Amazon DynamoDB: An Introduction
Amazon DynamoDB is a fully managed, serverless NoSQL database service offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS). Unlike traditional relational SQL databases, DynamoDB boasts a schema-less design, providing unparalleled flexibility in handling diverse data structures. This adaptability makes DynamoDB ideal for applications requiring rapid scaling and high availability. Its core strength lies in its ability to seamlessly handle massive volumes of data with minimal operational overhead. DynamoDB’s key features include automatic scaling, high performance, and robust security, making it a powerful tool for developers. The service’s unique approach contrasts sharply with the rigid structures of SQL databases, making it exceptionally well-suited for applications needing rapid evolution and dynamic data schemas. Understanding DynamoDB’s capabilities is crucial for building modern, scalable applications. DynamoDB’s scalability allows it to effortlessly adapt to changing data needs. This is a key advantage in today’s fast-paced digital landscape.
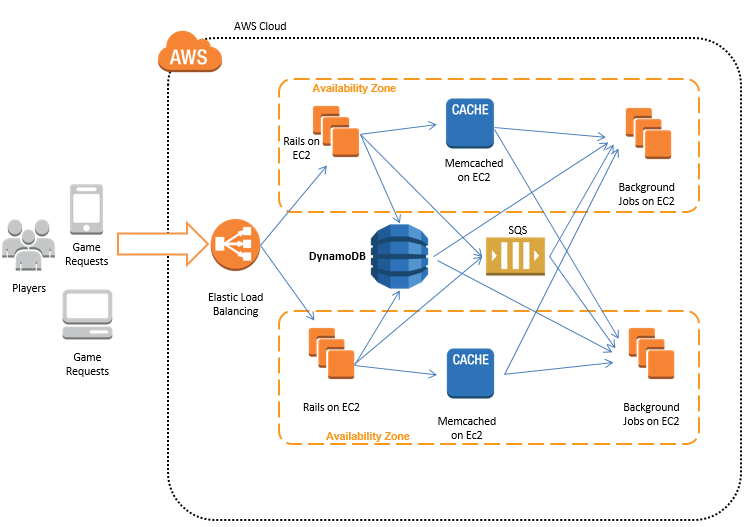
DynamoDB shines in scenarios demanding extreme scalability and rapid data access. Applications requiring quick responses to user requests benefit greatly from DynamoDB’s low latency. Furthermore, the ability to scale capacity independently, both read and write, provides precise control over performance and cost. This flexibility is crucial for applications with fluctuating workloads. DynamoDB’s schema-less design eliminates the rigid constraints of traditional databases. Developers can easily adapt the data model as their application evolves. This agility is a major benefit for projects with uncertain future requirements. The managed nature of DynamoDB minimizes administrative tasks, allowing developers to focus on application logic rather than database maintenance. Choosing DynamoDB often translates to faster development cycles and lower operational costs. DynamoDB’s versatility and performance characteristics make it a popular choice for various applications. The service manages all the underlying infrastructure, ensuring high availability and durability.
DynamoDB simplifies database management by abstracting away much of the complexity associated with traditional databases. This allows developers to focus on building features instead of managing infrastructure. The pay-as-you-go pricing model ensures that developers only pay for the resources they consume. This cost-effectiveness is an important consideration for businesses of all sizes. DynamoDB’s robust security features protect data from unauthorized access, guaranteeing data integrity and confidentiality. The service integrates seamlessly with other AWS services, further enhancing its versatility and usefulness. DynamoDB offers a compelling alternative to traditional relational databases, particularly when scalability and flexibility are paramount. Developers looking for a robust, cost-effective, and easily scalable database solution should seriously consider DynamoDB for their next project. The ability to handle massive datasets with ease makes DynamoDB a valuable asset to any cloud infrastructure.
DynamoDB Data Modeling Techniques
Effective data modeling is crucial for DynamoDB performance. The choice of primary key significantly impacts query speed and scalability. DynamoDB’s schema-less nature offers flexibility, but careful planning prevents future performance bottlenecks. A well-designed primary key ensures efficient data retrieval. Consider using composite keys for complex queries. This allows for efficient filtering and sorting within your dynmodb tables. The primary key selection directly affects your application’s efficiency and scalability. Understanding the trade-offs between different key types is vital for optimal dynmodb performance.
Secondary indexes in DynamoDB provide additional querying flexibility. They allow for efficient queries on attributes not included in the primary key. However, secondary indexes add to storage costs and can impact write performance. Careful consideration of which attributes to index is necessary. Over-indexing can negatively impact write performance and increase costs. Under-indexing limits querying capabilities. Balancing these factors is crucial for a well-performing dynmodb application. Proper index selection simplifies complex queries and improves overall application response times.
Data modeling for DynamoDB involves strategic choices. The goal is to align data structures with anticipated query patterns. This anticipates application needs. Consider partitioning strategies. This allows for distributing data across multiple nodes. Efficient partitioning improves scalability and reduces the impact of hot keys. Partitioning improves read and write performance. This improves the overall performance of your dynmodb database. Mastering DynamoDB data modeling leads to a highly efficient and scalable application. The initial effort in design yields significant long-term benefits in performance and cost.
Optimizing DynamoDB Performance
Optimizing DynamoDB performance is crucial for building responsive and cost-effective applications. Efficient DynamoDB usage involves several key strategies. Understanding read and write capacity units is fundamental. These units determine the throughput your DynamoDB tables can handle. Properly provisioning these units, based on anticipated workload, prevents performance bottlenecks. Regularly monitor usage patterns to adjust capacity as needed. Scaling capacity dynamically ensures optimal performance while minimizing unnecessary costs. DynamoDB’s autoscaling feature simplifies this process significantly. This proactive approach guarantees consistent application performance.
Caching is another effective technique to enhance DynamoDB performance. Caching frequently accessed data reduces the number of requests to DynamoDB. This reduces latency and improves application responsiveness. Different caching mechanisms exist. Consider using a distributed cache like Redis or Memcached in conjunction with DynamoDB. This layered approach allows for rapid data retrieval. Efficiently utilize DynamoDB’s built-in features. For instance, leverage secondary indexes appropriately. Well-designed indexes greatly accelerate query performance. However, excessive indexes add to operational costs. Careful consideration of the data access patterns is essential for optimal index selection in DynamoDB.
Data consistency models also significantly influence DynamoDB performance. DynamoDB offers various consistency levels, including strong and eventual consistency. Strong consistency ensures data is immediately reflected across all clients. Eventual consistency prioritizes availability and speed. Choosing the appropriate consistency model depends on your application’s requirements. For applications that require immediate data accuracy, strong consistency is necessary. However, eventual consistency often offers better performance for less sensitive applications. The selection impacts application design. Therefore, understand the trade-offs before implementation. DynamoDB’s flexible nature allows customization to specific performance needs. Efficient query design minimizes latency. Avoid overly complex queries, and optimize filter expressions to enhance speed. Careful planning and regular monitoring are key to maximizing DynamoDB’s performance and ensuring cost-effectiveness. Remember, understanding your application’s needs and tailoring DynamoDB accordingly is crucial for achieving optimal results.
Building Applications with DynamoDB: A Step-by-Step Guide
This section provides a practical guide to building a simple application using DynamoDB. The example uses Python with the boto3 library, a popular choice for interacting with AWS services. This walkthrough covers creating a DynamoDB table, performing basic read and write operations, and handling query responses. Understanding these fundamentals is crucial for leveraging DynamoDB’s capabilities effectively. Remember the data modeling principles discussed earlier; efficient table design directly impacts application performance and scalability. Properly structured DynamoDB tables are essential for optimal querying and data retrieval. The creation of DynamoDB tables requires careful consideration of the primary key and data structure. This step directly influences how you interact with your data later. Choosing the right primary key significantly impacts query performance in DynamoDB.
First, ensure you have boto3 installed: pip install boto3. Then, let’s create a simple DynamoDB table to store product information. The code below defines a table with a primary key named ‘product_id’. This primary key uniquely identifies each product within the DynamoDB table. The table also includes attributes for ‘name’ and ‘price’. This is a basic example and you can extend this to include additional relevant product attributes as required. DynamoDB’s flexibility makes it simple to adapt the table structure to changing needs. It is important to plan your DynamoDB tables carefully to ensure efficient querying and data management. The following code demonstrates how to create the table using boto3:
import boto3
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
table = dynamodb.create_table(TableName='Products', KeySchema=[{'AttributeName': 'product_id', 'KeyType': 'HASH'}], AttributeDefinitions=[{'AttributeName': 'product_id', 'AttributeType': 'S'}], ProvisionedThroughput={'ReadCapacityUnits': 5, 'WriteCapacityUnits': 5})
table.meta.client.get_waiter('table_exists').wait(TableName='Products')
print(f"Table Products created successfully.")
This code snippet creates a DynamoDB table named ‘Products’. Next, let’s add some data. After table creation, adding data is straightforward. Here’s how to add a new product using the put_item method:
response = table.put_item(Item={'product_id': 'A123', 'name': 'Widget', 'price': 25.99})
print(f"Product A123 added successfully.")get_item. To query for a specific product, you’d use the product_id. DynamoDB’s efficient querying is one of its key benefits. Remember to handle potential exceptions appropriately in a production environment. This practical example highlights the ease of use and efficiency offered by DynamoDB. By combining a well-defined data model with appropriate DynamoDB operations, you can build robust and scalable applications.
Advanced DynamoDB Features: Beyond the Basics
DynamoDB offers several advanced features that significantly enhance its capabilities. Global tables, for instance, allow for seamless data replication across multiple AWS regions. This ensures high availability and low latency for applications with geographically distributed users. DynamoDB’s global tables automatically handle data synchronization, providing a simplified approach to managing globally consistent data. This is a powerful tool for building truly scalable and resilient applications. Understanding how to configure and manage these tables is crucial for maximizing the potential of DynamoDB.
Transactions are another key advanced feature. DynamoDB supports atomic transactions, enabling developers to perform multiple operations as a single unit of work. This guarantees data consistency, even in high-concurrency scenarios. For example, transferring funds between two accounts requires atomic transactions to prevent inconsistencies. By grouping related updates into transactions, dynmodb maintains data integrity. This capability is essential for applications requiring strict data accuracy. Properly designing transactions requires careful consideration of data modeling and operation sequencing.
DynamoDB Streams provide a powerful mechanism for capturing changes to DynamoDB tables. These streams deliver a continuous stream of data representing modifications to items in the table. This enables real-time data processing and integration with other services. Applications can react immediately to data changes, fostering greater responsiveness and automation. Developers can use DynamoDB Streams to build sophisticated event-driven architectures, powering functions like audit trails, data analytics pipelines, and other applications that require real-time data updates. DynamoDB Streams integrate seamlessly with other AWS services like Kinesis and Lambda, facilitating advanced data processing workflows.
Choosing the Right DynamoDB Use Cases
DynamoDB excels as a NoSQL database solution for applications demanding high scalability and performance. Its schema-less design and flexible data modeling empower developers to adapt quickly to evolving data structures. DynamoDB shines when handling massive datasets with frequent read and write operations, such as mobile gaming leaderboards, e-commerce product catalogs, and real-time analytics dashboards. However, DynamoDB might not be the ideal choice for applications requiring complex relational queries or ACID transactions across multiple items. In such scenarios, a relational database like Amazon RDS might be a better fit.
The decision to use DynamoDB hinges on understanding application requirements. Consider the nature of your data, the expected query patterns, and the level of transactional consistency needed. For applications with simple key-value data structures and high throughput needs, DynamoDB provides an excellent solution. Its serverless nature simplifies management, allowing developers to focus on application logic rather than database administration. However, DynamoDB’s strengths also present limitations. The lack of joins and complex queries may necessitate data restructuring or application changes. Careful consideration of these trade-offs during the design phase is crucial to ensure successful deployment of DynamoDB.
Comparing DynamoDB with other AWS services helps clarify its optimal use cases. While both DynamoDB and RDS offer scalable storage, they cater to different data models and query patterns. DynamoDB’s schema-less design and focus on high-throughput operations make it well-suited for applications requiring rapid scaling and quick access to data items. In contrast, RDS provides a more traditional relational database experience, ideal for applications that heavily rely on joins, complex queries, and ACID transactions. Understanding these key differences allows developers to make informed decisions, selecting the database service best aligned with their specific application needs and constraints. Choosing the right tool depends on your workload demands, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency. DynamoDB offers a compelling solution when scalability and performance are paramount. Always assess your application’s data model and query patterns to determine if DynamoDB aligns with your specific requirements before deployment. Proper planning minimizes potential issues later on.
Cost Optimization with DynamoDB
Managing costs effectively is crucial when using DynamoDB. Understanding DynamoDB’s pricing model is the first step. Costs are primarily driven by provisioned read and write capacity units, and storage consumed. Monitoring these metrics closely allows for proactive cost management. DynamoDB provides detailed usage reports and cost allocation tools through the AWS console. Regularly review these reports to identify areas for potential savings. Unused capacity can significantly inflate costs. Right-sizing your provisioned capacity based on actual usage patterns is key to optimization. Utilize the Auto Scaling feature to dynamically adjust capacity based on real-time demand, preventing over-provisioning and reducing unnecessary expenses. This ensures that DynamoDB resources are efficiently allocated, minimizing waste and maximizing cost-effectiveness. Efficient data modeling also plays a crucial role in cost optimization. Optimize queries and access patterns to minimize read and write operations. Proper indexing can significantly reduce the number of consumed capacity units. Analyze your application’s access patterns. Consider whether you can consolidate or archive less frequently accessed data to further reduce storage costs. DynamoDB offers several tools for this purpose, including point-in-time recovery and backups. These features enable cost-effective data management without sacrificing data integrity.
Beyond capacity and storage, exploring DynamoDB’s serverless offerings can also improve cost efficiency. Serverless DynamoDB On-Demand provides a pay-per-request model, eliminating the need for upfront capacity planning. This option is ideal for workloads with unpredictable traffic patterns. It automatically scales resources based on demand, further optimizing costs by only paying for what is used. However, the on-demand model might have a higher per-request cost compared to provisioned capacity, so careful evaluation is needed. For infrequently accessed data, consider archiving it to Amazon S3. S3 provides a cost-effective solution for long-term storage, significantly reducing the overall DynamoDB storage costs. Remember, regular cost analysis is key. Implement a process to regularly review your DynamoDB costs. Identify trends, and adjust capacity and storage allocation accordingly. This proactive approach ensures that your DynamoDB deployment remains cost-effective over the long term. By combining these strategies, you can effectively manage DynamoDB costs while ensuring optimal performance for your applications.
DynamoDB’s flexible pricing model offers several options for managing costs. Choosing the right model—provisioned capacity, on-demand, or a hybrid approach—depends on the application’s requirements and usage patterns. Carefully plan your DynamoDB deployment. Consider factors such as expected traffic, data access patterns, and future scalability needs. Proactive planning and efficient resource utilization are essential for long-term cost optimization in DynamoDB. Remember, careful monitoring and regular adjustments are paramount to keeping dynmodb expenses under control. This proactive approach ensures that your dynmodb deployment remains cost-effective over the long term. By combining these strategies, you can effectively manage DynamoDB costs while ensuring optimal performance for your applications.
Troubleshooting DynamoDB Issues
DynamoDB, like any database system, can present challenges. Understanding common issues and effective troubleshooting strategies is crucial for maintaining application performance and stability. Resource exhaustion, for instance, frequently manifests as throttling errors. These errors indicate that the DynamoDB table has exceeded its provisioned read or write capacity. To resolve this, increase the provisioned capacity or optimize application code to reduce the load on DynamoDB. Monitoring your DynamoDB metrics closely helps in proactively identifying capacity bottlenecks before they impact performance.
Another common DynamoDB issue involves inefficient query patterns. Improperly designed queries can lead to performance degradation. Ensure your queries leverage appropriate indexes to minimize the amount of data scanned. Analyze your query patterns using DynamoDB’s metrics and logging capabilities. DynamoDB offers detailed logging that can pinpoint the root cause of slow queries. If the issue lies in your data modeling, consider restructuring your DynamoDB tables to improve query efficiency. Remember to thoroughly test any changes to your queries or data model in a non-production environment before deploying to production. Proactive monitoring and analysis of your DynamoDB usage are key to avoiding many potential problems.
Incorrectly configured access control lists (ACLs) can lead to authorization errors when applications attempt to interact with DynamoDB. Verify that your IAM roles and policies grant the necessary permissions to your application. Review your IAM configurations carefully, ensuring proper permissions are assigned without unnecessary access. Detailed error messages provided by DynamoDB are invaluable in diagnosing these issues. DynamoDB’s comprehensive documentation offers solutions for various access-related problems. Regular audits of IAM permissions are recommended to maintain security and prevent unauthorized access to your DynamoDB data. Addressing these potential problem areas proactively ensures a more robust and reliable application using DynamoDB.