Understanding the Shared Responsibility Model in Cloud Computing
In the era of digital transformation, cloud computing has become an integral part of businesses and personal lives. However, the increasing reliance on cloud services has raised concerns over data privacy and security. To ensure privacy in cloud solutions, it is essential to understand the shared responsibility model, where both the cloud service provider and the user share the responsibility of maintaining data privacy and security. This model impacts the overall data protection strategy, and understanding it can help users make informed decisions.
The shared responsibility model consists of three layers of security: infrastructure, platform, and application. The cloud service provider is responsible for the infrastructure layer, which includes physical security, network security, and virtualization security. The provider also ensures the availability and performance of the infrastructure.
The platform layer is shared between the provider and the user. The provider is responsible for the security of the underlying platform, while the user is responsible for securing the applications and data running on the platform. This includes configuring the security settings, managing access controls, and implementing data encryption.
The application layer is the user’s responsibility, which includes securing the applications, data, and user access. The user must implement security measures such as access control policies, data encryption, and monitoring and logging user activities.
Understanding the shared responsibility model is crucial for ensuring privacy in cloud solutions. By knowing who is responsible for what, users can implement appropriate security measures and make informed decisions about their cloud services.

Implementing Robust Access Control Policies in Cloud Solutions
Ensuring privacy in cloud solutions requires robust access control policies. Access control mechanisms, such as identity and access management (IAM), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and role-based access control (RBAC), help prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
Identity and access management (IAM) is a framework for managing user identities and access to resources. IAM allows administrators to create and manage user accounts, assign permissions, and monitor user activities. By implementing IAM, organizations can ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive data and applications.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security mechanism that requires users to provide two or more forms of authentication to access a resource. MFA can include something the user knows, such as a password, something the user has, such as a security token, or something the user is, such as a biometric factor. By implementing MFA, organizations can reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Role-based access control (RBAC) is a security mechanism that restricts access to resources based on the user’s role within the organization. RBAC allows administrators to define roles and assign permissions to those roles. By implementing RBAC, organizations can ensure that users only have access to the resources necessary for their job functions.
Implementing robust access control policies is essential for ensuring privacy in cloud solutions. By using IAM, MFA, and RBAC, organizations can prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
Encrypting Data at Rest and in Transit in Cloud Computing
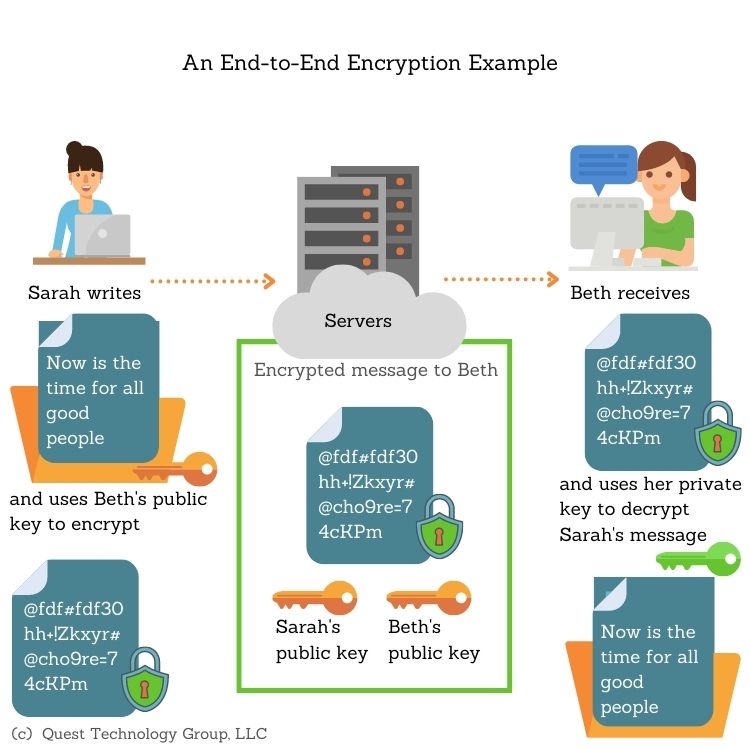
Ensuring privacy in cloud solutions requires robust data encryption strategies. Data encryption can protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, both at rest and in transit. In cloud computing, data is often transmitted between different layers of security, including infrastructure, platform, and application. Therefore, it is crucial to implement encryption techniques to secure data throughout its lifecycle.
Data encryption is the process of converting plain text into a coded format that can only be accessed with a decryption key. There are two main types of encryption techniques: symmetric and asymmetric encryption.
Symmetric encryption uses the same key for encryption and decryption. It is a faster and more efficient method but requires secure key management. Examples of symmetric encryption algorithms include Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and Data Encryption Standard (DES).
Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key encryption, uses two different keys for encryption and decryption. One key, the public key, is used for encryption, while the other key, the private key, is used for decryption. Asymmetric encryption is more secure than symmetric encryption but is slower and less efficient. Examples of asymmetric encryption algorithms include Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC).
In cloud computing, data encryption can be applied in different scenarios. For instance, data at rest can be encrypted using disk encryption techniques, such as whole-disk encryption or file-level encryption. Data in transit can be encrypted using secure communication protocols, such as Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) or Transport Layer Security (TLS).
Various cloud service providers offer encryption services as part of their security features. However, it is essential to understand the encryption key management policies and ensure that the encryption keys are stored securely.
Implementing robust data encryption strategies is crucial for ensuring privacy in cloud solutions. By using encryption techniques, organizations can protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, both at rest and in transit.
Monitoring and Logging User Activities in Cloud Solutions
Ensuring privacy in cloud solutions requires continuous monitoring and logging of user activities. Monitoring and logging can help detect and respond to security threats, such as unauthorized access, data breaches, and insider threats. By analyzing user activities, organizations can identify suspicious behavior patterns and take appropriate action to prevent security incidents.
Monitoring and logging user activities involve tracking user actions, such as login attempts, data access, and system changes. Cloud service providers offer various monitoring and logging tools, such as cloud-based security information and event management (SIEM) systems, to help organizations monitor user activities.
SIEM systems collect and aggregate log data from various sources, such as firewalls, servers, and applications, and analyze the data to detect security threats. SIEM systems can also generate alerts and reports to help organizations respond to security incidents.
Monitoring and logging user activities can help organizations comply with regulatory requirements, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). These regulations require organizations to maintain logs of user activities and provide evidence of data privacy and security.
However, monitoring and logging user activities can also raise privacy concerns. Organizations must ensure that they only collect and store the necessary data and use it for legitimate purposes. Organizations must also provide notice and obtain consent from users before collecting and storing their data.
Implementing robust monitoring and logging policies can help organizations maintain data privacy and security in cloud solutions. By monitoring and logging user activities, organizations can detect and respond to security threats, comply with regulatory requirements, and build trust with their users.
Implementing Data Backup and Disaster Recovery Strategies
In the context of ensuring privacy in cloud solutions, implementing data backup and disaster recovery strategies is of paramount importance. As businesses and individuals increasingly rely on cloud services to store and process sensitive information, the risk of data loss and downtime due to security breaches or system failures becomes more significant. Therefore, having a robust data backup and disaster recovery plan in place can help prevent data loss and minimize the impact of security incidents on business operations.
Data backup and disaster recovery strategies involve creating copies of data and applications and storing them in a secure location, such as a secondary data center or a cloud-based storage service. This allows organizations to quickly restore their operations in the event of a security breach or system failure, thereby minimizing the impact of the incident on their business operations and reputation.
There are various data backup and disaster recovery techniques that organizations can use in cloud solutions. Snapshots, for instance, are point-in-time copies of data and applications that can be taken at regular intervals. These snapshots can be used to quickly restore data and applications to a previous state in the event of a security breach or system failure. Replication, on the other hand, involves creating copies of data and applications and storing them in a secondary location, such as a secondary data center or a cloud-based storage service. This allows organizations to quickly switch to the secondary location in the event of a failure, thereby minimizing downtime.
Archiving is another data backup and disaster recovery technique that involves storing older data and applications in a secure location for long-term retention. This can help organizations meet regulatory requirements and ensure that they have access to historical data in the event of a legal dispute or audit. In addition, archiving can help organizations free up storage space in their primary data center or cloud-based storage service, thereby reducing costs.
When implementing data backup and disaster recovery strategies in cloud solutions, it is important to consider various factors, such as the cost of storage, the frequency of backups, and the recovery time objective (RTO) and recovery point objective (RPO). The RTO is the target time within which business operations must be restored after a failure, while the RPO is the maximum acceptable amount of data loss. By considering these factors, organizations can ensure that their data backup and disaster recovery strategies are aligned with their business needs and objectives.
In conclusion, implementing data backup and disaster recovery strategies is a critical component of ensuring privacy in cloud solutions. By creating copies of data and applications and storing them in a secure location, organizations can quickly restore their operations in the event of a security breach or system failure, thereby minimizing the impact of the incident on their business operations and reputation. When implementing these strategies, it is important to consider various factors, such as the cost of storage, the frequency of backups, and the RTO and RPO, to ensure that they are aligned with the organization’s business needs and objectives.
Choosing the Right Cloud Service Provider
When it comes to ensuring privacy in cloud solutions, selecting the right cloud service provider is a critical decision. Cloud service providers play a significant role in maintaining data privacy and security, and as such, users must carefully evaluate their options before choosing a provider. In this context, we will discuss the factors to consider when choosing a cloud service provider and how the provider’s security policies, certifications, and compliance can impact the overall data protection strategy.
First and foremost, users must consider the cloud service provider’s security policies and procedures. A reputable cloud service provider should have robust security policies and procedures in place, including access controls, data encryption, and regular security audits. Users should also ensure that the provider complies with relevant data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), depending on their industry and location.
Another important factor to consider is the cloud service provider’s certifications and compliance. Reputable cloud service providers should have various certifications, such as ISO 27001, SOC 1, and SOC 2, which demonstrate their commitment to data privacy and security. Users should also ensure that the provider complies with relevant industry standards, such as PCI DSS for payment card data or HITRUST for healthcare data.
In addition to security policies, certifications, and compliance, users must also consider the cloud service provider’s service model and its implications for data privacy and security. There are three main cloud service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each service model has different levels of control and responsibility for data privacy and security. For instance, IaaS provides users with the most control over their data and infrastructure, while SaaS provides the least control. Users must choose a service model that aligns with their data protection strategy and risk tolerance.
Finally, users must consider the cloud service provider’s reputation and track record. Users should research the provider’s history of data breaches and security incidents, as well as their response to such incidents. Users should also consider the provider’s customer support and service level agreements (SLAs) to ensure that they can quickly and effectively respond to security incidents.
In conclusion, choosing the right cloud service provider is a critical decision when it comes to ensuring privacy in cloud solutions. Users must consider various factors, such as the provider’s security policies, certifications, and compliance, service model, and reputation, to ensure that their data is protected in the cloud. By carefully evaluating their options, users can choose a cloud service provider that aligns with their data protection strategy and risk tolerance, thereby minimizing the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
Conclusion: Achieving Data Privacy and Security in Cloud Solutions
In conclusion, ensuring privacy in cloud solutions is a critical concern for businesses and individuals alike. A comprehensive data protection strategy is essential to prevent data breaches and other security incidents. This strategy should include robust access control policies, data encryption, monitoring and logging user activities, implementing data backup and disaster recovery strategies, and staying up-to-date with security best practices.
Access control policies, such as identity and access management (IAM), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and role-based access control (RBAC), can help prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Data encryption, both at rest and in transit, can protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. Monitoring and logging user activities can help detect and respond to security threats, such as unauthorized access, data breaches, and insider threats. Data backup and disaster recovery strategies can help prevent data loss and downtime in the event of a security breach or system failure.
When choosing a cloud service provider, it is essential to consider the provider’s security policies, certifications, and compliance. Different cloud service models, such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS), have different implications for data privacy and security. Staying up-to-date with security best practices is also crucial, as new security threats and vulnerabilities emerge regularly. Resources such as security blogs, forums, and conferences can help users stay informed and up-to-date.
In summary, achieving data privacy and security in cloud solutions requires a comprehensive data protection strategy that includes access control, encryption, monitoring, backup, and disaster recovery. By following best practices and staying informed about the latest security trends and threats, users can take proactive measures to protect their data and maintain privacy in the cloud. Remember, ensuring privacy in cloud solutions is not a one-time task but an ongoing process that requires regular attention and maintenance.