What are KPIs and Why are They Crucial for Business Success?
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are a set of measurable values that organizations use to evaluate their performance against strategic objectives. KPIs differ from traditional performance metrics in that they are tailored to the unique needs and goals of the business, and are used to track progress towards specific targets. By aligning KPIs with business strategies, organizations can ensure that their operational goals are aligned with their overall mission and vision.
KPIs play a critical role in driving business success by providing a clear and concise picture of an organization’s performance. By tracking KPIs over time, businesses can identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions that lead to better outcomes. In short, KPIs are a powerful tool for driving growth, improving efficiency, and achieving long-term success.
When it comes to creating KPIs, it’s important to focus on metrics that are relevant, actionable, and aligned with business goals. By selecting KPIs that are tailored to the unique needs and objectives of the organization, businesses can ensure that they are measuring what matters most, and making progress towards their strategic objectives.
In the following sections, we’ll explore the process of selecting relevant KPIs, setting SMART targets, collecting and analyzing KPI data, and communicating KPI results to stakeholders. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of how to create KPIs that drive business success.
Identifying Relevant KPIs for Your Business
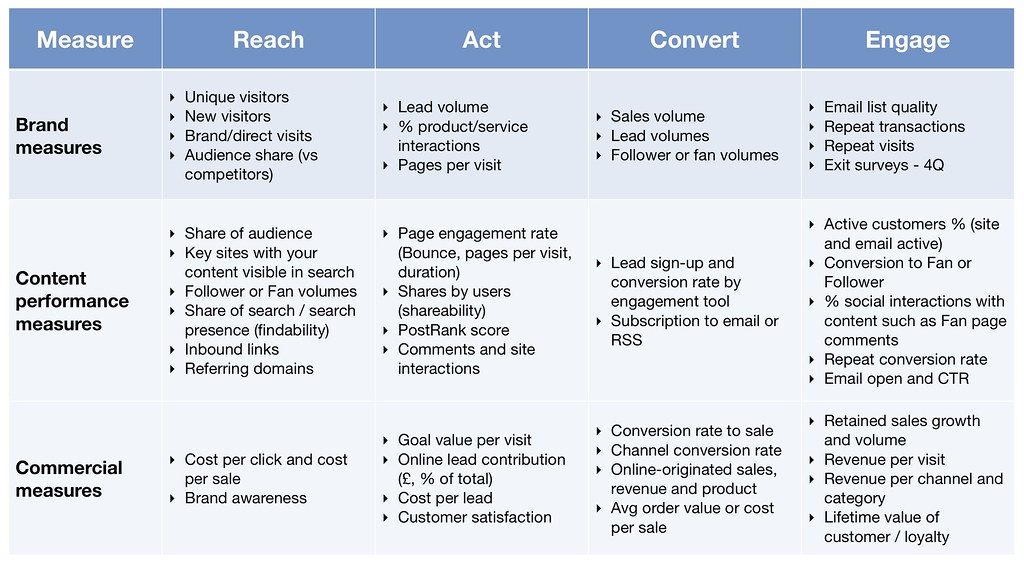
Now that we understand the importance of KPIs in measuring business success, it’s time to explore the process of selecting KPIs that are tailored to your unique needs and objectives. KPIs can be categorized into several areas, including financial, customer, internal process, and learning & growth. By understanding these categories, businesses can select KPIs that are aligned with their strategic objectives and provide meaningful insights into their performance.
Financial KPIs
Financial KPIs are used to measure the financial health and performance of an organization. Examples of financial KPIs include:
- Gross Profit Margin: Gross profit as a percentage of revenue.
- Return on Investment (ROI): The net profit from an investment as a percentage of the investment cost.
- Cash Flow: The amount of cash flowing in and out of the business.
Customer KPIs
Customer KPIs are used to measure the satisfaction and loyalty of a company’s customers. Examples of customer KPIs include:
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): The percentage of customers who are satisfied with their experience.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): The likelihood of customers to recommend the company to others.
- Customer Retention Rate: The percentage of customers who continue to do business with the company over a given period of time.
Internal Process KPIs
Internal process KPIs are used to measure the efficiency and effectiveness of a company’s internal processes. Examples of internal process KPIs include:
- Cycle Time: The time it takes to complete a specific process or task.
- Defect Rate: The percentage of products or services that do not meet quality standards.
- First Time Fix Rate: The percentage of issues that are resolved on the first attempt.
Learning & Growth KPIs
Learning & growth KPIs are used to measure the development and improvement of a company’s employees and systems. Examples of learning & growth KPIs include:
- Employee Turnover Rate: The percentage of employees who leave the company over a given period of time.
- Training Completion Rate: The percentage of employees who complete required training programs.
- Employee Engagement Score: The level of engagement and satisfaction of employees with their work and the company.
By selecting KPIs from these categories, businesses can ensure that they are measuring what matters most and making progress towards their strategic objectives. In the following sections, we’ll explore the importance of setting SMART targets for your KPIs and the process of collecting and analyzing KPI data.
Setting SMART KPI Targets
Now that we understand the importance of selecting relevant KPIs, it’s time to discuss the process of setting SMART targets for these KPIs. SMART targets are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound, and provide a clear and concise framework for tracking progress towards your KPIs.
Setting SMART targets involves several steps. First, you should review your current KPI data and identify areas for improvement. For example, if your customer satisfaction score is lower than you would like, you might set a target to increase it by a specific percentage over a given period of time.
Once you have identified the areas for improvement, you should create Specific targets that are aligned with your business objectives. For example, if your objective is to increase revenue, your KPI target might be to increase sales by a specific dollar amount over a given period of time.
Next, you should ensure that your targets are Measurable, so that you can track progress towards them over time. This might involve setting up a system for collecting and analyzing KPI data, such as a dashboard or report.
Your targets should also be Achievable, based on your current performance and resources. Setting unrealistic targets can lead to frustration and burnout, and can undermine the effectiveness of your KPI framework.
In addition, your targets should be Relevant to your business objectives and strategies. For example, if your objective is to improve customer satisfaction, your KPI targets should focus on metrics related to customer satisfaction, such as customer satisfaction scores or net promoter scores.
Finally, your targets should be Time-bound, with a clear start and end date. This will help you to track progress towards your targets over time and make adjustments as needed.
By setting SMART targets for your KPIs, you can ensure that you are making progress towards your business objectives and that you are able to track your progress over time. In the following sections, we’ll explore the process of collecting and analyzing KPI data, and best practices for communicating KPI results to stakeholders.
Collecting and Analyzing KPI Data
Once you have established your KPIs and set SMART targets, the next step is to collect and analyze data to track your progress. This involves gathering data from various sources, such as internal systems, external sources, or manual data collection methods. It is important to ensure that the data is accurate, consistent, and relevant to your KPIs.
Data visualization tools and techniques can be used to help you analyze and interpret your KPI data. These tools can help you to identify trends, patterns, and correlations in your data, and can provide insights into the performance of your KPIs. Some common data visualization techniques include charts, graphs, and dashboards.
When collecting and analyzing KPI data, it is important to keep in mind the following tips:
- Ensure data accuracy and consistency: It is important to ensure that the data you are collecting is accurate and consistent over time. This will help you to track your progress and identify trends and patterns in your KPI data.
- Identify trends and patterns: Use data visualization tools and techniques to help you identify trends and patterns in your KPI data. This can provide insights into the performance of your KPIs and help you to make data-driven decisions.
- Monitor data over time: Regularly monitor your KPI data over time to track your progress and identify areas for improvement. This will help you to ensure that your KPI framework remains relevant and effective.
- Use data to inform decision-making: Use the insights gained from your KPI data to inform decision-making and drive business success. This might involve making changes to your strategies, processes, or resources to improve the performance of your KPIs.
By collecting and analyzing KPI data, you can gain valuable insights into the performance of your KPIs and make data-driven decisions that drive business success. In the following sections, we’ll explore best practices for communicating KPI results to stakeholders and continuously improving your KPI framework.
Communicating KPI Results to Stakeholders
Once you have established your KPIs, set targets, and collected data, it’s time to communicate the results to stakeholders. Effective communication is crucial for ensuring that stakeholders understand the significance of the KPIs, the progress being made, and any areas for improvement. Here are some best practices for communicating KPI results:
- Use clear and concise reporting formats: Avoid cluttered or complicated reports that may overwhelm stakeholders. Instead, use simple, easy-to-understand charts, graphs, and tables that highlight the most important KPI data.
- Regularly schedule meetings and updates: Regular communication helps to ensure that stakeholders are informed and engaged in the KPI framework. Schedule regular meetings or updates to review KPI results, discuss progress, and address any concerns or questions.
- Align KPI results with business strategy: It’s important to communicate how KPI results relate to the overall business strategy. Explain how improvements in KPIs will contribute to the success of the organization and its goals.
- Be transparent and honest: Be open and honest about the performance of the KPIs, even if the results are not what you had hoped for. Use KPI data to identify areas for improvement and develop strategies to address any challenges.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that stakeholders are informed and engaged in the KPI framework, and that KPI results are aligned with the overall business strategy. In the next section, we’ll discuss the importance of continuously improving your KPI framework to ensure that it remains relevant and effective.
Continuously Improving Your KPI Framework
A successful KPI framework is not a one-time effort but requires continuous review and improvement. As your business evolves, so should your KPIs to ensure they remain relevant and effective in measuring success. Here are some tips for continuously improving your KPI framework:
- Regularly review KPIs: Schedule regular reviews of your KPIs to ensure they are still aligned with your business objectives. Remove any KPIs that are no longer relevant and add new ones as needed.
- Collect feedback: Solicit feedback from stakeholders, including employees, customers, and partners, to identify areas for improvement. Use this feedback to refine your KPIs and make them more effective.
- Monitor KPI performance: Regularly monitor the performance of your KPIs to identify trends and patterns. Use this data to make data-driven decisions about where to focus your efforts and resources.
- Experiment with new KPIs: Don’t be afraid to experiment with new KPIs to see how they perform. This can help you identify new areas for improvement and keep your KPI framework fresh and relevant.
By continuously improving your KPI framework, you can ensure that it remains a valuable tool for measuring the success and progress of your organization. In the next section, we’ll discuss some common mistakes to avoid when implementing KPIs.
Avoiding Common KPI Pitfalls
While KPIs can be a powerful tool for measuring business success, there are also common pitfalls that can derail their effectiveness. Here are some mistakes to avoid when implementing KPIs:
- Focusing on vanity metrics: Vanity metrics are metrics that may look good on paper but don’t actually contribute to business success. For example, a high number of social media followers may look impressive, but if those followers aren’t engaging with your content or converting into customers, they’re not providing value. Instead, focus on metrics that directly impact your business objectives.
- Setting unrealistic targets: Setting overly ambitious targets can lead to frustration and burnout. Instead, set realistic and achievable targets that align with your business objectives and capabilities. This will help to ensure that your KPIs are attainable and sustainable over the long term.
- Failing to align KPIs with business strategy: KPIs should be closely aligned with your business strategy and objectives. If your KPIs aren’t directly contributing to your business goals, they may not be providing value. Make sure that your KPIs are closely tied to your overall business strategy and that they are aligned with your operational goals.
- Neglecting data accuracy and consistency: Data accuracy and consistency are critical for ensuring the effectiveness of your KPIs. Make sure that your data is clean, accurate, and consistent over time. This will help to ensure that your KPIs are providing reliable and actionable insights.
- Ignoring external factors: External factors, such as market conditions, industry trends, and economic indicators, can impact the performance of your KPIs. Make sure that you’re taking these factors into account when analyzing your KPI data and making data-driven decisions.
By avoiding these common pitfalls, you can ensure that your KPI framework is effective, relevant, and aligned with your business objectives. In the next section, we’ll provide real-world examples of successful KPI frameworks from real-world businesses.
Real-World Examples of Successful KPI Frameworks
KPIs can be a powerful tool for measuring business success, but it can be challenging to know where to start. Here are some real-world examples of successful KPI frameworks from real-world businesses:
Example 1: A Retail Business
A retail business implemented a KPI framework to measure sales, customer satisfaction, and inventory management. The KPIs included:
- Sales per square foot
- Average transaction value
- Customer satisfaction score
- Inventory turnover rate
By tracking these KPIs, the business was able to identify areas for improvement, such as increasing sales per square foot and reducing inventory costs. The KPI framework helped the business to align its operational goals with its overall business strategy and improve its financial performance.
Example 2: A Software Company
A software company implemented a KPI framework to measure customer acquisition, customer retention, and product development. The KPIs included:
- Customer acquisition cost
- Customer lifetime value
- Customer churn rate
- Time to market for new products
By tracking these KPIs, the company was able to identify areas for improvement, such as reducing customer acquisition costs and improving time to market for new products. The KPI framework helped the company to align its operational goals with its overall business strategy and improve its financial performance.
Example 3: A Manufacturing Company
A manufacturing company implemented a KPI framework to measure production efficiency, quality control, and supply chain management. The KPIs included:
- Production efficiency rate
- Defect rate
- On-time delivery rate
- Supply chain cycle time
By tracking these KPIs, the company was able to identify areas for improvement, such as increasing production efficiency and reducing defect rates. The KPI framework helped the company to align its operational goals with its overall business strategy and improve its financial performance.
These examples demonstrate the power of KPIs in measuring business success and driving data-driven decision-making. By selecting relevant KPIs, setting SMART targets, collecting and analyzing data, and communicating KPI results to stakeholders, businesses can improve their operational performance and achieve their strategic objectives.