What are Deployment Models?
Deployment models refer to the various methods of deploying and managing IT infrastructure and services. In today’s digital age, deployment models play a crucial role in modern IT infrastructure, enabling businesses to choose the best approach that aligns with their specific needs and objectives. Different deployment models cater to various business requirements, such as scalability, security, cost, and customization.
The significance of deployment models lies in their ability to provide businesses with the flexibility to choose the right infrastructure that supports their applications, data, and workloads. By understanding the various deployment models available, businesses can make informed decisions that optimize their IT investments, enhance their operational efficiency, and improve their overall competitiveness in the market.
Key Considerations for Choosing Deployment Models
When choosing a deployment model, businesses must consider several factors to ensure that the chosen model aligns with their specific needs and objectives. Some of the key considerations include:
- Scalability: The ability to scale up or down based on changing business needs is a critical consideration. Public and private cloud deployment models offer scalability, while on-premises deployment models may require additional investment to scale.
- Security: Security is a significant concern for businesses, and the chosen deployment model must provide adequate protection for sensitive data and applications. Private cloud and on-premises deployment models offer enhanced security, while public cloud deployment models may pose data privacy and security concerns.
- Cost: The cost of deploying and managing IT infrastructure is a critical consideration for businesses. Public cloud deployment models offer cost-effectiveness, while on-premises deployment models may require significant upfront investment.
- Customization: The ability to customize IT infrastructure to meet specific business needs is essential. Private cloud and on-premises deployment models offer customization, while public cloud deployment models may have limitations.
By considering these factors, businesses can choose the right deployment model that aligns with their specific needs and objectives. It is essential to ensure that the chosen deployment model supports the business’s applications, data, and workloads, optimizes IT investments, enhances operational efficiency, and improves overall competitiveness in the market.
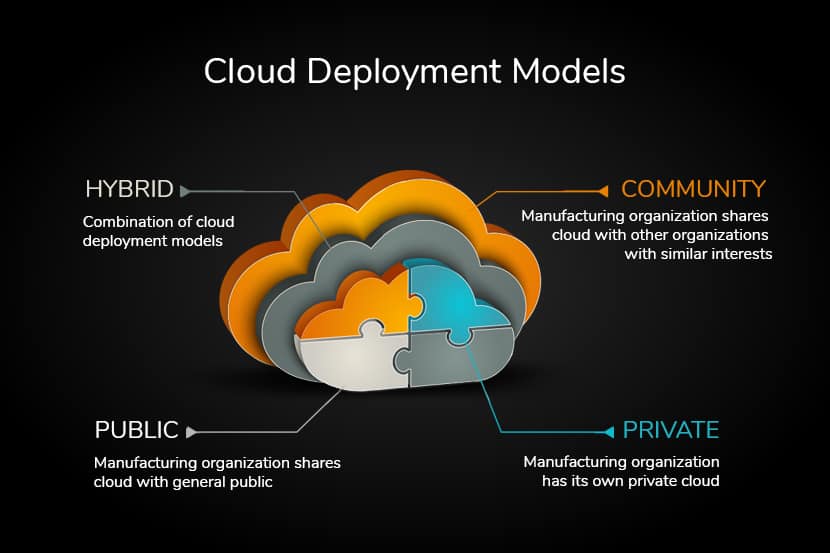
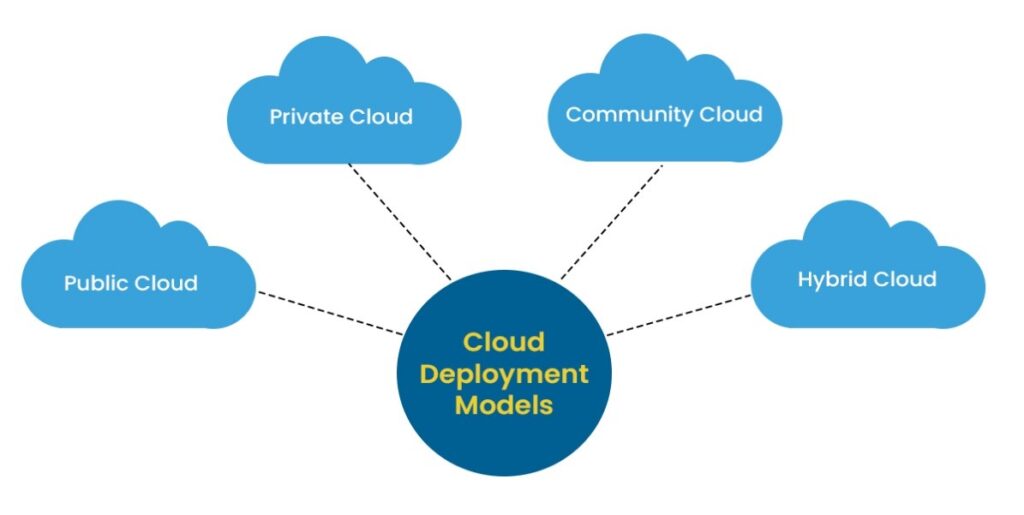
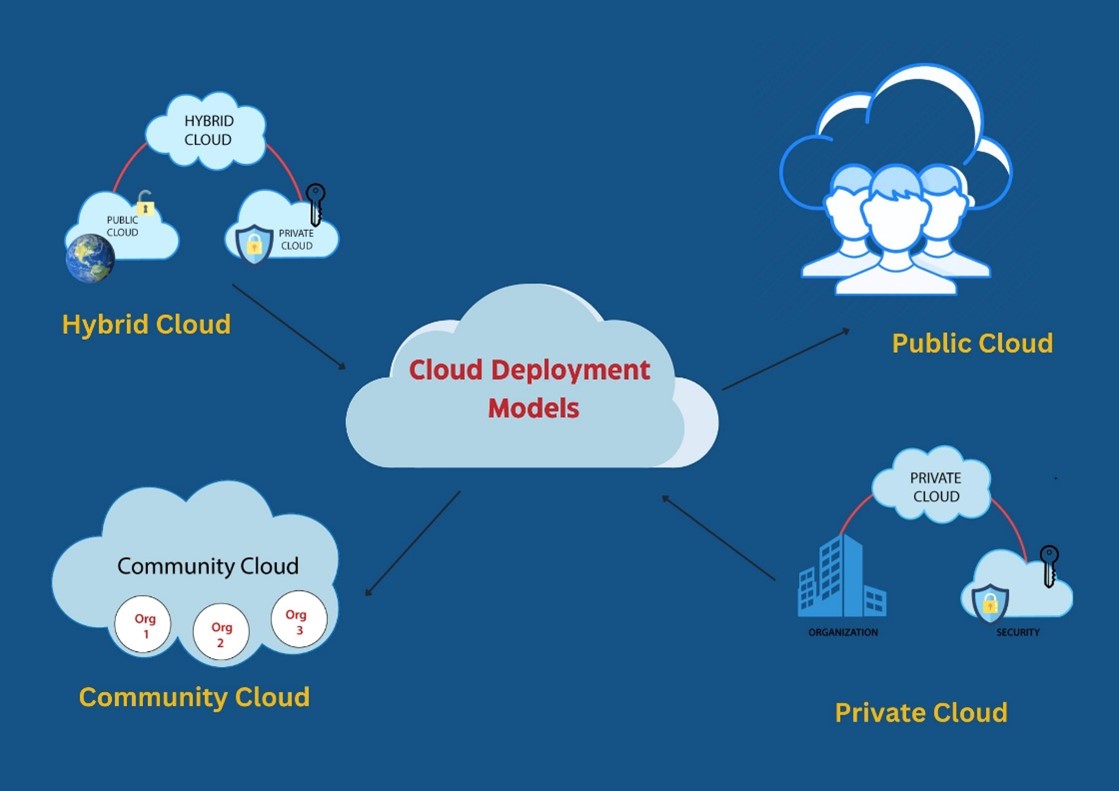
Types of Deployment Models
Businesses can choose from various deployment models, each with its unique benefits and drawbacks. The most common deployment models include:
On-Premises Deployment Models
On-premises deployment models involve deploying and managing IT infrastructure on-site, within the business’s premises. This model offers full control over the IT infrastructure, data security, and compliance. However, it requires significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance and management costs.
Public Cloud Deployment Models
Public cloud deployment models involve using a third-party provider’s infrastructure and services, which are accessible over the internet. This model offers scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, as businesses only pay for the resources they use. However, it may pose data privacy and security concerns, as sensitive data is stored off-site.
Private Cloud Deployment Models
Private cloud deployment models involve using a dedicated infrastructure and services, which are accessible over a private network. This model offers dedicated resources, enhanced security, and customization. However, it requires significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance and management costs.
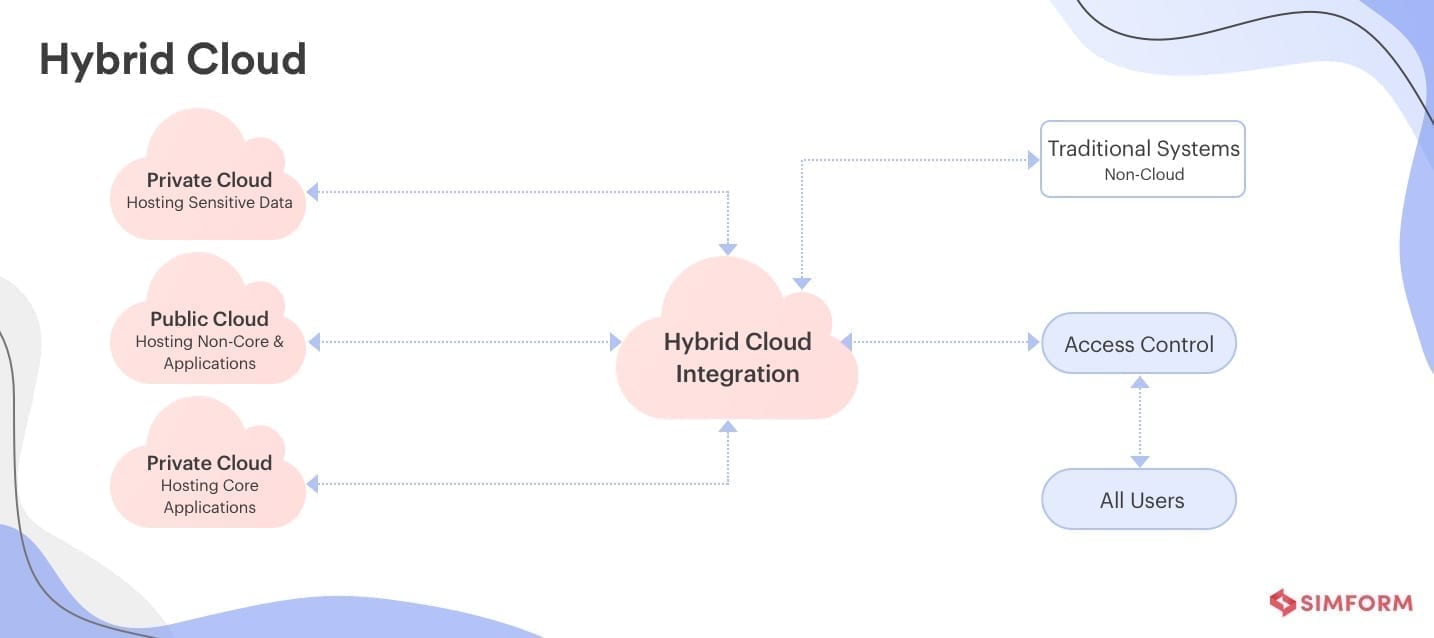
Hybrid Cloud Deployment Models
Hybrid cloud deployment models involve combining on-premises and cloud infrastructure. This model offers the benefits of both on-premises and cloud deployment models, such as full control over the IT infrastructure, data security, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. However, it may pose integration and management challenges.
Multi-Cloud Deployment Models
Multi-cloud deployment models involve using multiple cloud providers for redundancy, cost optimization, and flexibility. This model offers the benefits of using best-of-breed services from different providers, as well as redundancy and cost optimization. However, it may pose management and integration challenges.
By understanding the different deployment models available, businesses can choose the right model that aligns with their specific needs and objectives. It is essential to consider factors such as scalability, security, cost, and customization when choosing a deployment model to ensure that it supports the business’s applications, data, and workloads, optimizes IT investments, enhances operational efficiency, and improves overall competitiveness in the market.
On-Premises Deployment Models
On-premises deployment models refer to the traditional method of deploying and managing IT infrastructure within an organization’s premises. This method offers several advantages, including full control over the IT infrastructure, data security, and compliance. Here are some of the key features and benefits of on-premises deployment models:
- Full Control: On-premises deployment models offer full control over the IT infrastructure, including hardware, software, and network configurations. This level of control enables organizations to customize their infrastructure to meet their specific needs and requirements.
- Data Security: With on-premises deployment models, organizations have complete control over their data, including where it is stored and how it is accessed. This level of control enables organizations to implement robust security measures to protect their data from unauthorized access, theft, or loss.
- Compliance: On-premises deployment models enable organizations to comply with various regulations and standards, such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and GDPR, by maintaining full control over their IT infrastructure and data.
However, on-premises deployment models also have some drawbacks, including high upfront costs, ongoing maintenance and management costs, and the need for specialized skills and expertise to manage and maintain the infrastructure. Here are some of the challenges of managing and maintaining on-premises infrastructure:
- High Upfront Costs: On-premises deployment models require significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and network infrastructure. This level of investment can be a barrier to entry for small and medium-sized businesses.
- Ongoing Maintenance and Management Costs: On-premises deployment models require ongoing maintenance and management costs, including hardware and software upgrades, security patches, and technical support. These costs can add up over time and become a significant burden for organizations.
- Specialized Skills and Expertise: Managing and maintaining on-premises infrastructure requires specialized skills and expertise. Organizations may need to hire and train IT staff or outsource the management and maintenance of their infrastructure to third-party vendors.
Despite these challenges, on-premises deployment models remain a popular choice for organizations that require full control over their IT infrastructure, data security, and compliance. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of on-premises deployment models, organizations can make informed decisions about the best deployment model for their specific needs and requirements.
Public Cloud Deployment Models
Public cloud deployment models refer to the use of computing resources, such as servers, storage, and applications, that are owned and managed by a third-party provider and are available to the general public over the internet. Public cloud deployment models offer several benefits, including scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Here are some of the key features and benefits of public cloud deployment models:
- Scalability: Public cloud deployment models offer near-infinite scalability, enabling organizations to quickly and easily scale up or down their computing resources as needed.
- Flexibility: Public cloud deployment models offer flexibility, enabling organizations to choose from a range of computing resources, such as servers, storage, and applications, and only pay for what they use.
- Cost-effectiveness: Public cloud deployment models offer cost-effectiveness, enabling organizations to reduce their capital and operational expenses by outsourcing the management and maintenance of their computing resources to third-party providers.
However, public cloud deployment models also have some potential drawbacks, including data privacy and security concerns. Here are some of the potential drawbacks of public cloud deployment models:
- Data Privacy: Public cloud deployment models involve storing data on third-party servers, which may raise concerns about data privacy and security. Organizations may be required to comply with various regulations and standards, such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and GDPR, which may be difficult to achieve in a public cloud environment.
- Security: Public cloud deployment models may be vulnerable to security threats, such as hacking, data breaches, and cyber attacks. Organizations may need to implement additional security measures, such as encryption, firewalls, and access controls, to protect their data in a public cloud environment.
Despite these potential drawbacks, public cloud deployment models remain a popular choice for organizations that require scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. By understanding the benefits and drawbacks of public cloud deployment models, organizations can make informed decisions about the best deployment model for their specific needs and requirements.
Private Cloud Deployment Models
Private cloud deployment models refer to the use of computing resources, such as servers, storage, and applications, that are owned, operated, and managed by a single organization. Private cloud deployment models offer several benefits, including dedicated resources, enhanced security, and customization. Here are some of the key features and benefits of private cloud deployment models:
- Dedicated Resources: Private cloud deployment models offer dedicated resources, enabling organizations to allocate computing resources, such as servers, storage, and applications, based on their specific needs and requirements.
- Enhanced Security: Private cloud deployment models offer enhanced security, enabling organizations to implement robust security measures, such as firewalls, access controls, and encryption, to protect their data and applications.
- Customization: Private cloud deployment models offer customization, enabling organizations to tailor their computing resources, such as servers, storage, and applications, to meet their specific needs and requirements.
However, private cloud deployment models also have some potential drawbacks, including high upfront costs and the need for specialized skills and expertise to manage and maintain the infrastructure. Here are some of the potential drawbacks of private cloud deployment models:
- High Upfront Costs: Private cloud deployment models require significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and network infrastructure. This level of investment can be a barrier to entry for small and medium-sized businesses.
- Specialized Skills and Expertise: Managing and maintaining private cloud infrastructure requires specialized skills and expertise. Organizations may need to hire and train IT staff or outsource the management and maintenance of their infrastructure to third-party vendors.
Despite these potential drawbacks, private cloud deployment models remain a popular choice for organizations that require dedicated resources, enhanced security, and customization. By understanding the benefits and drawbacks of private cloud deployment models, organizations can make informed decisions about the best deployment model for their specific needs and requirements.
Hybrid Cloud Deployment Models
Hybrid cloud deployment models refer to the use of both on-premises and cloud infrastructure, enabling organizations to take advantage of the benefits of both deployment models. Hybrid cloud deployment models offer several benefits, including scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Here are some of the key features and benefits of hybrid cloud deployment models:
- Scalability: Hybrid cloud deployment models offer scalability, enabling organizations to quickly and easily scale up or down their computing resources as needed.
- Flexibility: Hybrid cloud deployment models offer flexibility, enabling organizations to choose the best deployment model for their specific needs and requirements.
- Cost-effectiveness: Hybrid cloud deployment models offer cost-effectiveness, enabling organizations to reduce their capital and operational expenses by outsourcing the management and maintenance of their computing resources to third-party providers.
However, hybrid cloud deployment models also have some potential drawbacks, including the challenges of integrating and managing hybrid cloud environments. Here are some of the potential drawbacks of hybrid cloud deployment models:
- Integration Challenges: Hybrid cloud deployment models require the integration of on-premises and cloud infrastructure, which can be complex and time-consuming.
- Management Challenges: Hybrid cloud deployment models require the management of both on-premises and cloud infrastructure, which can be complex and challenging.
Despite these potential drawbacks, hybrid cloud deployment models remain a popular choice for organizations that require scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. By understanding the benefits and drawbacks of hybrid cloud deployment models, organizations can make informed decisions about the best deployment model for their specific needs and requirements.
Multi-Cloud Deployment Models
Multi-cloud deployment models refer to the use of multiple cloud providers and platforms to support an organization’s IT infrastructure. Multi-cloud deployment models offer several benefits, including redundancy, cost optimization, and flexibility. Here are some of the key features and benefits of multi-cloud deployment models:
- Redundancy: Multi-cloud deployment models offer redundancy, enabling organizations to ensure the availability and reliability of their IT infrastructure by using multiple cloud providers and platforms.
- Cost Optimization: Multi-cloud deployment models offer cost optimization, enabling organizations to reduce their capital and operational expenses by using the most cost-effective cloud providers and platforms for their specific needs and requirements.
- Flexibility: Multi-cloud deployment models offer flexibility, enabling organizations to choose the best cloud providers and platforms for their specific needs and requirements.
However, multi-cloud deployment models also have some potential drawbacks, including the challenges of managing and integrating multi-cloud environments. Here are some of the potential drawbacks of multi-cloud deployment models:
- Management Challenges: Multi-cloud deployment models require the management of multiple cloud providers and platforms, which can be complex and challenging.
- Integration Challenges: Multi-cloud deployment models require the integration of multiple cloud providers and platforms, which can be complex and time-consuming.
Despite these potential drawbacks, multi-cloud deployment models remain a popular choice for organizations that require redundancy, cost optimization, and flexibility. By understanding the benefits and drawbacks of multi-cloud deployment models, organizations can make informed decisions about the best deployment model for their specific needs and requirements.
How to Choose the Right Deployment Model
Choosing the right deployment model is essential for the success of any organization’s IT infrastructure. The deployment model should align with the organization’s business objectives, technical requirements, and budget. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to choose the right deployment model:
Step 1: Assess Business Needs
The first step in choosing the right deployment model is to assess the organization’s business needs. This includes understanding the organization’s goals, objectives, and requirements. It is essential to consider factors such as scalability, security, cost, and customization when assessing business needs.
Step 2: Evaluate Technical Requirements
The second step is to evaluate the organization’s technical requirements. This includes assessing the organization’s current IT infrastructure, applications, and workloads. It is essential to consider factors such as performance, availability, and compatibility when evaluating technical requirements.
Step 3: Consider Cost and Scalability Factors
The third step is to consider cost and scalability factors. This includes assessing the organization’s budget and growth plans. It is essential to consider factors such as capital and operational expenses, return on investment, and long-term scalability when considering cost and scalability factors.
Step 4: Choose the Right Deployment Model
The final step is to choose the right deployment model based on the organization’s business needs, technical requirements, and cost and scalability factors. Here are some factors to consider when choosing the right deployment model:
- On-Premises Deployment Models: On-premises deployment models are ideal for organizations that require full control over their IT infrastructure, data security, and compliance. However, they can be challenging to manage and maintain.
- Public Cloud Deployment Models: Public cloud deployment models are ideal for organizations that require scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. However, they may have data privacy and security concerns.
- Private Cloud Deployment Models: Private cloud deployment models are ideal for organizations that require dedicated resources, enhanced security, and customization. However, they can be expensive to manage and maintain.
- Hybrid Cloud Deployment Models: Hybrid cloud deployment models are ideal for organizations that require the benefits of both on-premises and cloud infrastructure. However, they can be complex and challenging to integrate and manage.
- Multi-Cloud Deployment Models: Multi-cloud deployment models are ideal for organizations that require redundancy, cost optimization, and flexibility. However, they can be complex and challenging to manage and integrate.
By following these steps, organizations can choose the right deployment model that aligns with their business objectives, technical requirements, and cost and scalability factors.