policies allow organizations to control user access based on specific conditions, such as location, device, and application. By implementing conditional access policies, businesses can enhance security and minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
Establish a Naming Convention
Creating a consistent naming convention for users, groups, and objects within Azure AD simplifies management and searchability. A well-defined naming convention also promotes clarity and organization within the directory.
Azure AD’s Value Proposition
By adhering to these best practices, organizations can maximize the potential of Microsoft Azure Active Directory and ensure a secure, efficient, and compliant identity and access management solution. Regularly reviewing access rights, enabling MFA, monitoring audit logs, implementing conditional access policies, and establishing a naming convention are essential steps in optimizing Azure AD management.
Troubleshooting Common Microsoft Azure Active Directory Issues
Microsoft Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is a powerful identity and access management solution, but like any technology, it can encounter issues. This guide offers practical solutions and resources for troubleshooting common Azure AD problems, such as user access problems, synchronization errors, and password reset failures.
User Access Problems
If users experience difficulty accessing applications or services connected to Azure AD, follow these steps:
- Verify user credentials and ensure that the account is not locked or disabled.
- Check for any service outages or maintenance windows affecting Azure AD.
- Confirm that the application or service is correctly integrated with Azure AD.
- Review conditional access policies and ensure they are not blocking user access.
Synchronization Errors
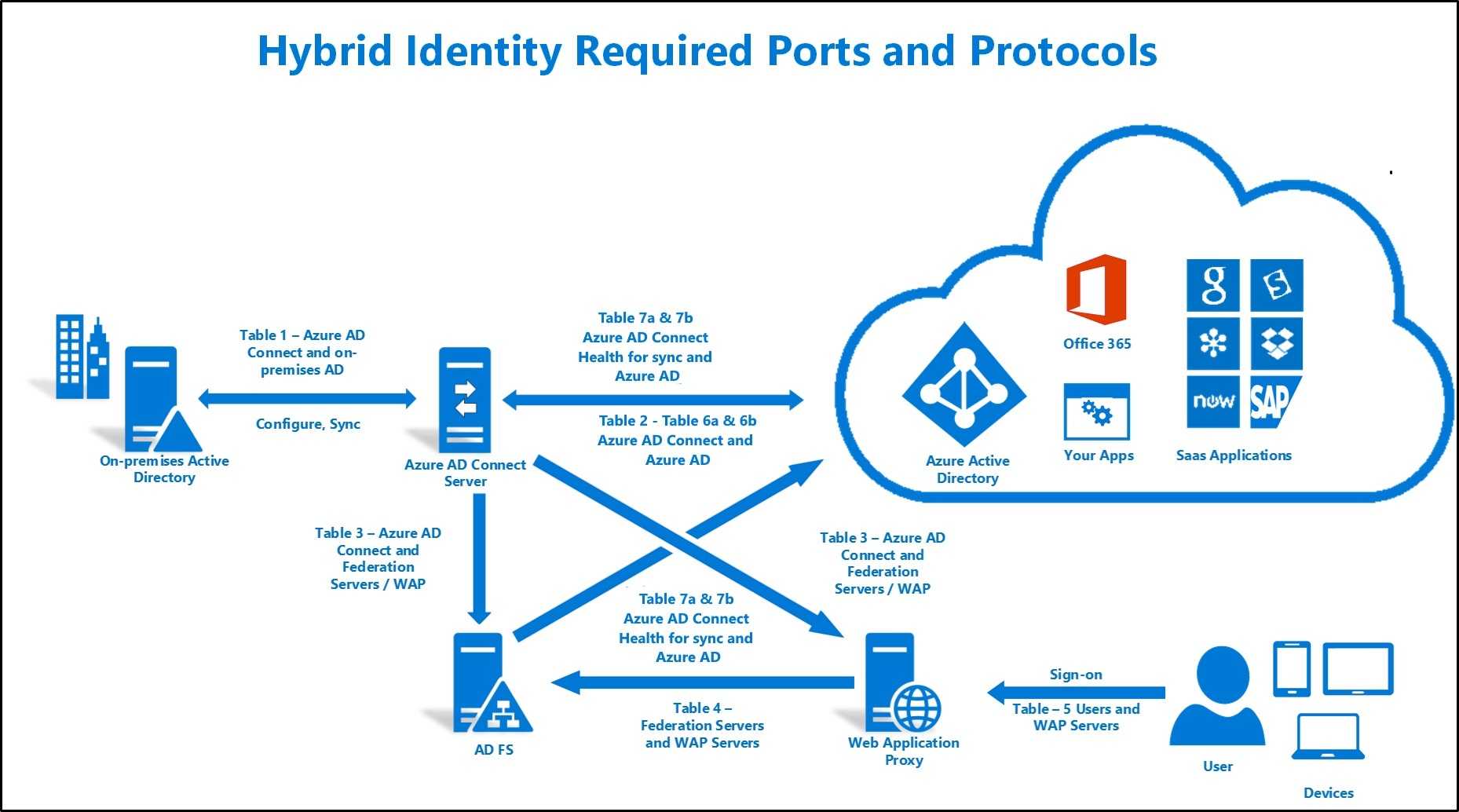
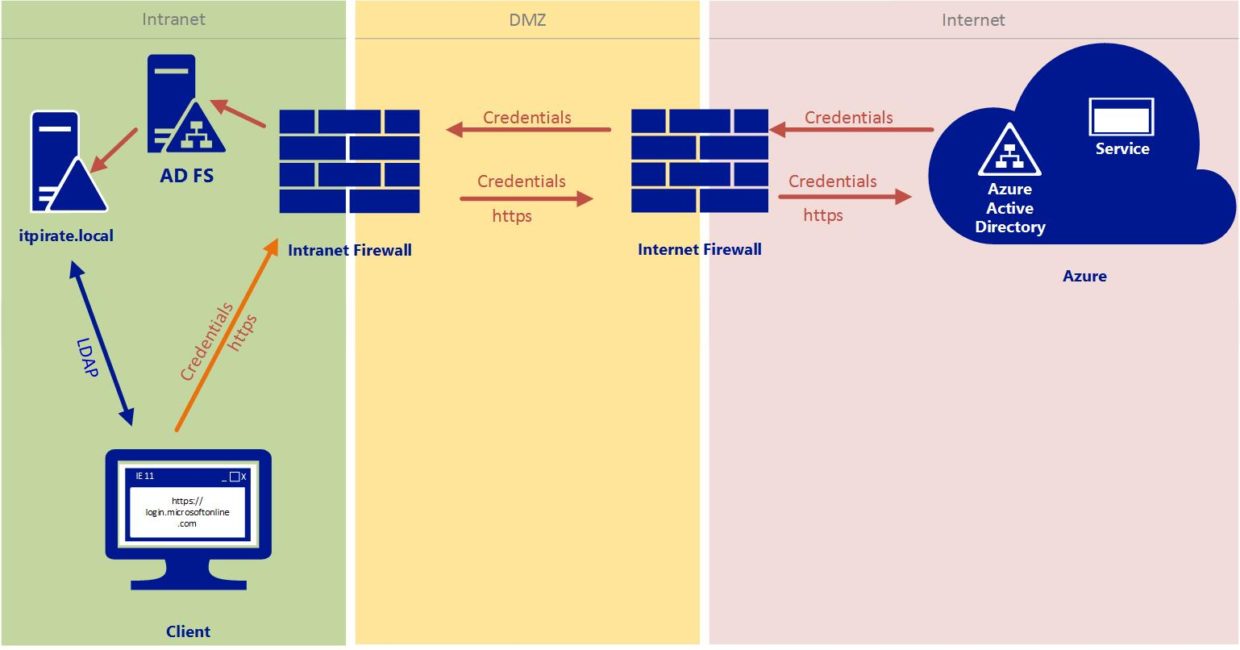
Synchronization errors between on-premises Active Directory and Azure AD can occur due to various reasons. To troubleshoot synchronization issues, consider the following:
- Ensure that the Azure AD Connect tool is properly installed and configured.
- Verify that the synchronization schedule is set up correctly and running as expected.
- Check for any discrepancies in the on-premises Active Directory that may be causing synchronization failures.
- Review Azure AD Connect logs for detailed error information and troubleshooting guidance.
Password Reset Failures
Password reset failures in Azure AD can be frustrating for users and impact productivity. To address password reset issues, try these steps:
- Confirm that the user has correctly followed the password reset process.
- Ensure that the user’s account meets the password complexity and length requirements.
- Verify that the user has not exceeded the maximum number of password reset attempts.
- Review Azure AD password reset policies and ensure they are configured correctly.
Azure AD’s Value Proposition
Microsoft Azure Active Directory is a robust and versatile identity and access management solution, but like any technology, it can encounter issues. By understanding how to troubleshoot common problems, organizations can ensure a smooth and secure user experience. Addressing user access problems, synchronization errors, and password reset failures are essential steps in maintaining a reliable Azure AD environment.