Why Choose Docker? Unleash the Power of Containerization
Docker simplifies application deployment and management. It uses containerization technology. This ensures consistent application behavior across different environments, from development to production. This consistency reduces deployment headaches. Imagine effortlessly moving your application between your laptop, a test server, and the cloud. Docker makes this a reality. Install Docker to experience this seamless portability. The benefits extend beyond simplified deployment. Docker enhances resource efficiency. Containers share the host operating system’s kernel. This reduces overhead compared to virtual machines. This leads to faster application startup times and reduced resource consumption. Improved collaboration is another key advantage. Developers can easily share their work. They can package applications and dependencies within containers. This eliminates the “it works on my machine” problem. Docker fosters a consistent and reproducible development environment for everyone involved. Install Docker today to improve team workflows and streamline application development. The consistent environment ensures predictable performance. This reduces debugging time and increases productivity. The result? Faster development cycles and happier developers.
Docker’s efficiency extends to improved resource utilization. Containers share the host operating system’s kernel. This minimizes the overhead associated with virtual machines. Applications start faster and consume fewer resources. This is crucial for cost-effective cloud deployments. Docker’s lightweight nature translates directly to lower infrastructure costs. Install Docker to unlock a streamlined workflow. It facilitates collaboration and reduces friction between developers and operations teams. The process of packaging and deploying applications becomes significantly simpler. This leads to faster delivery cycles. Install Docker and experience these benefits firsthand. You’ll quickly appreciate the impact on your productivity and efficiency. Docker’s versatility allows you to deploy applications to various platforms.
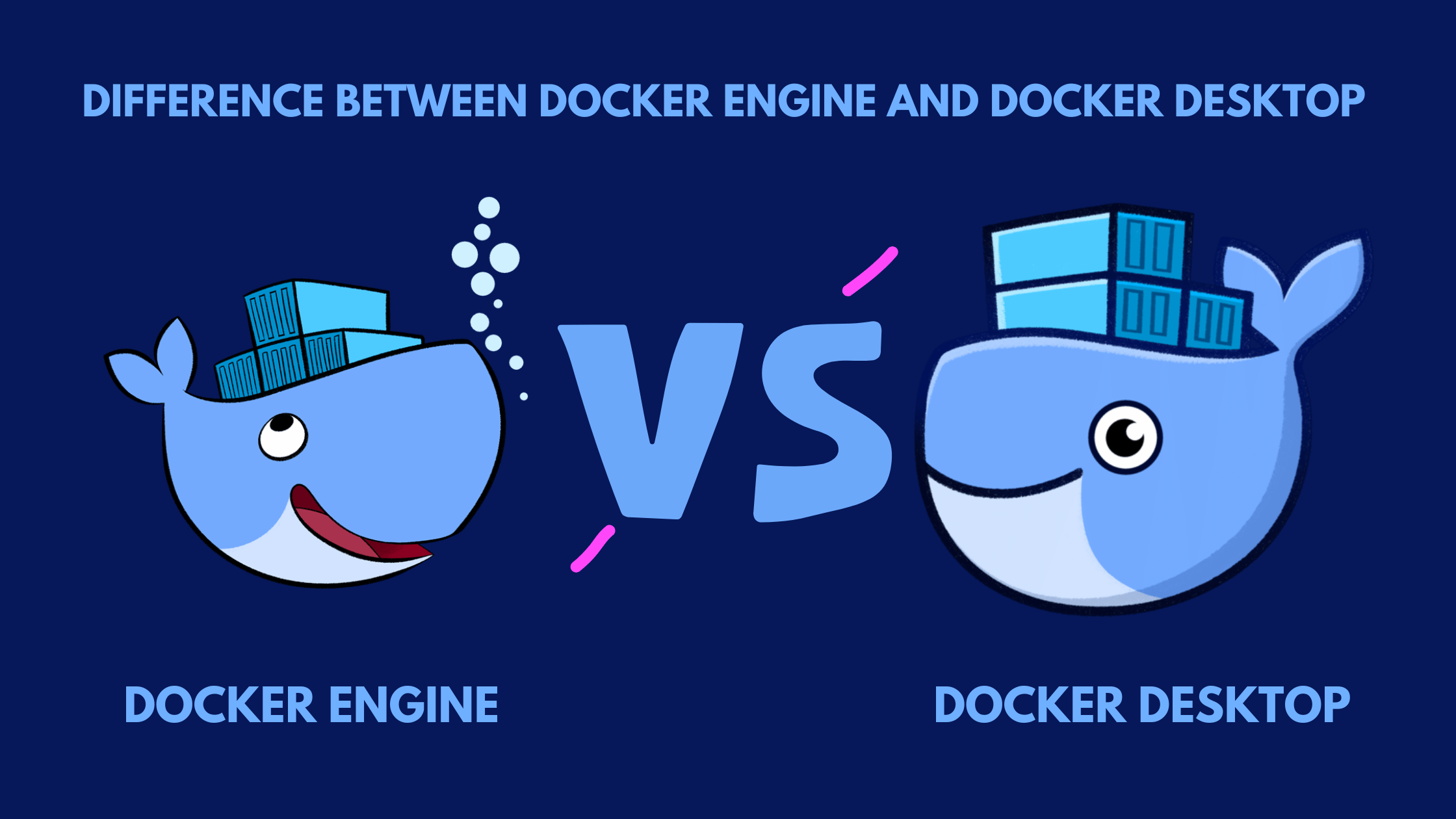
Choosing the right Docker edition is crucial for a smooth experience. Docker Desktop provides a user-friendly interface suitable for beginners. It integrates seamlessly with various development tools. The Docker Engine offers more advanced customization options for experienced users. It’s command-line-focused. The choice depends on your technical skills and project requirements. Regardless of your chosen edition, the installation process is relatively straightforward. Comprehensive documentation and community support are readily available to assist you. Install Docker and begin your journey into the world of containerization. The efficiency and consistency that Docker provides are invaluable for developers and operations teams. Docker’s benefits extend to all phases of the software development lifecycle. From development to testing and deployment, Docker streamlines every step.
Choosing the Right Docker Edition: Desktop vs. Engine
Docker offers two primary editions: Docker Desktop and Docker Engine. Docker Desktop provides a user-friendly interface, ideal for beginners. It bundles essential tools, simplifying the install docker process. Conversely, Docker Engine is a command-line-focused option offering greater customization and control. Experienced users often prefer this approach for its flexibility. The choice depends on technical expertise and project requirements. Beginners should generally opt for Docker Desktop for its ease of use and integrated tools. Successfully installing Docker, whether Desktop or Engine, hinges on selecting the appropriate edition for your skill level.
Downloading Docker Desktop is straightforward. Visit the official Docker website. Download the installer appropriate for your operating system: Windows, macOS, or Linux. Installation instructions are provided on the website. For Docker Engine, the process involves downloading the appropriate package from the Docker website, based on the specific OS. Then users follow the command-line instructions provided in the download documentation to install dockert. Remember to check system requirements before proceeding with the install dockert process for either edition. Understanding these differences enables you to choose the best option, streamlining the install docker process.
Regardless of your chosen edition, successful installation of Docker is crucial. Both options provide robust features. Docker Desktop offers a simplified user experience. It’s the perfect starting point for those new to containerization. Conversely, Docker Engine offers experienced users the granular control they need. It’s a powerful command-line tool allowing for advanced configurations. This careful selection ensures a smooth install docker experience. Choosing the right version sets the foundation for effective containerization. Therefore, carefully consider your technical skills and project requirements before deciding whether to install Docker Desktop or Engine. Following the respective installation guides will enable a smooth setup process.
How to Install Docker: A Step-by-Step Guide
This section details how to install Docker, covering Windows, macOS, and Linux. Follow the instructions carefully for your operating system. Remember, successfully installing Docker opens the door to a world of containerized applications. To install Docker, you must first download the installer relevant to your OS. The installation process is straightforward, but close attention to detail will ensure a smooth experience. Users may find that troubleshooting some minor issues is necessary to successfully install Docker.
Windows: Download the Docker Desktop installer from the official Docker website. Run the installer, following the on-screen prompts. You might need administrator privileges. After installation, restart your computer to ensure all changes take effect. Verify the installation by opening your terminal and typing `docker version`. If you encounter errors, check the Docker documentation for troubleshooting tips. Remember, a successful install dockert will allow you to start using Docker applications and containers. During the installation process, you may be prompted to enable the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). This step enhances Docker’s capabilities on Windows. This improves compatibility and performance of Docker for Windows users.
macOS: Download the Docker Desktop installer from the official website. Double-click the installer package and follow the instructions. You might need to allow Docker to access certain system components. After installation, open your terminal and type `docker version` to verify the install dockert process. If you encounter any issues, consult the official Docker documentation for macOS. Docker Desktop for Mac provides a streamlined installation and management experience. It offers a user-friendly interface for managing Docker containers and images. Successfully installing Docker will transform how you manage and deploy applications. Troubleshooting might involve checking your system’s permissions or ensuring that the necessary system components are enabled.
Linux: The install dockert process on Linux varies slightly based on your distribution (Ubuntu, Fedora, CentOS, etc.). Consult the official Docker documentation for your specific Linux distribution. Generally, this involves updating your package manager, adding the Docker repository, and then installing the `docker-ce` package. Post-installation, always verify by running `docker version` in your terminal. Common issues might involve needing to add your user to the `docker` group to avoid permission errors. This step is critical for granting your user the necessary permissions to interact with Docker. This ensures Docker runs correctly without facing permission-related problems. Remember, a properly completed install dockert operation is vital for seamless functionality.
Verifying Your Docker Installation: A Quick Test
After installing Docker, a crucial step is verifying the installation. This ensures Docker is functioning correctly and ready for use. The simplest method involves using the command line. Open your terminal or command prompt. For both Docker Desktop and Docker Engine installations, the primary command to use is `docker version`. This command displays information about the Docker client and server versions. Successful installation shows version numbers for both the client and the server. If you receive an error message, it indicates a problem with the install dockert process. Refer to the troubleshooting section for solutions to common installation issues. Another helpful command is `docker run hello-world`. This command downloads a test image and runs it in a container. A successful execution shows a “Hello from Docker!” message. This confirms that Docker is correctly set up and containers can be run. The absence of this message signals a problem with your install dockert procedure, possibly related to network connectivity or Docker daemon issues.
Troubleshooting installation problems often involves checking several key areas. First, ensure the Docker daemon is running. The daemon is the background process that manages Docker containers. On some systems, it might need to be started manually after installation. Check the Docker documentation specific to your operating system for instructions. Network connectivity is also critical for Docker to function correctly. Ensure your system has an active internet connection, as Docker often downloads images from online repositories. Firewall settings can also interfere with Docker’s operations. Temporarily disabling the firewall or configuring it to allow Docker through can resolve connectivity problems. Finally, some users encounter permission errors, particularly on Linux systems. These errors might necessitate adjusting user permissions or running Docker commands with elevated privileges, using `sudo` for instance. Remember to consult the official Docker documentation for your specific operating system and situation. It contains detailed troubleshooting guides that will help you through these challenges.
Successfully installing Docker opens up a world of possibilities for streamlined application deployment and management. If `docker version` reports version numbers and `docker run hello-world` displays the expected message, your install dockert process was successful. You are now ready to explore the power of containers. However, if you encounter problems, carefully review the error messages and consult the comprehensive troubleshooting resources available online. Remember to check the Docker daemon’s status, network connectivity, firewall settings, and user permissions. Persistent issues may require a complete reinstall of Docker, but the initial verification steps offer quick and effective diagnostics. Following these steps ensures a smoother transition into the world of Docker containerization.
Setting Up Your First Docker Container: A Hands-On Experience
This section provides a practical introduction to using Docker after a successful install dockert. The process will use a readily available image, “hello-world,” to demonstrate container creation and execution. This simple image requires minimal resources and serves as an ideal starting point for beginners learning how to use Docker. To begin, open your terminal or command prompt. Then, type the command `docker run hello-world`. This command downloads the “hello-world” image from Docker Hub, if it’s not already present, and then runs it within a new container. Observe the output; it will display a message confirming the successful execution of the container. This confirms Docker’s correct installation and functionality. The process is straightforward. After completing this step, you will have successfully run your first Docker container.
Understanding the `docker run` command is crucial. It’s a fundamental Docker command used for running images. The command automatically downloads the image if it is not already locally available. Once downloaded, it creates and starts a new container from that image, executes the commands inside the container, and then stops the container. The “hello-world” image is designed for this purpose. Its simplicity makes it ideal for verifying a correct install dockert and introducing basic Docker concepts. After running “hello-world,” you can explore other readily available Docker images using the `docker run` command and their respective image names. This is a vital step in learning to use Docker effectively.
After running your first container, consider exploring additional images available on Docker Hub. Docker Hub is a vast repository containing thousands of pre-built images. You can search for and pull images relevant to your projects. Remember to always check the image’s documentation to understand its usage and potential dependencies. This hands-on exercise enhances understanding and builds confidence in using Docker after successfully installing dockert. Successfully navigating this process will provide a strong foundation for future Docker projects. Experimentation is key to mastering the process.
Managing Docker Images and Containers: Essential Commands
After successfully installing Docker, managing images and containers is crucial. Docker images are read-only templates, while containers are running instances of those images. Efficient management improves workflow and resource utilization. Users who successfully install Docker often find this stage straightforward.
Pulling images is the first step. Use the command `docker pull
Running containers involves starting an instance of a pulled image. The command `docker run
Troubleshooting Common Docker Installation Problems
Successfully installing Docker is crucial for containerization. However, various issues can arise during the install Docker process. Permission errors frequently occur, especially on Linux systems. These errors often manifest as messages indicating insufficient privileges to perform certain actions. To resolve this, users should use the `sudo` command before executing Docker commands or add the current user to the `docker` group. Restarting the system after modifying group memberships is typically necessary for changes to take effect. Remember to verify your install Docker attempt was successful after performing these steps.
Network connectivity problems can also hinder the install Docker process. Docker relies on network access to download images and communicate with remote services. Firewall configurations or network restrictions may interfere with this process. Check firewall rules to ensure Docker’s required ports are open. Verify network connectivity by pinging Docker Hub or other relevant domains. If a proxy server is used, ensure its configuration is correct for Docker to function correctly. Resolving network issues ensures a smooth install Docker experience.
Conflicts with other software are another potential obstacle. Antivirus software or other applications that manage network connections or system processes might clash with Docker. Temporarily disabling such software during the installation process can help identify and resolve conflicts. Review the documentation for both Docker and any potentially conflicting software for compatibility guidance. Examine the system logs for errors indicating resource conflicts. Careful planning and troubleshooting minimize conflicts during the install Docker process. Users should address any such issues diligently to complete installation. Addressing these issues properly leads to a successful install Docker and smooth operation.
Optimizing Docker for Performance
Once you successfully install Docker, consider optimizing its performance for smoother operations. Resource allocation significantly impacts Docker’s speed and efficiency. Docker containers, by default, share the host system’s resources. However, you can customize this. Adjusting CPU and memory limits for individual containers prevents resource contention and ensures applications perform optimally. For instance, a resource-intensive application might require more CPU cores and RAM than a less demanding one. This careful allocation prevents performance bottlenecks and improves overall system responsiveness. Effective resource management is crucial for optimal Docker performance, particularly when running multiple containers simultaneously. Understanding and adjusting these settings is key to maximizing Docker’s capabilities.
Another aspect of performance optimization involves Docker’s storage configuration. The choice of storage driver affects I/O speed, impacting container startup times and data access. Docker offers various storage drivers, each with different characteristics. Consider using a fast storage driver like Overlay2 or a volume plugin tailored for your specific environment. Properly configuring storage and utilizing efficient drivers directly translates to faster operations. Investigating and choosing the most suitable driver based on your system’s setup and workload is vital for maximizing speed. This proactive approach prevents slowdowns and enhances the overall Docker experience. Remember, a well-configured storage system improves both the speed and reliability of your Docker setup. Choosing the correct driver for your needs will have a huge impact on your performance.
Regularly monitoring Docker’s resource usage provides valuable insights. Tools like Docker Stats or similar monitoring applications provide real-time data on CPU, memory, and I/O usage. This allows users to identify potential bottlenecks and adjust resource allocations accordingly. Proactive monitoring and fine-tuning are crucial for maintaining optimal Docker performance, particularly in production environments. By actively monitoring resource usage, users can promptly address any performance issues, ensuring smooth and efficient operation. This proactive approach to maintenance is an essential aspect of successfully managing and optimizing a Docker environment. Learning to use these monitoring tools will help users quickly troubleshoot their Docker setup, allowing for faster resolution and improved performance. Efficient resource management helps to optimize your Docker installation and ensure a smooth experience.