Understanding Cloud Computing: A Breakdown of Service Models
Cloud computing is a revolutionary technology that enables organizations and individuals to access and utilize computing resources, such as servers, storage, databases, and applications, over the internet. Instead of managing and maintaining physical infrastructure, users can leverage cloud services on-demand, paying only for what they use. When it comes to comparing cloud services, understanding the different service models is crucial.
The three primary cloud service models are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each model offers varying levels of control, management, and responsibility for the user.
- IaaS: IaaS provides users with virtualized computing resources, including servers, storage, and networking. Users have control over the operating systems, applications, and middleware, while the cloud service provider manages the infrastructure.
- PaaS: PaaS offers a platform for users to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure. The cloud service provider manages the infrastructure, including servers, storage, and networking, while users control the applications and data.
- SaaS: SaaS delivers fully functional applications to users over the internet. The cloud service provider manages everything from infrastructure to applications, and users simply access the software using a web browser or a thin client. Examples of popular SaaS applications include Gmail, Salesforce, and Dropbox.
Well-known cloud service providers for each category include Amazon Web Services (AWS) for IaaS, Microsoft Azure for PaaS, and Google Workspace (formerly G Suite) for SaaS. Each provider offers a range of services and tools tailored to various industries and use cases, allowing users to compare cloud services based on their specific needs and requirements.
Key Factors to Consider When Comparing Cloud Services
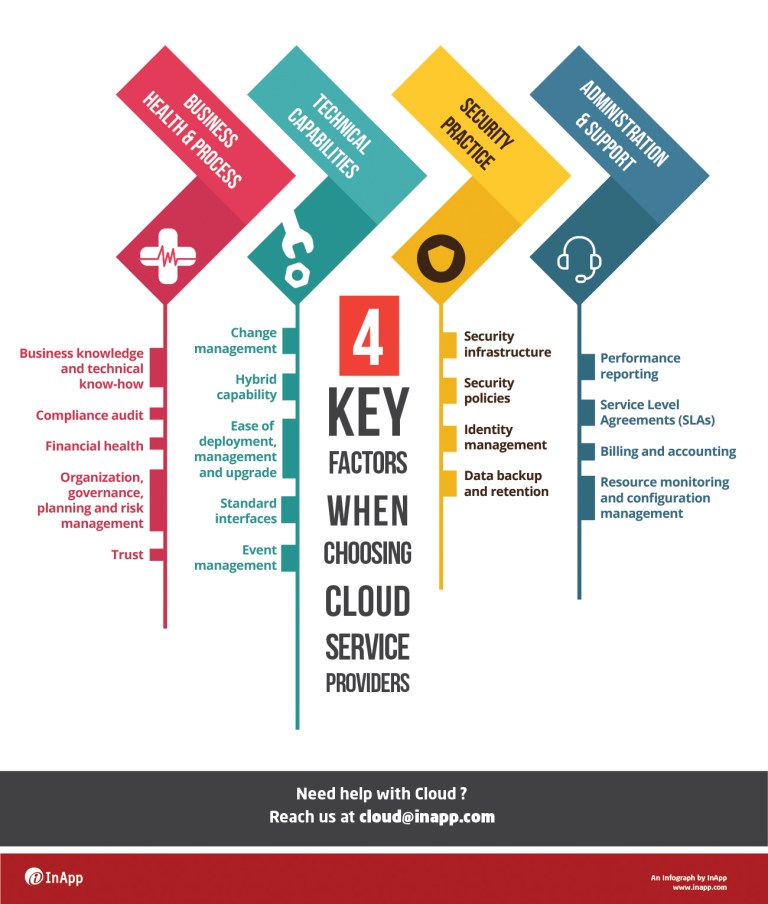
When evaluating cloud services, it’s essential to consider several key factors to ensure a reliable, secure, and cost-effective solution for your business. These factors include cost, performance, security, scalability, and data management capabilities.
- Cost: Compare the pricing models of different cloud service providers to understand the total cost of ownership. Consider factors such as upfront costs, pay-as-you-go pricing, reserved instances, and data transfer fees.
- Performance: Assess the performance of cloud services by evaluating factors such as latency, throughput, and availability. Look for service level agreements (SLAs) that guarantee uptime and performance.
- Security: Ensure that the cloud service provider follows industry best practices for data protection, encryption, and access control. Evaluate their compliance with relevant security standards, such as ISO 27001 and SOC 2.
- Scalability: Determine whether the cloud service can scale up or down based on demand. Assess the provider’s ability to handle peak loads and ensure consistent performance during high-traffic periods.
- Data Management Capabilities: Evaluate the cloud service provider’s data management features, such as backup, disaster recovery, and data migration tools. Consider their support for data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence.
By carefully considering these factors, businesses can compare cloud services effectively and make informed decisions based on their specific needs and requirements. Remember that the best cloud service provider for your organization will depend on your unique combination of budget, technical requirements, and long-term goals.
A Deep Dive into Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a comprehensive cloud computing platform that offers a vast array of services and tools for businesses and developers. As the oldest and most mature cloud service provider, AWS boasts an extensive customer base, including prominent companies like Netflix, Airbnb, and the BBC.
- Key Features: AWS provides on-demand computing resources, including storage, compute power, and databases. It also offers advanced services for machine learning, data analytics, and Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
- Benefits: AWS enables businesses to scale quickly, reduce capital expenditures, and accelerate innovation. Its global data center footprint ensures low-latency connections and fast content delivery worldwide.
- Drawbacks: While AWS is highly scalable and customizable, it can be complex to navigate, especially for smaller businesses or those new to cloud computing. Additionally, its cost structure can be difficult to manage, leading to unexpected expenses if not properly monitored.
- Real-Life Use Cases: AWS has been instrumental in enabling media companies like Netflix to deliver high-quality streaming content to millions of users. It also powers the infrastructure of fast-growing startups like Airbnb, allowing them to scale rapidly and manage complex data workloads.
By offering a wide range of services and tools, AWS has established itself as a dominant player in the cloud computing market. However, businesses should carefully evaluate their technical requirements and budget before committing to AWS, as its complexity and cost structure may not be suitable for all organizations.
Assessing Microsoft Azure: A Closer Look
Microsoft Azure is a robust cloud computing platform that offers a wide range of services and tools for businesses and developers. As a strong competitor to Amazon Web Services (AWS), Azure has gained significant traction in the market, with high-profile customers like Adobe, BMW, and 3M.
- Key Features: Azure provides on-demand computing resources, including virtual machines, databases, and storage. It also offers advanced services for machine learning, data analytics, and IoT applications. Additionally, Azure integrates seamlessly with Microsoft’s suite of productivity tools, such as Office 365 and Dynamics 365.
- Benefits: Azure enables businesses to scale quickly, reduce capital expenditures, and accelerate innovation. Its hybrid cloud capabilities allow organizations to leverage both on-premises and cloud-based resources, ensuring flexibility and consistency in their IT infrastructure.
- Drawbacks: While Azure offers a wide range of services, its user interface can be confusing and difficult to navigate, especially for those new to cloud computing. Additionally, its cost structure can be complex, making it challenging to predict and manage expenses.
- Comparing Azure with AWS: Azure excels in hybrid cloud integration and compatibility with Microsoft products. However, it currently lags behind AWS in terms of global data center availability and the breadth of advanced services offered. Nevertheless, Azure is continuously improving and expanding its offerings to better compete with AWS.
By providing a comprehensive set of cloud services and tools, Azure has become a formidable player in the cloud computing market. Businesses should carefully evaluate their technical requirements, budget, and existing IT infrastructure before choosing between Azure and AWS, as both platforms have their unique strengths and weaknesses.
Google Cloud Platform: Strengths and Weaknesses
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a powerful cloud computing platform that offers a wide range of services and tools for businesses and developers. As a strong competitor to Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure, GCP has gained a significant following, with notable customers like Spotify, Snapchat, and PayPal.
- Key Features: GCP provides on-demand computing resources, including virtual machines, databases, and storage. It also offers advanced services for machine learning, data analytics, and IoT applications. Moreover, GCP is renowned for its strong focus on artificial intelligence, big data, and open-source technologies.
- Benefits: GCP enables businesses to scale quickly, reduce capital expenditures, and accelerate innovation. Its robust infrastructure ensures high performance, reliability, and security, making it an attractive choice for data-intensive workloads and AI-powered applications.
- Drawbacks: While GCP offers a wide range of services, its ecosystem and marketplace are not as mature as those of AWS and Azure. This can make it challenging for businesses to find compatible third-party tools and integrations.
- Comparing GCP with AWS and Azure: GCP excels in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics capabilities. However, it currently lags behind AWS and Azure in terms of global data center availability and the breadth of services offered. Nevertheless, GCP is continuously improving and expanding its offerings to better compete with AWS and Azure.
By providing a robust set of cloud services and tools, GCP has become a strong player in the cloud computing market. Businesses should carefully evaluate their technical requirements, budget, and existing IT infrastructure before choosing between GCP, AWS, and Azure, as each platform has its unique strengths and weaknesses.
How to Choose the Right Cloud Service for Your Business
Selecting the ideal cloud service provider for your business is a critical decision that requires careful consideration of various factors. By following a systematic approach and evaluating your unique needs, you can make an informed choice that aligns with your budget, technical requirements, and long-term goals.
- Define Your Needs: Clearly outline your business requirements, including performance, security, scalability, and data management capabilities. Consider the specific services and tools you need to support your applications and workloads.
- Assess Budget and Cost: Evaluate the pricing models of different cloud service providers, comparing upfront costs, ongoing fees, and scalability expenses. Ensure that your chosen provider offers transparent and predictable pricing, helping you avoid unexpected costs.
- Evaluate Service and Support: Examine the quality of customer service and technical support offered by each provider. Look for resources such as documentation, community forums, and professional services to assist with migration, optimization, and troubleshooting.
- Consider Integration and Compatibility: Assess the compatibility of each cloud service provider with your existing IT infrastructure, applications, and tools. Opt for a provider that offers seamless integration and a rich ecosystem of third-party solutions.
- Security and Compliance: Ensure that your chosen cloud service provider adheres to industry best practices for security, data privacy, and compliance. Evaluate their encryption, access control, and monitoring capabilities to protect your sensitive data.
- Long-Term Vision: Consider the future growth and evolution of your business when selecting a cloud service provider. Opt for a provider that demonstrates innovation and a commitment to staying at the forefront of cloud computing trends and technologies.
By following this decision-making framework, businesses can effectively compare cloud services and choose the most suitable provider for their unique needs and objectives.
Navigating Cloud Migration: Best Practices and Pitfalls
Migrating to a cloud service can offer numerous benefits, including cost savings, increased scalability, and enhanced security. However, the migration process can be complex and fraught with potential pitfalls. By following best practices and addressing common challenges, businesses can ensure a smooth transition to their chosen cloud service provider.
- Planning: Develop a comprehensive migration plan that outlines your objectives, timeline, and resource allocation. Identify the applications, data, and workloads to be migrated and establish a clear strategy for each.
- Testing: Thoroughly test your applications and workloads in the target cloud environment before migrating. This will help you identify and resolve potential issues, ensuring a seamless transition.
- Monitoring: Continuously monitor your applications and workloads during and after migration. This will help you detect and troubleshoot any performance or security issues that may arise.
- Security: Maintain a strong focus on security throughout the migration process. Implement encryption, access control, and other security measures to protect your data and applications.
- Staff Training: Train your staff on the new cloud environment, including its features, tools, and best practices. This will help ensure a smooth adoption and minimize disruptions.
- Common Challenges: Be aware of common migration challenges, such as data transfer costs, application compatibility issues, and vendor lock-in. Develop strategies to mitigate these risks and ensure a successful migration.
By following these best practices and addressing potential challenges, businesses can effectively compare cloud services and navigate the migration process with confidence.
The Future of Cloud Computing: Trends and Predictions
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate, providing unparalleled scalability, flexibility, and cost savings. As the technology continues to evolve, several emerging trends and expert predictions will shape the future of cloud computing. By staying informed and adapting to these changes, businesses can maximize their cloud investments and maintain a competitive edge.
- Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Strategies: As businesses seek to optimize their cloud deployments, multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies will become increasingly popular. These approaches enable organizations to leverage the unique strengths of different cloud service providers and balance on-premises and cloud-based resources.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: The integration of AI and ML technologies with cloud computing will continue to accelerate, enabling businesses to harness the power of data-driven insights, automation, and predictive analytics.
- Serverless Computing: Serverless computing will gain traction as businesses aim to reduce infrastructure management overhead and focus on application development. This model enables developers to build and run applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure, allowing for greater agility and cost savings.
- Edge Computing: As IoT devices and applications proliferate, the need for edge computing will grow. By processing data closer to the source, edge computing can reduce latency, improve performance, and enhance security.
- Containerization and Kubernetes: Containerization technologies, such as Docker, and container orchestration tools, like Kubernetes, will become essential for managing and scaling applications in cloud environments.
- Security and Compliance: As cloud adoption increases, so too will the focus on security and compliance. Businesses will need to invest in advanced security measures, such as zero-trust architectures, to protect their data and applications in the cloud.
By staying informed about these trends and predictions, businesses can effectively compare cloud services and make strategic decisions about their cloud computing investments.