What is GoldenGate CDC and Why is it Important?
GoldenGate Change Data Capture (CDC) is a powerful real-time data integration tool, enabling organizations to efficiently capture and deliver changes in their data environments. By continuously monitoring and replicating data modifications, GoldenGate CDC ensures data consistency and accuracy, empowering businesses to make informed decisions based on up-to-date information. In today’s data-driven world, GoldenGate CDC plays a critical role in facilitating seamless data flow, supporting mission-critical applications, and driving digital transformation initiatives.
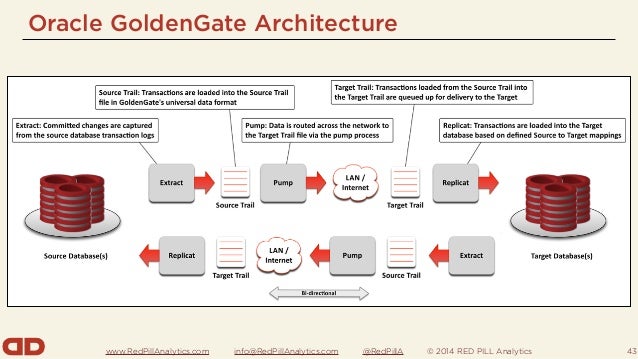
How GoldenGate CDC Works: Key Components and Processes
At the heart of GoldenGate CDC lies a sophisticated architecture designed for capturing, processing, and delivering data changes in real-time. The primary components include extract, transform, and load (ETL) operations, data pump, and trail files. Together, these elements facilitate seamless data replication, ensuring data consistency and accuracy.
The ETL process is the backbone of GoldenGate CDC, responsible for extracting data from source systems, transforming it into a format suitable for the target system, and loading it into the destination. This process enables data to be efficiently transferred between heterogeneous systems, supporting a wide range of data types and platforms.
Data pump is a crucial component that manages the transfer of data between the source and target systems. It handles the movement of data in a unidirectional or bidirectional manner, ensuring that data changes are accurately propagated across the environment. Data pump also supports various replication methods, such as full load, trickle feed, and real-time replication, catering to diverse use cases and performance requirements.
Trail files are another essential element of GoldenGate CDC, storing the extracted data changes in a sequential format. These files serve as the foundation for data replication, allowing GoldenGate to capture, process, and deliver changes with minimal impact on the source systems. By maintaining a record of data modifications, trail files ensure that data consistency is preserved, even in the face of network failures or system outages.
In summary, GoldenGate CDC’s key components and processes work in harmony to provide a robust and efficient real-time data integration solution. Understanding these fundamental elements is crucial for implementing and managing GoldenGate CDC effectively, ensuring seamless data flow and driving digital transformation initiatives.
Setting Up GoldenGate CDC: A Step-by-Step Guide
GoldenGate CDC is a powerful tool for real-time data integration, ensuring data consistency and accuracy by efficiently capturing and delivering changes. To harness its potential, setting it up correctly is crucial. This step-by-step guide covers prerequisites, installation, configuration, and testing, along with real-world examples and best practices.
Prerequisites:
Before starting the setup process, ensure you have:
A source and target system with compatible operating systems.
Oracle database software for both systems.
Sufficient privileges for GoldenGate CDC installation and configuration.
Installation:
Download the GoldenGate CDC software from the Oracle website.
Extract the downloaded files to a suitable directory.
Configure the environment variables for the GoldenGate CDC binaries.
Configuration:
Create a parameter file for the source and target systems, specifying the necessary parameters, such as the source and target databases, extract and replicat processes, and trail file locations.
Initialize the GoldenGate CDC manager process on both systems.
Start the extract and replicat processes on the respective systems.
Testing:
To verify the successful setup, perform the following tests:
Insert, update, and delete records in the source system.
Monitor the trail files for changes.
Check the target system for the corresponding changes.
Best Practices:
Regularly monitor and maintain the GoldenGate CDC processes.
Implement proper error handling and recovery procedures.
Utilize parallel processing for improved performance.
Optimize trail file management for efficient data replication.
By following this comprehensive guide, you can ensure a smooth implementation of GoldenGate CDC, unlocking its potential for real-time data integration in your organization.
Optimizing GoldenGate CDC Performance: Tips and Tricks
GoldenGate CDC is a powerful real-time data integration tool, and optimizing its performance is crucial for data-driven organizations. This section shares expert tips and techniques for enhancing the efficiency of GoldenGate CDC, focusing on trail file management, data pump settings, and parallel processing. Additionally, the importance of regular monitoring and maintenance is discussed.
Managing Trail Files:
Trail files are essential components of GoldenGate CDC, storing captured changes. To optimize performance, consider the following:
Set appropriate trail file sizes and numbers to balance disk space and processing time.
Utilize the CHECKPOINTTABLE parameter to manage trail files more efficiently.
Implement proper backup and recovery procedures for trail files.
Adjusting Data Pump Settings:
Data pumps in GoldenGate CDC can be fine-tuned for better performance:
Adjust the PACE parameter to control the data transfer rate.
Optimize the DISCARDFILE parameter to handle discarded records.
Utilize the GROUPTRANSOPS parameter to group transactions for improved performance.
Leveraging Parallel Processing:
Parallel processing can significantly improve GoldenGate CDC performance:
Implement multiple extract and replicat processes for parallel data transfer.
Use the PARALLEL parameter to specify the number of parallel processes.
Optimize the THROUGHPUT parameter to balance processing speed and resource utilization.
Monitoring and Maintenance:
Regular monitoring and maintenance are vital for optimal GoldenGate CDC performance:
Monitor the performance metrics, such as latency and throughput.
Implement alerts and notifications for performance degradation or errors.
Regularly review and update the configuration parameters based on performance analysis.
By following these tips and tricks, organizations can optimize the performance of their GoldenGate CDC implementations, ensuring real-time data integration and seamless operations.
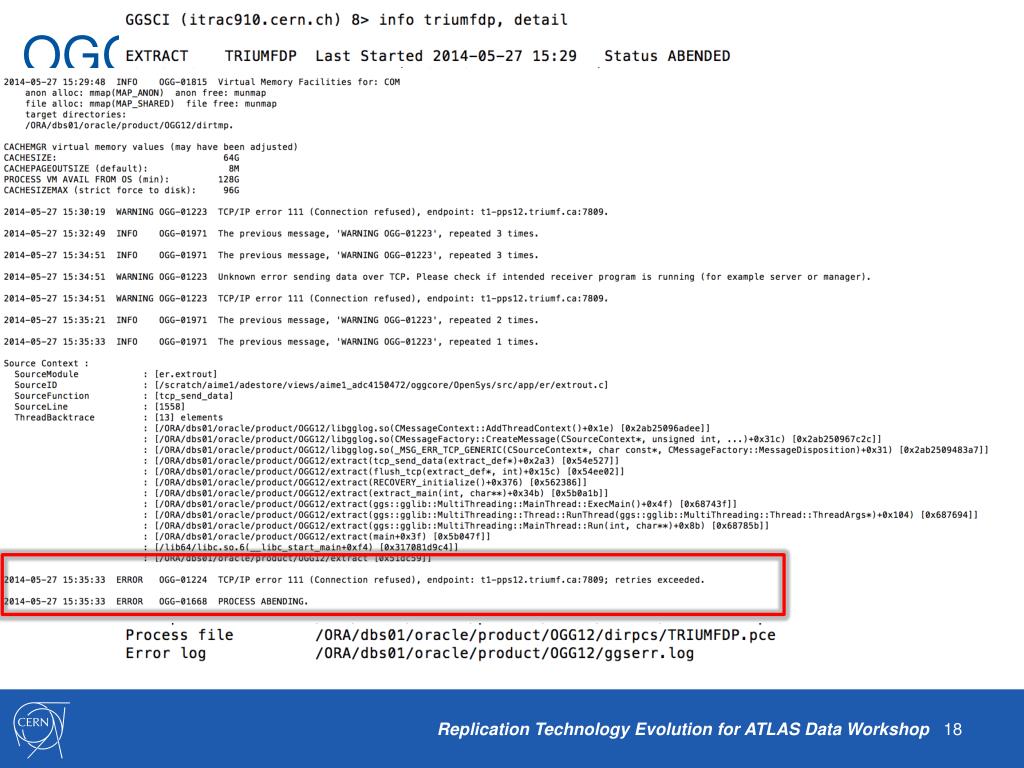
Troubleshooting Common GoldenGate CDC Issues
Implementing and managing GoldenGate CDC can present challenges and issues that, if not addressed promptly, may negatively impact data integration. This section identifies common GoldenGate CDC issues and offers actionable solutions and workarounds, addressing topics like managing latency, handling errors, and resolving data discrepancies.
Managing Latency:
Latency in GoldenGate CDC refers to the time delay between the source and target systems. To manage latency, consider the following:
Optimize trail file management, as excessive trail files can increase latency.
Adjust the data transfer rate using the PACE parameter.
Implement parallel processing to reduce latency.
Handling Errors:
Errors during data replication can lead to data inconsistencies. To handle errors effectively:
Implement error handling procedures using the ERRORMAP parameter.
Utilize the DISCARDFILE parameter to store discarded records for further analysis.
Regularly monitor error logs and performance metrics.
Resolving Data Discrepancies:
Data discrepancies can occur due to various reasons, such as data transformation issues or data corruption. To resolve data discrepancies:
Implement robust data validation procedures.
Use the MAP parameter to define data transformation rules.
Regularly compare source and target data to identify and resolve discrepancies.
By addressing these common issues and implementing best practices, organizations can ensure seamless data integration using GoldenGate CDC and minimize potential disruptions.
Integrating GoldenGate CDC with Other Technologies
GoldenGate CDC can be integrated with various technologies to enhance data integration capabilities and address diverse use cases. This section discusses the benefits and challenges of integrating GoldenGate CDC with data warehouses, big data platforms, and cloud services, providing real-world examples and case studies.
Integrating GoldenGate CDC with Data Warehouses:
Data warehouses can benefit from real-time data updates provided by GoldenGate CDC. By integrating both systems, organizations can:
Improve data freshness and accuracy.
Enable near-real-time analytics and reporting.
Reduce data latency and ETL processing time.
For example, Oracle Exadata can be integrated with GoldenGate CDC to provide real-time data warehousing capabilities.
Integrating GoldenGate CDC with Big Data Platforms:
GoldenGate CDC can be used to stream data into big data platforms, such as Hadoop or Apache Kafka, for further processing and analysis. Key benefits include:
Seamless data ingestion from various sources.
Real-time data processing and analysis.
Scalability and fault-tolerance.
Integrating GoldenGate CDC with Cloud Services:
Cloud services, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure, can be integrated with GoldenGate CDC for various purposes:
Data replication between on-premises and cloud systems.
Real-time data integration for cloud-based analytics and machine learning.
Disaster recovery and high availability solutions.
For instance, Oracle GoldenGate for Big Data can be used to integrate Oracle databases with Apache Hadoop on AWS.
By integrating GoldenGate CDC with other technologies, organizations can unlock new possibilities for data integration, analytics, and real-time decision-making. However, careful planning and consideration are required to address challenges such as data compatibility, security, and system complexity.
The Future of GoldenGate CDC: Trends and Predictions
GoldenGate CDC has been a vital tool for real-time data integration, and its significance will continue to grow as data-driven organizations adapt to emerging trends. This section discusses the future of GoldenGate CDC, focusing on the increasing importance of real-time data, the growth of cloud-based solutions, and the role of artificial intelligence in data integration.
Real-time Data Integration:
The demand for real-time data integration is growing, as businesses seek to make quicker, more informed decisions. GoldenGate CDC can help organizations meet this need by providing:
Seamless, near-real-time data replication.
Improved data consistency and accuracy.
Enhanced data-driven decision-making capabilities.
Cloud-based Solutions:
Cloud adoption is on the rise, and GoldenGate CDC can be leveraged to facilitate data integration between on-premises and cloud systems. Key trends include:
Hybrid cloud environments.
Data replication for disaster recovery and high availability.
Real-time data integration for cloud-based analytics and machine learning.
Artificial Intelligence:
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are becoming increasingly important in data integration. GoldenGate CDC can benefit from AI/ML in several ways:
Automated issue detection and resolution.
Intelligent data transformation and mapping.
Predictive analytics for performance optimization.
By staying up-to-date with these trends and incorporating them into their GoldenGate CDC strategies, organizations can ensure they are well-positioned to harness the full potential of real-time data integration.

Conclusion: Embracing the Power of GoldenGate CDC
GoldenGate CDC has proven to be an invaluable tool for real-time data integration, addressing the needs of modern data-driven organizations. By capturing and delivering changes efficiently, GoldenGate CDC ensures data consistency and accuracy, empowering businesses to make informed decisions based on up-to-date information.
Understanding the key components and processes of GoldenGate CDC, such as ETL operations, data pump, and trail files, is essential for a successful implementation. Following a step-by-step guide, including prerequisites, installation, configuration, and testing, can help ensure a smooth setup process.
Optimizing GoldenGate CDC performance is crucial for maintaining efficiency and addressing potential challenges. Techniques such as managing trail files, adjusting data pump settings, and leveraging parallel processing can significantly improve performance. Regular monitoring and maintenance are also essential to ensure optimal performance.
Troubleshooting common GoldenGate CDC issues, like managing latency, handling errors, and resolving data discrepancies, requires a proactive approach. Identifying potential problems and implementing actionable solutions and workarounds can help maintain data consistency and accuracy.
Integrating GoldenGate CDC with other technologies, such as data warehouses, big data platforms, and cloud services, offers numerous benefits and opportunities. However, careful planning and consideration are required to address challenges and ensure seamless integration.
The future of GoldenGate CDC is promising, with emerging trends like the increasing importance of real-time data, the growth of cloud-based solutions, and the role of artificial intelligence in data integration. Staying informed and adapting to these trends will help organizations maximize the potential of their GoldenGate CDC implementations.
In conclusion, embracing the power of GoldenGate CDC can significantly enhance real-time data integration capabilities. By understanding its key components, optimizing performance, troubleshooting issues, and integrating with other technologies, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data-driven strategies. Staying up-to-date with the latest developments in data integration technologies, including GoldenGate CDC, is vital for success in today’s fast-paced, data-driven world.
