Getting Started with Azure Command-Line Tools
Azure PowerShell is a powerful command-line tool designed for managing Azure resources, offering an efficient way to automate tasks and streamline your cloud operations. This scripting environment enables users to interact with Azure services through a series of cmdlets, allowing for precise control and repeatable configurations. One of the key advantages of utilizing Azure PowerShell stems from its ability to automate complex processes, which reduces the risk of human error, increases consistency, and significantly cuts down on the time needed for routine administrative work. This capability is invaluable for environments where speed and reliability are paramount. The benefits include the ability to perform batch operations, easily manage multiple resources, and create reproducible deployments and infrastructure configurations, and so the need to install windows azure powershell becomes a critical step to begin working with these powerful capabilities. Through simple, text-based commands, users can achieve granular control over their Azure environment. This introduces the upcoming need to understand the procedures needed to install windows azure powershell, which will lead naturally into the next topic.
The use of command-line tools, such as Azure PowerShell, provides a departure from traditional graphical user interfaces, offering a more direct and programmable interaction with the Azure cloud platform. This approach facilitates the creation of automated workflows and scripts, making it possible to manage complex deployments without manual intervention. Furthermore, by learning to install windows azure powershell, users unlock the ability to version control their infrastructure configurations, using PowerShell scripts as reusable building blocks. This capability ensures repeatability, making it easier to manage and audit changes to your Azure environment. This not only improves overall management efficiency but also promotes a higher level of operational consistency. The command line’s inherently more concise and precise nature facilitates the creation of complex configurations that can be easily version controlled and replicated across different environments. As we proceed, we will delve into the core process required to install windows azure powershell, ensuring you have the necessary setup to maximize these advantages.
How to Download and Install Azure PowerShell Modules
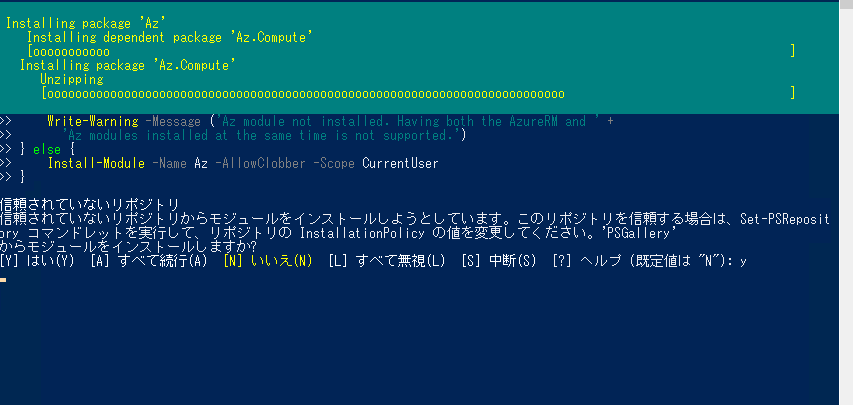
To effectively manage Azure resources, installing the Azure PowerShell modules is the crucial first step. Several methods exist for installing windows azure powershell, each offering varying levels of control and convenience. The most straightforward approach leverages the PowerShell Gallery, a centralized repository for PowerShell modules. Open PowerShell as an administrator and execute the command `Install-Module -Name Az`. This command will download and install the AzureAz module, containing a comprehensive set of cmdlets for interacting with Azure services. The process might prompt for confirmation; simply agree to proceed. Successful installation will be indicated by a completion message. Remember, a reliable internet connection is essential during this phase to ensure seamless download and installation of the necessary files. Regularly checking for updates is recommended to leverage the latest features and improvements. Consider the `Install-Module` command a cornerstone of successful Azure PowerShell usage.
Alternatively, for users requiring more granular control, manual installation from the Microsoft Download Center is an option. This method involves downloading the module package directly and then using PowerShell to install it. This approach provides more control, allowing users to select specific versions or components of the module. However, it requires navigating the Microsoft Download Center, identifying the appropriate package, and executing an install command. This approach is less convenient and is generally recommended for advanced users or troubleshooting scenarios. When considering manual download and install windows azure powershell, ensure you download from a trusted source to avoid malicious software. Careful verification of the downloaded file integrity is also highly recommended before execution. This method requires a deeper understanding of PowerShell’s functionality and file management.
Before initiating the installation of windows azure powershell, verifying system prerequisites is essential. Ensure the system meets the minimum requirements for PowerShell and .NET Framework versions. Outdated versions might lead to compatibility issues, hindering a smooth installation process. The specific requirements can be found in the official Microsoft documentation. Checking these requirements proactively prevents potential installation errors and ensures optimal functionality. For example, a certain PowerShell version might be needed to ensure complete compatibility with the Az module, which contains vital cmdlets used extensively throughout the Azure PowerShell experience. Therefore, it’s paramount to confirm that all dependencies are met to achieve a successful installation and flawless subsequent usage of Azure PowerShell. Addressing prerequisites proactively saves time and prevents unnecessary troubleshooting down the line, paving the way for efficient Azure resource management. Moreover, this step guarantees compatibility and stability, preventing potential conflicts that could arise from version mismatches.
Verifying a Successful Azure PowerShell Installation
After completing the install windows azure powershell process, it’s crucial to verify the successful installation of the Azure PowerShell modules. This ensures that the necessary components are correctly configured and accessible within your PowerShell environment. Begin by opening a new PowerShell session. One effective method to check for the presence of the Azure PowerShell modules is to use the `Get-Module` cmdlet. This command lists all installed PowerShell modules, allowing for a quick review of whether the Azure modules, such as `Az`, are present. For instance, executing `Get-Module -ListAvailable Az` will display available Azure modules and their versions. To check installed modules, use `Get-Module -Name Az*`. The asterisk acts as a wildcard, listing all modules beginning with “Az”. The output should clearly indicate the Azure PowerShell modules, along with their respective versions, confirming a successful install windows azure powershell.
If the Azure modules are not listed, several troubleshooting steps can be taken. First, ensure that the PowerShell execution policy allows running scripts. Use `Get-ExecutionPolicy` to check and `Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned` (or a less restrictive policy if needed) to adjust if necessary. This addresses potential permission issues that might prevent the modules from being recognized. Another common issue relates to the PowerShell module path. The path needs to correctly point to the directory where the Azure PowerShell modules were installed. This information can be found in the installation logs or documentation if further investigation is required. It is recommended to restart the PowerShell session after any changes to the execution policy or module paths to ensure changes take effect. It’s also important to consider the version of PowerShell being used, as compatibility issues can arise if the Azure modules are not supported by the current PowerShell environment. Always check the system requirements for install windows azure powershell.
Beyond checking module presence, validating functionality is equally important. A simple test involves attempting a basic Azure command, like `Connect-AzAccount`. A successful connection signifies that the installation was successful and the environment is correctly configured to interact with your Azure subscription. If the command results in errors, the nature of the error message will often provide clues to identify the root cause. Common error messages could point to missing dependencies, authentication problems, or network connectivity issues. Examining error messages carefully and consulting the Azure PowerShell documentation will be beneficial in resolving such problems. Remember, a fully functioning install windows azure powershell should allow for seamless connection and interaction with your Azure resources. Addressing these checks ensures both effective and successful utilization of the installed modules.
Connecting to Your Azure Account
After successfully completing the installation and verification of the Azure PowerShell modules, the next crucial step involves connecting to your Azure subscription. This process requires authentication, and Azure PowerShell offers several methods to suit various scenarios. The most common approach for individual users is the device code login, which prompts you to open a browser and enter a unique code provided by the PowerShell console to authenticate your access to Azure. To initiate this, you would typically use the command Connect-AzAccount. Upon execution, you are guided through a secure browser authentication process where you log in with your Azure credentials. Alternatively, in automated environments or for server applications, using a service principal or managed identities is highly recommended for enhanced security and ease of management. A service principal is an application within Azure Active Directory and its credentials allow PowerShell scripts to authenticate without requiring user interaction. For such connections you may use the command Connect-AzAccount -ServicePrincipal -Credential $cred where $cred stores the client secret and application id. Managed identities eliminate the need to manage credentials by providing identities for Azure resources that automatically authenticate against services that support Azure AD authentication. The correct method for accessing your Azure account may be influenced by the scenario. When running a quick command on your machine, device code login is the most straightforward method. For production environments, a service principal or managed identities would provide a more secure and manageable long-term solution after you install windows azure powershell.
It’s essential to choose an authentication method that aligns with both security best practices and the specific requirements of your project. Using a service principal, you need to obtain the required application ID, client secret, and tenant ID from the Azure portal, which is necessary for connecting via the Connect-AzAccount cmdlet using the -ServicePrincipal parameter. For managed identities, Azure automatically provides the authentication necessary for the resource to connect to other Azure services, simplifying the process significantly when dealing with Azure virtual machines or other services that support managed identities. Regardless of the chosen method, the commands are essential after you install windows azure powershell. Furthermore, after a successful connection, you can verify your connection using the command Get-AzContext which will display the active Azure subscription and account information. This also confirms that the authentication process has been successful. When you install windows azure powershell, remember to pay careful attention to user authentication methods. Understanding these nuances allows for a more secure and efficient interaction with your Azure resources directly through PowerShell. This crucial step ensures that all subsequent operations are performed under your authenticated session. This is very important for your workflow.
Exploring Basic Azure PowerShell Commands
Once you have successfully authenticated with your Azure account, the real power of Azure PowerShell begins to unfold. This section introduces practical commands to interact with Azure resources, showcasing the efficiency and automation capabilities that command-line tools provide. One of the fundamental operations you can perform after you install windows azure powershell is retrieving information about your existing Azure resources. For example, to list all resource groups within your subscription, you would use the command Get-AzResourceGroup. This command, when executed in your PowerShell session, will output a list of your resource groups, displaying details such as their names and locations. It’s a simple yet fundamental step in getting acquainted with your Azure environment. To create a new resource group, you would use the command New-AzResourceGroup -Name "YourResourceGroupName" -Location "YourAzureRegion" replacing `”YourResourceGroupName”` with your desired name and `”YourAzureRegion”` with the Azure region where you intend to create the group. This command shows how straightforward it is to manage resources through PowerShell. Further, interacting with specific services is made easy with dedicated cmdlets. For example, to view a list of all virtual machines within a resource group, you might use Get-AzVM -ResourceGroupName "YourResourceGroupName". Remember to replace `”YourResourceGroupName”` with the appropriate name. These examples provide a starting point for automating common management tasks with Azure. The capability to install windows azure powershell and then execute these commands demonstrates the agility and efficiency the technology provides, allowing for complex operations to be automated with relative ease.
These basic examples illustrate the simplicity of working with Azure PowerShell. Beyond merely listing resources, you can also use commands to create, modify, or delete resources. For example, to create a new Azure storage account, you can utilize a command similar to New-AzStorageAccount -ResourceGroupName "YourResourceGroupName" -Name "YourStorageAccountName" -SkuName "Standard_LRS" -Location "YourAzureRegion", where `”YourResourceGroupName”`, `”YourStorageAccountName”` and `”YourAzureRegion”` should be replaced by your specific needs. This not only shows how to install windows azure powershell but also illustrates that it’s capable of creating resources. The `-SkuName` parameter specifies the replication type and the `-Location` defines the data center. Working through examples such as this, you’ll begin to grasp the breadth and power of Azure PowerShell to automate tasks. You can also utilize pipelines to chain commands together, performing complex sequences of actions with a single line. For instance, you could pipe the output of Get-AzVM into another command to filter the virtual machines by a specific property, enhancing the flexibility of the command-line tool. This approach allows for significant time savings when it comes to management and deployment activities, as well as facilitating detailed management of your cloud assets.
By exploring these commands, you’re building a solid foundation for managing your Azure infrastructure effectively. The use of commands to interact with Azure resources is crucial and begins to showcase the flexibility of the tool. Remember that these examples are just the beginning; as you become more proficient, you’ll find that Azure PowerShell allows you to manage every aspect of your Azure environment, from virtual networks to web apps, all through a consistent interface. With the ability to script complex operations and automate workflows, you will come to realize the full potential after you install windows azure powershell. Moreover, as you progress you will become better at managing the cloud resources using PowerShell, improving your ability to operate and manage cloud environments with precision and efficiency. It’s essential to familiarize yourself with the documentation and available cmdlets to unlock the full capabilities of Azure PowerShell, as there are hundreds more commands at your disposal to master.
Tips for Effective Azure PowerShell Usage
To maximize efficiency when working with Azure PowerShell, several advanced techniques can significantly enhance your experience. Mastering these practices not only speeds up your tasks but also makes your scripts more robust and maintainable. One crucial aspect is the strategic use of variables. Instead of hardcoding values, assigning them to variables enables dynamic script behavior and easier updates. This is especially valuable when scripting deployments across different environments or resource groups. Furthermore, leveraging the power of PowerShell pipelines allows you to chain commands together, passing the output of one command as the input to the next. This streamlined approach reduces the need for intermediate variables and complex nested loops, resulting in cleaner and more concise code. To effectively install windows azure powershell you should also use loops and conditional statements for performing repetitive actions or managing resources based on certain criteria, automating complex processes. Moreover, understanding how to effectively manage command output is critical. Employing techniques like `Select-Object` to filter properties or `Export-Csv` to store data in a readable format enhances the usability of your scripts, allowing you to easily extract and analyze crucial information related to your Azure resources. Another important technique is to understand the differences between cmdlets and how you can use them to optimize your work.
For enhanced performance and script clarity when you install windows azure powershell, familiarize yourself with the common cmdlets that pertain to each Azure service and the specific parameters they support. You can learn to create functions to encapsulate reusable blocks of code. This makes your scripts more organized and easier to modify and understand. Avoid unnecessary retrieval of large datasets. Always use filters in `Get-*` commands to retrieve specific information related to your Azure resources. For instance, when retrieving Virtual Machines, specify the resource group and the VM name, rather than retrieving all VMs and filtering them locally. This approach greatly reduces network traffic and speeds up the process. Also, error handling is essential. Incorporate `try-catch` blocks to handle unexpected errors in a controlled manner, improving the resilience of your scripts. You should also be mindful of the output formats. Azure PowerShell returns objects, but you can customize the output to JSON, CSV, or XML by using `ConvertTo-*` cmdlets as needed. This enables better integration with other systems and tools. By implementing these best practices, your Azure PowerShell experience will be significantly improved, resulting in a more efficient, organized and robust management of your cloud resources.
Troubleshooting Common Azure PowerShell Errors
Encountering errors while using Azure PowerShell is a common experience, but with a systematic approach, most issues can be resolved efficiently. A frequent problem stems from authentication failures, often indicated by messages related to invalid credentials or authorization issues. When this occurs, it’s important to double-check the authentication method used, ensuring it aligns with the environment and the type of account being accessed. For device code login, verify the code is entered correctly and within the allotted time. When using service principals, confirm that the credentials (client ID, client secret, or certificate) are correctly configured. Another common issue relates to command failures, which can manifest due to syntax errors or incorrect parameter usage. Refer to the official documentation to cross-reference cmdlet names and their associated parameters. Error messages will frequently provide hints about the type of mistake, for instance, an invalid resource name or unavailable location. Also, the process to install windows azure powershell requires checking for correct module installation and version compatibility. This means that a mismatch between the modules and the environment can result in unexpected failures. Ensuring that the module path is properly configured allows PowerShell to load the necessary Azure modules. It is important to verify the module paths and permissions if the issue persists.
Network connectivity is another source of Azure PowerShell errors, especially when working in constrained network environments or when Azure services are temporarily unavailable. If there are connection timeouts, examine your network configuration, including firewalls and proxy settings. Sometimes the error will result from an unstable or unreliable internet connection. Additionally, ensure your network configuration permits communication with the necessary Azure endpoints. Often, PowerShell errors result from simple typos or case-sensitive input mistakes, especially for resource names and parameter values. Make sure to carefully check for any inaccuracies. Furthermore, it’s important to keep the Azure PowerShell modules updated since outdated versions may not be compatible with the latest Azure service APIs, leading to execution issues. If none of these are the cause, consider a thorough review of the error details by using verbose mode, with the -Verbose parameter, which can offer more insight into underlying issues. When you encounter an error, begin by attempting to pinpoint if the problem resides within authentication, command syntax, networking or module versions. The ability to install windows azure powershell successfully is also affected by the state of your network.
Finally, permission issues in your Azure account may also prevent certain commands from executing successfully. Verify the user account you’re using has the required Azure roles and permissions to perform the operations that you are attempting. For example, if you’re trying to create a resource group or change settings of a specific resource, it is essential to have the ‘Contributor’ role or a more granular role on the related resources or management groups. Remember to review the official documentation, which often presents troubleshooting guides. If all else fails, searching the error message on the web or checking the Azure documentation or forums can provide valuable solutions from other users, developers and experts. Always remember that troubleshooting is a methodical process, carefully review the steps and test after each step so that you install windows azure powershell and have a successful and productive experience.
Keeping Azure PowerShell Up-to-Date
Maintaining the latest versions of Azure PowerShell modules is crucial for accessing the newest features, security patches, and bug fixes. Regular updates ensure optimal performance and compatibility with Azure services. To update, use the command Update-Module -Name Az. This command will check for newer versions of all installed Az modules and install them automatically. Remember to run this command periodically, perhaps as part of a regular maintenance schedule. Checking for updates before undertaking significant Azure management tasks is also recommended. Users installing Windows Azure PowerShell for the first time should also run this command to ensure they have the most current version. Consistent updates are key to a smoothly functioning and secure Azure management environment. The process for install windows azure powershell and its subsequent updating is straightforward and contributes to a robust and reliable Azure experience. This simple yet vital step should not be overlooked.
Before updating, it’s advisable to back up any important scripts or configurations that utilize Azure PowerShell. While updates are generally smooth, unforeseen issues can occasionally arise. Having a backup readily available mitigates potential disruptions to your workflow. After running the update command, it’s beneficial to verify the updated versions by using the Get-Module -ListAvailable -Name Az command. This will display a list of available Azure modules and their versions, allowing confirmation of successful updates. For users who are installing Windows Azure PowerShell for the first time, this step provides immediate validation of a successful installation. By following these steps consistently, users can ensure that their Azure PowerShell environment remains current and functional, improving overall efficiency and reducing the risk of encountering outdated commandlets.
Occasionally, updates might require specific prerequisites, such as a newer version of PowerShell itself or the .NET Framework. Azure will usually notify users about such dependencies during the update process, providing guidance on how to address them. Addressing any prerequisites before initiating the update ensures a seamless upgrade. Remember, a proactive approach to updating your Azure PowerShell modules is vital for ensuring that you are leveraging the latest improvements and that your management tasks benefit from enhanced stability, security, and efficiency. For optimal performance and security in managing your Azure resources, regular updates should be part of any regular maintenance routine; this is especially critical for users of install windows azure powershell. Neglecting updates can create vulnerabilities and hinder access to the latest Azure capabilities.