Understanding Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Its Importance
In today’s digital age, cloud-based services have become an integral part of many organizations’ IT infrastructure. While cloud services offer numerous benefits, they also come with security risks, including unauthorized access to sensitive data. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a crucial security feature that helps mitigate these risks by adding an extra layer of security to user authentication. MFA requires users to provide at least two forms of identification before granting access to cloud resources, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
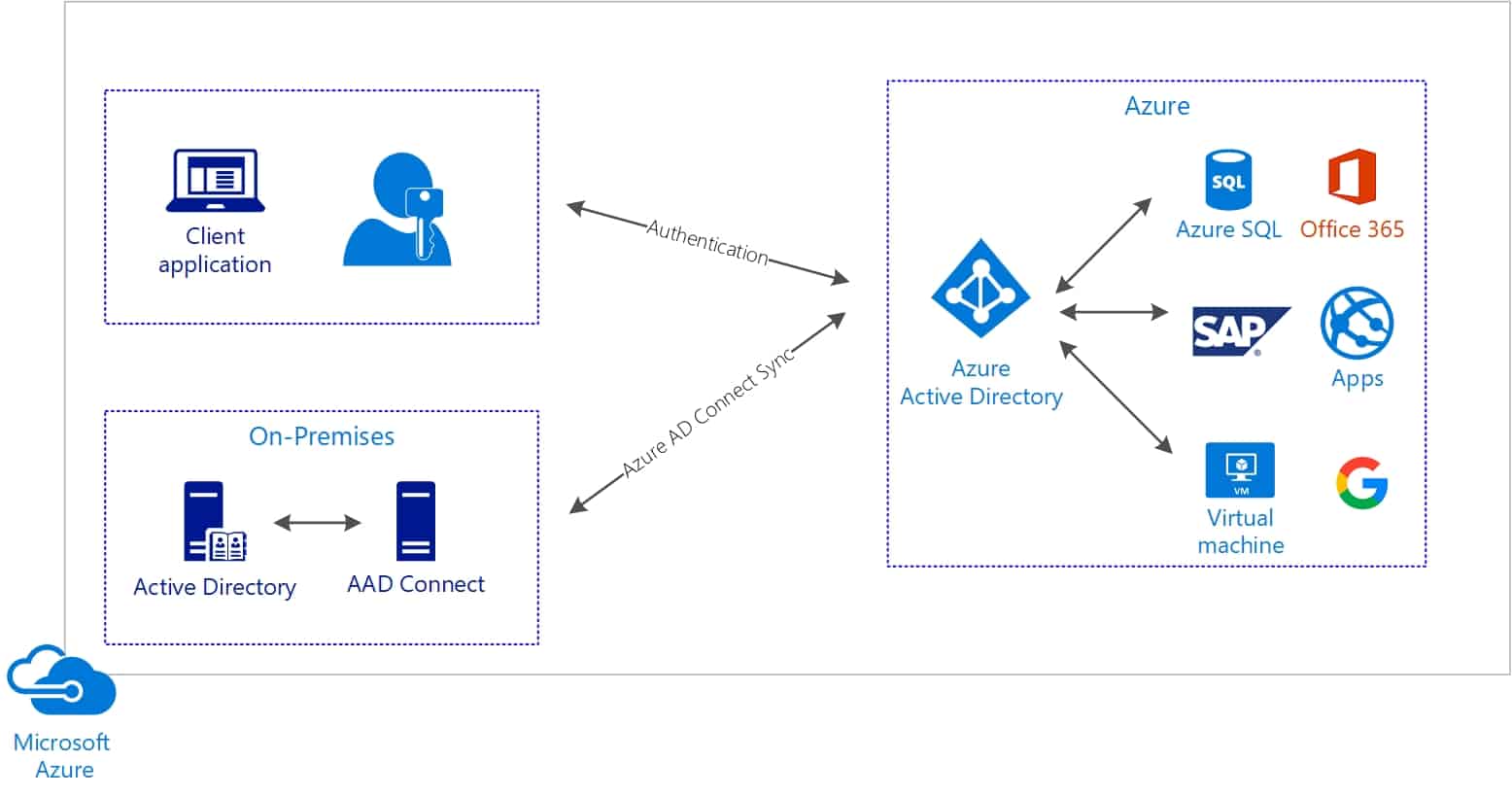
Microsoft Azure is a popular cloud platform that offers various MFA options to help secure access to your cloud resources. By implementing MFA options in Azure, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access, meet compliance requirements, and improve their overall security posture. MFA options in Azure include Azure Multi-Factor Authentication, Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) MFA, and Conditional Access, among others.
MFA options in Azure work by requiring users to provide at least two forms of identification, such as something they know (e.g., a password), something they have (e.g., a security token), or something they are (e.g., biometric data). By requiring multiple forms of identification, MFA options in Azure make it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access, even if they have obtained a user’s password through phishing or other means.
Microsoft Azure’s Built-In MFA Options
Microsoft Azure offers several built-in Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) options to help secure access to your cloud resources. These options include Azure Multi-Factor Authentication, Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) MFA, and Conditional Access. Each of these options has its own features, benefits, and limitations, making them suitable for different use cases.
Azure Multi-Factor Authentication
Azure Multi-Factor Authentication is a cloud-based authentication solution that provides an additional layer of security to user sign-ins and transactions. It works by requiring users to verify their identity using a second form of authentication, such as a phone call, text message, or mobile app notification. Azure Multi-Factor Authentication can be easily enabled for individual users or groups of users, and it can be integrated with a variety of applications and services, including Azure AD, Microsoft 365, and third-party applications.
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) MFA
Azure AD MFA is a feature of Azure Active Directory that provides an additional layer of security to user sign-ins and transactions. It works by requiring users to verify their identity using a second form of authentication, such as a phone call, text message, or mobile app notification. Azure AD MFA is typically used to secure access to cloud-based applications and services, such as Microsoft 365, Dynamics 365, and other SaaS applications. It can also be used to secure on-premises applications that are integrated with Azure AD.
Conditional Access
Conditional Access is a feature of Azure Active Directory that allows you to define access control policies based on specific conditions, such as user location, device compliance, and application risk level. Conditional Access policies can be used to require Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for specific users, groups, or applications, providing an additional layer of security to user sign-ins and transactions. Conditional Access policies can also be used to block sign-ins from specific locations, require device compliance, and enforce other security requirements.
Azure Multi-Factor Authentication: An In-Depth Overview
Azure Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a cloud-based authentication solution that provides an additional layer of security to user sign-ins and transactions. It works by requiring users to verify their identity using a second form of authentication, such as a phone call, text message, or mobile app notification. Azure MFA is a built-in feature of Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), but it can also be used as a standalone service to secure a variety of applications and services, including on-premises applications.
Features of Azure Multi-Factor Authentication
Azure MFA offers several features that make it a powerful authentication solution for organizations. These features include:
- Easy setup and management: Azure MFA can be easily set up and managed through the Azure portal, allowing administrators to enable MFA for individual users or groups of users.
- Integration with a variety of applications and services: Azure MFA can be integrated with a wide range of applications and services, including Azure AD, Microsoft 365, Dynamics 365, and third-party applications.
- Customizable authentication methods: Azure MFA offers several authentication methods, including phone calls, text messages, mobile app notifications, and verification codes. Administrators can customize these methods based on their organization’s needs and requirements.
- Conditional Access policies: Azure MFA can be used in conjunction with Conditional Access policies to require MFA based on specific conditions, such as user location, device compliance, and application risk level.
Benefits and Limitations of Azure Multi-Factor Authentication
Azure MFA offers several benefits, including improved security, reduced risk of unauthorized access, and compliance with various regulations and standards. However, it also has some limitations. For example, it may require additional setup and management time, and it may not be suitable for all applications and services. Additionally, some users may find the additional authentication steps inconvenient or confusing.
Setting Up and Managing Azure Multi-Factor Authentication
Azure MFA can be easily set up and managed through the Azure portal. To enable MFA for a user, administrators can simply navigate to the Azure Active Directory section of the portal, select the user, and enable MFA. They can also customize authentication methods, set up Conditional Access policies, and monitor MFA usage and activity through the portal.
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) Multi-Factor Authentication: An Overview
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a built-in feature of Azure AD that provides an additional layer of security to user sign-ins and transactions. It works by requiring users to verify their identity using a second form of authentication, such as a phone call, text message, or mobile app notification. Azure AD MFA is typically used to secure access to cloud-based applications and services, such as Microsoft 365, Dynamics 365, and other SaaS applications. It can also be used to secure on-premises applications that are integrated with Azure AD.
Differences Between Azure Multi-Factor Authentication and Azure AD MFA
While both Azure Multi-Factor Authentication and Azure AD MFA provide an additional layer of security to user sign-ins and transactions, there are some differences between the two. Azure Multi-Factor Authentication is a standalone service that can be used to secure a variety of applications and services, both in the cloud and on-premises. Azure AD MFA, on the other hand, is a built-in feature of Azure AD that is typically used to secure cloud-based applications and services. Additionally, Azure AD MFA is designed to work seamlessly with other Azure AD features, such as Conditional Access and Identity Protection.
When to Use Azure Multi-Factor Authentication vs. Azure AD MFA
The decision to use Azure Multi-Factor Authentication or Azure AD MFA will depend on your specific needs and requirements. If you need to secure a variety of applications and services, both in the cloud and on-premises, Azure Multi-Factor Authentication may be the better option. However, if you primarily need to secure cloud-based applications and services that are integrated with Azure AD, Azure AD MFA may be the more convenient and cost-effective option.
Setting Up and Managing Azure AD MFA
Azure AD MFA can be easily set up and managed through the Azure portal. To enable MFA for a user, administrators can simply navigate to the Azure Active Directory section of the portal, select the user, and enable MFA. They can also customize authentication methods, set up Conditional Access policies, and monitor MFA usage and activity through the portal.
Conditional Access in Azure: A Key Component of Multi-Factor Authentication
Conditional Access is a feature in Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) that enables organizations to manage how users access cloud applications based on specific conditions. When used in conjunction with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), Conditional Access can provide an additional layer of security to user sign-ins and transactions. By setting up Conditional Access policies, organizations can require MFA based on specific conditions, such as user location, device compliance, and application risk level.
Features of Conditional Access in Azure
Conditional Access in Azure offers several features that make it a powerful tool for managing user access to cloud applications. These features include:
- Customizable conditions: Conditional Access policies can be customized based on a variety of conditions, such as user location, device compliance, and application risk level.
- Integration with Multi-Factor Authentication: Conditional Access policies can be used to require Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) based on specific conditions.
- Session controls: Conditional Access policies can be used to control user sessions, such as limiting access to specific applications or requiring users to sign in again after a certain period of time.
- Reporting and monitoring: Azure AD provides reporting and monitoring capabilities for Conditional Access policies, allowing organizations to track user activity and identify potential security threats.
Setting Up and Managing Conditional Access Policies in Azure
Conditional Access policies can be easily set up and managed through the Azure portal. To create a Conditional Access policy, administrators can navigate to the Azure Active Directory section of the portal, select Conditional Access, and follow the prompts to create a new policy. They can customize the policy based on specific conditions, such as user location, device compliance, and application risk level, and specify the actions to take when those conditions are met.
Third-Party MFA Options for Azure: Pros, Cons, and Setup
While Azure Multi-Factor Authentication and Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) Multi-Factor Authentication are powerful MFA solutions, they may not always meet the specific needs and requirements of every organization. In such cases, third-party MFA solutions can be integrated with Azure to provide additional functionality and customization. This section will discuss the benefits and limitations of using third-party MFA options for Azure, as well as how to set them up.
Benefits of Using Third-Party MFA Options for Azure
Third-party MFA solutions can offer several benefits for organizations using Azure, including:
- Customization: Third-party MFA solutions may offer more customization options than Azure Multi-Factor Authentication or Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication, allowing organizations to tailor their MFA solution to their specific needs and requirements.
- Integration with existing systems: Third-party MFA solutions may integrate more seamlessly with existing systems and applications, making it easier to implement and manage MFA across the organization.
- Advanced features: Third-party MFA solutions may offer advanced features, such as biometric authentication or adaptive authentication, that are not available in Azure Multi-Factor Authentication or Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication.
Limitations of Using Third-Party MFA Options for Azure
However, third-party MFA solutions may also have limitations, such as:
- Cost: Third-party MFA solutions may be more expensive than Azure Multi-Factor Authentication or Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication, especially for larger organizations.
- Complexity: Integrating third-party MFA solutions with Azure may be more complex than using Azure Multi-Factor Authentication or Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication, requiring additional setup and management time.
- Support: Organizations may need to rely on the third-party vendor for support, which may not be as responsive or knowledgeable as Microsoft support.
Setting Up Third-Party MFA Options for Azure
To set up a third-party MFA solution for Azure, organizations can follow these general steps:
- Choose a third-party MFA solution that meets their specific needs and requirements.
- Follow the vendor’s instructions for setting up and configuring the MFA solution.
- Integrate the MFA solution with Azure by configuring the necessary settings in Azure Active Directory.
- Test the MFA solution to ensure it is working properly and meets the organization’s security and usability requirements.
Choosing the Right MFA Option for Your Organization: Factors to Consider
With several MFA options available in Microsoft Azure, choosing the right one for your organization can be challenging. To help you make an informed decision, consider the following factors:
Cost
Cost is an important consideration when choosing an MFA option. Azure Multi-Factor Authentication and Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) Multi-Factor Authentication are built-in Azure services that do not incur additional costs beyond your Azure subscription. However, third-party MFA solutions may have additional costs associated with them. Consider your organization’s budget and the potential return on investment when choosing an MFA option.
Ease of Use
Ease of use is another important consideration. Azure Multi-Factor Authentication and Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication are designed to be easy to set up and manage, with user-friendly interfaces and step-by-step instructions. However, third-party MFA solutions may have more complex setups and management interfaces. Consider your organization’s technical capabilities and the level of expertise required to set up and manage the MFA solution.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integration with existing systems is also an important consideration. Azure Multi-Factor Authentication and Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication can be easily integrated with other Azure services and applications. However, third-party MFA solutions may require additional setup and configuration to integrate with existing systems. Consider your organization’s existing systems and the level of integration required when choosing an MFA option.
Customization
Customization is a key benefit of third-party MFA solutions. While Azure Multi-Factor Authentication and Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication offer basic customization options, third-party MFA solutions may offer more advanced customization options, such as biometric authentication or adaptive authentication. Consider your organization’s specific security needs and requirements when choosing an MFA option.
Support and Maintenance
Support and maintenance are also important considerations. Azure Multi-Factor Authentication and Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication are supported by Microsoft, which offers 24/7 support and regular updates. However, third-party MFA solutions may have different support and maintenance models. Consider your organization’s support and maintenance requirements when choosing an MFA option.
Best Practices for Implementing MFA in Azure
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) in Azure can significantly improve your organization’s security posture. However, it’s essential to follow best practices to ensure a successful implementation. Here are some best practices to consider:
Enable MFA for All Users
To maximize the security benefits of MFA, enable it for all users in your organization. This includes regular users, administrators, and guest accounts. Enforcing MFA for all users reduces the risk of unauthorized access and strengthens your organization’s overall security.
Require MFA for Privileged Accounts
Privileged accounts, such as administrator accounts, have elevated access to your organization’s resources. Requiring MFA for these accounts adds an extra layer of security and reduces the risk of compromised accounts.
Regularly Review and Update MFA Policies
Regularly reviewing and updating your MFA policies ensures that they remain effective and up-to-date with the latest security threats. Consider reviewing your MFA policies at least annually or whenever there are significant changes to your organization’s security posture.
Use Risk-Based MFA
Risk-based MFA evaluates the risk level of a sign-in attempt based on various factors, such as user location, device, and behavior. Requiring MFA only for high-risk sign-in attempts reduces user friction and improves the user experience while maintaining strong security.
Provide User Training and Education
User training and education are essential for ensuring the successful implementation of MFA. Provide users with clear instructions on how to set up and use MFA, as well as the importance of MFA in securing their accounts. Regularly communicating with users about security best practices can also help to reinforce the importance of MFA.
Monitor MFA Usage and Activity
Monitoring MFA usage and activity can help you identify potential security threats and ensure that MFA is working as intended. Consider using Azure Monitor or other monitoring tools to track MFA usage and activity and alert you to any suspicious behavior.