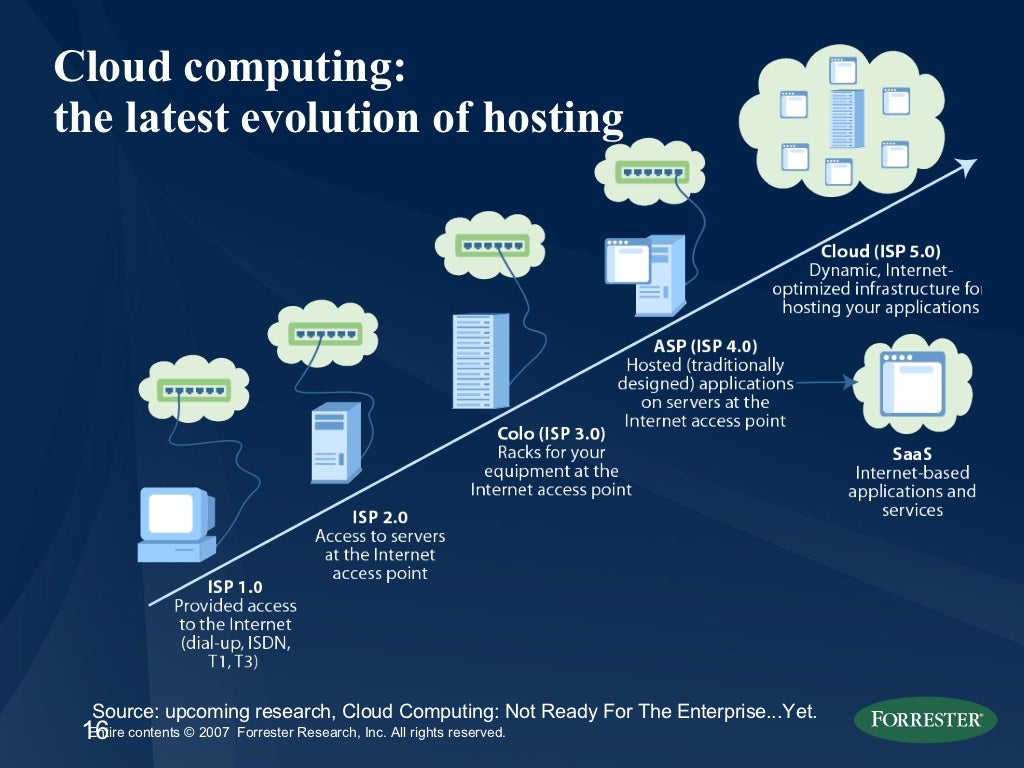
Introduction to IBM Cloud: A Historical Perspective
IBM Cloud, also known as IBM Cloud Computing, is a comprehensive cloud platform that offers a wide range of services and solutions for businesses and individuals. The history of IBM Cloud dates back to the early 2000s when cloud computing was still in its infancy. However, it was not until IBM’s acquisition of SoftLayer Technologies in 2013 that IBM made a significant entry into the cloud computing market. Since then, IBM Cloud has evolved significantly, becoming a major player in the cloud computing industry.
The Emergence of IBM Cloud: Early Beginnings
IBM Cloud’s early beginnings can be traced back to IBM’s acquisition of SoftLayer Technologies in 2013. This acquisition marked IBM’s entry into the cloud computing market, providing the company with a robust infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) offering. SoftLayer’s technology and expertise in cloud computing enabled IBM to quickly establish itself as a major player in the industry.
Following the acquisition, IBM rebranded SoftLayer as IBM Cloud and integrated it into its existing cloud offerings. This integration allowed IBM to provide a comprehensive suite of cloud services, including IaaS, platform-as-a-service (PaaS), and software-as-a-service (SaaS) offerings. The acquisition also enabled IBM to expand its global data center footprint, providing customers with greater flexibility and scalability in their cloud deployments.
Since the acquisition, IBM Cloud has continued to grow and expand, forming partnerships with leading technology companies and launching new products and services. These efforts have helped to solidify IBM Cloud’s position as a major player in the cloud computing industry, providing businesses and individuals with a wide range of cloud services and solutions.
IBM Cloud’s Growth and Expansion: Key Milestones
Since its inception, IBM Cloud has experienced significant growth and expansion, marked by a series of key milestones and achievements. In 2014, just a year after the acquisition of SoftLayer, IBM announced the launch of IBM Bluemix, a cloud-based platform-as-a-service (PaaS) offering that enables developers to build, deploy, and manage applications in the cloud. Bluemix quickly gained popularity among developers, providing a powerful tool for building cloud-native applications.
In 2015, IBM formed a partnership with Twitter to provide developers with access to Twitter data through the IBM Cloud. This partnership enabled developers to build applications that leverage Twitter data for insights and analytics, providing new opportunities for businesses and individuals alike. IBM also announced the launch of its Watson cognitive computing platform on the IBM Cloud, providing developers with access to advanced artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities.
In 2016, IBM announced the acquisition of Gravitant, a cloud-based brokerage platform that enables businesses to manage and optimize their cloud resources. This acquisition further strengthened IBM Cloud’s offerings, providing businesses with greater flexibility and control over their cloud deployments. IBM also announced the launch of its Cloud Foundry-based platform, enabling developers to build and deploy applications using open-source technology.
In 2017, IBM announced the launch of its IBM Cloud Private platform, a cloud-native platform that enables businesses to build and deploy applications in a private cloud environment. This platform provides businesses with greater control over their cloud deployments, enabling them to leverage the benefits of cloud computing while maintaining control over their data and infrastructure.
In 2018, IBM announced the launch of its IBM Cloud for VMware Solutions, providing businesses with a simple and seamless way to migrate their existing VMware workloads to the IBM Cloud. This solution enables businesses to leverage the benefits of cloud computing while maintaining compatibility with their existing VMware environments.
These key milestones and achievements highlight IBM Cloud’s growth and expansion since its inception. Through partnerships, acquisitions, and product launches, IBM Cloud has established itself as a major player in the cloud computing industry, providing businesses and individuals with a wide range of cloud services and solutions.
IBM Cloud’s Current Offerings: A Diverse Portfolio
IBM Cloud offers a wide range of cloud services and solutions, catering to a diverse set of industries and use cases. The company’s offerings can be broadly categorized into three main categories: Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS).
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
IBM Cloud’s IaaS offerings provide businesses with access to a scalable and flexible infrastructure, enabling them to build and deploy applications in the cloud. The company’s IaaS offerings include virtual servers, bare metal servers, and storage solutions, providing businesses with the flexibility to choose the right infrastructure for their needs.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
IBM Cloud’s PaaS offerings provide developers with a powerful platform for building, deploying, and managing applications in the cloud. The company’s PaaS offerings include Cloud Foundry, Kubernetes, and Red Hat OpenShift, enabling developers to build cloud-native applications using their preferred tools and frameworks.
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
IBM Cloud’s SaaS offerings provide businesses with access to a wide range of software applications, enabling them to streamline their operations and improve their productivity. The company’s SaaS offerings include IBM Watson, IBM Cloud Pak for Data, and IBM Maximo, providing businesses with access to advanced AI, data analytics, and asset management capabilities.
IBM Cloud’s diverse portfolio of offerings caters to a wide range of industries and use cases, including healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing. The company’s cloud services and solutions enable businesses to leverage the benefits of cloud computing, including scalability, flexibility, and cost savings, while maintaining control over their data and infrastructure.
How to Leverage IBM Cloud: Best Practices and Use Cases
IBM Cloud offers a wide range of benefits for businesses and individuals, from scalability and flexibility to cost savings and advanced capabilities. However, to fully leverage the power of IBM Cloud, it’s important to follow best practices and understand how to optimize costs, ensure security, and improve performance.
Optimizing Costs
One of the key benefits of using IBM Cloud is the ability to optimize costs and reduce expenses. To do this, it’s important to carefully monitor usage and utilization, and to take advantage of cost-saving measures such as reserved instances and spot instances. Additionally, businesses can leverage IBM Cloud’s pricing models, such as pay-as-you-go and subscription-based pricing, to further optimize costs and reduce expenses.
Ensuring Security
Security is a top concern for businesses and individuals using cloud services, and IBM Cloud takes this issue seriously. The company offers a wide range of security features and capabilities, including encryption, access control, and network security. To ensure security, it’s important to follow best practices such as using strong passwords, enabling multi-factor authentication, and regularly monitoring security logs and alerts.
Improving Performance
IBM Cloud offers a wide range of performance-enhancing features and capabilities, including load balancing, auto-scaling, and caching. To improve performance, it’s important to carefully monitor usage and utilization, and to take advantage of these features as needed. Additionally, businesses can leverage IBM Cloud’s content delivery network (CDN) and edge computing capabilities to further improve performance and reduce latency.
Real-World Use Cases
IBM Cloud is used by a wide range of businesses and individuals, from startups and small businesses to large enterprises and government agencies. Some real-world use cases for IBM Cloud include:
- Developing and deploying cloud-native applications using IBM Cloud’s PaaS offerings
- Building and managing big data and analytics pipelines using IBM Cloud’s IaaS offerings
- Leveraging IBM Watson for advanced AI and machine learning capabilities
- Using IBM Cloud Pak for Data to manage and analyze large volumes of data
- Building and deploying hybrid cloud environments using IBM Cloud’s hybrid cloud offerings
By following best practices and understanding how to optimize costs, ensure security, and improve performance, businesses and individuals can fully leverage the power of IBM Cloud and unlock its many benefits.
IBM Cloud’s Future Outlook: Trends and Predictions
The cloud computing industry is constantly evolving, and IBM Cloud is at the forefront of this transformation. With its robust infrastructure, innovative services, and commitment to open-source technologies, IBM Cloud is well-positioned to shape the future of the industry.
One of the key trends in the cloud computing industry is the increasing adoption of hybrid and multi-cloud strategies. According to a recent survey by Finextra, 76% of organizations plan to use multiple clouds by 2021. IBM Cloud is well-suited to support this trend, with its ability to manage and integrate workloads across multiple cloud environments.
Another trend is the growing importance of edge computing. As more devices and sensors come online, there is a need to process and analyze data closer to the source. IBM Cloud offers a range of edge computing solutions, including its Edge Application Manager, which allows organizations to manage and deploy edge applications at scale.
In addition, there is a growing focus on artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in the cloud computing industry. IBM Cloud offers a range of AI and ML services, including its Watson Assistant, which enables organizations to build conversational interfaces powered by AI. IBM Cloud is also committed to open-source technologies, such as Kubernetes, which is becoming increasingly important in the cloud computing industry.
Looking ahead, IBM Cloud is expected to continue to innovate and expand its offerings. The company is investing in new technologies, such as quantum computing and blockchain, which have the potential to transform industries. IBM Cloud is also focused on sustainability, with a commitment to using renewable energy and reducing its carbon footprint.
In conclusion, the future outlook for IBM Cloud is promising, with trends and predictions pointing to continued growth and innovation in the cloud computing industry. IBM Cloud’s commitment to hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, edge computing, AI and ML, open-source technologies, and sustainability position it well to shape the future of the industry and deliver value to businesses and society.
Challenges and Limitations of IBM Cloud: Addressing Concerns
While IBM Cloud offers a wide range of benefits and features, there are also some challenges and limitations to consider. Here are some of the most common concerns and potential solutions for overcoming them:
Cost
One of the biggest challenges of using IBM Cloud is managing costs. IBM Cloud offers a wide range of services and features, which can make it easy to overspend. To optimize costs, consider the following best practices:
- Monitor usage and set up alerts to avoid unexpected charges.
- Use reserved instances and spot instances to save on compute costs.
- Consider using IBM Cloud’s cost management tools, such as the Cost and Asset Management service.
Security
Security is a top concern for any cloud computing platform. IBM Cloud offers a range of security features, including encryption, identity and access management, and network security. To ensure security, consider the following best practices:
- Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication.
- Regularly review access controls and permissions.
- Implement encryption for data at rest and in transit.
Performance
Performance can be a concern for any cloud computing platform, especially for applications with high traffic or complex workloads. To improve performance, consider the following best practices:
- Use load balancing to distribute traffic across multiple instances.
- Optimize database performance with caching and indexing.
- Use content delivery networks (CDNs) to improve content delivery speed.
Complexity
IBM Cloud offers a wide range of services and features, which can make it complex to use. To address complexity, consider the following best practices:
- Use IBM Cloud’s automation and orchestration tools, such as Terraform and Ansible.
- Consider using IBM Cloud’s managed services to reduce complexity.
- Take advantage of IBM Cloud’s documentation and training resources.
In conclusion, while there are challenges and limitations to using IBM Cloud, there are also potential solutions for overcoming these concerns. By following best practices for cost, security, performance, and complexity, organizations can leverage the benefits of IBM Cloud while minimizing potential drawbacks.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of IBM Cloud
IBM Cloud has come a long way since its early beginnings in 2013. From its acquisition of SoftLayer Technologies to its current diverse portfolio of Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) offerings, IBM Cloud has established itself as a major player in the cloud computing industry.
IBM’s contributions to the cloud computing industry are significant. The company has been a pioneer in the development of cloud computing technologies, and its commitment to open-source technologies has helped to drive innovation and adoption in the industry. IBM Cloud’s focus on hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, edge computing, AI and ML, open-source technologies, and sustainability position it well to shape the future of the industry and deliver value to businesses and society.
While there are challenges and limitations to using IBM Cloud, there are also potential solutions for overcoming these concerns. By following best practices for cost, security, performance, and complexity, organizations can leverage the benefits of IBM Cloud while minimizing potential drawbacks.
In conclusion, the History of IBM Cloud is marked by innovation, growth, and a commitment to delivering value to businesses and society. With its diverse portfolio of offerings, IBM Cloud is well-positioned to continue to shape the future of the cloud computing industry and deliver value to businesses and society for years to come.