Understanding DynamoDB’s Scaling Needs
DynamoDB, like other NoSQL databases, presents unique scalability challenges. Managing read/write capacity units (RCUs/WCUs) effectively is crucial for optimal performance. Throughput limitations can easily become bottlenecks, especially during peak usage. Without proactive scaling, applications may suffer from reduced availability and responsiveness. Addressing these challenges requires a strategic approach to resource allocation. DynamoDB autoscale emerges as a powerful solution. It dynamically adjusts provisioned capacity to meet application demands. This ensures consistent performance without manual intervention. Understanding the inherent challenges of NoSQL databases is the first step toward effective scaling.
The importance of proactive scaling cannot be overstated. Applications need to remain responsive, even under heavy load. DynamoDB autoscale helps achieve this by automatically adjusting RCUs and WCUs. It monitors traffic patterns and scales capacity accordingly. This ensures that the database can handle sudden spikes in demand. Failing to scale appropriately can lead to performance degradation and even application outages. DynamoDB autoscale eliminates the need for manual capacity planning. It also removes the risk of under-provisioning resources. Embracing autoscaling is essential for maintaining application availability and a positive user experience. It provides a flexible and efficient way to manage database capacity.
Consider the alternative to DynamoDB autoscale: manual scaling. This requires constant monitoring of database performance. Administrators must manually adjust RCUs and WCUs based on observed traffic. This process is time-consuming and prone to errors. It is also difficult to predict future traffic patterns accurately. DynamoDB autoscale automates this process. It uses sophisticated algorithms to predict and respond to changes in demand. This frees up administrators to focus on other tasks. It also ensures that the database is always running at optimal capacity. DynamoDB autoscale is a valuable tool for any organization that relies on DynamoDB. It simplifies database management and improves application performance. Ultimately, DynamoDB autoscale contributes to cost savings by optimizing resource utilization. Implementing dynamodb autoscale is key for a robust and scalable application.
Exploring DynamoDB Autoscaling Features
DynamoDB offers robust autoscaling capabilities to dynamically adjust read and write capacity in response to fluctuating application demands. This proactive approach ensures optimal performance and cost efficiency by automatically scaling resources up or down as needed. The core of DynamoDB autoscale lies in its ability to monitor traffic patterns and adjust provisioned capacity accordingly. Understanding the available options and parameters is crucial for effective implementation. DynamoDB autoscale automatically modifies Read Capacity Units (RCUs) and Write Capacity Units (WCUs) to maintain target utilization levels, eliminating the need for manual intervention.
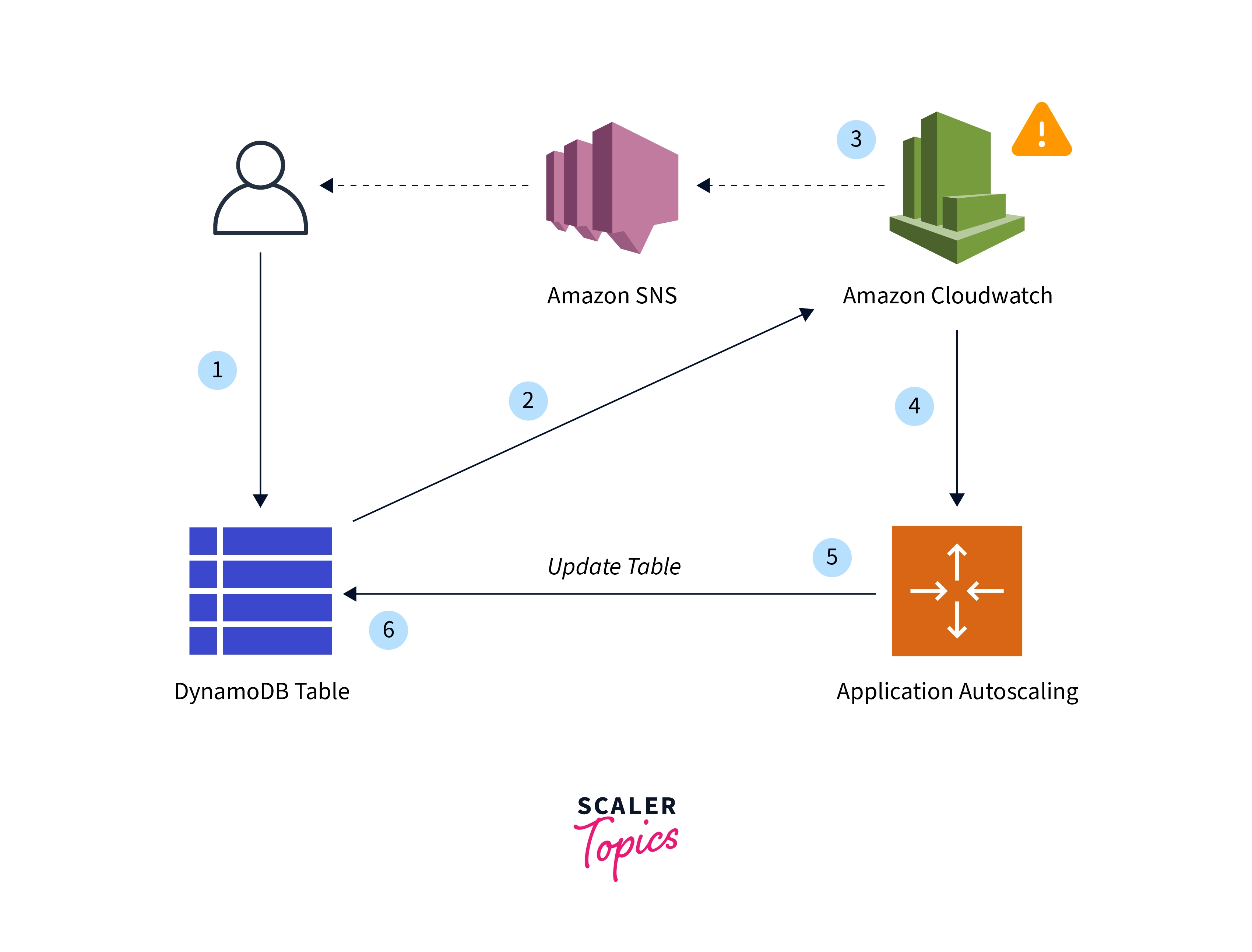
Several key parameters govern the behavior of DynamoDB autoscale. Target utilization represents the desired percentage of consumed capacity, guiding the scaling process. Scaling thresholds define the boundaries for triggering scaling actions. For example, a high threshold might initiate scaling up when consumed capacity exceeds a certain percentage, while a low threshold triggers scaling down when capacity utilization drops. Scaling limits define the minimum and maximum RCU and WCU values, preventing excessive scaling and ensuring budget control. Properly configuring these parameters is essential for balancing performance and cost. The AWS Management Console and AWS CLI provide interfaces for defining and managing these settings, making DynamoDB autoscale accessible to users with varying technical expertise. DynamoDB autoscale leverages CloudWatch metrics to monitor resource utilization and trigger scaling events.
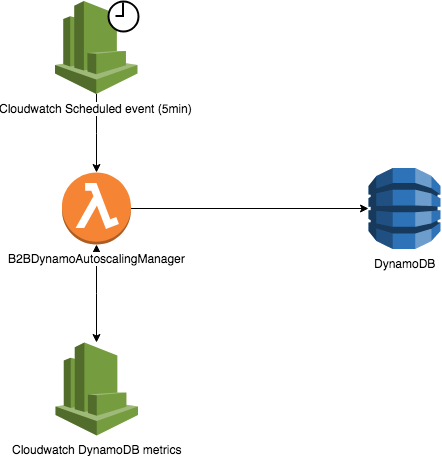
Different scaling strategies exist within DynamoDB autoscale, each with its own advantages. One common strategy involves using CloudWatch metrics like `ConsumedReadCapacityUnits` and `ConsumedWriteCapacityUnits` to track actual resource consumption. When these metrics exceed predefined thresholds, scaling policies are automatically invoked to increase capacity. Conversely, if consumption falls below thresholds, capacity is reduced. Another strategy involves using Application Auto Scaling, a service that provides a unified interface for managing autoscaling across multiple AWS resources, including DynamoDB. This approach offers greater flexibility and control over scaling behavior. Choosing the right scaling strategy depends on the specific application requirements and performance goals. DynamoDB autoscale empowers developers to create highly scalable and resilient applications without the burden of manual capacity management. Effective utilization of DynamoDB autoscale ensures that applications can handle peak loads while minimizing costs during periods of low activity, making DynamoDB autoscale a valuable tool.
How to Configure DynamoDB Autoscaling for Optimal Performance
Configuring DynamoDB autoscale effectively is crucial for maintaining application performance and managing costs. This section provides a practical guide to setting up DynamoDB autoscale using the AWS Management Console. First, navigate to the DynamoDB service in the AWS Console and select the table you want to configure. In the table details, find the “Capacity” tab. Here, you’ll see options for both read and write capacity. Choose “Autoscale” for the capacity type you wish to manage dynamically. To configure DynamoDB autoscale, you’ll need to define a target utilization percentage. This represents the percentage of consumed capacity units you want DynamoDB to maintain. For example, a target utilization of 70% means DynamoDB will automatically adjust capacity to keep utilization around this level. Next, set the minimum and maximum capacity units. These values define the boundaries within which DynamoDB can scale. Setting appropriate limits is important for cost control and preventing over-provisioning.
To proceed configuring DynamoDB autoscale, create a scaling policy. The AWS Management Console will guide you through this process. You’ll need to choose a CloudWatch metric to monitor. Common metrics include `ConsumedReadCapacityUnits` and `ConsumedWriteCapacityUnits`. Selecting the right metric is critical for effective scaling. You can also configure scaling policies using the AWS CLI. The `aws application-autoscaling register-scalable-target` and `aws application-autoscaling put-scaling-policy` commands are essential for this. For example, the following CLI command registers a scalable target for a DynamoDB table’s read capacity:
`aws application-autoscaling register-scalable-target –service-namespace dynamodb –resource-id table/YourTableName –scalable-dimension dynamodb:table:ReadCapacityUnits –min-capacity 5 –max-capacity 20` Remember to replace `YourTableName` with your actual table name and adjust the minimum and maximum capacity values to suit your needs. Similarly, you can create a scaling policy using `aws application-autoscaling put-scaling-policy`.
Common pitfalls when setting up DynamoDB autoscale include setting overly aggressive scaling thresholds, which can lead to excessive scaling activity and increased costs. Also, ensure that your IAM role has the necessary permissions to allow DynamoDB to adjust capacity on your behalf. Always test your autoscaling configuration thoroughly, monitoring CloudWatch metrics to ensure it behaves as expected under different traffic conditions. Effective DynamoDB autoscale helps to ensure your application remains responsive even during peak load, while also optimizing costs during periods of low activity. Monitoring your DynamoDB autoscale configuration via CloudWatch metrics will also help keep your dynamodb autoscale cost-effective.
Choosing the Right Autoscaling Metrics
Selecting the appropriate CloudWatch metrics is crucial for effective DynamoDB autoscale. Different metrics provide insights into various aspects of table performance, and the choice directly impacts how DynamoDB responds to changing workloads. Understanding the implications of each metric ensures that the dynamodb autoscale configuration aligns with application needs. Metrics like `ConsumedReadCapacityUnits` and `ConsumedWriteCapacityUnits` reflect the actual read and write activity, providing a direct measure of resource utilization. These are often preferred for basic dynamodb autoscale setups.
Using `ThrottledRequests` as a metric offers a different perspective. It indicates when requests are being rejected due to insufficient capacity. While reacting to throttling seems intuitive, it’s a reactive approach. Autoscaling based solely on `ThrottledRequests` might lead to performance degradation before scaling kicks in. Consider the application’s sensitivity to latency when choosing this metric. A proactive strategy using `ConsumedReadCapacityUnits` or `ConsumedWriteCapacityUnits` generally allows dynamodb autoscale to respond before throttling occurs, maintaining a smoother user experience. Furthermore, evaluate the difference between average and maximum values for these metrics. Spikes in consumed capacity might not be accurately reflected by average values, potentially delaying scaling responses.
The selection of the right metric for dynamodb autoscale depends heavily on the specific application requirements. Applications with predictable workloads can benefit from metrics tied to consumed capacity. Applications experiencing unpredictable spikes might require a more reactive approach, potentially incorporating `ThrottledRequests` as a secondary indicator. Careful analysis of application behavior and performance goals is necessary for choosing the most appropriate metrics. Experimentation and monitoring are also vital to fine-tune dynamodb autoscale policies and ensure optimal performance and cost efficiency. Remember that the goal is to automatically adjust capacity to meet demand, preventing both performance bottlenecks and unnecessary resource allocation. Consider combining multiple metrics and using more sophisticated scaling policies for complex scenarios.
Optimizing Autoscaling Policies for Cost Efficiency
Cost optimization is paramount when leveraging DynamoDB autoscale. Inefficiently configured autoscaling policies can lead to substantial and unnecessary expenses. DynamoDB autoscale continuously adjusts read and write capacity units (RCUs/WCUs). Therefore, understanding how to fine-tune these adjustments is critical for managing costs effectively. This involves a careful balancing act. The goal is to ensure application performance without over-provisioning resources. By refining scaling policies, users can minimize costs while maintaining acceptable levels of service. Several practical tips can guide this optimization process.
Adjusting scaling thresholds is a key strategy. The target utilization setting determines when DynamoDB autoscale adds or removes capacity. A lower target utilization triggers scaling events more frequently. While this can improve responsiveness, it can also lead to higher costs. Conversely, a higher target utilization reduces the frequency of scaling events. This can save money, but it may also result in performance degradation during peak loads. Setting appropriate scaling limits is equally important. Scaling limits define the minimum and maximum capacity that DynamoDB autoscale can provision. Setting a maximum limit prevents runaway costs during unexpected traffic surges. Setting a minimum limit ensures that sufficient capacity is always available to handle baseline traffic. Different scaling strategies can also impact cost efficiency. For example, consider using target tracking scaling policies. These policies automatically adjust capacity to maintain a specific target utilization. Another consideration is using scheduled scaling. Scheduled scaling adjusts capacity based on predictable traffic patterns. This is useful for known peak periods, such as during specific hours of the day or days of the week. Dynamodb autoscale will efficiently manage capacity if properly setup.
Regularly review and analyze CloudWatch metrics. This is essential for identifying areas where autoscaling policies can be improved. Look for patterns of over-provisioning or under-provisioning. Consider implementing step scaling policies. These policies allow you to define different scaling adjustments based on the size of the capacity deficit or surplus. Also evaluate the impact of scaling policies on application performance. Tools are available to simulate traffic and test the effectiveness of scaling policies. This allows you to identify and address potential issues before they impact production workloads. Remember that optimizing DynamoDB autoscale for cost efficiency is an ongoing process. It requires continuous monitoring, analysis, and refinement of scaling policies. This ensures that you are getting the most value from DynamoDB while minimizing unnecessary expenses.DynamoDB autoscale provides capabilities to ensure cost efficient configuration.
Handling Spikes and Unexpected Traffic Bursts with DynamoDB Autoscaling
DynamoDB autoscaling effectively manages sudden traffic spikes. Scaling policies rapidly adjust read and write capacity units (RCUs/WCUs). This ensures sustained application performance. The system dynamically responds to increased demand. It prevents performance degradation during unexpected traffic bursts. Properly configured dynamodb autoscale policies are crucial. They ensure smooth operation even under high load. Understanding scaling behavior is key for effective dynamodb autoscale management. Regular monitoring provides insights into performance under pressure.
Predictive scaling leverages historical data to anticipate traffic patterns. This proactive approach minimizes response times during predictable surges. Integrating dynamodb autoscale with other AWS services enhances its capabilities. For example, Application Load Balancers distribute traffic evenly. This prevents overload on individual DynamoDB tables. Lambda functions can trigger scaling actions based on custom logic. This allows for fine-grained control over resource allocation. DynamoDB’s dynamodb autoscale features provide robust solutions for handling various traffic scenarios. They ensure optimal performance and resource utilization.
Mitigating the impact of large traffic spikes requires a multi-faceted strategy. Consider implementing queuing mechanisms. This buffers incoming requests during periods of high load. Careful capacity planning helps prevent overwhelming the system. Regular load testing identifies bottlenecks. It helps refine scaling policies for optimal response to unexpected traffic bursts. Monitoring key metrics, such as throttled requests, provides early warnings of potential issues. These alerts trigger proactive adjustments to dynamodb autoscale settings. A well-designed dynamodb autoscale system minimizes the impact of unexpected traffic surges. It maintains application availability and responsiveness.
Monitoring and Managing DynamoDB Autoscaling
Effective monitoring is crucial for optimizing dynamodb autoscale performance and cost efficiency. Regularly review CloudWatch metrics to assess the effectiveness of your scaling policies. Key metrics include ConsumedReadCapacityUnits, ConsumedWriteCapacityUnits, ThrottledRequests, and ProvisionedReadCapacityUnits/ProvisionedWriteCapacityUnits. Analyzing these metrics reveals whether your dynamodb autoscale configuration adequately handles traffic demands. High throttled request counts suggest insufficient capacity, while consistently low utilization indicates over-provisioning and wasted resources. DynamoDB autoscaling dashboards provide a visual representation of these metrics, facilitating quick identification of potential issues. Setting up automated alerts based on critical thresholds ensures proactive responses to scaling problems. For example, an alert can trigger when throttled requests exceed a predefined percentage, prompting immediate investigation and adjustment of scaling policies. This proactive approach prevents performance degradation and ensures optimal dynamodb autoscale.
Addressing identified problems requires careful analysis and strategic adjustments to your dynamodb autoscale configuration. If throttling is frequent, increase scaling limits or adjust scaling thresholds to allow for quicker capacity increases. Conversely, consistently low utilization warrants a reduction in provisioned capacity to minimize costs. Experimentation with different scaling strategies, such as using different target utilization levels or adjusting scaling cooldown periods, can significantly impact performance and cost. Remember to document all changes made to scaling policies for future reference and troubleshooting. Maintaining detailed records improves understanding of past adjustments and their impact, guiding future optimization efforts. Continuous monitoring and iterative refinement of your dynamodb autoscale configuration are essential for long-term success.
Leverage CloudWatch alarms to proactively address potential issues. Configure alarms to trigger notifications or automated actions when key metrics deviate from established baselines. This proactive monitoring approach ensures swift responses to performance issues, minimizing disruptions and maintaining optimal dynamodb autoscale. For instance, an alarm triggered by high throttled requests can automatically initiate a scaling event, instantly increasing capacity. Integrating dynamodb autoscale with other AWS services, such as automated scaling of EC2 instances, further enhances responsiveness to traffic fluctuations. This integrated approach provides a holistic scaling solution, ensuring consistent application performance under varying load conditions. Remember, efficient dynamodb autoscale management requires continuous attention, iterative adjustments, and a commitment to data-driven decision-making. Regularly review and refine your strategies to maintain optimal performance and cost efficiency. The goal is a self-regulating system that adapts smoothly to changing demands, providing high availability and minimizing operational costs.
Advanced DynamoDB Autoscaling Techniques and Best Practices
Predictive scaling offers a proactive approach to dynamodb autoscale management. By analyzing historical data, DynamoDB can anticipate future traffic demands. This allows for preemptive scaling adjustments, preventing performance bottlenecks before they occur. Integration with other AWS services enhances dynamodb autoscale capabilities. For instance, Application Load Balancers distribute traffic efficiently across multiple DynamoDB tables. Lambda functions can trigger automated scaling actions based on specific events. These integrations create a robust, responsive, and highly available system. Proper architecture design is crucial for effective dynamodb autoscale. Consider using sharding strategies to distribute data and traffic across multiple tables. This approach enhances scalability and resilience. Employing global tables allows for geographically distributed deployments, improving latency and availability for users worldwide.
Handling extreme traffic conditions requires a layered approach to dynamodb autoscale. Implement robust error handling and retry mechanisms within your application code. This ensures that transient errors do not cascade and impact overall system performance. Utilize DynamoDB’s provisioned capacity modes strategically. While autoscaling offers flexibility, provisioned capacity provides predictable costs and performance for known workloads. Careful selection and monitoring of dynamodb autoscale metrics are paramount. Regularly review CloudWatch metrics to identify areas for optimization. Adjust scaling policies based on observed behavior and performance goals. The choice of metrics greatly influences the efficiency of dynamodb autoscale. For example, using throttled requests as a primary metric can provide early warnings of impending capacity issues.
Best practices for maximizing dynamodb autoscale effectiveness include regular policy reviews and adjustments. Ensure scaling limits are set appropriately, preventing runaway costs while maintaining adequate capacity. Implement automated alerts and dashboards to proactively monitor performance and identify anomalies. Regularly test your dynamodb autoscale configurations under simulated load conditions. This proactive approach helps validate policy effectiveness and identify potential weaknesses before they impact production systems. By adopting these advanced techniques and best practices, organizations can fully leverage DynamoDB’s autoscaling capabilities to achieve optimal performance, cost-efficiency, and high availability. The goal is seamless dynamodb autoscale that adapts to any workload demands without impacting user experience.