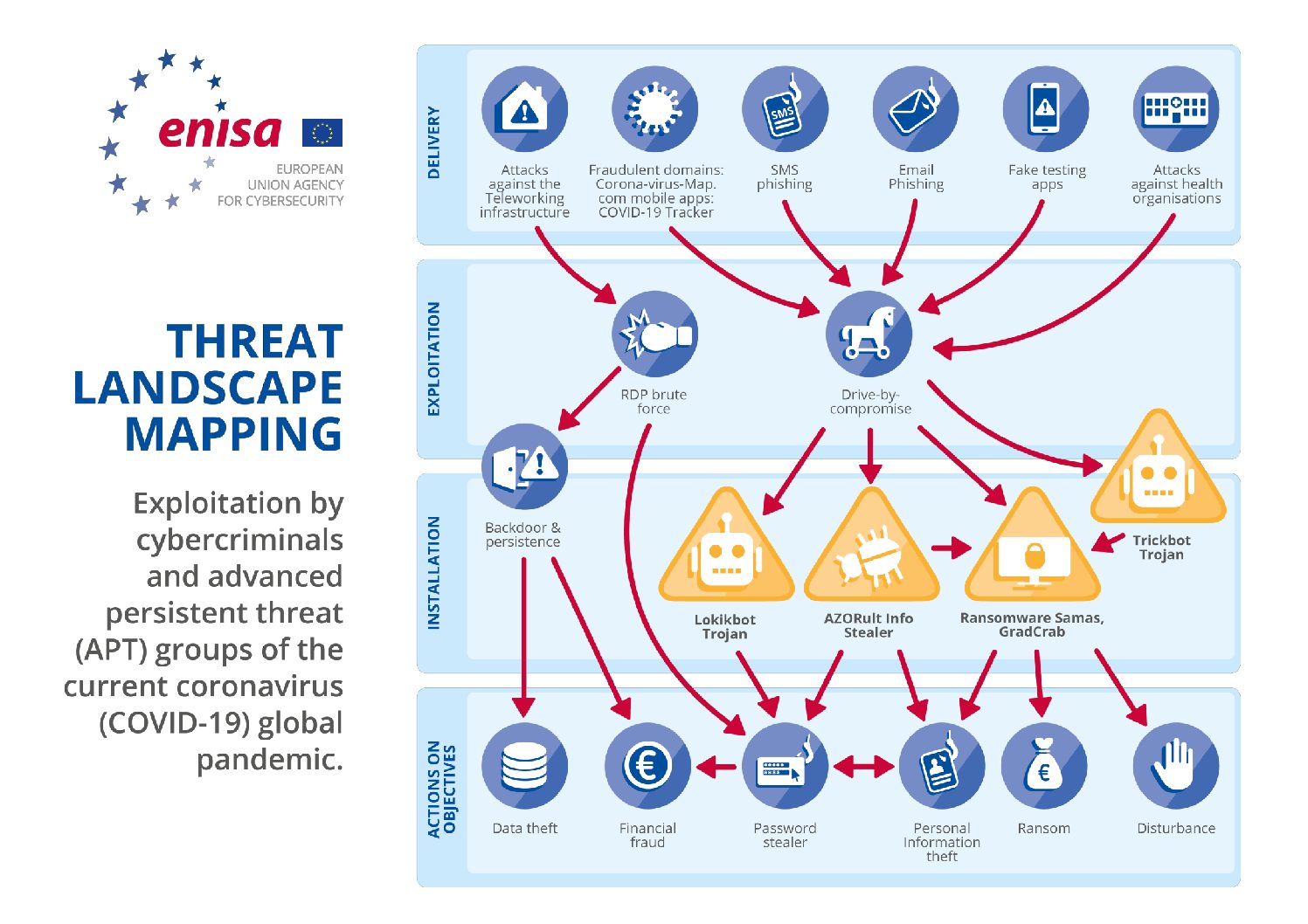
The Intersection of Internet Security and Threat Intelligence in the Cloud
In today’s digital age, the cloud has become an integral part of many organizations’ IT infrastructure. The convenience, scalability, and cost-effectiveness of cloud services have led to an increasing number of businesses migrating their operations to the cloud. However, this shift has also introduced new challenges related to internet security and threat intelligence in the cloud. Protecting digital assets in a cloud environment is a critical concern for businesses of all sizes.
Internet security in the cloud involves safeguarding data, applications, and infrastructure from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. It encompasses a wide range of measures, including access management, data encryption, and security monitoring. Threat intelligence, on the other hand, refers to the process of gathering, analyzing, and sharing information about potential or current threats to an organization’s assets. By combining internet security and threat intelligence, organizations can better protect their digital assets in the cloud and stay ahead of emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
The benefits of integrating threat intelligence into a cloud security strategy are numerous. Threat intelligence can help organizations identify and respond to threats more quickly, reduce the impact of security incidents, and improve their overall security posture. By sharing threat intelligence within communities, organizations can also benefit from the collective knowledge and experience of their peers, further enhancing their ability to detect and respond to threats. Threat intelligence platforms can facilitate this process by automating the collection, analysis, and dissemination of threat intelligence, making it easier for organizations to incorporate threat intelligence into their cloud security strategy.

Understanding the Cloud Security Landscape
The cloud security landscape is constantly evolving, with new threats and vulnerabilities emerging every day. To protect their digital assets in the cloud, organizations need to understand the various security models, service models, and deployment models available. They also need to recognize the critical role that threat intelligence plays in enhancing cloud security.
Cloud security models refer to the different approaches used to secure cloud environments. These models include infrastructure security, platform security, and software security. Infrastructure security focuses on securing the physical and virtual infrastructure that supports the cloud. Platform security involves securing the cloud platform itself, including the operating system, databases, and middleware. Software security focuses on securing the applications that run on the cloud platform.
Cloud service models refer to the different levels of service provided by cloud service providers. These models include Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS provides organizations with access to virtualized infrastructure, such as servers, storage, and networking. PaaS provides organizations with a platform for developing, running, and managing applications. SaaS provides organizations with access to software applications over the internet.
Cloud deployment models refer to the different ways in which cloud services can be deployed. These models include public clouds, private clouds, and hybrid clouds. Public clouds are hosted by cloud service providers and are available to the general public. Private clouds are hosted by organizations for their exclusive use. Hybrid clouds combine elements of both public and private clouds.
Threat intelligence plays a critical role in enhancing cloud security by providing organizations with information about potential or current threats to their digital assets. By incorporating threat intelligence into their cloud security strategy, organizations can better understand the risks they face and take appropriate measures to mitigate those risks. Threat intelligence can also help organizations detect and respond to security incidents more quickly, reducing the impact of those incidents and improving their overall security posture.
To fully leverage the benefits of threat intelligence, organizations should consider sharing threat intelligence within communities. By sharing threat intelligence, organizations can benefit from the collective knowledge and experience of their peers, further enhancing their ability to detect and respond to threats. Threat intelligence platforms can facilitate this process by automating the collection, analysis, and dissemination of threat intelligence, making it easier for organizations to incorporate threat intelligence into their cloud security strategy.

Implementing a Robust Cloud Security Strategy
As the use of cloud computing continues to grow, so do the challenges of securing digital assets in a cloud environment. A robust cloud security strategy is essential for protecting sensitive data and maintaining business continuity. This strategy should include access management, data encryption, and security monitoring, as well as the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning to automate threat detection and response.
Access management is a critical component of any cloud security strategy. It involves controlling who has access to what data and resources in the cloud. Access management can be achieved through the use of strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication, and access control policies, such as role-based access control. By implementing access management, organizations can reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Data encryption is another essential component of a robust cloud security strategy. It involves converting plaintext data into ciphertext, which can only be read with a decryption key. Data encryption can be used to protect data at rest, in transit, and in use. By using data encryption, organizations can ensure that their data is protected from unauthorized access, even if it falls into the wrong hands.
Security monitoring is also critical for detecting and responding to security incidents in the cloud. It involves continuously monitoring cloud environments for signs of suspicious activity, such as unusual login attempts or data access patterns. Security monitoring can be achieved through the use of security information and event management (SIEM) systems, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), and security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) platforms. By implementing security monitoring, organizations can detect and respond to security incidents more quickly, reducing the impact of those incidents and improving their overall security posture.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) can be used to automate threat detection and response in the cloud. AI and ML algorithms can analyze large volumes of data in real-time, identifying patterns and anomalies that may indicate a security threat. By using AI and ML, organizations can detect threats more quickly and respond to them more effectively, reducing the workload on security teams and improving overall security.
In conclusion, implementing a robust cloud security strategy is essential for protecting digital assets in a cloud environment. Access management, data encryption, and security monitoring are critical components of this strategy, as is the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning to automate threat detection and response. By implementing these measures, organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents, maintaining business continuity and protecting their reputation.

How to Evaluate Cloud Service Providers’ Security Measures
As more organizations move their digital assets to the cloud, evaluating the security measures of cloud service providers has become increasingly important. A cloud service provider’s security measures can significantly impact an organization’s overall security posture, making it essential to choose a provider with robust security controls. In this article, we will discuss the key factors to consider when evaluating a cloud service provider’s security measures, including certifications, compliance, and transparency.
Certifications are an essential factor to consider when evaluating a cloud service provider’s security measures. Certifications, such as SOC 2, ISO 27001, and PCI DSS, demonstrate that a cloud service provider has implemented specific security controls and undergone independent audits to verify their effectiveness. By choosing a cloud service provider with relevant certifications, organizations can be confident that their digital assets are being protected by a provider that has been independently verified to meet specific security standards.
Compliance is another critical factor to consider when evaluating a cloud service provider’s security measures. Compliance with industry-specific regulations, such as HIPAA for healthcare organizations or GDPR for European organizations, is essential for maintaining regulatory compliance. By choosing a cloud service provider that is compliant with relevant regulations, organizations can be confident that their digital assets are being protected in a manner that meets regulatory requirements.
Transparency is also essential when evaluating a cloud service provider’s security measures. Transparency refers to the provider’s willingness to share information about their security controls and practices. A cloud service provider that is transparent about their security measures is more likely to be trusted by their customers. Organizations should look for cloud service providers that provide regular security updates, offer security training and awareness programs, and have clear incident response plans in place.
In addition to certifications, compliance, and transparency, organizations should also consider the following factors when evaluating a cloud service provider’s security measures:
- Data encryption: Data encryption is essential for protecting data at rest and in transit. Organizations should look for cloud service providers that offer robust data encryption capabilities.
- Access controls: Strong access controls are essential for preventing unauthorized access to digital assets. Organizations should look for cloud service providers that offer multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, and other access control mechanisms.
- Security monitoring: Security monitoring is critical for detecting and responding to security incidents in real-time. Organizations should look for cloud service providers that offer security information and event management (SIEM) systems, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), and other security monitoring capabilities.
- Incident response: Incident response is essential for minimizing the impact of security incidents. Organizations should look for cloud service providers that have clear incident response plans in place and can demonstrate their ability to respond to security incidents effectively.
In conclusion, evaluating a cloud service provider’s security measures is essential for maintaining a robust security posture in the cloud. Organizations should look for cloud service providers with relevant certifications, compliance with industry-specific regulations, and transparency about their security controls and practices. By choosing a cloud service provider with robust security measures, organizations can be confident that their digital assets are being protected effectively in the cloud.

Best Practices for Securing Data in the Cloud
As more organizations adopt cloud computing, securing data in the cloud has become a critical priority. Cloud environments offer numerous benefits, including scalability, flexibility, and cost savings. However, they also introduce new security challenges that organizations must address to protect their digital assets. In this article, we will discuss best practices for securing data in the cloud, including implementing strong access controls, using encryption, and regularly backing up data. We will also discuss the importance of data loss prevention and incident response planning.
Implementing strong access controls is essential for securing data in the cloud. Access controls refer to the mechanisms that regulate who can access what data and under what circumstances. By implementing robust access controls, organizations can prevent unauthorized access to their data and reduce the risk of data breaches. Access controls can include measures such as multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, and access control lists. Organizations should also consider implementing principles of least privilege, which means granting access only to the minimum level necessary for users to perform their job functions.
Using encryption is another critical best practice for securing data in the cloud. Encryption is the process of converting plain text into cipher text, which is unreadable without the decryption key. By encrypting data, organizations can protect it from unauthorized access, even if the data is intercepted or accessed without authorization. Organizations should consider using encryption for both data at rest and data in transit. Data at rest refers to data that is stored in the cloud, while data in transit refers to data that is being transferred between the cloud and other locations.
Regularly backing up data is also essential for securing data in the cloud. Data backups provide a critical safety net in the event of data loss or corruption. Organizations should consider implementing a regular backup schedule, with backups stored in a secure location separate from the primary data store. Organizations should also consider implementing data loss prevention measures, such as monitoring for unusual data access patterns or using data classification tools to identify sensitive data.
Incident response planning is also critical for securing data in the cloud. An incident response plan is a set of procedures that an organization follows in the event of a security incident, such as a data breach or cyber attack. An incident response plan should include procedures for identifying, containing, and remediating security incidents. Organizations should also consider implementing a communication plan to keep stakeholders informed of the incident and its impact.
In conclusion, securing data in the cloud requires a multi-faceted approach that includes implementing strong access controls, using encryption, regularly backing up data, and implementing incident response planning. By following these best practices, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents in the cloud. It is essential to remember that cloud security is a shared responsibility between the cloud service provider and the customer. By working together, organizations can ensure that their digital assets are protected in the cloud.
The Role of Threat Intelligence in Cloud Security
As cloud computing continues to grow in popularity, so do the associated security challenges. One critical aspect of cloud security is threat intelligence, which involves gathering and analyzing data on potential security threats to prevent or mitigate cyber attacks. In this article, we will discuss how threat intelligence can help organizations stay ahead of emerging threats and vulnerabilities in the cloud, as well as the benefits of sharing threat intelligence within communities and the role of threat intelligence platforms.
Threat intelligence is essential for organizations operating in the cloud because it enables them to proactively identify and respond to security threats. By collecting and analyzing data on potential threats, organizations can gain insights into the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by cybercriminals. This information can then be used to develop effective security strategies and countermeasures to protect against these threats. Threat intelligence can also help organizations prioritize their security efforts by identifying the most significant threats and focusing their resources on addressing them.
Sharing threat intelligence within communities is another critical aspect of cloud security. By sharing threat intelligence, organizations can benefit from the collective knowledge and experience of the community, enabling them to identify and respond to threats more quickly and effectively. Threat intelligence sharing can take many forms, including information sharing platforms, industry groups, and government-sponsored initiatives. By participating in these communities, organizations can stay up-to-date on the latest threats and vulnerabilities and collaborate with other organizations to develop effective security strategies.
Threat intelligence platforms are specialized software solutions that help organizations collect, analyze, and share threat intelligence. These platforms can automate the process of collecting and analyzing data from various sources, such as security information and event management (SIEM) systems, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and threat feeds. Threat intelligence platforms can also provide advanced analytics and machine learning capabilities to help organizations identify patterns and trends in the data. By using a threat intelligence platform, organizations can streamline their threat intelligence processes and improve their overall security posture.
In conclusion, threat intelligence is a critical component of cloud security, enabling organizations to proactively identify and respond to security threats. By sharing threat intelligence within communities and using threat intelligence platforms, organizations can benefit from the collective knowledge and experience of the community and improve their overall security posture. As the cloud security landscape continues to evolve, threat intelligence will become increasingly important in helping organizations stay ahead of emerging threats and vulnerabilities.

Emerging Trends and Future Perspectives in Cloud Security
As the cloud computing landscape continues to evolve, so do the associated security challenges. In this article, we will explore emerging trends and future perspectives in cloud security, including zero trust security models, serverless security, and the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for advanced threat detection. By understanding these trends, organizations can better prepare themselves for the future of cloud security and ensure the protection of their digital assets.
One of the most significant emerging trends in cloud security is the adoption of zero trust security models. Traditional security models are based on the idea of a trusted network perimeter, where everything inside the perimeter is considered safe. However, with the increasing use of cloud computing and remote work, this model is no longer effective. Zero trust security models assume that there is no trusted network perimeter and that all access requests must be verified and authenticated, regardless of where they originate. By implementing zero trust security models, organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches and ensure that only authorized users have access to their cloud resources.
Another emerging trend in cloud security is the rise of serverless security. Serverless computing is a model where the cloud provider manages the infrastructure, and the application runs in response to events. While serverless computing offers many benefits, such as reduced costs and increased scalability, it also introduces new security challenges. To address these challenges, organizations must implement security measures that are specifically designed for serverless environments. This includes using serverless security platforms, implementing runtime security controls, and monitoring application behavior for signs of suspicious activity.
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning is also becoming increasingly important in cloud security. These technologies can be used to automate threat detection and response, enabling organizations to identify and respond to security threats more quickly and effectively. By using machine learning algorithms to analyze large volumes of data, organizations can identify patterns and trends that would be difficult for humans to detect. This can help organizations stay ahead of emerging threats and vulnerabilities in the cloud and improve their overall security posture.
In conclusion, the future of cloud security is likely to be characterized by the adoption of zero trust security models, serverless security, and the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for advanced threat detection. By understanding these trends and implementing the necessary security measures, organizations can better protect their digital assets in the cloud and ensure their long-term security and success.

Conclusion: Navigating the Evolving Cloud Security Landscape
In conclusion, internet security and threat intelligence in the cloud are critical components of a robust cloud security strategy. As cloud computing continues to evolve, organizations must stay vigilant and adapt to emerging threats and vulnerabilities. By understanding the current cloud security landscape, implementing a robust cloud security strategy, evaluating cloud service providers’ security measures, and following best practices for securing data in the cloud, organizations can better protect their digital assets and ensure their long-term success.
One of the key takeaways from this article is the importance of threat intelligence in enhancing cloud security. By staying informed about emerging threats and vulnerabilities, organizations can proactively identify and mitigate potential security risks. Sharing threat intelligence within communities can also help organizations stay ahead of emerging threats and improve their overall security posture.
Another important takeaway is the role of artificial intelligence and machine learning in automating threat detection and response. By using these technologies to analyze large volumes of data, organizations can identify patterns and trends that would be difficult for humans to detect. This can help organizations stay ahead of emerging threats and improve their overall security posture.
As the cloud computing landscape continues to evolve, so do the associated security challenges. Organizations must stay vigilant and adapt to emerging trends and future perspectives in cloud security, such as zero trust security models, serverless security, and the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for advanced threat detection. By understanding these trends and implementing the necessary security measures, organizations can better protect their digital assets in the cloud and ensure their long-term success.
In conclusion, the ever-evolving cloud security landscape requires continuous learning and adaptation. By staying informed about emerging threats and vulnerabilities, implementing robust cloud security strategies, and leveraging the latest technologies, organizations can better protect their digital assets in the cloud and ensure their long-term success.