What is Compute Infrastructure on Demand and Why Should You Care?
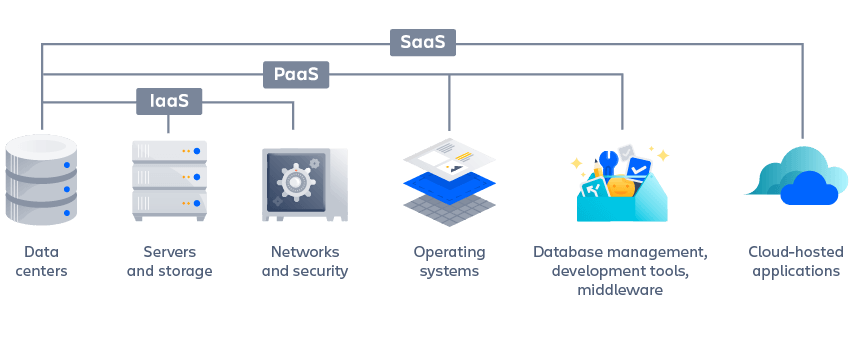
Compute infrastructure on demand, also known as scalable computing resources or cloud-based infrastructure, represents a fundamental shift in how organizations access and utilize computing power. This model, a cornerstone of infrastructure as a service in cloud computing, provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, eliminating the need for businesses to invest in and maintain their own physical data centers. Users gain access to servers, storage, and networking components on a pay-as-you-go basis, offering unprecedented flexibility and control. The core of infrastructure as a service in cloud computing is delivering on-demand access to computing resources, allowing businesses to adapt swiftly to evolving needs.
The advantages of leveraging infrastructure as a service in cloud computing are manifold. Scalability is a primary benefit; businesses can easily scale their computing resources up or down based on demand, ensuring they have the capacity needed to handle peak workloads without incurring unnecessary costs during quieter periods. Cost-effectiveness is another compelling factor. By only paying for the resources they consume, organizations can significantly reduce capital expenditures and operational expenses associated with traditional IT infrastructure. This scalability ensures that businesses can handle unexpected surges in traffic or data processing requirements without experiencing performance bottlenecks. Furthermore, infrastructure as a service in cloud computing promotes agility by enabling rapid deployment and experimentation with new applications and services.
Flexibility is a key differentiator of infrastructure as a service in cloud computing. Organizations have the freedom to choose the operating systems, programming languages, and development tools that best suit their needs. This level of customization allows for greater innovation and faster time-to-market. The ability to provision and deprovision resources on demand allows companies to respond quickly to changing market conditions and customer demands. Moreover, infrastructure as a service in cloud computing often integrates seamlessly with other cloud services, providing a comprehensive and cohesive cloud ecosystem. Businesses gain access to a broad range of services, including databases, analytics tools, and artificial intelligence platforms, further enhancing their capabilities and accelerating their digital transformation. In essence, infrastructure as a service in cloud computing empowers businesses to focus on their core competencies while leaving the management of underlying infrastructure to the experts.
How to Build Your Application on a Virtualized Server Landscape
Building an application using infrastructure as a service in cloud computing offers unparalleled flexibility. The initial step involves selecting a suitable provider that aligns with your application’s requirements and budget. Numerous providers offer compute infrastructure on demand, each with varying features and pricing models. Once a provider is chosen, the next step is to select a virtual machine (VM) instance. This selection should be based on the application’s resource demands, considering factors such as CPU, memory, and storage.
After selecting a VM instance, configuring the operating system is crucial. Most providers offer a range of operating system images, including Linux distributions and Windows Server. Choose an operating system that is compatible with your application and that your team is familiar with. Following the OS configuration, deploying the application involves transferring the application code and dependencies to the virtualized server landscape. This can be achieved through various methods, such as secure file transfer protocol (SFTP) or version control systems like Git. Ensure that all necessary dependencies are installed and configured correctly.
The beauty of infrastructure as a service in cloud computing lies in its scalability. As your application’s user base grows, you can easily scale resources as needed. This involves increasing the size of your VM instance or adding more instances to handle the increased load. Auto-scaling features offered by most providers can automatically adjust resources based on predefined metrics, such as CPU utilization or network traffic. Monitoring your application’s performance is essential to identify bottlenecks and optimize resource allocation. Utilizing cloud-based monitoring tools can provide valuable insights into your application’s health and performance. This step-by-step approach allows you to harness the power of compute infrastructure on demand without being tied to specific vendor implementations, ensuring your application remains portable and scalable within the infrastructure as a service in cloud computing ecosystem.
Key Features to Consider When Choosing a Virtual Server Provider
Selecting the right infrastructure as a service in cloud computing provider is a critical decision that significantly impacts your application’s performance, security, and cost-effectiveness. Several key features should be carefully evaluated before making a choice. Pricing models are a primary consideration. Understand the different pricing structures offered, such as pay-as-you-go, reserved instances, or spot instances, and determine which model best aligns with your usage patterns and budget. Look for transparent pricing with no hidden fees. Security measures are non-negotiable. Verify that the provider has robust security protocols in place, including data encryption, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits. Compliance certifications, such as SOC 2, ISO 27001, and HIPAA, demonstrate a commitment to meeting industry standards for security and data privacy. Service Level Agreements (SLAs) define the provider’s commitment to uptime and performance. Review the SLA carefully to understand the guaranteed levels of service and the penalties for failing to meet those levels. Geographic availability is crucial for ensuring low latency and meeting data residency requirements. Choose a provider with data centers located in regions that are close to your users and that comply with relevant data privacy regulations. The types of virtual machines offered dictate the resources available to your applications. Consider the CPU, memory, storage, and network bandwidth options, and select instances that are appropriately sized for your workloads. Ensure the provider offers a variety of instance types to accommodate different application needs. Integration capabilities with other cloud services are essential for building a comprehensive cloud solution. Check whether the provider seamlessly integrates with other services, such as databases, storage, networking, and analytics. This can simplify your architecture and improve overall efficiency. The availability of comprehensive documentation, responsive technical support, and a vibrant community forum can greatly enhance your experience with the provider. Look for providers that offer multiple support channels and a wealth of resources to help you troubleshoot issues and optimize your infrastructure as a service in cloud computing. Finally, consider the provider’s reputation and track record. Read reviews, talk to other users, and assess the provider’s experience in delivering reliable and scalable cloud services. A provider with a strong reputation is more likely to provide a positive and successful experience with infrastructure as a service in cloud computing.
When assessing infrastructure as a service in cloud computing, it’s important to look at scalability and flexibility. Can the provider easily scale resources up or down based on demand? Does it offer the flexibility to customize virtual machine configurations to meet specific application requirements? A scalable and flexible infrastructure allows you to adapt to changing business needs without incurring unnecessary costs or downtime. Another important aspect is the ease of management. Does the provider offer a user-friendly console or API for managing your virtual machines and other resources? Are there tools available for monitoring resource utilization, tracking costs, and automating tasks? A well-managed infrastructure reduces operational overhead and allows you to focus on your core business. Consider the provider’s commitment to innovation. Does it regularly release new features and services? Is it actively involved in the open-source community? A provider that is committed to innovation is more likely to provide you with access to the latest technologies and capabilities. It’s also crucial to evaluate the provider’s disaster recovery and business continuity capabilities. Does it offer options for backing up your data and replicating your infrastructure to multiple regions? Does it have a well-defined disaster recovery plan in place? A robust disaster recovery strategy is essential for protecting your business from unforeseen events.
In summary, carefully evaluate these key features to select an infrastructure as a service in cloud computing provider that meets your specific needs and helps you achieve your business goals. Considering these aspects will lead to a more informed decision in choosing your infrastructure as a service in cloud computing.
Comparing Amazon EC2, Google Compute Engine, and Microsoft Azure VMs
When exploring infrastructure as a service in cloud computing, comparing the major players is essential. Amazon EC2, Google Compute Engine, and Microsoft Azure VMs represent the leading choices for organizations seeking scalable computing resources. Each offers a unique set of features, pricing models, and strengths. This comparison highlights key differences to aid in selecting the most suitable platform. This will help users to understand the infrastructure as a service in cloud computing market.
Amazon EC2 stands out for its maturity and extensive feature set. Its pricing is complex, offering various instance types and purchasing options like On-Demand, Reserved, and Spot Instances. This provides flexibility but can also be challenging to navigate. EC2 supports a wide range of operating systems and offers deep integration with other Amazon Web Services. It’s a robust solution for businesses already invested in the AWS ecosystem. In terms of infrastructure as a service in cloud computing, EC2 has a substantial history and broad adoption.
Google Compute Engine (GCE) is known for its sustained use discounts and commitment to open-source technologies like Kubernetes. Its pricing model emphasizes per-minute billing and automatic discounts for long-running workloads. GCE provides a streamlined experience, particularly for those leveraging containerization and orchestration. This makes it a strong contender for modern application development. The platform offers competitive performance and integrates well with Google’s data analytics and machine learning services. Many see Google Compute Engine as an innovative option for infrastructure as a service in cloud computing. Microsoft Azure VMs are tightly integrated with the Microsoft ecosystem, making it a natural choice for organizations using Windows Server, .NET, and other Microsoft technologies. Azure offers a comprehensive suite of services, including virtual machines, databases, and AI tools. It also provides hybrid cloud solutions, enabling businesses to seamlessly integrate on-premises infrastructure with the cloud. Azure’s pricing structure includes options like pay-as-you-go and reserved instances. Businesses using Microsoft products often find Azure’s infrastructure as a service in cloud computing to be a convenient and powerful option.
The Impact of Cloud Compute on Business Agility and Innovation
Infrastructure as a service in cloud computing empowers businesses to achieve unprecedented levels of agility and innovation. By providing on-demand access to scalable computing resources, infrastructure as a service in cloud computing removes traditional infrastructure barriers, allowing organizations to respond swiftly to evolving market demands and opportunities. This translates into a significant competitive advantage for businesses of all sizes.
The agility afforded by infrastructure as a service in cloud computing manifests in several key ways. Firstly, it allows for rapid application deployment. Instead of spending weeks or months procuring and configuring physical servers, businesses can instantly provision virtual machines and deploy applications with minimal delay. This accelerated deployment cycle enables faster time-to-market for new products and services. Secondly, infrastructure as a service in cloud computing fosters experimentation. The pay-as-you-go model enables businesses to experiment with new technologies and ideas without significant upfront investment. This reduces the risk associated with innovation, encouraging organizations to explore new possibilities. Infrastructure as a service in cloud computing allows for scalable resources, so businesses can easily adjust computing power as needed.
Furthermore, infrastructure as a service in cloud computing facilitates rapid scaling. Businesses can seamlessly scale their computing resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency. This scalability is particularly crucial for businesses experiencing rapid growth or seasonal fluctuations in demand. Ultimately, infrastructure as a service in cloud computing empowers businesses to embrace a culture of agility and innovation, enabling them to thrive in today’s dynamic and competitive landscape. The flexibility and scalability inherent in infrastructure as a service in cloud computing frees up valuable resources, allowing businesses to focus on core competencies and strategic initiatives.
Security Considerations When Managing Your Cloud Environment
Securing your compute infrastructure as a service in cloud computing environment is paramount. While IaaS providers secure the underlying infrastructure, users are responsible for securing their applications, data, and operating systems. This shared responsibility model necessitates a proactive approach to cloud security. Data encryption, both in transit and at rest, is a critical first step. Employ robust encryption algorithms and manage encryption keys securely. Access control mechanisms should be implemented to restrict access to sensitive resources based on the principle of least privilege. Strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), should be enforced for all users and administrators.
Identity management plays a crucial role in securing your infrastructure as a service in cloud computing deployments. Implement a centralized identity provider and integrate it with your cloud environment. Regularly review user permissions and revoke access when it’s no longer needed. Vulnerability scanning should be performed regularly to identify and remediate security weaknesses in your applications and operating systems. Employ automated scanning tools to continuously monitor your environment for vulnerabilities. Patch management is also essential. Keep your operating systems, applications, and other software up to date with the latest security patches. A web application firewall (WAF) can protect your applications from common web attacks, such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). Network segmentation can isolate different parts of your environment and limit the impact of a security breach.
Compliance with industry regulations and standards is another key consideration when securing your infrastructure as a service in cloud computing. Understand the compliance requirements that apply to your business and ensure that your cloud environment meets those requirements. Implement security controls to meet those compliance standards. Regularly audit your cloud environment to ensure that your security controls are effective. Security information and event management (SIEM) systems can help you to detect and respond to security incidents in your cloud environment. These systems collect security logs from various sources and analyze them to identify potential threats. Implement an incident response plan to quickly and effectively respond to security incidents when they occur. Regularly test your incident response plan to ensure that it is effective. By implementing these security best practices, you can effectively secure your IaaS environment and protect your valuable data.
Optimizing Your Compute Infrastructure for Cost Efficiency
Managing costs effectively is crucial when leveraging infrastructure as a service in cloud computing. Optimizing your cloud compute infrastructure can significantly reduce spending without sacrificing performance. Several strategies can be implemented to achieve cost efficiency. One key approach is rightsizing instances. This involves selecting the appropriate virtual machine size based on actual workload requirements. Monitoring resource utilization is essential to identify instances that are over-provisioned. Downgrading to a smaller instance size can lead to substantial cost savings. It’s important to analyze CPU, memory, and storage usage patterns to determine the optimal instance configuration. Regular monitoring and adjustments are necessary to maintain cost-effectiveness over time when using infrastructure as a service in cloud computing.
Reserved instances or spot instances offer alternative pricing models that can lower costs. Reserved instances provide a significant discount compared to on-demand pricing in exchange for a commitment to use the instance for a specific period, typically one or three years. Spot instances allow you to bid on unused compute capacity at a lower price. However, spot instances can be terminated with little notice, making them suitable for fault-tolerant workloads. Auto-scaling is another valuable tool for cost optimization. By automatically adjusting the number of instances based on demand, you can avoid paying for idle resources during periods of low traffic. Implementing auto-scaling ensures that you only consume the resources you need, when you need them and can also be implemented in infrastructure as a service in cloud computing.
Leveraging cost management tools can provide valuable insights into your cloud spending. These tools offer features such as cost tracking, budgeting, and forecasting. They can help you identify areas where costs can be reduced and track your progress over time. Regularly review your cloud spending reports to identify any anomalies or unexpected charges. Implement cost allocation tags to track the costs associated with different projects or departments. This allows you to gain a better understanding of where your cloud spending is going and identify opportunities for optimization. By proactively managing your cloud costs, you can maximize the value of your infrastructure as a service in cloud computing investment and ensure that you are only paying for the resources you actually need. Cost optimization is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and adjustments to maintain efficiency.
Future Trends in Cloud Compute Resources and Their Implications
The landscape of infrastructure as a service in cloud computing is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing business needs. Several key trends are poised to reshape how organizations leverage cloud compute resources in the coming years. Serverless computing, edge computing, and containerization represent significant shifts in the way applications are built, deployed, and managed within the cloud. Understanding these trends is crucial for businesses looking to stay ahead of the curve and optimize their cloud strategies.
Serverless computing, also known as Function as a Service (FaaS), allows developers to execute code without managing servers. This model abstracts away the underlying infrastructure, enabling developers to focus solely on writing code. Infrastructure as a service in cloud computing benefits significantly from serverless architectures through reduced operational overhead, automatic scaling, and pay-per-use billing. Edge computing, another prominent trend, brings compute resources closer to the data source or end-user. This approach reduces latency and improves performance for applications that require real-time processing, such as IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, and augmented reality. The rise of edge computing expands the reach of infrastructure as a service in cloud computing, enabling new possibilities for distributed applications.
Containerization, particularly with technologies like Docker and Kubernetes, has become a cornerstone of modern cloud deployments. Containers provide a consistent and portable environment for running applications, regardless of the underlying infrastructure. This facilitates seamless migration between different cloud providers and on-premises environments, enhancing flexibility and resilience. Furthermore, infrastructure as a service in cloud computing environments are enhanced with containerization by allowing for efficient resource utilization and simplified application management. These trends collectively point towards a future where cloud compute resources are more agile, scalable, and distributed. Businesses must adapt their strategies to embrace these changes and unlock the full potential of infrastructure as a service in cloud computing.