Mastering Agile Estimation: A Comprehensive Guide to Scrum Estimation
The Role of Estimation in Scrum Project Management
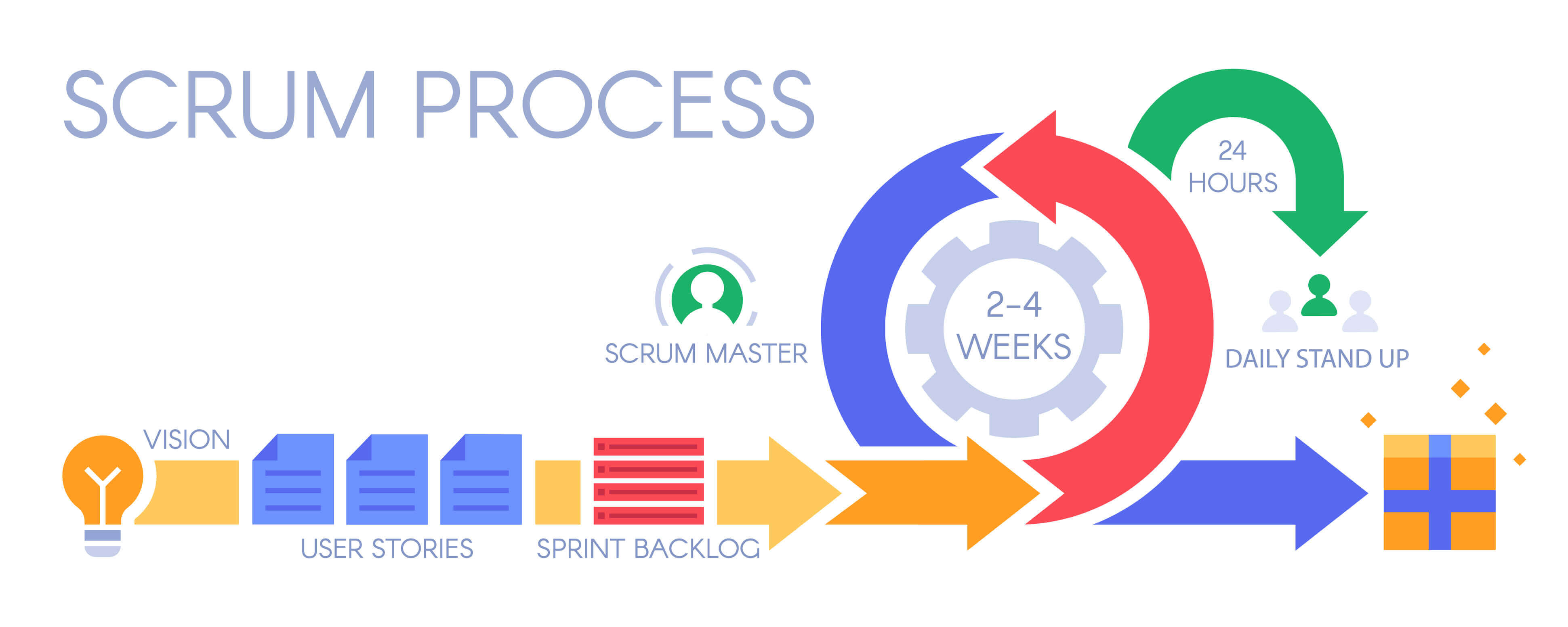
Estimation in Scrum plays a crucial role in project management, enabling teams to plan sprints, allocate resources, and track progress effectively. By assigning story points to user stories, teams can create a shared understanding of the effort required to complete each task. Story points provide a more abstract and flexible measurement than hours, allowing teams to account for complexity, uncertainty, and risk. Accurate estimations in Scrum contribute to better velocity tracking, improved predictability, and enhanced overall project management.
How to Implement Effective Estimation Techniques in Scrum
When implementing estimation techniques in Scrum, teams can choose from various methods, such as Planning Poker, Wideband Delphi, and T-shirt sizing. Each method has its benefits and drawbacks, and the choice depends on the team’s preferences and project requirements. For example, Planning Poker is a collaborative approach that encourages team members to reach a consensus on story point values, while Wideband Delphi relies on expert judgment and multiple rounds of anonymous estimation. T-shirt sizing, on the other hand, is a more straightforward method that uses relative sizing to estimate user stories.
Planning Poker: A Collaborative Approach to Scrum Estimation
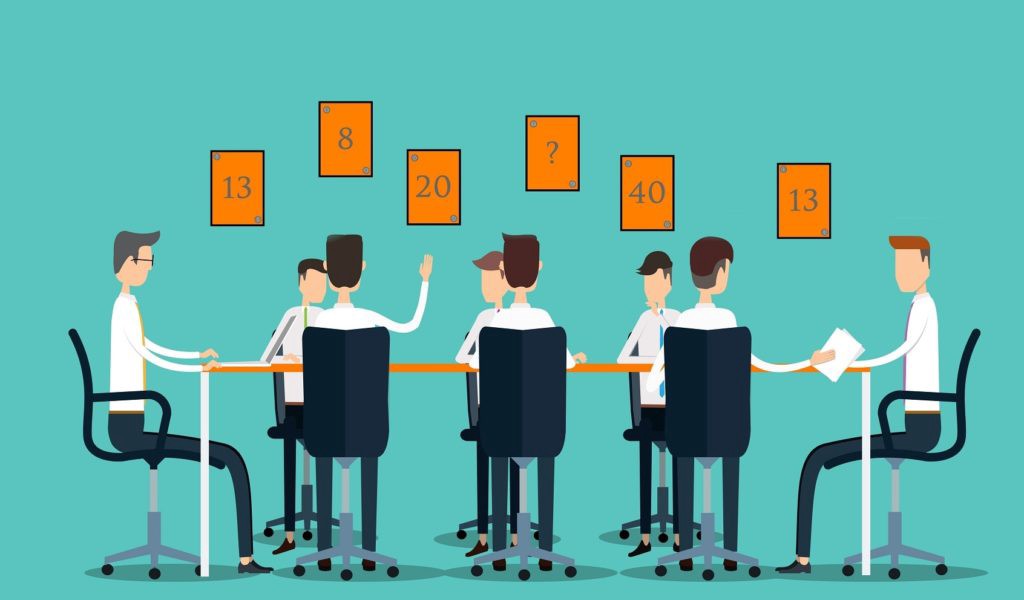
Planning Poker is a popular estimation technique in Scrum that involves team members collaborating to assign story points to user stories. The process begins with the team discussing the user story and its requirements. Each team member then privately selects a story point value that reflects their understanding of the effort required to complete the task. The team then reveals their estimates simultaneously, and if there is disagreement, they discuss the reasons for the discrepancy and re-estimate until they reach a consensus.
Dealing with Estimation Uncertainty in Scrum
Estimation uncertainty is an inherent challenge in Scrum estimation, as teams often face changing requirements, incomplete information, and unforeseen obstacles. To address estimation uncertainty, teams should focus on continuous improvement, learning from past experiences, and incorporating feedback into the estimation process. By regularly reviewing their estimations and adjusting their techniques, teams can improve their accuracy and reduce uncertainty over time.
The Impact of Changing Requirements on Scrum Estimation
Changing requirements can significantly affect Scrum estimation, as new information or shifting priorities can impact the effort required to complete user stories. To maintain accurate estimations and meet project goals, teams should embrace techniques such as re-estimation and re-prioritization. By regularly reassessing their estimations and adapting to changing requirements, teams can ensure that their efforts align with project objectives and stakeholder expectations.
Monitoring and Adjusting Scrum Estimations: Best Practices
Effective monitoring and adjusting of Scrum estimations involve best practices such as regular sprint reviews, retrospectives, and stakeholder communication. Transparency and continuous improvement are essential in the estimation process, as teams should strive to learn from their experiences and refine their techniques. By fostering a culture of openness and collaboration, teams can improve their estimation accuracy and enhance their overall project management capabilities.
Real-World Applications: Case Studies of Scrum Estimation
Scrum estimation techniques have been successfully implemented in various industries and teams, leading to improved project outcomes and better resource allocation. By examining real-world case studies and lessons learned, teams can gain valuable insights into the practical application of Scrum estimation and identify strategies that can be adapted to their unique contexts.
Overcoming Common Pitfalls in Scrum Estimation
Common pitfalls in Scrum estimation include unrealistic expectations, lack of team involvement, and insufficient refinement of the estimation process. To overcome these challenges, teams should focus on setting realistic expectations, involving the entire team in the estimation process, and continuously refining their techniques. By fostering a culture of collaboration, learning, and improvement, teams can enhance their Scrum estimation capabilities and achieve better project outcomes.
Mastering Agile Estimation: A Comprehensive Guide to Scrum Estimation
How to Implement Effective Estimation Techniques in Scrum
When implementing Scrum estimation techniques, teams can choose from various methods, each with its benefits and drawbacks. Selecting the right method depends on the team’s preferences and project requirements. Here are three popular estimation techniques in Scrum:
Planning Poker
Planning Poker is a collaborative approach that encourages team members to reach a consensus on story point values. The process involves each team member privately selecting a story point value that reflects their understanding of the effort required to complete the task. The team then reveals their estimates simultaneously, and if there is disagreement, they discuss the reasons for the discrepancy and re-estimate until they reach a consensus.
Wideband Delphi
Wideband Delphi is another estimation technique that relies on expert judgment and multiple rounds of anonymous estimation. After each round, the team discusses the estimates and the reasoning behind them, and then proceeds to the next round until a consensus is reached. This method is useful when dealing with complex or uncertain tasks, as it allows for a more thorough analysis of the effort required.
T-shirt sizing
T-shirt sizing is a more straightforward method that uses relative sizing to estimate user stories. The team assigns sizes such as XS, S, M, L, XL to user stories based on their relative effort. This method is useful for teams new to Scrum estimation, as it provides a simple and intuitive way to estimate tasks without getting bogged down in the details.
Planning Poker: A Collaborative Approach to Scrum Estimation
Planning Poker is a popular estimation technique in Scrum due to its collaborative nature. This method encourages team members to share their perspectives and reach a consensus on story point values. By involving the entire team in the estimation process, Planning Poker helps to ensure that everyone has a shared understanding of the effort required to complete each task. This, in turn, can lead to more accurate estimations and improved project outcomes.
Dealing with Estimation Uncertainty in Scrum
Estimation uncertainty is a common challenge in Scrum estimation. To address this challenge, teams should focus on continuous improvement, learning from past experiences, and incorporating feedback into the estimation process. By regularly reviewing their estimations and adjusting their techniques, teams can improve their accuracy and reduce uncertainty over time.
The Impact of Changing Requirements on Scrum Estimation
Changing requirements can significantly affect Scrum estimation. To maintain accurate estimations and meet project goals, teams should embrace techniques such as re-estimation and re-prioritization. By regularly reassessing their estimations and adapting to changing requirements, teams can ensure that their efforts align with project objectives and stakeholder expectations.
Monitoring and Adjusting Scrum Estimations: Best Practices
Effective monitoring and adjusting of Scrum estimations involve best practices such as regular sprint reviews, retrospectives, and stakeholder communication. Transparency and continuous improvement are essential in the estimation process, as teams should strive to learn from their experiences and refine their techniques. By fostering a culture of openness and collaboration, teams can improve their estimation accuracy and enhance their overall project management capabilities.
Real-World Applications: Case Studies of Scrum Estimation
Scrum estimation techniques have been successfully implemented in various industries and teams, leading to improved project outcomes and better resource allocation. By examining real-world case studies and lessons learned, teams can gain valuable insights into the practical application of Scrum estimation and identify strategies that can be adapted to their unique contexts.
Overcoming Common Pitfalls in Scrum Estimation
Common pitfalls in Scrum estimation include unrealistic expectations, lack of team involvement, and insufficient refinement of the estimation process. To overcome these challenges, teams should focus on setting realistic expectations, involving the entire team, and continuously refining their techniques. By fostering a culture of collaboration, learning, and improvement, teams can enhance their Scrum estimation capabilities and achieve better project outcomes.
Mastering Agile Estimation: A Comprehensive Guide to Scrum Estimation
Planning Poker: A Collaborative Approach to Scrum Estimation
Planning Poker is a widely-used estimation technique in Scrum that encourages team collaboration and consensus-building. This method involves team members estimating the effort required to complete user stories or tasks by assigning story points, which are relative units of measure that consider complexity, uncertainty, and risk.
The Benefits of Planning Poker
Planning Poker offers several benefits, including:
- Encouraging team collaboration and communication
- Promoting a shared understanding of the effort required to complete tasks
- Reducing the impact of individual biases and assumptions
- Providing a structured and consistent approach to estimation
The Planning Poker Process
The Planning Poker process typically involves the following steps:
- A team member facilitates the Planning Poker session and presents a user story or task to the team.
- Each team member privately selects a story point value that reflects their understanding of the effort required to complete the task.
- The team members reveal their estimates simultaneously.
- If there is disagreement, the team members discuss the reasons for the discrepancy and share their perspectives.
- The team then re-estimates the task until they reach a consensus.
Tools for Planning Poker
There are various tools available that can facilitate Planning Poker sessions, including:
- Physical Planning Poker cards
- Online Planning Poker tools, such as Scrumwise, Planbox, and Scrum Poker
Dealing with Estimation Uncertainty in Scrum
Estimation uncertainty is a common challenge in Scrum estimation. To address this challenge, teams should focus on continuous improvement, learning from past experiences, and incorporating feedback into the estimation process. By regularly reviewing their estimations and adjusting their techniques, teams can improve their accuracy and reduce uncertainty over time.
The Impact of Changing Requirements on Scrum Estimation
Changing requirements can significantly affect Scrum estimation. To maintain accurate estimations and meet project goals, teams should embrace techniques such as re-estimation and re-prioritization. By regularly reassessing their estimations and adapting to changing requirements, teams can ensure that their efforts align with project objectives and stakeholder expectations.
Monitoring and Adjusting Scrum Estimations: Best Practices
Effective monitoring and adjusting of Scrum estimations involve best practices such as regular sprint reviews, retrospectives, and stakeholder communication. Transparency and continuous improvement are essential in the estimation process, as teams should strive to learn from their experiences and refine their techniques. By fostering a culture of openness and collaboration, teams can improve their estimation accuracy and enhance their overall project management capabilities.
Real-World Applications: Case Studies of Scrum Estimation
Scrum estimation techniques have been successfully implemented in various industries and teams, leading to improved project outcomes and better resource allocation. By examining real-world case studies and lessons learned, teams can gain valuable insights into the practical application of Scrum estimation and identify strategies that can be adapted to their unique contexts.
Overcoming Common Pitfalls in Scrum Estimation
Common pitfalls in Scrum estimation include unrealistic expectations, lack of team involvement, and insufficient refinement of the estimation process. To overcome these challenges, teams should focus on setting realistic expectations, involving the entire team, and continuously refining their techniques. By fostering a culture of collaboration, learning, and improvement, teams can enhance their Scrum estimation capabilities and achieve better project outcomes.
Mastering Agile Estimation: A Comprehensive Guide to Scrum Estimation
Dealing with Estimation Uncertainty in Scrum
Estimation uncertainty is a common challenge in Scrum estimation. Despite a team’s best efforts to estimate user stories accurately, unforeseen challenges and changing requirements can impact the accuracy of these estimates. To address this challenge, Scrum teams should focus on continuous improvement, learning from past experiences, and incorporating feedback into the estimation process.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is the practice of regularly reviewing and refining processes, techniques, and tools to improve efficiency, accuracy, and effectiveness. In the context of Scrum estimation, continuous improvement involves:
- Regularly reviewing past estimates and comparing them to actual results
- Identifying patterns and trends in estimation errors
- Incorporating lessons learned into future estimates
- Refining estimation techniques and tools based on feedback and experience
Learning from Past Experiences
Learning from past experiences involves reflecting on past estimates and identifying areas for improvement. This process can involve:
- Conducting retrospectives to identify estimation errors and their causes
- Sharing lessons learned with the team and stakeholders
- Updating documentation and training materials to reflect new insights and best practices
Incorporating Feedback
Incorporating feedback involves soliciting input from team members, stakeholders, and other relevant parties to improve the estimation process. This can involve:
- Encouraging open and honest communication
- Providing opportunities for team members to share their perspectives and insights
- Incorporating feedback into the estimation process and tools
The Importance of Continuous Improvement, Learning, and Feedback
Continuous improvement, learning from past experiences, and incorporating feedback are essential components of effective Scrum estimation. By focusing on these areas, Scrum teams can improve their estimation accuracy, reduce uncertainty, and enhance their overall project management capabilities. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, learning, and feedback, Scrum teams can achieve better project outcomes and deliver greater value to stakeholders.
The Impact of Changing Requirements on Scrum Estimation
Changing requirements can significantly affect Scrum estimation. To maintain accurate estimations and meet project goals, Scrum teams should embrace techniques such as re-estimation and re-prioritization. By regularly reassessing their estimations and adapting to changing requirements, Scrum teams can ensure that their efforts align with project objectives and stakeholder expectations.
Monitoring and Adjusting Scrum Estimations: Best Practices
Effective monitoring and adjusting of Scrum estimations involve best practices such as regular sprint reviews, retrospectives, and stakeholder communication. Transparency and continuous improvement are essential in the estimation process, as teams should strive to learn from their experiences and refine their techniques.
Real-World Applications: Case Studies of Scrum Estimation
Scrum estimation techniques have been successfully implemented in various industries and teams, leading to improved project outcomes and better resource allocation. By examining real-world case studies and lessons learned, teams can gain valuable insights into the practical application of Scrum estimation and identify strategies that can be adapted to their unique contexts.
Overcoming Common Pitfalls in Scrum Estimation
Common pitfalls in Scrum estimation include unrealistic expectations, lack of team involvement, and insufficient refinement of the estimation process. To overcome these challenges, teams should focus on setting realistic expectations, involving the entire team, and continuously refining the estimation process.
The Impact of Changing Requirements on Scrum Estimation
In the dynamic world of Agile project management, changing requirements are a common occurrence. The flexibility to adapt to these changes is one of the primary advantages of using Scrum methodologies. However, evolving requirements can significantly impact estimation in Scrum, making it crucial to have effective strategies in place to manage such situations. This article will discuss techniques for handling changing requirements and maintaining accurate estimations to meet project goals.
Scrum teams rely on initial estimates to plan sprints and allocate resources. However, changing requirements can introduce uncertainty into the estimation process. To address this challenge, Scrum teams should embrace adaptability and incorporate techniques such as re-estimation and re-prioritization. These strategies help maintain accurate estimations and ensure that the team remains on track to achieve project goals despite shifting requirements.
Re-estimation: Updating Estimates Based on Changing Requirements
Re-estimation is the process of updating initial estimates based on new information or changing requirements. This technique allows Scrum teams to maintain accurate estimations throughout the project lifecycle. Re-estimation can be performed during sprint planning, sprint reviews, or any time new information becomes available. By updating estimates regularly, Scrum teams can ensure that their plans remain relevant and aligned with the project’s evolving needs.
Re-prioritization: Adjusting the Backlog to Accommodate Changing Requirements
Re-prioritization involves adjusting the product backlog to accommodate changing requirements. By reassessing the priority of user stories, Scrum teams can ensure that the most critical and up-to-date features are addressed first. Regular backlog grooming sessions can help teams stay on top of changing requirements and maintain an accurate understanding of the project’s scope and direction. Re-prioritization also enables Scrum teams to adapt their estimations to better align with the current state of the project.
Continuous Improvement and Learning
Continuous improvement and learning are essential components of effective Scrum estimation. By regularly reviewing past estimations and incorporating lessons learned into future planning, Scrum teams can enhance their estimation skills and better adapt to changing requirements. This ongoing process of refinement helps teams become more adept at managing uncertainty and maintaining accurate estimations, even as requirements evolve.
Communication and Collaboration
Clear and consistent communication between the Scrum team, stakeholders, and product owners is vital for managing changing requirements. Regular stakeholder meetings and sprint reviews help ensure that all parties are aligned on project goals, priorities, and estimations. By fostering a collaborative environment, Scrum teams can more effectively adapt to changing requirements and maintain accurate estimations throughout the project lifecycle.
Monitoring and Adjusting Scrum Estimations: Best Practices
Accurate estimation in Scrum is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and adjustment. By incorporating best practices for tracking and refining estimations, Scrum teams can ensure that their plans remain relevant and aligned with the project’s evolving needs. This article will discuss essential strategies for monitoring and adjusting Scrum estimations, emphasizing transparency and continuous improvement.
Regular Sprint Reviews
Regular sprint reviews are a critical component of effective Scrum estimation. These meetings provide an opportunity for the Scrum team to assess the accuracy of their initial estimations and make necessary adjustments. By reviewing completed user stories and comparing actual time spent to initial estimates, teams can identify patterns and trends that inform future estimations. Regular sprint reviews also foster a culture of transparency and continuous improvement, enabling teams to refine their estimation skills over time.
Sprint Retrospectives
Sprint retrospectives offer Scrum teams an opportunity to reflect on their estimation practices and identify areas for improvement. By examining what worked well and what didn’t during the sprint, teams can make data-driven decisions about how to refine their estimation process. Sprint retrospectives also encourage open communication and collaboration, helping to build trust and cohesion within the team. By incorporating lessons learned into future planning, Scrum teams can enhance their estimation accuracy and better adapt to changing project requirements.
Stakeholder Communication
Clear and consistent communication with stakeholders is vital for managing expectations and ensuring alignment on project goals and estimations. Regular stakeholder meetings and progress updates help maintain transparency and trust, enabling teams to adapt their estimations as needed to accommodate changing requirements. By involving stakeholders in the estimation process, Scrum teams can foster a shared understanding of project priorities and better manage expectations around timelines and resource allocation.
Continuous Improvement and Learning
Continuous improvement and learning are essential components of effective Scrum estimation. By regularly reviewing past estimations and incorporating lessons learned into future planning, Scrum teams can enhance their estimation skills and better adapt to changing project needs. This ongoing process of refinement helps teams become more adept at managing uncertainty and maintaining accurate estimations, even as requirements evolve.
Embracing Change
In the dynamic world of Agile project management, the ability to adapt to changing requirements is crucial. By embracing change and incorporating techniques such as re-estimation and re-prioritization, Scrum teams can maintain accurate estimations and ensure that their plans remain relevant and aligned with the project’s evolving needs. This flexibility is a key advantage of using Scrum methodologies and can help teams deliver high-quality products that meet user needs and expectations.
Real-World Applications: Case Studies of Scrum Estimation
Scrum estimation techniques have been successfully implemented across various industries and teams, leading to improved project outcomes and increased efficiency. This article will explore real-world examples of Scrum estimation in action, highlighting successful case studies and lessons learned.
Case Study 1: Software Development Firm
A software development firm adopted Planning Poker to estimate user stories for a complex web application project. By involving the entire team in the estimation process, the company was able to leverage diverse perspectives and expertise, resulting in more accurate estimations and improved sprint planning. The team also used regular sprint reviews and retrospectives to refine their estimation process, leading to continuous improvement and enhanced collaboration.
Case Study 2: Digital Marketing Agency
A digital marketing agency implemented T-shirt sizing for high-level estimations of marketing campaigns. By using simple, intuitive categories (e.g., XS, S, M, L, XL), the team could quickly and efficiently estimate the effort required for each campaign. This approach allowed the agency to allocate resources more effectively and provide clients with more accurate timelines, leading to increased client satisfaction and trust.
Case Study 3: Manufacturing Company
A manufacturing company used Wideband Delphi to estimate the time and resources required for new product development. By incorporating feedback from various stakeholders, including engineers, designers, and marketing professionals, the team was able to create more accurate estimations and identify potential risks and challenges early in the process. This collaborative approach helped the company streamline its product development cycle and reduce time-to-market.
Lessons Learned
These case studies demonstrate the value of effective Scrum estimation techniques in various industries and contexts. Key takeaways include:
- Involving the entire team in the estimation process can lead to more accurate estimations and improved collaboration.
- Using simple, intuitive estimation methods can help teams quickly and efficiently estimate effort, enabling better resource allocation and client communication.
- Collaborative estimation techniques, such as Wideband Delphi, can help identify potential risks and challenges early in the project lifecycle, enabling teams to proactively address issues and streamline processes.
- Regular sprint reviews and retrospectives are essential for continuous improvement and refining the estimation process over time.
By learning from these real-world examples, Scrum teams can implement effective estimation techniques to improve project outcomes and enhance their Agile practice.
Overcoming Common Pitfalls in Scrum Estimation
While Scrum estimation techniques can significantly improve project outcomes, teams may encounter various challenges throughout the estimation process. Identifying and addressing these common pitfalls is essential for continuous improvement and ensuring the long-term success of Scrum estimation. This article will discuss common issues in Scrum estimation and offer strategies to overcome them.
Setting Unrealistic Expectations
Unrealistic expectations can lead to inaccurate estimations and decreased team morale. To avoid this pitfall, it’s crucial to establish a culture of transparency and trust, where team members feel comfortable providing honest assessments of effort and time requirements. Encourage the use of data-driven estimation techniques, such as Planning Poker and Wideband Delphi, to ensure that estimations are grounded in objective information and consensus.
Lack of Team Involvement
Excluding team members from the estimation process can result in inaccurate estimations and missed opportunities for collaboration. To prevent this, involve the entire Scrum team in estimation activities, leveraging their diverse perspectives and expertise to create more accurate estimations. Encourage open communication and active participation, ensuring that all team members have a voice in the estimation process.
Insufficient Historical Data
Without adequate historical data, Scrum teams may struggle to create accurate estimations. To address this, maintain a comprehensive database of past project data, including completed user stories, time spent, and story point values. Regularly review and analyze this data to inform future estimations, incorporating lessons learned into the estimation process.
Inconsistent Estimation Techniques
Inconsistent estimation techniques can lead to confusion and inaccurate estimations. To avoid this, establish a standardized estimation process, using techniques such as Planning Poker, Wideband Delphi, or T-shirt sizing consistently across projects and teams. Provide training and resources to ensure that all team members understand and can effectively apply these techniques.
Continuous Improvement and Refinement
Effective Scrum estimation requires continuous improvement and refinement. Regularly review and adjust the estimation process, incorporating feedback from team members and stakeholders. Encourage experimentation with new estimation techniques and tools, and be open to adapting the process as needed to better meet the team’s needs and goals.
By addressing these common pitfalls and implementing strategies to overcome them, Scrum teams can enhance their estimation accuracy, foster collaboration, and improve project outcomes. Emphasize the importance of transparency, continuous improvement, and team involvement to create a culture where Scrum estimation thrives and delivers value to the organization.