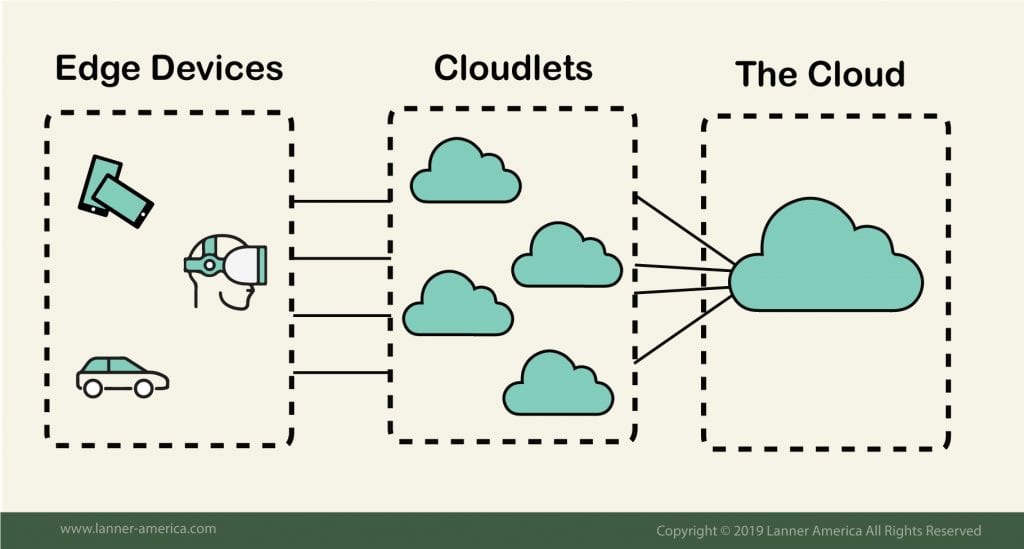
What is Edge Computing and How it Enhances Cloud Services
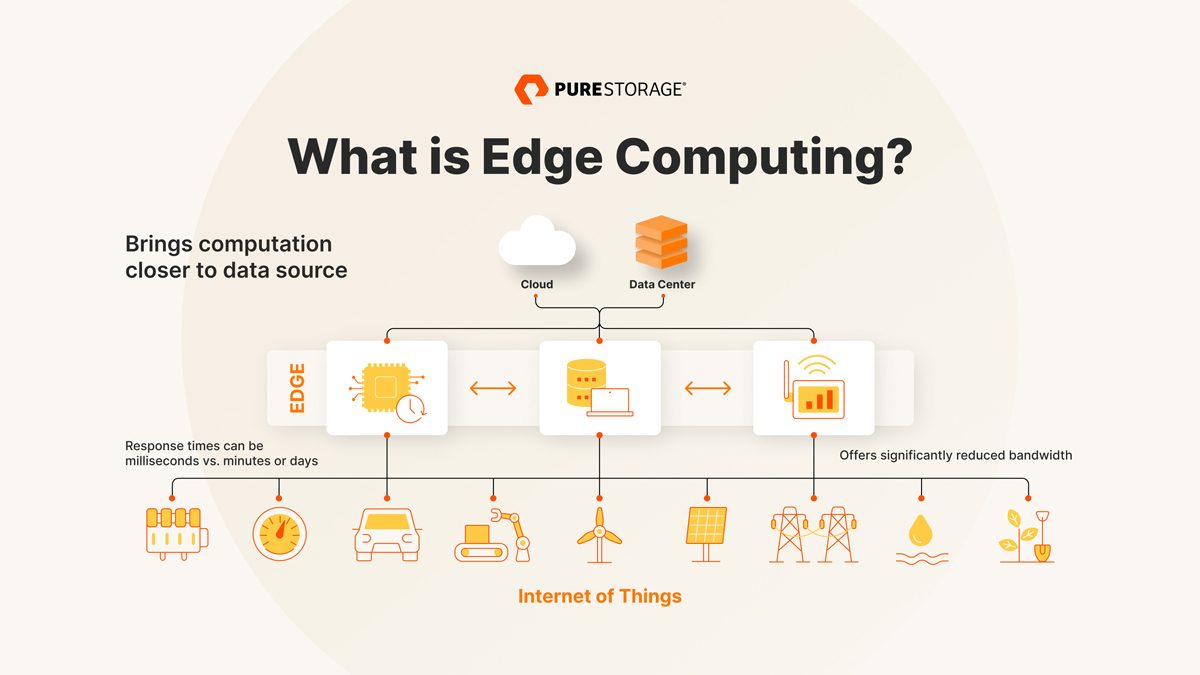
Edge computing refers to a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it’s needed, thus reducing latency and bandwidth usage. By processing data at the “edge” of the network, instead of transmitting it to a centralized cloud server, edge computing for low-latency cloud services significantly improves the user experience and enables real-time applications. In recent years, the increasing demand for high-performance, low-latency cloud services has led to the widespread adoption of edge computing. This technology is particularly beneficial for applications that require real-time processing, such as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and IoT devices. By reducing the distance between the data source and the processing unit, edge computing enables faster decision-making and more efficient resource utilization.
Moreover, edge computing for low-latency cloud services offers several advantages over traditional cloud computing models. For instance, it reduces the dependency on high-speed internet connections, making it suitable for remote or hard-to-reach areas. Additionally, edge computing enhances data privacy and security by processing sensitive information locally, thereby minimizing the risk of data breaches during transmission.
In conclusion, edge computing plays a pivotal role in enabling low-latency cloud services, which are essential for a wide range of applications and industries. By harnessing the power of edge computing, businesses can unlock new opportunities, improve operational efficiency, and create better user experiences.
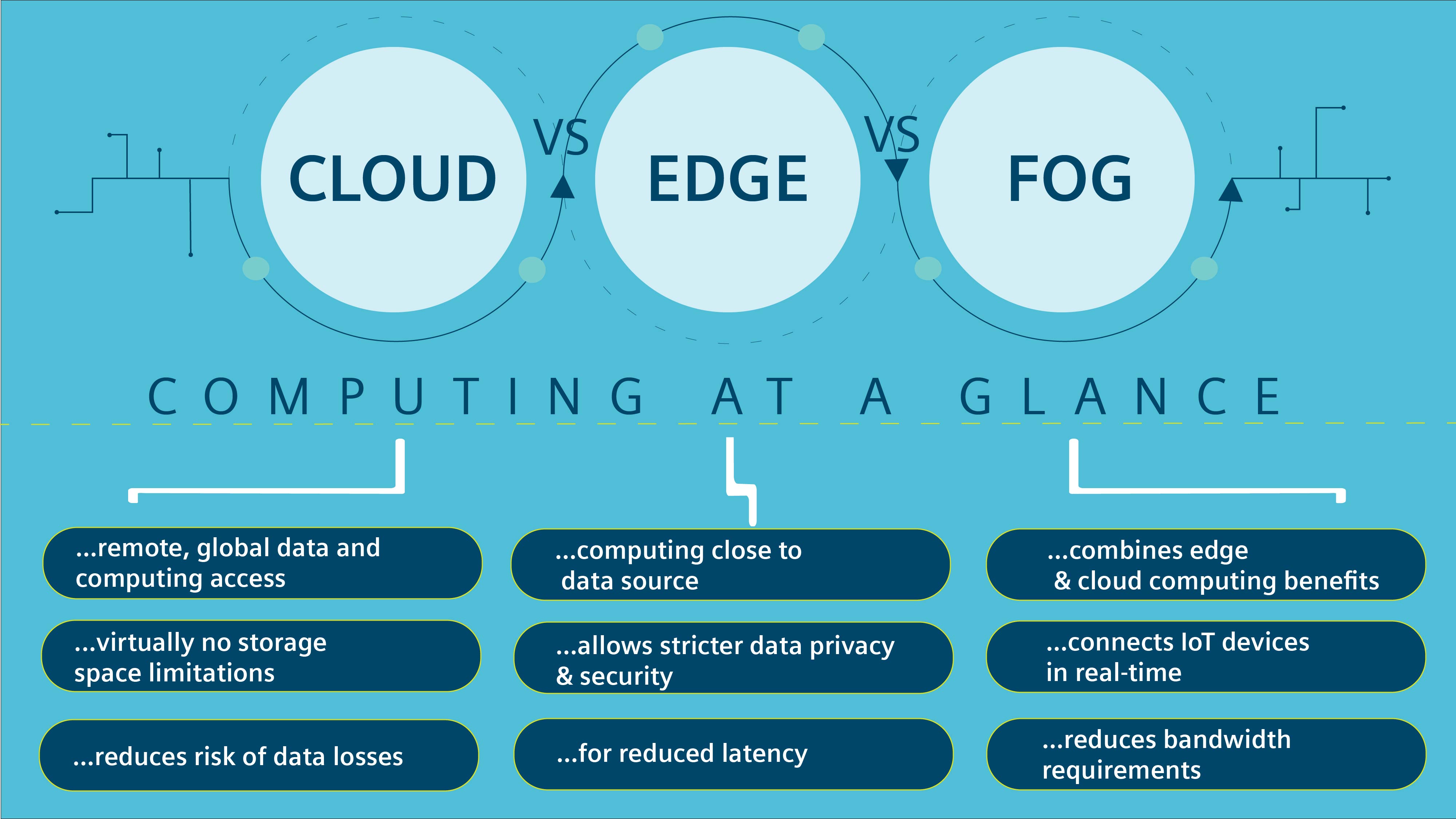
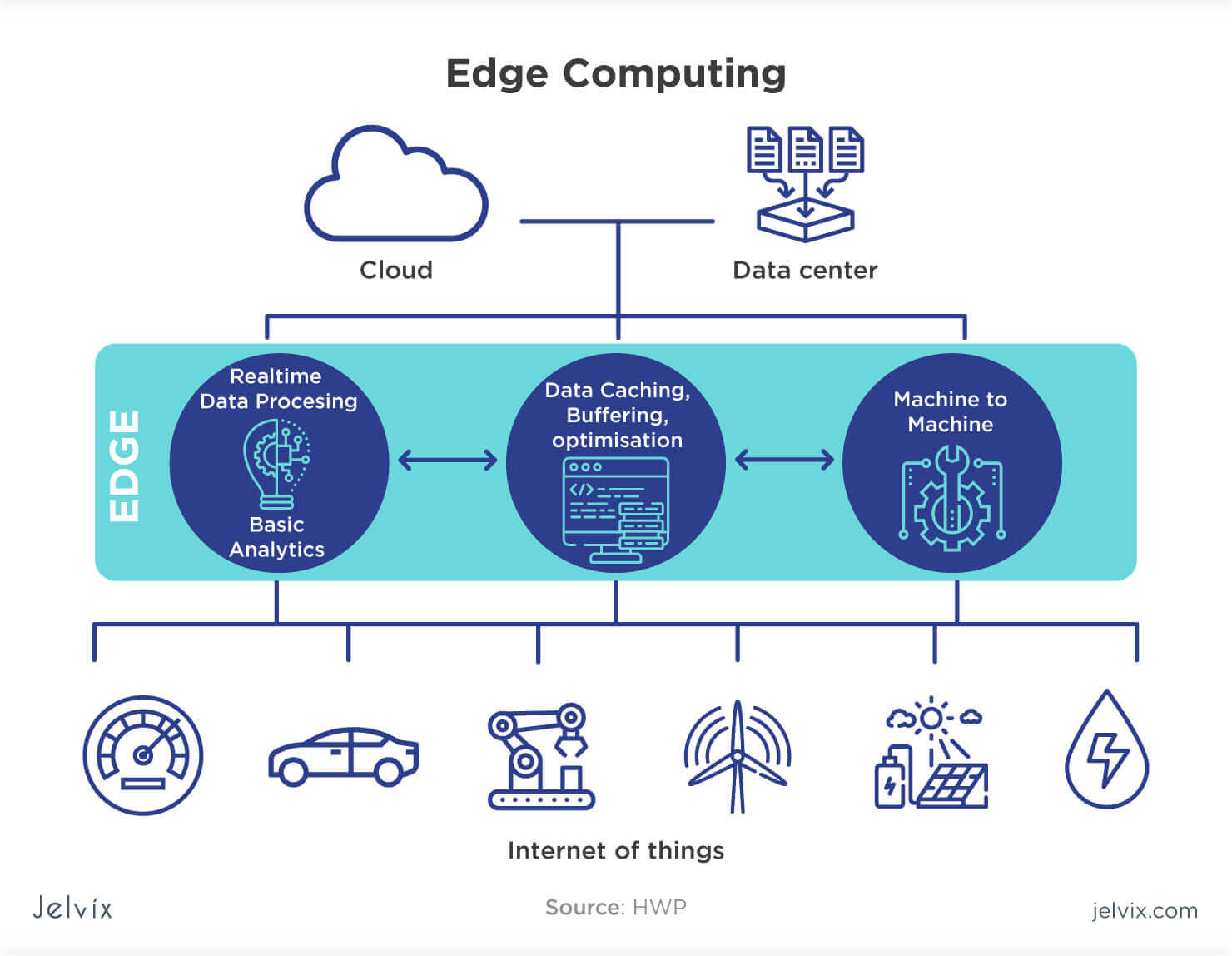
Key Components and Architecture of Edge Computing Systems
Edge computing systems consist of several interconnected components that work together to process, analyze, and transmit data closer to the source. These components include edge devices, edge gateways, and edge servers, which form a hierarchical architecture for data flow and processing.
Edge Devices: These are the most basic and numerous components in an edge computing system. Edge devices can be any device or sensor that generates data and requires real-time processing. Examples include smartphones, wearables, industrial machines, and IoT devices. Edge devices typically have limited computational power and storage capacity, making them unsuitable for handling large-scale data processing tasks.
Edge Gateways: Edge gateways serve as intermediaries between edge devices and edge servers. They aggregate data from multiple edge devices, perform initial data processing, and filter or cleanse the data before transmitting it to edge servers. Edge gateways often have more computational power and storage capacity than edge devices, enabling them to handle more complex tasks. They also provide security and network connectivity features, such as data encryption, access control, and protocol translation.
Edge Servers: Edge servers are the most powerful components in an edge computing system. They are responsible for processing large-scale data, running complex algorithms, and providing cloud services to edge devices. Edge servers typically have high-performance processors, large memory capacity, and fast storage systems. They can also provide caching, load balancing, and other optimization features to ensure low-latency cloud services.
The hierarchical architecture of edge computing systems enables efficient data flow and processing. Edge devices generate data and transmit it to edge gateways for initial processing. Edge gateways then transmit the filtered data to edge servers for further processing and analysis. Edge servers can also provide cloud services to edge devices, such as data storage, application hosting, and real-time analytics.
In summary, edge computing systems consist of edge devices, edge gateways, and edge servers, which form a hierarchical architecture for data flow and processing. By processing data closer to the source, edge computing systems enable low-latency cloud services and real-time applications, thereby improving user experience and unlocking new opportunities for businesses.
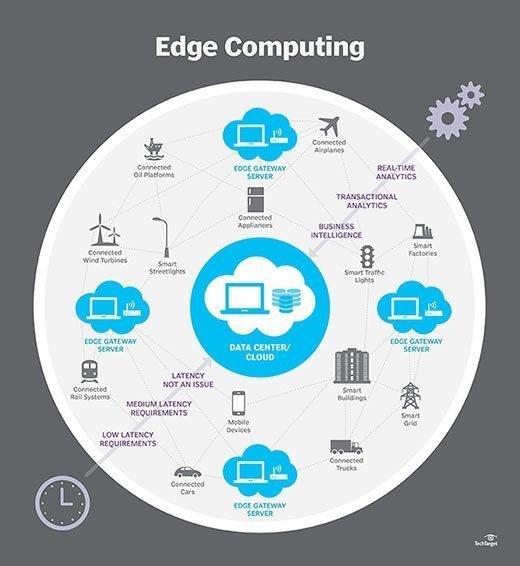
Use Cases: Real-World Applications of Edge Computing in Low-Latency Cloud Services
Edge computing has numerous real-world applications in various industries, from autonomous vehicles to smart cities and IoT devices. By processing data closer to the source, edge computing enables low-latency cloud services and real-time applications, thereby improving user experience and unlocking new opportunities for businesses.
Autonomous Vehicles: Autonomous vehicles generate vast amounts of data from sensors, cameras, and other onboard devices. Processing this data in real-time requires low-latency cloud services, which can be achieved through edge computing. By deploying edge servers in vehicles, manufacturers can reduce latency, improve safety, and enhance the driving experience.
Smart Cities: Smart cities rely on IoT devices, such as traffic cameras, air quality sensors, and waste management systems, to collect and analyze data in real-time. Edge computing enables low-latency cloud services by processing data closer to the source, reducing network congestion, and improving response times.
IoT Devices: IoT devices, such as smart home appliances, industrial machines, and wearables, generate massive amounts of data that require real-time processing and analysis. Edge computing enables low-latency cloud services by reducing the distance between devices and servers, thereby improving performance and user experience.
Industrial Automation: Industrial automation systems, such as robotics and machine learning, require real-time processing and analysis of data. Edge computing enables low-latency cloud services by reducing the distance between machines and servers, thereby improving efficiency and productivity.
Healthcare: Healthcare systems, such as telemedicine and remote patient monitoring, require real-time processing and analysis of data. Edge computing enables low-latency cloud services by reducing the distance between devices and servers, thereby improving patient outcomes and reducing costs.
In summary, edge computing has numerous real-world applications in various industries, from autonomous vehicles to smart cities and IoT devices. By processing data closer to the source, edge computing enables low-latency cloud services and real-time applications, thereby improving user experience and unlocking new opportunities for businesses. As edge computing technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications and use cases in the future.
How to Implement Edge Computing for Low-Latency Cloud Services
Implementing edge computing for low-latency cloud services requires careful planning and execution. By following a systematic approach, businesses can design and deploy an edge computing infrastructure that meets their needs and delivers value to their customers. Here are the essential steps to implement edge computing for low-latency cloud services:
1. Identify Use Cases and Requirements
The first step in implementing edge computing for low-latency cloud services is to identify use cases and requirements. Businesses should consider the following questions:
What are the specific use cases for edge computing in the business?
What are the performance, security, and scalability requirements?
What are the data processing and storage requirements?
2. Choose the Right Edge Computing Architecture
The next step is to choose the right edge computing architecture. Businesses should consider the following factors:
The number and type of edge devices, edge gateways, and edge servers required.
The hierarchical architecture and data flow.
The communication protocols and network topology.
3. Design and Deploy the Edge Computing Infrastructure
After choosing the right edge computing architecture, businesses should design and deploy the infrastructure. This step involves:
Configuring and deploying edge devices, edge gateways, and edge servers.
Setting up communication protocols and network topology.
Implementing security measures, such as access control, encryption, and firewalls.
4. Monitor and Optimize Performance
The final step is to monitor and optimize performance. Businesses should:
Monitor the performance of edge devices, edge gateways, and edge servers.
Analyze data processing and storage performance.
Optimize performance through software updates, configuration changes, and hardware upgrades.
Considerations for Security, Scalability, and Interoperability
When implementing edge computing for low-latency cloud services, businesses should consider the following:
Security: Implementing security measures, such as access control, encryption, and firewalls, is crucial to protect data and prevent unauthorized access.
Scalability: The edge computing infrastructure should be scalable to handle increasing data processing and storage requirements.
Interoperability: The edge computing infrastructure should be compatible with different devices, platforms, and applications.
In conclusion, implementing edge computing for low-latency cloud services requires careful planning and execution. By following a systematic approach, businesses can design and deploy an edge computing infrastructure that meets their needs and delivers value to their customers. Security, scalability, and interoperability are critical considerations in implementing edge computing for low-latency cloud services.
Choosing the Right Edge Computing Solutions for Your Business
Selecting the right edge computing solutions for your business is a critical decision that requires careful consideration. By evaluating various factors, such as cost, performance, and vendor support, businesses can choose the right edge computing technologies that meet their needs and deliver value to their customers. Here are some factors to consider when choosing edge computing solutions for low-latency cloud services:
1. Cost
Cost is a crucial factor when choosing edge computing solutions. Businesses should consider the upfront costs of hardware, software, and deployment, as well as ongoing costs, such as maintenance, support, and upgrades. It’s essential to balance cost and performance to ensure that the chosen solution is both affordable and effective.
2. Performance
Performance is another critical factor when choosing edge computing solutions. Businesses should consider the processing power, memory, and storage capacity of edge devices, edge gateways, and edge servers. They should also evaluate the communication protocols and network topology to ensure low-latency data transfer and processing.
3. Vendor Support
Vendor support is essential when choosing edge computing solutions. Businesses should choose vendors that provide reliable and responsive support, as well as regular software updates and security patches. They should also consider the vendor’s reputation, track record, and experience in edge computing for low-latency cloud services.
Specific Edge Computing Solutions
There are various edge computing solutions available in the market, such as:
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Outposts: AWS Outposts is a fully managed service that extends AWS infrastructure, services, APIs, and tools to edge locations.
Microsoft Azure Stack Edge: Azure Stack Edge is a hybrid cloud solution that brings compute, storage, and intelligence to the edge.
Google Cloud Anthos: Anthos is a hybrid and multi-cloud platform that enables businesses to build, deploy, and manage applications on-premises and in the cloud.
When choosing edge computing solutions, businesses should consider their specific needs and requirements. They should also evaluate the vendor’s capabilities, track record, and reputation in the industry. By choosing the right edge computing solutions, businesses can design and deploy an edge computing infrastructure that delivers low-latency cloud services and enhances user experience.
In conclusion, choosing the right edge computing solutions for your business requires careful consideration of various factors, such as cost, performance, and vendor support. By evaluating these factors and considering specific edge computing solutions, businesses can design and deploy an edge computing infrastructure that meets their needs and delivers value to their customers. It’s essential to stay informed about the latest developments in edge computing for low-latency cloud services and choose vendors that provide reliable and responsive support.

Challenges and Best Practices in Edge Computing Deployments
Edge computing for low-latency cloud services offers numerous benefits, such as reduced latency, improved user experience, and enhanced data processing capabilities. However, deploying and managing edge computing infrastructure can be complex and challenging. Here are some common issues and best practices for successful edge computing deployments:
Managing Distributed Data
Managing distributed data is a significant challenge in edge computing for low-latency cloud services. Edge devices generate vast amounts of data, which needs to be processed, analyzed, and stored in real-time. Businesses should consider implementing data management strategies, such as data compression, caching, and synchronization, to ensure efficient data processing and storage.
Ensuring Network Connectivity
Edge computing for low-latency cloud services relies on reliable and high-speed network connectivity. Businesses should ensure that edge devices have adequate network connectivity, such as Wi-Fi, cellular, or wired connections, to enable real-time data transfer and processing. They should also consider implementing network redundancy and failover mechanisms to ensure network availability and reliability.
Maintaining System Reliability
Maintaining system reliability is essential in edge computing for low-latency cloud services. Edge devices should be designed and deployed with high availability and fault tolerance in mind. Businesses should consider implementing redundant and failover mechanisms, such as backup power supplies, to ensure system reliability and uptime.
Best Practices for Successful Edge Computing Deployments
Here are some best practices for successful edge computing deployments:
Conduct a thorough assessment of the edge computing requirements, including data processing, storage, and network connectivity.
Choose edge computing technologies that meet the specific needs and requirements of the business.
Implement data management strategies, such as data compression, caching, and synchronization, to ensure efficient data processing and storage.
Ensure reliable and high-speed network connectivity for edge devices.
Implement redundant and failover mechanisms to ensure system reliability and uptime.
Monitor and manage edge computing infrastructure using centralized management tools and platforms.
Implement security measures, such as encryption, authentication, and access control, to protect edge computing infrastructure and data.
In conclusion, edge computing for low-latency cloud services offers numerous benefits, but deploying and managing edge computing infrastructure can be complex and challenging. By addressing common issues, such as managing distributed data, ensuring network connectivity, and maintaining system reliability, businesses can ensure successful edge computing deployments. Best practices, such as conducting a thorough assessment, choosing the right technologies, implementing data management strategies, and ensuring network connectivity, can help businesses achieve their edge computing goals and deliver low-latency cloud services to their customers.

The Future of Edge Computing and Low-Latency Cloud Services
Edge computing for low-latency cloud services is an ever-evolving field, with new trends and innovations emerging regularly. Here are some of the most exciting developments that have the potential to impact low-latency cloud services and user experience:
5G Networks
5G networks are expected to revolutionize edge computing for low-latency cloud services. With faster speeds, lower latency, and higher capacity than previous generations, 5G networks will enable real-time data transfer and processing, making edge computing more efficient and effective. 5G networks will also enable new use cases, such as remote surgery, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities, where real-time data processing is critical.
AI-Powered Edge Devices
AI-powered edge devices are becoming increasingly popular in edge computing for low-latency cloud services. These devices can process and analyze data locally, reducing the need for data transfer to the cloud and improving response times. AI-powered edge devices can also learn from data and make decisions based on patterns and trends, enabling new use cases, such as predictive maintenance and anomaly detection.
Decentralized Architectures
Decentralized architectures are another emerging trend in edge computing for low-latency cloud services. Decentralized architectures distribute data processing and storage across multiple nodes, reducing the reliance on a centralized cloud infrastructure. Decentralized architectures can also improve system reliability and fault tolerance, making them ideal for use cases where real-time data processing is critical.
Potential Impact on Low-Latency Cloud Services and User Experience
These emerging trends and innovations have the potential to significantly impact low-latency cloud services and user experience. Faster speeds, lower latency, and higher capacity enabled by 5G networks will enable new use cases and improve the efficiency and effectiveness of edge computing. AI-powered edge devices will enable real-time data processing and decision-making, while decentralized architectures will improve system reliability and fault tolerance.
In conclusion, edge computing for low-latency cloud services is a rapidly evolving field, with new trends and innovations emerging regularly. 5G networks, AI-powered edge devices, and decentralized architectures are just a few of the most exciting developments that have the potential to impact low-latency cloud services and user experience. By staying informed about the latest developments and trends, businesses can leverage edge computing to deliver low-latency cloud services and improve user experience.

Conclusion: Making the Most of Edge Computing for Low-Latency Cloud Services
In conclusion, edge computing for low-latency cloud services is a powerful tool that can significantly improve user experience and enhance cloud services. By processing data closer to the source, edge computing reduces latency and enables real-time data processing, making it ideal for use cases where real-time data processing is critical.
The key components of edge computing systems, including edge devices, edge gateways, and edge servers, work together to create a hierarchical architecture that enables efficient data flow. Real-world applications of edge computing in low-latency cloud services include autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and IoT devices, among others.
When implementing edge computing for low-latency cloud services, it is essential to consider security, scalability, and interoperability. By selecting the right edge computing technologies, businesses can ensure cost-effective and high-performance solutions that meet their specific needs. Factors to consider when selecting edge computing technologies include cost, performance, and vendor support.
Edge computing projects can present common issues and pitfalls, such as managing distributed data, ensuring network connectivity, and maintaining system reliability. By following best practices and recommendations for successful deployments, businesses can overcome these challenges and leverage edge computing to deliver low-latency cloud services and improve user experience.
Emerging trends and innovations in edge computing, such as 5G networks, AI-powered edge devices, and decentralized architectures, have the potential to significantly impact low-latency cloud services and user experience. By staying informed about the latest developments and trends, businesses can leverage edge computing to deliver low-latency cloud services and improve user experience.
In summary, edge computing for low-latency cloud services is a rapidly evolving field that offers significant benefits for businesses and users alike. By understanding the key components and architecture of edge computing systems, exploring real-world applications, and following best practices for implementation and deployment, businesses can leverage edge computing to deliver low-latency cloud services and improve user experience.