Understanding the Nuances: Database and Data Migration Defined
Data migration vs database migration are frequently used terms, but they represent distinct processes. Understanding the difference is crucial for selecting the appropriate strategy for any project. Database migration specifically focuses on moving an entire database system from one platform to another. For instance, transferring from MySQL to PostgreSQL is a database migration. Data migration, on the other hand, is a broader concept encompassing the movement of data between any two systems, whether databases or not. This could involve transferring data from a legacy system to a cloud-based data warehouse. Think of data migration as moving items from one container (system) to another. Database migration is like swapping one container type for another. Real-world examples include migrating customer data from an old CRM to a new one, or transferring sales figures from an on-premises system to a cloud-based data repository.
The key distinction lies in the scope of the undertaking. Data migration involves the transfer of data itself, while database migration involves the migration of the entire database system. Factors like source and target systems, data volume and type, budget, and timeline all play a significant role in deciding on the suitable approach for a particular scenario. Choosing the right strategy for data migration versus database migration involves a thorough evaluation of the specific needs of the project. Careful consideration of data volume, format, and the capabilities of the target and source systems is essential to ensure a smooth and efficient data transfer process. The complexity of data migration will vary greatly, depending on the specific situation.
Choosing the right approach for data migration vs database migration often involves considering the existing systems and the desired outcomes. A clear understanding of the data volume, data types, and compatibility between the source and target systems is essential for successful migration. For instance, migrating data from a legacy system that stores customer records might be different than migrating data from an e-commerce system that collects millions of transactions daily. The volume and complexity of the data will largely determine the complexity of the entire migration process. This comprehensive understanding helps to identify the specific steps required to complete the project effectively, saving time and resources. This in turn leads to a smooth and efficient data transfer process.
Identifying Your Migration Needs: Choosing the Right Approach
Determining the appropriate data migration strategy hinges on careful analysis of the situation. Understanding the nuances of data migration vs database migration is crucial. A systematic approach to evaluating the source and target systems, data volume and types, budget constraints, and timelines is vital. Evaluating the specific needs of a data migration project is critical. For instance, migrating data from a legacy system to a cloud-based data warehouse might require a different approach than simply switching database systems. This careful consideration helps to ensure a smooth and successful transition.
Factors like the complexity of the source and target systems heavily influence the choice of migration strategy. The volume and type of data play a significant role. A large volume of data requires a more robust and potentially more complex data migration vs database migration process. The available budget and timeline also determine the best strategy. A well-defined budget and realistic timelines directly impact the achievable outcome. This multi-faceted evaluation helps to identify the appropriate data migration vs database migration path. Consider establishing a decision tree or flowchart to guide the selection process. For example, a decision tree could evaluate factors such as the size of the data, the complexity of the systems, and the available resources to recommend the most suitable data migration strategy.
A detailed assessment of the source and target systems is fundamental. Detailed information about the source and target systems is imperative. Analyzing compatibility, data formats, and system limitations is vital. Thorough data profiling is important to analyze the volume, types, and structure of the data to be migrated. Resource constraints need to be taken into account. Assessing and planning the budget and timeline allocations for the entire data migration vs database migration process is critical. The decision-making process should use a structured approach with clear criteria. Using tools or methodologies that assist with evaluating data migration vs database migration needs is highly recommended.
Planning Your Data Migration: A Step-by-Step Guide
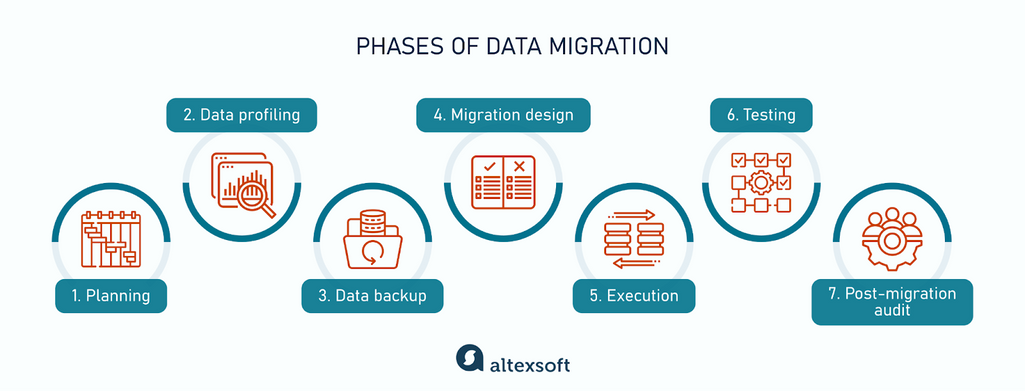
A well-structured approach to data migration vs database migration is crucial for a successful outcome. This step-by-step guide provides a roadmap for planning and executing a data migration project. Thorough planning minimizes risks and maximizes the chances of a smooth transition.
Assessment: Begin by thoroughly assessing the current state of the source system and target system. Identify the volume and types of data, and the format inconsistencies that might hinder a smooth data migration. This assessment helps in estimating the time, resources, and potential complications. Determine the available resources, including the necessary tools and personnel required. Also, define clear success metrics for the data migration vs database migration to track progress and measure results.
Planning: Create a detailed project plan, outlining the timelines, milestones, and responsibilities. Document the entire process clearly and concisely, including communication protocols for the data migration vs database migration project. The project plan should encompass a detailed timeline, budget considerations, and risk mitigation strategies. Thoroughly consider potential issues and develop contingency plans. Define clear communication channels for team members to promptly share concerns or feedback.
Data Extraction: Employ the appropriate tools to extract data from the source system. Validate the extracted data by comparing it to the source system data. Ensure the data integrity of this extraction phase. Implement quality controls. Data validation and verification are crucial to prevent issues during the data migration vs database migration process. This ensures the integrity of the data and avoids discrepancies.
Transformation: This crucial step involves cleaning and transforming the data to meet the target system’s requirements. Address inconsistencies in data formats, resolve missing values, and handle duplicates. Data profiling identifies any unusual data characteristics or problems. Deduplication eliminates redundant entries. Ensure the data adheres to target standards and formats, aligning with the target data structure. This critical step determines the overall quality of the data migration vs database migration process.
Loading (ETL): Load the transformed data into the target system. Establish effective procedures to ensure data consistency and accuracy. Validate the loaded data to confirm its integrity and consistency with the target system specifications. Continuously monitor and track any errors during the loading phase.
Testing: Implement various testing strategies to verify the correctness of the migrated data and functionality of the target system. Rigorous testing, including unit, integration, and user acceptance testing, ensures the reliability of the entire data migration vs database migration system. Addressing any discrepancies found during testing is vital to ensure an error-free migration.
Cutover: Transition from the source system to the target system. This is a critical phase in data migration vs database migration. Define clear cut-over procedures. This will involve testing, monitoring, and adjustments as required to ensure a smooth changeover. Carefully plan the cutover process to minimize downtime and disruptions.
Data Cleansing and Transformation: Ensuring Data Integrity
Data cleansing and transformation are critical during data migration vs database migration. These processes ensure data integrity and accuracy in the target system. Common data quality issues include inconsistent data formats, missing values, and duplicate entries. These problems can lead to inaccurate analysis and flawed decision-making. Addressing these issues proactively is essential for a successful migration.
Techniques for data cleansing involve identifying and correcting inconsistencies. This might include standardizing date formats, handling missing values through imputation or deletion, and deduplicating records using various algorithms. Data profiling tools help analyze data quality, identifying potential issues before they impact the migration process. Data transformation involves converting data into a format compatible with the target system. This often requires data type conversions, data normalization, and potentially data enrichment.
Consider the challenges in data migration vs database migration. For example, a large dataset with complex relationships requires careful planning and robust tools. Choosing the right approach depends on the scale of the migration and the complexity of the data. Effective data cleansing and transformation minimize errors and ensure the migrated data is reliable and usable. A well-executed data cleansing strategy prevents errors downstream and contributes to the long-term success of the data migration project. Tools like data profiling software and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools facilitate efficient cleansing and transformation processes. Careful attention to these steps contributes significantly to the overall success of any data migration project.
Database Migration Techniques: A Comparative Analysis
Choosing the right approach for database migration is crucial for a successful data migration vs database migration project. Several techniques exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. In-place upgrades involve updating the database system directly without significant data movement. This method minimizes downtime but carries a higher risk of failure, especially with complex databases. It’s best suited for smaller databases with low complexity and high tolerance for brief interruptions.
Parallel migrations, a popular choice for data migration vs database migration projects, involve setting up a new database system in parallel with the existing one. Data is then migrated to the new system, after which the old system is decommissioned. This technique reduces downtime significantly and provides a safety net. The process can be more complex, requiring careful planning and execution, and it involves higher initial costs. The choice between this and in-place upgrade will depend on the specific needs of the data migration vs database migration process, downtime requirements, budget, and the complexity of the database system.
Phased migrations offer a more granular approach. Data is moved in stages, migrating subsets of the database at a time. This method minimizes disruption and allows for thorough testing at each phase. However, it extends the overall migration timeline, increasing the potential for unforeseen problems. The phased approach is ideal for large, complex databases where a complete outage is unacceptable. The data migration vs database migration strategy needs to account for data consistency and potential conflicts across different phases. Careful planning and a robust testing strategy are essential for any successful database migration strategy, especially when considering the impact of data migration vs database migration. The decision depends on factors such as downtime tolerance, data volume, complexity, and budget constraints. Each technique offers a unique set of trade-offs that must be carefully considered when planning a data migration vs database migration project.
Choosing the Right Tools: Streamlining the Migration Process
Selecting the appropriate tools is crucial for a successful data migration vs database migration project. The optimal choice depends on several factors, including the scale of the migration, the complexity of the data, and the source and target systems. For instance, a small-scale database migration from MySQL to PostgreSQL might be handled effectively with command-line tools or built-in database utilities. However, large-scale data migrations involving complex data transformations and considerable data volume necessitate more robust solutions.
Several powerful tools cater specifically to data and database migration. Informatica PowerCenter, a widely-used ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tool, offers comprehensive capabilities for handling intricate data transformations and migrations. It excels in managing large datasets and complex mappings. AWS Schema Conversion Tool (SCT) proves particularly valuable for migrating databases to Amazon Web Services (AWS). This tool streamlines the process of converting database schemas and migrating data to various AWS database services. Talend Open Studio, an open-source ETL tool, provides a flexible and cost-effective option for smaller projects or organizations with limited budgets. It offers a user-friendly interface and supports a wide array of data sources and formats.
Other specialized tools exist for specific database systems or migration scenarios. Some tools focus on schema conversion, while others excel at data cleansing and transformation. The selection process often involves evaluating factors such as ease of use, scalability, cost, and integration with existing infrastructure. A thorough evaluation of available tools, considering the specific requirements of the data migration vs database migration project, is essential for ensuring efficiency and minimizing risks. Careful consideration of the tool’s capabilities in handling data quality issues, such as data cleansing and transformation, is equally important for achieving data integrity.
Testing and Validation: Guaranteeing Data Accuracy
Rigorous testing and validation are critical throughout the data migration process. This ensures data integrity and accuracy after the migration. A multi-layered approach, incorporating various testing strategies, is essential. Unit testing verifies individual components of the migration process. Integration testing checks the interaction between different components. User acceptance testing (UAT) validates the migrated system against user requirements. These testing phases help identify and resolve discrepancies early, minimizing disruptions. In data migration vs database migration projects, comprehensive testing is crucial for success.
Data validation plays a vital role in ensuring data accuracy. This involves comparing the source and target data to identify discrepancies. Techniques like checksums and record counts verify data completeness. Data profiling helps identify data quality issues like inconsistencies or missing values before migration. Automated validation tools can significantly speed up this process, flagging potential problems for manual review. The goal is to confirm that the migrated data is accurate, complete, and consistent with the source data. Addressing discrepancies promptly is key to preventing issues in the post-migration phase. Thorough validation reduces the risk of errors, improving the reliability of the migrated data.
During testing, discrepancies might arise due to data transformation errors or issues with the migration tools. A well-defined process for handling discrepancies is essential. This involves documenting the issues, investigating their root causes, and implementing corrective actions. This might include data cleansing, correcting transformation rules, or adjusting the migration tools. Retesting is crucial after addressing discrepancies to ensure they are resolved. Proper documentation throughout the testing and validation phase facilitates future analysis and problem-solving. A robust testing strategy minimizes disruptions, ensures data quality, and ultimately contributes to a successful data migration vs database migration project.
Post-Migration Monitoring and Maintenance: Ensuring Long-Term Success
Successful data migration vs database migration isn’t a one-time event; it requires ongoing attention. Post-migration monitoring is crucial for ensuring the continued smooth operation of the new system and the accuracy of the migrated data. Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be established before the migration to provide a benchmark for post-migration performance. These KPIs might include data processing speed, query response times, storage utilization, and error rates. Regular monitoring allows for the early detection of potential problems, preventing them from escalating into major issues. A comprehensive monitoring system should be in place to track these KPIs and alert administrators to any significant deviations from expected performance.
Data validation continues to play a vital role even after the migration is complete. Regular data quality checks should be conducted to identify and address any inconsistencies or errors that may have emerged since the migration. This process might involve comparing the migrated data to the original source data to identify discrepancies. It also involves verifying data integrity and accuracy against established business rules and expectations. Addressing these issues promptly minimizes the risk of inaccurate reporting or flawed decision-making based on faulty data. This proactive approach is essential in maintaining the long-term value of the migration project.
A robust post-migration support plan is an essential component of a successful data migration vs database migration strategy. This plan should detail procedures for troubleshooting issues, handling emergencies, and providing ongoing technical support. It should also include provisions for regular system maintenance, including software updates, security patches, and performance tuning. The support plan ensures a seamless transition and helps minimize disruptions after the migration. Regular communication between the IT team and business stakeholders is critical for maintaining transparency and ensuring that any emerging challenges are promptly addressed. This collaborative approach is key to the long-term success of any data migration or database migration project.