From Humble Beginnings: The Emergence of Google’s Cloud Services
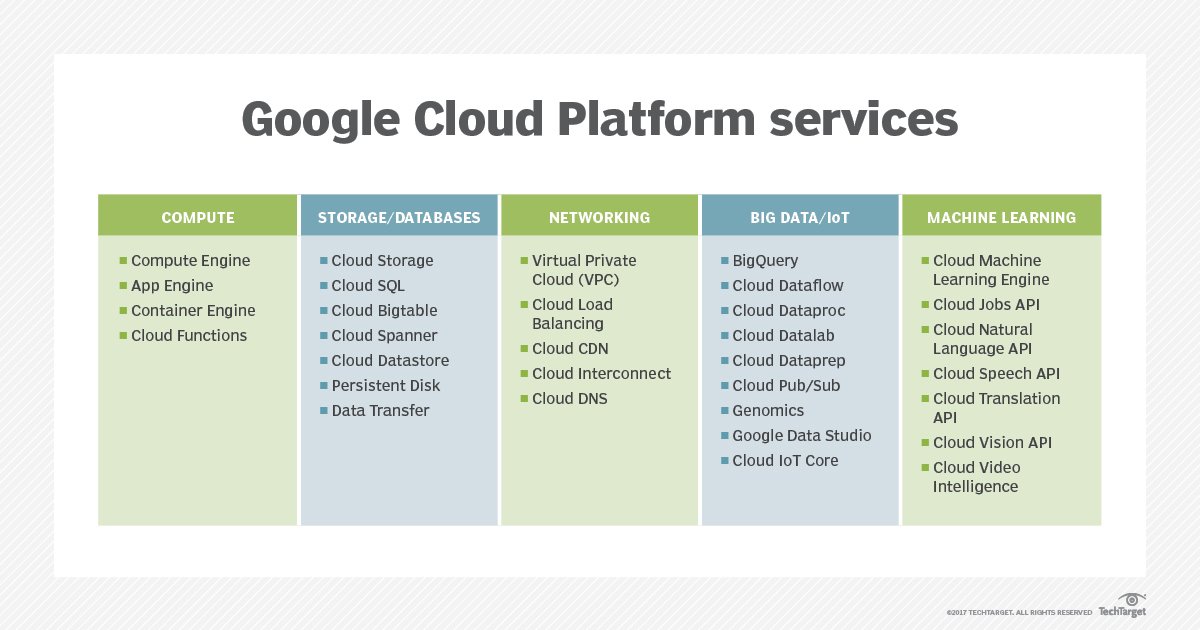
Google’s foray into cloud computing began in 2008 when the tech giant launched its App Engine platform, enabling developers to build and host web applications in the cloud. This marked the beginning of the History of Goggle Cloud, which has since grown into a comprehensive suite of services catering to various industries and use cases. Over time, Google expanded its cloud offerings, introducing storage, networking, big data, and machine learning solutions, among others.
Key Milestones in Google Cloud’s History
Google Cloud has experienced several significant milestones since its inception. In 2010, Google Compute Engine, a service providing virtual machines (VMs) on demand, was launched, followed by Google Cloud Storage in 2012. These introductions expanded Google Cloud’s capabilities, catering to a broader range of user needs. In 2014, Google acquired Stackdriver, a monitoring and diagnostics company, which later became a crucial component of Google Cloud’s observability features. The following year, Google rebranded its cloud services as Google Cloud Platform (GCP), marking a more focused approach to the cloud computing market.
Google Cloud’s strategic partnerships have also played a crucial role in its development. In 2017, Google and Cisco formed an alliance to create hybrid cloud solutions, combining the strengths of both companies. Additionally, Google Cloud’s collaboration with SAP, announced in 2018, has enabled businesses to run their SAP workloads seamlessly in the cloud.
In 2019, Google Cloud’s parent company, Alphabet Inc., made a strategic investment in the Finnish telecommunications provider Elisa, aiming to accelerate the adoption of cloud services in the Nordic region.
These milestones have contributed to the History of Goggle Cloud, shaping its growth and solidifying its position in the cloud computing landscape.
Innovations and Pioneering Achievements in Google Cloud
Google Cloud has consistently introduced groundbreaking innovations and contributed significantly to the cloud computing landscape. Its Kubernetes container orchestration system, open-sourced in 2014, has revolutionized the way developers manage and scale applications. Google Cloud’s Anthos platform, launched in 2019, enables businesses to build, deploy, and manage applications across multiple clouds and on-premises environments. Google Cloud’s commitment to artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) has also set it apart from competitors. The company’s TensorFlow ML platform, introduced in 2015, has become a popular choice for developers and researchers working on AI-driven projects. Moreover, Google Cloud’s AutoML tools, released in 2018, enable users with limited ML expertise to build custom models, further democratizing AI and ML capabilities.
In the field of data analytics, Google Cloud’s BigQuery, a serverless, highly scalable data warehouse, has empowered businesses to analyze vast amounts of data in real-time. Additionally, Google Cloud’s Dataflow and Dataproc services enable users to process and analyze data using Apache Beam and Apache Hadoop & Spark, respectively.
These innovations and achievements have solidified Google Cloud’s position as a leader in the cloud computing landscape, making it an attractive choice for businesses and developers seeking cutting-edge technology and services.
How Google Cloud Competes in the Current Market
Google Cloud competes in the highly competitive cloud computing market by offering a wide range of services, focusing on innovation, and targeting specific audience segments. Google Cloud’s unique selling points include its strong foundation in AI and ML, robust data analytics capabilities, and user-friendly interface. Google Cloud’s target audience includes businesses of all sizes, from startups to large enterprises, as well as individual developers and researchers. The platform’s flexibility and scalability make it an attractive choice for organizations looking to modernize their IT infrastructure, migrate workloads to the cloud, or leverage advanced AI and ML capabilities.
Google Cloud’s market share has been steadily growing, with the company currently holding a strong third-place position behind Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure. Google Cloud’s competitive pricing strategy, commitment to open-source technologies, and strategic partnerships have contributed to its success in the market.
In summary, Google Cloud competes in the current market by emphasizing its innovative technologies, catering to a diverse audience, and continuously improving its offerings to meet the evolving needs of businesses and developers.
The Future of Google Cloud: Trends and Predictions
As the cloud computing landscape continues to evolve, Google Cloud is poised to play a significant role in shaping its future. Several emerging trends and predictions highlight the platform’s potential growth areas and impact on various industries. One key trend is the increasing adoption of multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies, allowing businesses to leverage the strengths of multiple cloud providers and on-premises environments. Google Cloud’s Anthos platform is well-positioned to support this trend, offering a consistent experience across various cloud and on-premises environments.
Another trend is the growing importance of edge computing, which involves processing data closer to the source rather than relying solely on centralized data centers. Google Cloud’s partnership with companies like Ericsson and NVIDIA, as well as its investments in edge computing technologies, indicate its commitment to this emerging field.
Furthermore, the continued growth of AI and ML technologies is expected to drive demand for cloud services capable of handling complex data processing and analysis tasks. Google Cloud’s expertise in AI and ML, as demonstrated by its TensorFlow platform and AutoML tools, position it as a leader in this area.
Lastly, sustainability and environmental responsibility are becoming increasingly important considerations for businesses when choosing a cloud provider. Google Cloud’s commitment to renewable energy and its efforts to minimize the environmental footprint of its data centers and operations demonstrate its dedication to these values.
Assessing Google Cloud’s Environmental Impact
Google Cloud has demonstrated a strong commitment to sustainability and reducing its environmental footprint. The company has been a leader in using renewable energy sources to power its data centers and operations. As of 2021, Google has matched 100% of its global electricity consumption with purchases of renewable energy, making it the first major company to achieve this milestone. Google Cloud’s data centers are designed with energy efficiency in mind, incorporating advanced cooling systems and hardware optimizations to minimize energy consumption. The company has also implemented data center location strategies to take advantage of regions with abundant renewable energy sources, further reducing its carbon footprint.
Google Cloud’s sustainability efforts extend beyond its data centers. The company offers a Carbon-Intelligent Computing service, which automatically shifts compute workloads to the most energy-efficient data centers, further reducing emissions. Additionally, Google Cloud has partnered with organizations like the Renewable Energy Buyers Alliance (REBA) to help businesses transition to renewable energy sources.
Google Cloud’s commitment to sustainability is an essential aspect of its history and ongoing development. By prioritizing environmental responsibility, Google Cloud not only contributes to the global effort to combat climate change but also sets an example for other companies in the cloud computing landscape.
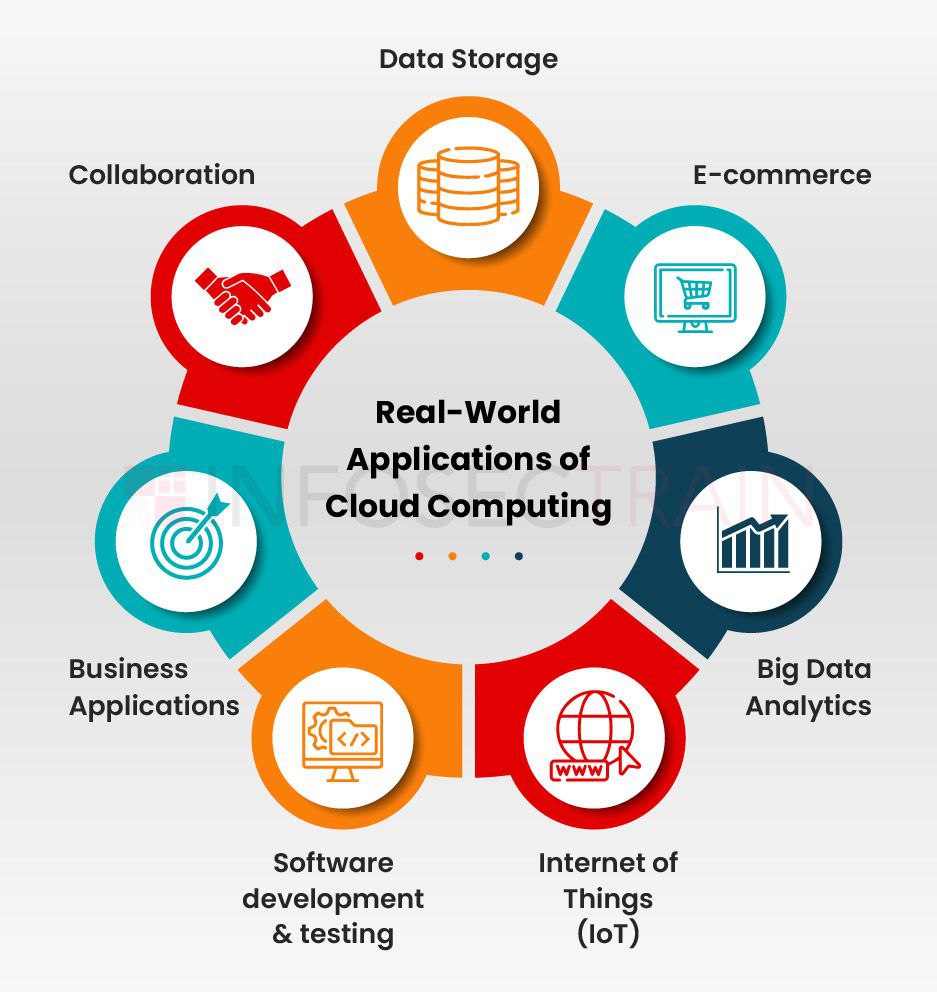
Real-World Applications of Google Cloud: Success Stories and Case Studies
Google Cloud has transformed various industries and scenarios with its innovative solutions and services. This section highlights inspiring success stories and case studies that demonstrate the platform’s potential to drive business growth, improve operational efficiency, and enable digital transformation.
Case Study 1: Media and Entertainment
A prominent media and entertainment company leveraged Google Cloud’s AI and machine learning capabilities to automate the process of video captioning and translation. By implementing Google Cloud’s AutoML Vision and Natural Language APIs, the company significantly reduced manual labor costs and improved accessibility for its global audience.
Case Study 2: Retail
A leading retailer utilized Google Cloud’s data analytics and machine learning tools to optimize its inventory management and supply chain processes. By integrating Google Cloud’s BigQuery and AutoML Tables, the retailer gained valuable insights into customer buying patterns, enabling it to make data-driven decisions and improve overall profitability.
Case Study 3: Healthcare
A healthcare provider harnessed Google Cloud’s AI and machine learning capabilities to develop a predictive analytics model for patient risk assessment. By implementing Google Cloud’s AutoML Tables and AI Platform, the provider improved patient outcomes, reduced hospital readmissions, and enhanced the overall quality of care.
Case Study 4: Manufacturing
A manufacturing company leveraged Google Cloud’s IoT and edge computing solutions to optimize its production processes and reduce equipment downtime. By integrating Google Cloud’s IoT Core and Edge TPU, the company improved operational efficiency, reduced maintenance costs, and increased overall productivity.
These success stories and case studies showcase Google Cloud’s transformative power in various industries and scenarios. By harnessing the platform’s innovative technologies and services, businesses can unlock new growth opportunities, streamline operations, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
Getting Started with Google Cloud: A How-To Guide for Beginners
Google Cloud offers a wide range of services and features, making it an attractive choice for businesses and developers. To help new users get started, this section provides a step-by-step guide to setting up a Google Cloud account, exploring its features, and experimenting with its services.
Step 1: Create a Google Cloud Account
Visit the Google Cloud website (https://cloud.google.com/) and click on the “Try it free” button. Follow the prompts to create a new account, providing your email address, password, and billing information. Note that Google Cloud offers a 90-day free trial with a $300 credit for new users to explore its services.
Step 2: Familiarize Yourself with the Google Cloud Console
Once your account is set up, log in to the Google Cloud Console (https://console.cloud.google.com/). The console provides a user-friendly interface for managing your Google Cloud resources, including virtual machines, databases, and storage buckets. Take some time to explore the various features and options available in the console.
Step 3: Set Up a Project
In the Google Cloud Console, create a new project by clicking on the project drop-down menu and selecting “New Project.” Provide a name and billing information for your project, then click “Create.” This project will serve as a container for your Google Cloud resources, enabling you to organize and manage them more effectively.
Step 4: Explore Google Cloud’s Services
Google Cloud offers a wide range of services, including compute, storage, networking, data analytics, AI and machine learning, and more. To explore these services, navigate to the Google Cloud Console and click on the “Services” drop-down menu. Select a service that interests you and familiarize yourself with its features, documentation, and use cases.
Step 5: Start Experimenting with Google Cloud
Once you have identified a service that you would like to explore further, create a new resource within your project and start experimenting with it. Google Cloud provides extensive documentation, tutorials, and sample code to help you get started. As you become more comfortable with the platform, consider attending Google Cloud events, joining online communities, and engaging with Google Cloud experts to deepen your understanding and expertise.
By following these steps, new users can quickly and easily set up a Google Cloud account, explore its features, and start experimenting with its services. With its innovative technologies, robust ecosystem, and commitment to sustainability, Google Cloud is an excellent choice for businesses and developers looking to drive growth, improve operational efficiency, and minimize their environmental impact.