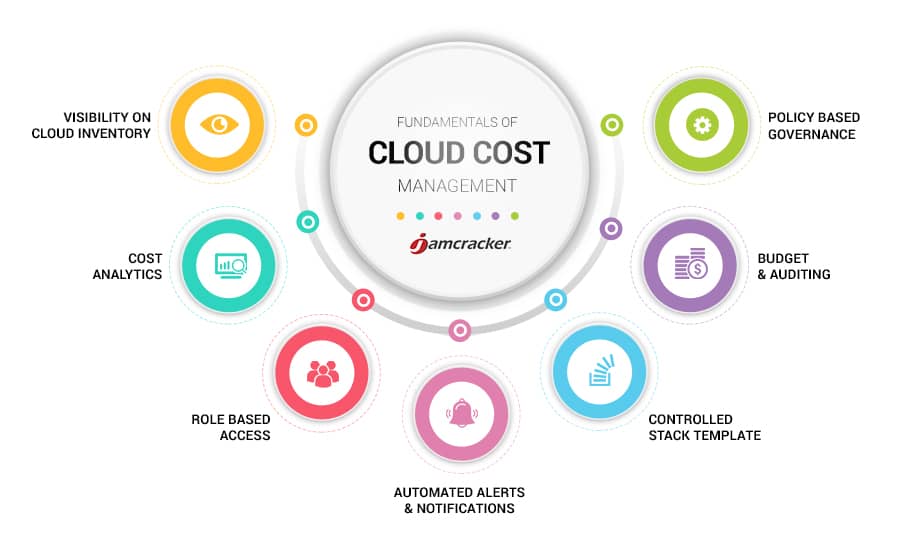
Understanding Cloud SQL Costs: An Overview
Cloud SQL costs are a critical aspect of managing cloud-based database services for businesses and individuals. As more organizations adopt cloud infrastructure, understanding and optimizing these costs become increasingly important. Various factors contribute to Cloud SQL expenses, including compute resources, storage, and backup costs. Compute resources involve the processing power and memory required to run the database, while storage costs are associated with the amount of data stored in the database.
Backup costs, on the other hand, are related to the storage and management of backup data, ensuring business continuity and data recovery. It is essential to monitor and analyze these costs to ensure cost-effectiveness and avoid unexpected financial burdens. By understanding the main contributing factors, organizations can implement strategies to minimize Cloud SQL expenses without compromising performance.
How to Analyze and Monitor Cloud SQL Costs
Monitoring and analyzing Cloud SQL costs are essential for maintaining cost-effectiveness and ensuring that expenses remain within budget. Various tools and methods are available for tracking Cloud SQL expenses, including built-in cloud provider dashboards and third-party monitoring solutions. These tools provide detailed insights into Cloud SQL costs, enabling organizations to identify trends, optimize resource utilization, and avoid unexpected financial burdens.
Built-in cloud provider dashboards offer a user-friendly interface for monitoring Cloud SQL costs. For instance, Google Cloud SQL, Amazon RDS, and Microsoft Azure SQL provide comprehensive dashboards that display real-time cost data, usage trends, and historical cost breakdowns. These dashboards often include features for setting up alerts and notifications, allowing users to be notified when costs exceed predefined thresholds.
Third-party monitoring solutions can complement built-in cloud provider dashboards by offering additional features and customization options. These tools often provide advanced analytics, machine learning algorithms for cost prediction, and integration with other cloud services. By leveraging both built-in dashboards and third-party monitoring solutions, organizations can gain a holistic view of their Cloud SQL costs and optimize their infrastructure for cost efficiency.
Strategies to Reduce Cloud SQL Costs
Reducing Cloud SQL costs is essential for maintaining a cost-effective and high-performing cloud infrastructure. Various strategies can help minimize expenses without compromising performance. These techniques include rightsizing instances, using reserved or spot instances, optimizing storage, and implementing backup policies.
Rightsizing instances involves selecting the most cost-effective instance type and size based on the workload requirements. Regularly reviewing and adjusting instance sizes can help ensure that resources are utilized optimally, reducing unnecessary costs. Utilizing reserved or spot instances can also lead to significant cost savings. Reserved instances offer discounted prices in exchange for a long-term commitment, while spot instances allow users to bid on spare computing capacity at a much lower price.
Optimizing storage is another critical aspect of Cloud SQL cost management. Implementing data tiering, where frequently accessed data is stored on high-performance storage and infrequently accessed data is moved to lower-cost storage, can help reduce costs. Additionally, regularly monitoring and archiving unused data can help minimize storage expenses.
Implementing backup policies is essential for ensuring data protection and recovery while also optimizing costs. Configuring automated backups during off-peak hours and retaining backups for the minimum required period can help reduce backup costs. Additionally, leveraging backup data for disaster recovery drills and testing can help organizations ensure their backup strategies are effective and efficient.
Selecting the Right Cloud SQL Provider for Cost Efficiency
Choosing the right Cloud SQL provider is crucial for ensuring cost efficiency and optimal performance. This section compares Google Cloud SQL, Amazon RDS, and Microsoft Azure SQL regarding cost efficiency, unique features, pricing models, and cost-saving opportunities.
Google Cloud SQL
Google Cloud SQL offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model with no upfront costs or long-term commitments. It provides machine types optimized for database workloads and automatic storage management. Google Cloud SQL also offers committed use discounts, which can lead to significant cost savings for predictable workloads. Additionally, Google Cloud SQL provides a free tier for limited usage, making it an attractive option for small-scale projects and testing.
Amazon RDS
Amazon RDS offers a variety of pricing models, including on-demand, reserved, and spot instances. It supports various database engines, such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle, providing flexibility in choosing the right engine for specific workloads. Amazon RDS also offers cost-saving opportunities through Reserved Instances, which can reduce costs by up to 75% compared to On-Demand pricing. Additionally, Amazon RDS provides a free tier for limited usage, similar to Google Cloud SQL.
Microsoft Azure SQL
Microsoft Azure SQL offers a flexible pricing model, including pay-as-you-go, reserved instances, and serverless options. The serverless option automatically scales compute resources based on workload demand, providing cost efficiency and simplified management. Azure SQL also offers cost-saving opportunities through Azure Hybrid Benefit, which allows businesses to use their existing on-premises SQL Server licenses with Azure SQL Database, reducing costs by up to 55%.
When selecting a Cloud SQL provider, it is essential to consider factors such as pricing models, cost-saving opportunities, and unique features. Each provider offers distinct advantages, and understanding these differences can help organizations make informed decisions and optimize Cloud SQL costs.
Real-World Case Studies: Successful Cloud SQL Cost Optimization
Exploring real-world case studies can provide valuable insights into successful Cloud SQL cost optimization strategies. This section highlights two success stories, one from a growing e-commerce business and another from a large enterprise, demonstrating how they effectively managed their Cloud SQL costs.
Case Study 1: E-commerce Business
An e-commerce business sought to optimize its Cloud SQL costs while maintaining high performance during peak shopping seasons. By implementing a combination of rightsizing instances, optimizing storage, and utilizing reserved instances, the company achieved a 35% reduction in Cloud SQL expenses. Additionally, they implemented automated backup policies and scheduled backups during off-peak hours, further reducing backup costs.
Case Study 2: Large Enterprise
A large enterprise with a complex multi-cloud environment aimed to reduce its Cloud SQL costs while maintaining service level agreements (SLAs) and data security. By adopting a multi-cloud cost management strategy, the enterprise centralized cost tracking and monitoring across all cloud providers. They also leveraged serverless databases and automated scaling features, which led to a 40% reduction in Cloud SQL costs. Furthermore, the enterprise utilized artificial intelligence and machine learning tools for cost prediction and optimization, ensuring long-term cost efficiency.
These case studies demonstrate the potential benefits of implementing effective Cloud SQL cost optimization strategies. By learning from these examples, businesses and individuals can adopt best practices and achieve similar cost savings in their cloud-based database services.
Best Practices for Ongoing Cloud SQL Cost Management
Effective Cloud SQL cost management requires continuous monitoring, regular audits, and staying informed about pricing updates and promotions. This section outlines best practices for managing Cloud SQL costs over time, emphasizing the importance of involving all relevant stakeholders in the cost management process.
1. Regular Cost Audits
Conducting regular cost audits helps identify areas of potential cost savings and ensures that Cloud SQL expenses remain within budget. Audits should include a thorough review of compute resources, storage, and backup costs, as well as an assessment of the effectiveness of cost optimization strategies. Utilize built-in cloud provider tools or third-party solutions to simplify the auditing process.
2. Continuous Monitoring
Implementing continuous monitoring enables organizations to detect and address cost inefficiencies promptly. Set up alerts and notifications for cost thresholds and abnormal usage patterns to ensure timely intervention. Leverage both built-in cloud provider dashboards and third-party monitoring solutions to gain a comprehensive view of Cloud SQL costs.
3. Stay Informed About Pricing Updates and Promotions
Cloud providers frequently update their pricing models, introduce new cost-saving opportunities, and offer promotions. Staying informed about these changes can lead to significant cost savings. Regularly review pricing updates and promotions from your Cloud SQL provider and adjust your infrastructure and cost management strategies accordingly.
4. Involve All Relevant Stakeholders
Effective Cloud SQL cost management involves collaboration between various stakeholders, including IT teams, finance teams, and decision-makers. Encourage open communication and ensure that all relevant parties are informed about Cloud SQL costs, cost optimization strategies, and their roles in the cost management process.
By following these best practices, organizations can maintain a cost-effective Cloud SQL infrastructure, ensuring optimal performance and minimizing expenses over time.
Emerging Trends in Cloud SQL Cost Optimization
As cloud computing continues to evolve, new trends and innovations emerge in Cloud SQL cost optimization. This section discusses emerging trends, such as serverless databases, multi-cloud strategies, and the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning for cost prediction and optimization.
1. Serverless Databases
Serverless databases offer a pay-per-use model, automatically scaling resources based on demand. This approach can lead to significant cost savings, as organizations only pay for the resources they consume. Major cloud providers, including Google Cloud SQL, Amazon RDS, and Microsoft Azure SQL, offer serverless database options, enabling businesses to optimize Cloud SQL costs further.
2. Multi-Cloud Strategies
Adopting a multi-cloud strategy can help organizations leverage the unique features and cost-saving opportunities of multiple cloud providers. However, managing multi-cloud environments can be complex. Implementing centralized cost tracking and monitoring tools can help businesses maintain cost efficiency while taking advantage of the benefits of a multi-cloud approach.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) tools can help predict and optimize Cloud SQL costs. These technologies can analyze usage patterns, identify inefficiencies, and suggest cost optimization strategies. By incorporating AI and ML into their Cloud SQL cost management processes, businesses can achieve long-term cost efficiency and maintain high performance.
Staying informed about emerging trends in Cloud SQL cost optimization can help businesses and individuals take advantage of new opportunities and maintain a cost-effective cloud infrastructure. As the cloud computing landscape continues to evolve, adopting innovative cost management strategies will become increasingly important for long-term success.
Navigating Potential Challenges in Cloud SQL Cost Optimization
While optimizing Cloud SQL costs can lead to significant savings, businesses and individuals may encounter potential challenges and pitfalls. This section addresses common issues, such as the trade-off between cost and performance, the complexity of managing multi-cloud environments, and the need for ongoing monitoring and management. We also provide guidance on how to overcome these challenges and maintain a cost-effective Cloud SQL infrastructure.
1. Balancing Cost and Performance
Striking the right balance between cost and performance can be challenging. To ensure optimal performance, businesses may be tempted to overprovision resources, leading to unnecessary expenses. To address this challenge, consider implementing a tiered approach to resource allocation, where critical workloads receive higher-performance resources while less critical tasks utilize more cost-effective options.
2. Managing Multi-Cloud Environments
Managing multi-cloud environments can be complex, as each cloud provider has its unique features, pricing models, and cost-saving opportunities. Implementing centralized cost tracking and monitoring tools can help businesses maintain cost efficiency while taking advantage of the benefits of a multi-cloud approach. Additionally, consider working with a managed service provider (MSP) experienced in multi-cloud environments to streamline cost management and optimization.
3. Ongoing Monitoring and Management
Cloud SQL cost optimization is not a one-time task but an ongoing process. Regularly reviewing Cloud SQL expenses, usage patterns, and cost optimization strategies is essential to maintaining a cost-effective infrastructure. Establish a routine for monitoring and analyzing Cloud SQL costs, and ensure that all relevant stakeholders are involved in the process. Additionally, consider leveraging AI and ML tools for cost prediction and optimization to achieve long-term efficiency.
Navigating potential challenges in Cloud SQL cost optimization requires a proactive, strategic approach. By addressing these issues and implementing best practices, businesses and individuals can maintain a cost-effective Cloud SQL infrastructure, ensuring optimal performance and minimizing expenses over time.