Unveiling the Benefits of Managed SQL Solutions
Opting for managed SQL Server solutions presents a compelling value proposition for businesses seeking to streamline database management. The advantages span across reduced operational overhead, enhanced security, and improved scalability, ultimately contributing to increased efficiency and cost savings. Managed SQL Server offerings alleviate the burden of day-to-day database administration tasks, such as patching, backups, and performance tuning. This allows internal IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives that drive business growth rather than being bogged down by routine maintenance. A core benefit of a managed sql server is the offloading of responsibilities.
Enhanced security is another significant advantage of managed SQL Server solutions. Providers invest heavily in security infrastructure and expertise to protect customer data from evolving threats. This includes implementing robust access controls, data encryption, vulnerability management, and intrusion detection systems. By leveraging a managed environment, businesses can benefit from a higher level of security than they might be able to achieve on their own. This is especially true for smaller organizations with limited security resources. Furthermore, compliance with industry regulations such as HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS becomes easier to achieve with a managed sql server that adheres to these standards.
Scalability is a crucial factor for businesses experiencing growth or fluctuating workloads. Managed SQL Server solutions offer the flexibility to easily scale resources up or down as needed, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency. This eliminates the need for costly hardware investments and complex capacity planning. The ability to quickly adapt to changing demands is a key advantage in today’s dynamic business environment. Whether it’s handling peak season traffic or supporting a new application launch, a managed SQL server provides the agility needed to stay ahead of the competition. In conclusion, choosing a managed sql server offers a blend of efficiency, security, and scalability that empowers businesses to thrive.
How to Choose the Right Managed SQL Server Provider
Selecting the right managed SQL server provider is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, security, and cost-effectiveness for your database infrastructure. A systematic approach is essential to making an informed decision. The initial step involves defining your organization’s specific needs and requirements. Consider factors such as database size, transaction volume, uptime requirements, and compliance mandates. Understanding these needs will help you evaluate potential providers and their offerings more effectively.
Next, carefully assess the service level agreements (SLAs) offered by different providers. The SLA should clearly outline the provider’s guarantees regarding uptime, performance, and support response times. Pay close attention to the penalties for failing to meet these guarantees. Security certifications are another critical consideration. Ensure that the provider holds relevant certifications such as ISO 27001, SOC 2, or HIPAA, depending on your industry’s regulatory requirements. These certifications demonstrate the provider’s commitment to maintaining a secure and compliant environment for your managed SQL server instance. Evaluate the support options offered by each provider. Do they offer 24/7 support? What are the available channels for support (e.g., phone, email, chat)? A responsive and knowledgeable support team is essential for resolving any issues that may arise.
Finally, compare the pricing models of different managed SQL server providers. Understand the different pricing tiers and what resources are included in each tier. Consider factors such as compute, storage, and bandwidth costs. Look for any hidden fees or charges. It is important to understand the provider’s reputation and customer reviews. Read online reviews and testimonials from other customers to get a sense of their experience with the provider. Look for patterns in the reviews, both positive and negative. Request references from the provider and speak to current customers to get their firsthand perspective. Selecting a managed SQL server provider requires careful consideration of several factors. By following this step-by-step guide, you can choose a provider that meets your specific needs and helps you maximize the benefits of a managed SQL server solution. This ensures the smooth and efficient operation of your managed SQL server environment.
Comparing Top Managed SQL Server Offerings
The landscape of managed SQL Server solutions is populated by several prominent vendors, each offering distinct advantages and catering to diverse needs. Analyzing these offerings is crucial for making an informed decision. Amazon RDS for SQL Server, Azure SQL Managed Instance, and Google Cloud SQL for SQL Server represent leading options in the cloud-based managed SQL Server space. Each one delivers a unique set of features, performance characteristics, and pricing structures.
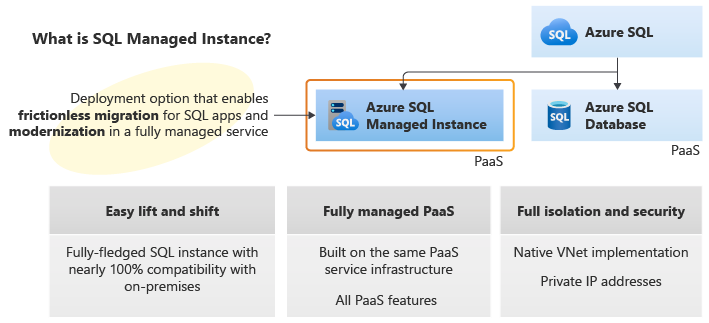
Amazon RDS for SQL Server is known for its ease of use and broad compatibility. It simplifies database administration tasks, allowing businesses to focus on application development. Azure SQL Managed Instance provides near-100% compatibility with on-premises SQL Server instances, making it an attractive choice for organizations seeking to migrate existing databases to the cloud with minimal code changes. It offers a comprehensive set of features, including advanced security and performance capabilities. Google Cloud SQL for SQL Server emphasizes scalability and cost-effectiveness, offering flexible pricing options and automated maintenance features. The best managed SQL Server option depends on specific requirements, existing infrastructure, and budget constraints.
While cloud-based solutions dominate the managed SQL Server market, on-premise managed solutions also exist. These solutions often involve partnering with a managed service provider (MSP) that assumes responsibility for the day-to-day management of SQL Server infrastructure within a company’s own data center. This approach can be beneficial for organizations with strict data residency requirements or those seeking greater control over their infrastructure. Key considerations when evaluating on-premise managed SQL Server solutions include the provider’s expertise, service level agreements, and security protocols. Whether opting for a cloud-based or on-premise managed SQL Server solution, a thorough comparison of available options is essential to ensure alignment with business objectives and technical requirements. The selection of the right managed sql server provider will impact performance and costs.
Cost Optimization Strategies for Your Managed SQL Server Instance
Strategies for optimizing costs associated with managed SQL Server solutions are crucial for businesses seeking to maximize their return on investment. Efficient resource allocation is a primary area for cost reduction. Analyzing workload demands and adjusting the provisioned resources, such as CPU, memory, and storage, can significantly lower expenses. Many managed SQL Server providers offer flexible scaling options. This allows organizations to dynamically adjust resources based on real-time needs, avoiding over-provisioning and unnecessary costs. Regularly reviewing resource utilization and identifying idle or underutilized instances is a recommended practice. Properly sizing the managed SQL server, based on actual needs instead of projected needs, it’s a good start to keep a cost-optimized environment. Another cost-optimization point is, turning off the instance when there are not used like at night or weekends, it will drastically reduces costs.
Performance tuning is another effective method for cost optimization within a managed SQL Server environment. Optimizing database queries, indexing strategies, and overall database design can improve performance and reduce resource consumption. Identifying and resolving performance bottlenecks allows the managed SQL Server instance to handle workloads more efficiently. This reduces the need for additional resources. Utilizing query optimization tools and techniques to fine-tune database operations is essential. Selecting the appropriate service tier based on the organization’s specific requirements is also crucial. Managed SQL Server providers typically offer various service tiers with different performance characteristics and pricing structures. Carefully evaluating the features and resources included in each tier helps to choose the most cost-effective option. This ensures the managed SQL Server environment meets performance needs without exceeding budget constraints. These are good practices to achieve a managed SQL server cost optimized environment.
Monitoring usage patterns plays a vital role in identifying opportunities for cost reduction in managed SQL Server deployments. Implementing comprehensive monitoring tools provides insights into resource utilization, performance metrics, and overall system behavior. Analyzing these data allows identifying areas where costs can be optimized. For instance, identifying peak usage periods and scaling resources accordingly can help to avoid over-provisioning during off-peak hours. Proactive monitoring can also detect anomalies and potential issues. Addressing them promptly prevents performance degradation and resource waste. Utilizing cost management tools provided by managed SQL Server vendors can provide detailed cost breakdowns and recommendations for optimization. Regularly reviewing these reports and implementing the suggested improvements can lead to substantial cost savings. The key to cost optimization in a managed SQL server environment lies in continuous monitoring, analysis, and proactive adjustments based on actual usage patterns and performance data. And of course, all of the major providers of managed SQL Server provide recommendations and tools for cost optimization.
Security Best Practices for Managed SQL Environments
Securing managed SQL Server deployments is critical. Robust security measures protect sensitive data. They also maintain compliance. Access control is a foundational element. Implement the principle of least privilege. Grant users only the necessary permissions. Regularly review and update access rights. Strong authentication mechanisms are essential. Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security. Data encryption protects data at rest and in transit. Use Transparent Data Encryption (TDE). This encrypts the database files. For data in transit, use SSL/TLS encryption. This secures connections between clients and the server. Vulnerability management is an ongoing process. Regularly scan for vulnerabilities. Apply patches promptly. Keep the SQL Server instance and operating system up to date. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) monitor network traffic. They identify suspicious activity. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems centralize log data. They provide a comprehensive view of security events.
Adhering to industry security standards is vital. Compliance regulations dictate specific security requirements. Examples include HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS. A well-defined security policy is crucial. It outlines security procedures and responsibilities. Regular security audits assess the effectiveness of security controls. Penetration testing simulates attacks. It identifies weaknesses in the security posture. Proper configuration of the managed SQL Server is key. Disable unnecessary features. Harden the operating system. Firewalls restrict network access. They only allow authorized traffic. Database activity monitoring (DAM) tracks user actions. It helps detect suspicious behavior. Data masking and redaction protect sensitive data. They prevent unauthorized access to confidential information. Effective security practices are crucial. They protect managed SQL Server environments.
Protecting your managed SQL Server environment involves a multi-layered approach. A defense-in-depth strategy combines various security controls. This mitigates risks. Regular security awareness training educates users. It teaches them about potential threats. It also explains how to avoid them. Incident response planning is essential. It outlines the steps to take in the event of a security breach. Regular backups ensure data can be restored. It is after a disaster. Managed SQL Server providers offer various security features. Evaluate these features carefully. Choose a provider that meets your security requirements. The goal is to ensure the security and integrity of your data. Focusing on these key areas strengthens the security of your managed SQL Server, a key process of a managed sql server deployment.
Migrating to a Managed SQL Server: A Seamless Transition
Migrating existing SQL Server databases to a managed environment requires careful planning and execution. The goal is to minimize downtime and ensure data integrity. Before initiating the migration to a managed sql server, assess the compatibility of your database with the target managed sql server platform. This involves reviewing database features, versions, and dependencies to identify potential issues. A thorough assessment will pave the way for a smoother transition.
Selecting the appropriate data transfer method is crucial for a successful migration to a managed sql server. Several options are available, including backup and restore, database mirroring, and online migration tools. Backup and restore is a common approach, involving creating a backup of your on-premise database and restoring it to the managed sql server instance. Database mirroring provides a near real-time replication of data, minimizing downtime during the cutover. Online migration tools, offered by many managed sql server providers, streamline the process with automated data transfer and schema conversion. The choice depends on database size, downtime tolerance, and network bandwidth. Minimizing downtime is often a key requirement when migrating to a managed sql server. Strategies include incremental backups, data synchronization, and phased cutovers. Incremental backups reduce the amount of data that needs to be transferred during the final migration step. Data synchronization keeps the on-premise and managed sql server databases in sync, allowing for a quick switchover. Phased cutovers involve migrating applications and users in stages, minimizing the impact on business operations. It is a significant change so plan carefully to get the most of your managed sql server.
Various migration tools and strategies can facilitate the transition to a managed sql server. SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) provides tools for backup and restore operations. Azure Database Migration Service offers a comprehensive solution for migrating databases to Azure SQL Managed Instance. AWS Database Migration Service helps migrate databases to Amazon RDS for SQL Server. These tools automate many aspects of the migration process, reducing the risk of errors and accelerating the timeline. Regularly test the migrated database in the managed sql server environment to ensure functionality and performance. This includes verifying data integrity, application compatibility, and query performance. Address any issues promptly to ensure a seamless transition and optimal performance of your managed sql server. Finally, properly configured and optimized, the migrated database will allow you to experience the full advantages of your new managed sql server.
Monitoring and Maintaining Your Managed SQL Server
Effective monitoring and maintenance are crucial for ensuring the optimal performance and reliability of a managed SQL Server instance. Proactive monitoring allows for the early detection and resolution of potential issues, preventing them from escalating and impacting business operations. This involves establishing a comprehensive monitoring strategy that covers various aspects of the managed SQL Server environment. One key area is performance monitoring, which involves tracking metrics like CPU utilization, memory usage, disk I/O, and query execution times. By analyzing these metrics, administrators can identify performance bottlenecks and optimize database configurations. Tools like SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) and Azure Monitor provide valuable insights into server performance. Regular log analysis is another critical aspect of maintenance. SQL Server logs contain valuable information about errors, warnings, and other events that can indicate underlying problems. Analyzing these logs can help identify security threats, performance issues, and hardware failures.
Backup and recovery are paramount for data protection and business continuity within a managed SQL Server environment. Regularly scheduled backups should be performed to ensure that data can be restored in the event of a disaster or data corruption. Managed SQL Server providers typically offer automated backup solutions, simplifying the backup process. However, it’s essential to verify the integrity of backups and test the recovery process regularly. Disaster recovery planning is equally important. This involves creating a plan for restoring SQL Server services in the event of a major outage. The plan should include procedures for failing over to a secondary site, restoring backups, and verifying data integrity. Managed SQL Server solutions often provide disaster recovery features like replication and failover clustering to minimize downtime. Consistently monitoring the managed SQL Server, analyzing logs, implementing robust backup and recovery procedures, and establishing a comprehensive disaster recovery plan are all critical for maintaining a healthy and resilient managed SQL Server environment.
Maintaining a managed SQL Server also requires proactive vulnerability management. Regularly scanning for security vulnerabilities and applying patches is crucial for protecting the database from cyber threats. Managed SQL Server providers typically handle patching and security updates, but it’s essential to verify that these updates are being applied promptly. Access control is another critical security measure. Implementing the principle of least privilege, which restricts user access to only the resources they need to perform their job functions, minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. Regularly review user permissions and remove unnecessary access. Thorough monitoring and consistent maintenance are essential for a robust managed sql server deployment. Implementing these strategies ensures the reliable and secure operation of your databases, which is key to supporting critical business applications and processes. Choosing a robust managed sql server offering is an important decision.
Future Trends in SQL Server Management
The landscape of SQL Server management is constantly evolving, driven by innovations in cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and automation. Several key trends are poised to reshape how organizations manage their data estates, particularly within managed SQL Server environments. The rise of serverless databases represents a significant shift, allowing for on-demand resource allocation and pay-per-use pricing models. This approach eliminates the need for manual capacity planning and reduces operational overhead, making it an attractive option for applications with fluctuating workloads. Serverless managed SQL Server offerings are becoming increasingly sophisticated, providing enhanced scalability and cost efficiency.
AI-powered optimization is another trend gaining momentum in managed SQL Server. Machine learning algorithms can analyze performance data to identify bottlenecks, recommend indexing strategies, and automate query tuning. This proactive approach improves database performance, reduces resource consumption, and minimizes the need for manual intervention. Furthermore, AI can enhance security by detecting anomalous behavior and identifying potential threats. Automation is playing a crucial role in streamlining routine tasks such as patching, backups, and disaster recovery. By automating these processes, organizations can free up valuable IT resources and reduce the risk of human error. Managed SQL Server providers are increasingly incorporating automation capabilities into their platforms, simplifying database administration and improving overall efficiency. These advancements collectively contribute to a more agile and cost-effective approach to managed SQL Server.
Looking ahead, we can expect to see further integration of these technologies into managed SQL Server solutions. Serverless architectures will become more prevalent, offering greater flexibility and scalability. AI-powered optimization will become more sophisticated, providing deeper insights and automated remediation. Automation will extend to more complex tasks, such as schema evolution and data migration. The convergence of these trends will lead to a future where managed SQL Server is more intelligent, self-managing, and cost-effective. Embracing these innovations will be essential for organizations seeking to maximize the value of their data and maintain a competitive edge. As managed SQL Server continues to evolve, understanding these future trends is critical for making informed decisions about database strategy and technology adoption. Investing in managed SQL Server ensures organizations can focus on innovation and growth, rather than the complexities of database administration.