The Role of Disaster Recovery Planning for Cloud-Based Systems
Disaster recovery planning for cloud-based systems is a critical aspect of ensuring business continuity and minimizing the impact of unforeseen incidents. With the increasing adoption of cloud computing, organizations are leveraging the benefits of data protection, infrastructure redundancy, and incident response. However, neglecting disaster recovery planning can result in severe consequences, such as data loss, downtime, and financial impact.
Cloud-based systems offer numerous advantages over traditional on-premises infrastructure, including scalability, flexibility, and cost savings. However, these benefits also introduce new challenges in terms of disaster recovery planning. For instance, data and applications may be distributed across multiple cloud environments, making it difficult to ensure consistent recovery and continuity.
A robust disaster recovery plan for cloud-based systems should include several essential components, such as risk assessment, data backup, recovery sites, and incident response. By identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities, organizations can proactively address potential issues and minimize the impact of disruptions. Data backup is crucial for ensuring data availability and integrity, while recovery sites provide a redundant infrastructure to maintain business operations during an incident.
Incident response is another critical component of disaster recovery planning for cloud-based systems. By defining clear procedures and protocols, organizations can ensure a swift and effective response to incidents, minimizing the impact on business operations and reducing downtime. Moreover, regular testing and maintenance of the disaster recovery plan can help ensure its effectiveness and efficiency.
In conclusion, disaster recovery planning for cloud-based systems is essential for ensuring business continuity and minimizing the impact of unforeseen incidents. By incorporating essential components such as risk assessment, data backup, recovery sites, and incident response, organizations can proactively address potential issues and maintain business operations during disruptions. With the increasing adoption of cloud computing, it is crucial for organizations to prioritize disaster recovery planning and ensure the availability and integrity of their data and applications.

Key Components of a Robust Disaster Recovery Plan
Disaster recovery planning for cloud-based systems is a critical aspect of ensuring business continuity and minimizing the impact of unforeseen incidents. A robust disaster recovery plan should include several essential components, such as risk assessment, data backup, recovery sites, and incident response. These components contribute to a successful disaster recovery strategy by providing a comprehensive approach to managing potential disruptions.
Risk assessment is the first step in developing a disaster recovery plan for cloud-based systems. By identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities, organizations can proactively address potential issues and minimize the impact of disruptions. Risk assessment should consider factors such as data security, infrastructure reliability, and regulatory compliance. By understanding the potential risks, organizations can prioritize their disaster recovery efforts and allocate resources effectively.
Data backup is another critical component of a robust disaster recovery plan. By ensuring the availability and integrity of data, organizations can maintain business operations during an incident. Data backup should include regular backups of critical data, as well as redundant storage solutions to ensure data availability. Organizations should also consider data backup frequency, retention policies, and backup locations to ensure a comprehensive data backup strategy.
Recovery sites provide a redundant infrastructure to maintain business operations during an incident. By replicating critical applications and data to a secondary site, organizations can ensure business continuity during a disruption. Recovery sites can be physical or virtual, and organizations should consider factors such as location, infrastructure, and cost when selecting a recovery site. Organizations should also ensure that recovery sites are regularly tested and updated to ensure their effectiveness and efficiency.
Incident response is the final component of a robust disaster recovery plan. By defining clear procedures and protocols, organizations can ensure a swift and effective response to incidents, minimizing the impact on business operations and reducing downtime. Incident response should include procedures for identifying, containing, and resolving incidents, as well as communication protocols to ensure stakeholders are informed of the incident and its resolution.
In conclusion, disaster recovery planning for cloud-based systems is essential for ensuring business continuity and minimizing the impact of unforeseen incidents. By incorporating essential components such as risk assessment, data backup, recovery sites, and incident response, organizations can proactively address potential issues and maintain business operations during disruptions. With the increasing adoption of cloud computing, it is crucial for organizations to prioritize disaster recovery planning and ensure the availability and integrity of their data and applications.
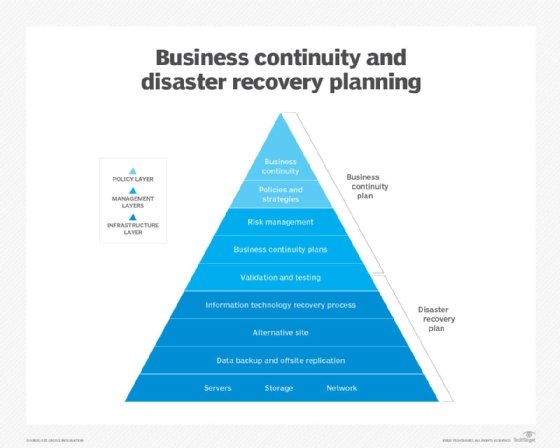
How to Develop a Disaster Recovery Plan for Cloud-Based Systems: A Practical Guide
Disaster recovery planning for cloud-based systems is a critical aspect of ensuring business continuity and minimizing the impact of unforeseen incidents. By developing a robust disaster recovery plan, organizations can protect their data, maintain infrastructure redundancy, and ensure effective incident response. In this practical guide, we will outline the steps involved in developing a disaster recovery plan for cloud-based systems.
Define the scope and objectives: The first step in developing a disaster recovery plan for cloud-based systems is to define the scope and objectives. This involves identifying the critical applications and data that need to be protected, as well as the recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) for each application. By defining the scope and objectives, organizations can ensure that their disaster recovery plan aligns with their business requirements and priorities.
Identify the critical applications and data: The next step is to identify the critical applications and data that need to be protected. This involves conducting a risk assessment to identify potential vulnerabilities and threats, as well as evaluating the business impact of downtime or data loss. By identifying the critical applications and data, organizations can prioritize their disaster recovery efforts and allocate resources effectively.
Select the recovery sites and technologies: The third step is to select the recovery sites and technologies that will be used in the event of a disruption. This involves evaluating the different recovery site options, such as hot sites, warm sites, and cold sites, as well as the different recovery technologies, such as replication, backup, and failover. By selecting the appropriate recovery sites and technologies, organizations can ensure that they can quickly and effectively recover their critical applications and data in the event of a disruption.
Test the plan: The fourth step is to test the disaster recovery plan to ensure that it is effective and efficient. This involves conducting regular testing and simulations to evaluate the plan’s effectiveness and identify any areas for improvement. By testing the plan, organizations can ensure that they are prepared to respond effectively to incidents and minimize the impact on business operations.
Maintain the plan: The final step is to maintain the disaster recovery plan to ensure that it remains up-to-date and relevant. This involves regularly reviewing and updating the plan based on changes in the cloud environment and the business requirements. By maintaining the plan, organizations can ensure that they are prepared to respond effectively to incidents and maintain business continuity.
In conclusion, developing a disaster recovery plan for cloud-based systems is essential for ensuring business continuity and minimizing the impact of unforeseen incidents. By following this practical guide, organizations can develop a robust disaster recovery plan that aligns with their business requirements and priorities. With the increasing adoption of cloud computing, it is crucial for organizations to prioritize disaster recovery planning and ensure the availability and integrity of their data and applications.

Implementing a Disaster Recovery Plan for Cloud-Based Systems: Best Practices and Considerations
Disaster recovery planning for cloud-based systems is a critical aspect of ensuring business continuity and minimizing the impact of unforeseen incidents. Once a disaster recovery plan has been developed, the next step is to implement it effectively. In this section, we will discuss the steps involved in implementing a disaster recovery plan for cloud-based systems, as well as best practices and considerations to keep in mind.
Configure the recovery sites and technologies: The first step in implementing a disaster recovery plan for cloud-based systems is to configure the recovery sites and technologies. This involves setting up the recovery sites, such as hot sites, warm sites, or cold sites, and configuring the recovery technologies, such as replication, backup, and failover. By configuring the recovery sites and technologies, organizations can ensure that they are prepared to quickly and effectively recover their critical applications and data in the event of a disruption.
Train the staff: The next step is to train the staff on the disaster recovery plan and the recovery sites and technologies. This involves providing training and education to the relevant staff members on their roles and responsibilities in the event of a disruption, as well as the steps involved in recovering the critical applications and data. By training the staff, organizations can ensure that they are prepared to respond effectively to incidents and minimize the impact on business operations.
Test the plan: The third step is to test the disaster recovery plan to ensure that it is effective and efficient. This involves conducting regular testing and simulations to evaluate the plan’s effectiveness and identify any areas for improvement. By testing the plan, organizations can ensure that they are prepared to respond effectively to incidents and minimize the impact on business operations.
Best practices and considerations: When implementing a disaster recovery plan for cloud-based systems, there are several best practices and considerations to keep in mind. These include:
- Automating the recovery processes: By automating the recovery processes, organizations can ensure that they are executed quickly and efficiently in the event of a disruption.
- Involving the key stakeholders: By involving the key stakeholders, such as the business units, IT, and security, organizations can ensure that the disaster recovery plan aligns with the business requirements and priorities.
- Integrating the plan with the business continuity plan: By integrating the disaster recovery plan with the business continuity plan, organizations can ensure that they have a comprehensive approach to managing incidents and minimizing the impact on business operations.
In conclusion, implementing a disaster recovery plan for cloud-based systems is essential for ensuring business continuity and minimizing the impact of unforeseen incidents. By following this practical guide, organizations can implement a robust disaster recovery plan that aligns with their business requirements and priorities. With the increasing adoption of cloud computing, it is crucial for organizations to prioritize disaster recovery planning and ensure the availability and integrity of their data and applications.
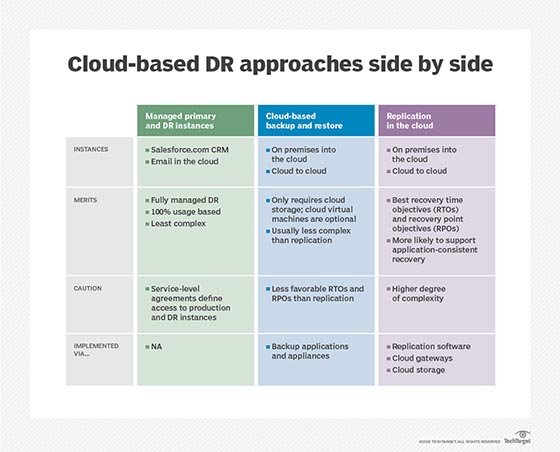
Reviewing and Improving a Disaster Recovery Plan for Cloud-Based Systems: Tips and Strategies
Disaster recovery planning for cloud-based systems is an ongoing process that requires regular evaluation and refinement. By reviewing and improving the disaster recovery plan, organizations can ensure that it remains effective and up-to-date with the changes in the cloud environment and the business requirements. In this section, we will discuss the importance of regularly reviewing and refining a disaster recovery plan for cloud-based systems, as well as tips and strategies for improving the plan’s efficiency and accuracy.
Evaluate the effectiveness of the plan: The first step in reviewing and improving a disaster recovery plan for cloud-based systems is to evaluate its effectiveness. This involves assessing the plan’s performance during testing and simulations, as well as its ability to meet the business requirements and objectives. By evaluating the effectiveness of the plan, organizations can identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments.
Test the plan: The second step is to test the disaster recovery plan regularly to ensure that it is effective and efficient. This involves conducting regular testing and simulations to evaluate the plan’s performance and identify any areas for improvement. By testing the plan, organizations can ensure that they are prepared to respond effectively to incidents and minimize the impact on business operations.
Update the plan based on the changes in the cloud environment and the business requirements: The third step is to update the disaster recovery plan based on the changes in the cloud environment and the business requirements. This involves reviewing and updating the plan regularly to ensure that it remains aligned with the business requirements and priorities, as well as the changes in the cloud environment. By updating the plan, organizations can ensure that they are prepared to respond effectively to incidents and minimize the impact on business operations.
Tips and strategies for improving the plan’s efficiency and accuracy: When reviewing and improving a disaster recovery plan for cloud-based systems, there are several tips and strategies to keep in mind. These include:
- Automating the disaster recovery processes: By automating the disaster recovery processes, organizations can ensure that they are executed quickly and efficiently in the event of a disruption.
- Involving the key stakeholders: By involving the key stakeholders, such as the business units, IT, and security, organizations can ensure that the disaster recovery plan aligns with the business requirements and priorities.
- Integrating the plan with the business continuity plan: By integrating the disaster recovery plan with the business continuity plan, organizations can ensure that they have a comprehensive approach to managing incidents and minimizing the impact on business operations.
In conclusion, regularly reviewing and refining a disaster recovery plan for cloud-based systems is essential for ensuring business continuity and minimizing the impact of unforeseen incidents. By following these tips and strategies, organizations can improve the efficiency and accuracy of their disaster recovery plan and ensure that they are prepared to respond effectively to incidents. With the increasing adoption of cloud computing, it is crucial for organizations to prioritize disaster recovery planning and ensure the availability and integrity of their data and applications.
Case Study: A Successful Disaster Recovery Implementation in the Cloud
Disaster recovery planning for cloud-based systems is a critical aspect of ensuring business continuity and minimizing the impact of unforeseen incidents. In this case study, we will explore a successful disaster recovery implementation in the cloud, highlighting the challenges faced, the solutions implemented, and the outcomes achieved.
XYZ Corporation, a mid-sized financial services firm, decided to migrate its business-critical applications and data to the cloud to improve scalability, flexibility, and disaster recovery capabilities. However, the company faced several challenges in implementing a robust disaster recovery plan for its cloud-based systems.
First, the company struggled to identify the critical applications and data that required disaster recovery protection. Additionally, the company lacked a clear understanding of the recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) for its cloud-based systems. Furthermore, the company faced challenges in selecting the appropriate recovery sites and technologies that aligned with its business requirements and budget.
To address these challenges, XYZ Corporation engaged a cloud disaster recovery service provider to assist with the implementation of a robust disaster recovery plan. The service provider helped the company identify the critical applications and data, set the appropriate RTOs and RPOs, and select the recovery sites and technologies that aligned with its business requirements and budget.
The service provider also automated the disaster recovery processes, involving the key stakeholders, and integrating the plan with the business continuity plan. Additionally, the service provider conducted regular testing and simulations to evaluate the plan’s performance and identify any areas for improvement.
As a result of the successful implementation of the disaster recovery plan, XYZ Corporation achieved several outcomes. The company improved its recovery time and recovery point objectives, minimizing the impact of unforeseen incidents on business operations. Additionally, the company reduced the risk of data loss, downtime, and financial impact. Furthermore, the company improved its compliance posture, meeting the regulatory requirements for disaster recovery.
In conclusion, this case study highlights the importance of implementing a robust disaster recovery plan for cloud-based systems. By engaging a cloud disaster recovery service provider, XYZ Corporation was able to overcome the challenges it faced and achieve several outcomes, including improved recovery time and recovery point objectives, reduced risk of data loss, downtime, and financial impact, and improved compliance posture. By prioritizing disaster recovery planning, organizations can ensure business continuity and minimize the impact of unforeseen incidents in the cloud.

Emerging Trends and Technologies in Cloud-Based Disaster Recovery
Disaster recovery planning for cloud-based systems is an ever-evolving field, with new trends and technologies emerging regularly. In this section, we will explore some of the most significant trends and technologies in cloud-based disaster recovery, including artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation. We will also discuss how these technologies can improve disaster recovery planning and response.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are two of the most promising technologies in cloud-based disaster recovery. These technologies can help organizations automate disaster recovery processes, reduce recovery times, and improve overall disaster recovery planning and response. For example, AI and ML can be used to analyze data patterns, identify potential threats, and predict disaster scenarios. This information can then be used to develop more effective disaster recovery plans and response strategies.
Automation is another critical trend in cloud-based disaster recovery. Automation can help organizations reduce the time and effort required to manage disaster recovery processes. For example, automated disaster recovery solutions can be used to automatically backup critical data, replicate virtual machines, and failover to backup sites. Automation can also help organizations reduce the risk of human error, which is a leading cause of disaster recovery failures.
Another emerging trend in cloud-based disaster recovery is the use of cloud-native disaster recovery solutions. Cloud-native disaster recovery solutions are designed to work seamlessly with cloud-based systems and applications. These solutions can provide several benefits, including reduced costs, improved scalability, and increased flexibility. Cloud-native disaster recovery solutions can also help organizations take advantage of the inherent disaster recovery capabilities of cloud platforms, such as automatic data replication and failover.
In conclusion, emerging trends and technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation, are transforming cloud-based disaster recovery planning and response. By leveraging these technologies, organizations can improve their disaster recovery capabilities, reduce recovery times, and minimize the impact of unforeseen incidents. As cloud-based systems continue to evolve, it is essential to stay up-to-date with the latest trends and technologies in cloud-based disaster recovery to ensure business continuity and minimize the risk of data loss, downtime, and financial impact.
Addressing Common Misconceptions about Cloud-Based Disaster Recovery
Disaster recovery planning for cloud-based systems is a critical aspect of ensuring business continuity and minimizing the impact of unforeseen incidents. However, there are several misconceptions surrounding cloud-based disaster recovery that may discourage organizations from implementing it. Here, we aim to debunk these myths and clarify the benefits of cloud-based disaster recovery planning.
Myth 1: Cloud-based disaster recovery is too expensive for small businesses. In reality, cloud-based disaster recovery can be more cost-effective than traditional on-premises solutions. Small businesses can leverage the economies of scale provided by cloud service providers, paying only for the resources they need and avoiding the upfront costs associated with building and maintaining their own disaster recovery infrastructure.
Myth 2: Cloud-based disaster recovery is complex and difficult to manage. While there may be a learning curve when implementing cloud-based disaster recovery, many cloud service providers offer user-friendly interfaces and extensive documentation to guide businesses through the process. Additionally, managed service providers can be engaged to handle the implementation and management of the disaster recovery plan, further simplifying the process for businesses.
Myth 3: Cloud-based disaster recovery is less secure than on-premises solutions. Cloud service providers invest heavily in security measures and adhere to stringent compliance standards, often providing a more secure environment than individual businesses can maintain. Furthermore, cloud-based disaster recovery solutions can be customized to meet specific security requirements, ensuring the protection of sensitive data and systems.
Myth 4: Cloud-based disaster recovery is only for large enterprises. Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) can also benefit significantly from cloud-based disaster recovery planning. In fact, SMBs may have even more to gain, as they typically have fewer resources to dedicate to disaster recovery and are often more vulnerable to the financial and reputational impacts of downtime and data loss.
Myth 5: Cloud-based disaster recovery is a “set it and forget it” solution. While cloud-based disaster recovery solutions offer a high degree of automation, it is essential to regularly review and test the disaster recovery plan to ensure it remains effective and up-to-date. This includes monitoring the cloud environment, updating the plan based on changes in business requirements, and conducting regular testing to identify and address any potential issues.
By addressing these common misconceptions, businesses can better understand the benefits and value of cloud-based disaster recovery planning and make informed decisions about implementing a solution tailored to their specific needs and requirements.

