What is Identity and Access Management (IAM) in Cloud Computing?
Identity and Access Management (IAM) in cloud computing refers to the security practices and technologies used to manage user identities, authenticate their access, and control their permissions to cloud resources. IAM systems aim to ensure data security, prevent unauthorized access, and maintain regulatory compliance in cloud environments. By implementing IAM solutions, organizations can streamline user access management, enhance their security posture, and improve the overall user experience.

Key Components of IAM in Cloud Systems
Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems in cloud environments consist of several essential components that work together to ensure secure and controlled access to cloud resources. These components include user identification, authentication, authorization, and access control.
User Identification
User identification is the process of defining and distinguishing individual users within a cloud environment. Each user is assigned a unique identifier, such as an email address or a username, which serves as their digital identity. This unique identifier allows IAM systems to track user activities and enforce access controls based on the user’s identity.
Authentication
Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user. In IAM systems, users are typically required to provide one or more authentication factors, such as a password, a security token, or a biometric factor, to prove their identity. Multi-factor authentication (MFA), which requires users to provide multiple authentication factors, is a common and effective method for strengthening the authentication process.
Authorization
Authorization is the process of granting or denying users access to specific cloud resources based on their identity, authentication status, and predefined access policies. Access policies can be based on various factors, such as user roles, group memberships, or individual permissions. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a common authorization strategy that simplifies access management by assigning predefined roles to users and groups.
Access Control
Access control is the process of enforcing authorized access to cloud resources. IAM systems use various access control models, such as discretionary access control (DAC), mandatory access control (MAC), or role-based access control (RBAC), to ensure that users can only access the resources they are permitted to access. Access control mechanisms, such as access keys, security groups, or network ACLs, are used to implement access control policies and restrict unauthorized access to cloud resources.
By combining these components, IAM systems in cloud environments provide a robust and secure framework for managing user access to cloud resources. Effective IAM strategies ensure that only authorized users can access the resources they need, while preventing unauthorized access and reducing the risk of data breaches and security incidents.
Benefits of Implementing IAM Solutions in Cloud Environments
Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions offer numerous advantages to organizations that adopt them in cloud environments. These benefits include enhanced security, improved user experience, and centralized access management.
Enhanced Security
IAM solutions provide robust security features that help organizations protect their cloud resources from unauthorized access and data breaches. By implementing strong authentication and access control policies, IAM systems can prevent unauthorized users from accessing sensitive data and applications. Additionally, IAM solutions can help organizations comply with various security regulations and standards, such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and GDPR, by enforcing access controls and monitoring user activities.
Improved User Experience
IAM solutions can also improve the user experience by simplifying the process of accessing cloud resources. By providing a single sign-on (SSO) portal, IAM systems allow users to access multiple applications and services with a single set of credentials. This eliminates the need for users to remember multiple passwords and reduces the risk of password-related security incidents. Furthermore, IAM solutions can provide self-service portals that allow users to manage their own identities, reset forgotten passwords, and request access to resources without requiring assistance from IT staff.
Centralized Access Management
IAM solutions enable organizations to manage user access to cloud resources centrally, reducing the complexity and overhead of managing access controls across multiple systems and applications. By defining access policies and permissions at a central location, IAM systems can ensure consistent access controls across the entire cloud environment. Additionally, IAM solutions can provide real-time visibility into user activities and access patterns, enabling organizations to monitor and audit user access and detect potential security threats.
In summary, IAM solutions offer numerous benefits to organizations that adopt them in cloud environments. By providing enhanced security, improved user experience, and centralized access management, IAM solutions can help organizations protect their cloud resources, comply with security regulations, and improve operational efficiency.
Challenges in Managing Identity and Access in Cloud Computing
Identity and Access Management (IAM) in cloud environments offers numerous benefits, but it also presents several challenges that organizations must address to ensure data security and regulatory compliance. Some of the common challenges organizations face when implementing IAM in cloud computing include data privacy concerns, managing multiple identities, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Data Privacy Concerns
Data privacy is a significant concern for organizations that use cloud computing services. IAM systems must ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive data and applications. However, managing data privacy in cloud environments can be challenging due to the distributed nature of cloud resources and the complexity of access controls. Organizations must ensure that IAM systems are configured to protect data privacy and comply with data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
Managing Multiple Identities
In cloud environments, users may have multiple identities across different systems and applications. Managing these identities can be challenging, especially when users have different roles and access levels. IAM systems must provide a unified view of user identities and access permissions across all cloud resources. Additionally, IAM systems must enable users to manage their own identities and access permissions, reducing the burden on IT staff and improving user experience.
Ensuring Compliance with Regulations
Cloud computing environments must comply with various regulations and standards, such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and GDPR. IAM systems must enforce access controls and monitor user activities to ensure compliance with these regulations. However, ensuring compliance can be challenging due to the complexity of access controls and the distributed nature of cloud resources. IAM systems must provide real-time visibility into user activities and access patterns, enabling organizations to detect potential security threats and comply with regulatory requirements.
In summary, managing identity and access in cloud computing environments presents several challenges, including data privacy concerns, managing multiple identities, and ensuring compliance with regulations. Organizations must address these challenges by implementing robust IAM systems that provide a unified view of user identities and access permissions, ensure data privacy, and comply with regulatory requirements. By addressing these challenges, organizations can ensure data security, improve operational efficiency, and comply with regulatory requirements.

How to Implement Effective IAM Strategies in Cloud Environments
Implementing effective Identity and Access Management (IAM) strategies in cloud environments is crucial for ensuring data security and controlling user access to cloud resources. In this section, we will provide a step-by-step guide on implementing effective IAM strategies in cloud environments, including setting up user identities, configuring access policies, and monitoring user activities.
Step 1: Setting Up User Identities
The first step in implementing effective IAM strategies is to set up user identities. This involves creating a centralized repository of user identities, including usernames, passwords, and other authentication factors. Organizations can use cloud-based IAM solutions or on-premises IAM solutions to create and manage user identities. It is essential to ensure that user identities are unique, accurate, and up-to-date to prevent unauthorized access to cloud resources.
Step 2: Configuring Access Policies
Once user identities are set up, the next step is to configure access policies. Access policies define who can access what resources and under what conditions. Organizations can use role-based access control (RBAC) or attribute-based access control (ABAC) to define access policies. RBAC allows organizations to assign roles to users based on their job functions, while ABAC allows organizations to define access policies based on user attributes, such as department, location, and time of day.
Step 3: Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication
Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) is essential for enhancing security in cloud environments. MFA requires users to provide two or more authentication factors, such as a password and a fingerprint, to access cloud resources. MFA can prevent unauthorized access to cloud resources, even if user credentials are compromised.
Step 4: Monitoring User Activities
Monitoring user activities is crucial for detecting potential security threats and ensuring compliance with regulations. Organizations can use cloud-based monitoring tools or on-premises monitoring tools to monitor user activities, such as login attempts, file access, and API calls. Monitoring user activities can help organizations detect anomalies, such as unusual login attempts or file access patterns, and respond to potential security threats promptly.
Step 5: Regularly Reviewing Access Policies
Regularly reviewing access policies is essential for ensuring that access controls are up-to-date and effective. Organizations should review access policies periodically, such as quarterly or annually, to ensure that access controls are aligned with business requirements and regulatory requirements. Regular reviews can help organizations detect potential security threats, such as unused user accounts or outdated access permissions, and take corrective action promptly.
In summary, implementing effective IAM strategies in cloud environments involves setting up user identities, configuring access policies, implementing multi-factor authentication, monitoring user activities, and regularly reviewing access policies. By following these steps, organizations can ensure data security, improve operational efficiency, and comply with regulatory requirements. It is essential to choose the right IAM solution and partner with a trusted cloud service provider to implement effective IAM strategies in cloud environments.
Popular IAM Solutions for Cloud Computing
Identity and access management (IAM) solutions are essential for securing cloud environments and controlling user access to cloud resources. In this section, we will review some of the popular IAM solutions for cloud computing, such as Okta, OneLogin, and Auth0, and discuss their features, benefits, and limitations.
Okta
Okta is a cloud-based IAM solution that provides a range of features, including user authentication, provisioning, and deprovisioning. Okta supports multi-factor authentication (MFA) and integrates with a wide range of third-party applications, such as Salesforce, Google Workspace, and Microsoft 365. Okta also provides a user-friendly interface and robust reporting and analytics capabilities. However, Okta can be expensive for small and medium-sized businesses, and some users have reported issues with customer support.
OneLogin
OneLogin is another popular IAM solution for cloud computing that provides user authentication, provisioning, and deprovisioning. OneLogin supports MFA and integrates with over 5,000 third-party applications. OneLogin also provides real-time security alerts and user activity tracking. However, OneLogin can be complex to set up and configure, and some users have reported issues with the user interface.
Auth0
Auth0 is a cloud-based IAM solution that provides user authentication, authorization, and multi-factor authentication. Auth0 supports a wide range of third-party applications and integrates with social login providers, such as Google, Facebook, and Twitter. Auth0 also provides a user-friendly interface and robust reporting and analytics capabilities. However, Auth0 can be expensive for large organizations, and some users have reported issues with the pricing model.
In summary, Okta, OneLogin, and Auth0 are popular IAM solutions for cloud computing that provide a range of features, including user authentication, provisioning, and deprovisioning. These solutions support MFA and integrate with a wide range of third-party applications. However, each solution has its limitations, such as cost, complexity, and user interface issues. It is essential to evaluate each solution based on business requirements and regulatory requirements to ensure effective IAM in cloud environments.
When choosing an IAM solution for cloud computing, organizations should consider factors such as cost, ease of use, integration with third-party applications, and compliance with regulatory requirements. It is also essential to partner with a trusted cloud service provider that provides robust IAM capabilities and supports the chosen IAM solution. By following these best practices, organizations can ensure effective IAM in cloud environments and protect their cloud resources from unauthorized access and potential security threats.

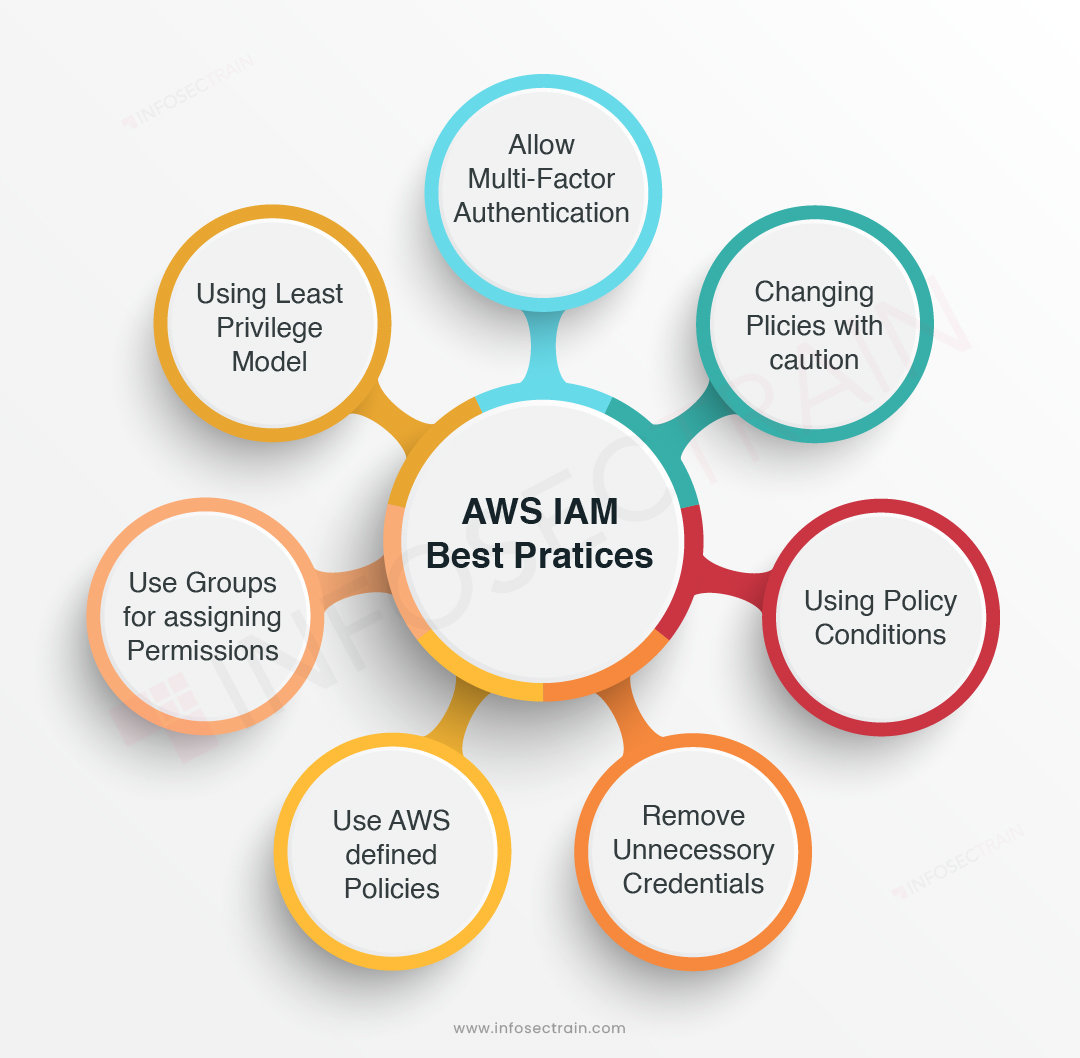
Best Practices for Identity and Access Management in Cloud Environments
Identity and access management (IAM) is a critical aspect of cloud computing that ensures data security and controls user access to cloud resources. Implementing effective IAM strategies is essential for organizations to protect their cloud resources from unauthorized access and potential security threats. In this section, we will outline best practices for managing IAM in cloud environments, such as implementing multi-factor authentication, regularly reviewing access policies, and using role-based access control.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security measure that requires users to provide two or more forms of authentication to access cloud resources. MFA adds an extra layer of security to user authentication, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access to cloud resources. Organizations should implement MFA for all users, including administrators and privileged users, to ensure maximum security.
Regularly Review Access Policies
Regularly reviewing access policies is essential for ensuring that only authorized users have access to cloud resources. Organizations should establish a regular review process to ensure that access policies are up-to-date and reflect the current state of the organization’s security posture. Access policies should be reviewed and updated regularly to reflect changes in user roles, responsibilities, and access requirements.
Use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-based access control (RBAC) is a security measure that grants access to cloud resources based on a user’s role within the organization. RBAC simplifies access management by assigning predefined roles to users, reducing the complexity of managing individual access rights. Organizations should use RBAC to ensure that users have the minimum level of access required to perform their job functions.
Monitor User Activities
Monitoring user activities is essential for detecting and responding to potential security threats. Organizations should monitor user activities, such as login attempts, access to sensitive data, and changes to access policies, to ensure that only authorized users are accessing cloud resources. Monitoring user activities can help organizations detect and respond to potential security threats in real-time, reducing the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
Establish a Strong Password Policy
Establishing a strong password policy is essential for ensuring that users choose strong and unique passwords. Organizations should require users to choose complex passwords that include a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters. Passwords should be changed regularly, and password reuse should be discouraged. Organizations should also consider implementing passwordless authentication, such as biometric authentication, to further enhance security.
Implement Least Privilege Principle
The principle of least privilege (PoLP) is a security measure that grants users the minimum level of access required to perform their job functions. PoLP reduces the risk of data breaches and other security incidents by limiting the amount of damage that can be done if a user’s account is compromised. Organizations should implement PoLP to ensure that users have the minimum level of access required to perform their job functions.
In summary, implementing effective IAM strategies in cloud environments is essential for ensuring data security and controlling user access to cloud resources. Best practices for managing IAM in cloud environments include implementing multi-factor authentication, regularly reviewing access policies, using role-based access control, monitoring user activities, establishing a strong password policy, and implementing the principle of least privilege. By following these best practices, organizations can ensure effective IAM in cloud environments and protect their cloud resources from unauthorized access and potential security threats.

Best Practices for Identity and Access Management in Cloud Environments
Identity and access management (IAM) is a critical aspect of cloud computing that ensures data security and controls user access to cloud resources. Implementing effective IAM strategies is essential for organizations to protect their cloud resources from unauthorized access and potential security threats. In this section, we will outline best practices for managing IAM in cloud environments, such as implementing multi-factor authentication, regularly reviewing access policies, and using role-based access control.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security measure that requires users to provide two or more forms of authentication to access cloud resources. MFA adds an extra layer of security to user authentication, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access to cloud resources. Organizations should implement MFA for all users, including administrators and privileged users, to ensure maximum security.
Regularly Review Access Policies
Regularly reviewing access policies is essential for ensuring that only authorized users have access to cloud resources. Organizations should establish a regular review process to ensure that access policies are up-to-date and reflect the current state of the organization’s security posture. Access policies should be reviewed and updated regularly to reflect changes in user roles, responsibilities, and access requirements.
Use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-based access control (RBAC) is a security measure that grants access to cloud resources based on a user’s role within the organization. RBAC simplifies access management by assigning predefined roles to users, reducing the complexity of managing individual access rights. Organizations should use RBAC to ensure that users have the minimum level of access required to perform their job functions.
Monitor User Activities
Monitoring user activities is essential for detecting and responding to potential security threats. Organizations should monitor user activities, such as login attempts, access to sensitive data, and changes to access policies, to ensure that only authorized users are accessing cloud resources. Monitoring user activities can help organizations detect and respond to potential security threats in real-time, reducing the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
Establish a Strong Password Policy
Establishing a strong password policy is essential for ensuring that users choose strong and unique passwords. Organizations should require users to choose complex passwords that include a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters. Passwords should be changed regularly, and password reuse should be discouraged. Organizations should also consider implementing passwordless authentication, such as biometric authentication, to further enhance security.
Implement Least Privilege Principle
The principle of least privilege (PoLP) is a security measure that grants users the minimum level of access required to perform their job functions. PoLP reduces the risk of data breaches and other security incidents by limiting the amount of damage that can be done if a user’s account is compromised. Organizations should implement PoLP to ensure that users have the minimum level of access required to perform their job functions.
In summary, implementing effective IAM strategies in cloud environments is essential for ensuring data security and controlling user access to cloud resources. Best practices for managing IAM in cloud environments include implementing multi-factor authentication, regularly reviewing access policies, using role-based access control, monitoring user activities, establishing a strong password policy, and implementing the principle of least privilege. By following these best practices, organizations can ensure effective IAM in cloud environments and protect their cloud resources from unauthorized access and potential security threats.

