What is Elastic Load Balancing and Why is it Crucial?
AWS Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) is a service that distributes incoming application traffic across multiple targets. These targets can be EC2 instances, containers, or IP addresses. A classic load balancer aws ensures no single target is overwhelmed. This distribution enhances application availability and fault tolerance. If one target fails, the classic load balancer aws automatically redirects traffic to the remaining healthy targets. This prevents downtime and maintains a seamless user experience. Scalability is another key benefit. As application traffic grows, the classic load balancer aws can distribute the load across more targets. This ensures consistent performance even during peak demand.
Elastic Load Balancing offers several types of load balancers. These include the Application Load Balancer, Network Load Balancer, and Gateway Load Balancer. Each type is designed for specific use cases. However, this guide focuses on the Classic Load Balancer (CLB). The Classic Load Balancer is still a relevant option for certain applications. It provides basic load balancing features. These include HTTP/HTTPS and TCP protocol support. Understanding the role of a classic load balancer aws is critical for designing resilient applications. By efficiently distributing traffic, it prevents overload and improves response times.
The advantages of using a classic load balancer aws extend beyond basic traffic distribution. Health checks are performed regularly by a classic load balancer aws, these checks monitor the health of registered targets. If a target becomes unhealthy, the load balancer stops sending traffic to it until it recovers. This proactive approach minimizes the impact of failures on users. Moreover, ELB integrates with other AWS services. This integration allows for automated scaling and monitoring. A well-configured classic load balancer aws is a cornerstone of a highly available and scalable application architecture. It ensures that your application can handle varying levels of traffic. It also ensures that users have a consistent experience.
Demystifying the Classic Load Balancer: A Deep Dive
The Classic Load Balancer (CLB) stands as a foundational element within AWS Elastic Load Balancing, expertly managing incoming application traffic across multiple destinations, such as EC2 instances. It offers a robust set of features tailored to cater to diverse application needs. These features include support for both HTTP/HTTPS and TCP protocols, ensuring compatibility with web applications and other network-based services. A crucial aspect of the classic load balancer aws functionality lies in its health check capabilities, which proactively monitor the health of registered instances. This ensures that traffic is only directed to healthy and responsive targets, contributing to high application availability. Session affinity, another key feature, allows the CLB to maintain user sessions by consistently routing requests from the same user to the same instance. This is particularly important for applications that rely on session state. The classic load balancer aws is very useful on the cloud.
While the Classic Load Balancer excels in many scenarios, it’s essential to understand its position within the broader AWS Elastic Load Balancing ecosystem. Other ELB types, namely the Application Load Balancer (ALB), Network Load Balancer (NLB), and Gateway Load Balancer, offer distinct advantages for specific use cases. The Application Load Balancer provides advanced routing capabilities based on HTTP headers and content, making it ideal for microservices architectures. The Network Load Balancer is designed for ultra-high performance and low-latency applications, operating at the transport layer (TCP/SSL). The Gateway Load Balancer simplifies the deployment and management of virtual appliances. Understanding the differences among these load balancer types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate option for a given application. However, this article focuses specifically on the classic load balancer aws, so we will not go into detail about the other options.
The Classic Load Balancer remains a relevant choice for certain scenarios, particularly legacy applications that were designed with CLB in mind. Its simplicity and broad compatibility make it suitable for applications that do not require the advanced features of the newer load balancer types. For instance, applications that rely on sticky sessions or require support for both HTTP/HTTPS and TCP protocols may find the CLB to be the most straightforward solution. Furthermore, the classic load balancer aws can be a cost-effective option for simpler applications with predictable traffic patterns. Ultimately, the decision to use a CLB should be based on a thorough evaluation of the application’s requirements and the capabilities of each load balancer type. In summary, the classic load balancer aws is a great choice for basic load balancing needs within the AWS ecosystem.
How to Configure a Classic Load Balancer: A Step-by-Step Guide
Configuring a classic load balancer aws involves a series of steps within the AWS Management Console. This guide offers detailed instructions and screenshots to streamline the process. First, access the AWS Management Console and navigate to the EC2 service. From the EC2 dashboard, locate “Load Balancing” in the left-hand navigation pane and select “Load Balancers.” Click the “Create Load Balancer” button. Choose “Classic Load Balancer” as the load balancer type and proceed to define the load balancer settings.
Next, configure the listener. This involves specifying the protocol and port for incoming traffic. For example, you might configure a listener for HTTP traffic on port 80 or HTTPS traffic on port 443. Select the VPC where your EC2 instances are located. Choose the availability zones where your instances reside. It’s crucial to select multiple Availability Zones for high availability. Configure security groups to control traffic to and from the classic load balancer aws. Ensure that the security group allows incoming traffic on the configured listener ports (e.g., 80 or 443) and allows traffic from the load balancer to your EC2 instances.
Now, register your target EC2 instances with the classic load balancer aws. You will select the instances from a list of available instances within your VPC. Next, configure health checks. This is important to ensure that the load balancer only routes traffic to healthy instances. Specify the health check protocol (HTTP, HTTPS, or TCP), path, port, interval, timeout, unhealthy threshold, and healthy threshold. The load balancer uses these settings to determine the health status of your instances. Create the classic load balancer aws after reviewing your configuration settings. Once created, the load balancer will begin routing traffic to your registered instances based on the configured listeners and health checks. You can monitor the health of your instances and the performance of your load balancer from the EC2 console. This step-by-step guide provides a practical understanding of how to set up a classic load balancer aws, improving application availability and scalability.
Classic Load Balancer Health Checks: Ensuring Application Availability
Health checks are a critical component of maintaining application availability when using a classic load balancer aws. They enable the classic load balancer aws to determine the health status of registered instances and route traffic only to those that are deemed healthy. Without proper health checks, a classic load balancer aws may direct traffic to failing or unresponsive instances, leading to application downtime and a poor user experience. This innovative feature confirms optimal performance.
A classic load balancer aws supports various health check types, including HTTP, HTTPS, and TCP. HTTP and HTTPS health checks involve sending a request to a specific URL on the instance and verifying that the instance returns a success code (e.g., 200 OK). TCP health checks, on the other hand, attempt to establish a TCP connection with the instance on a specified port. The configuration options for health checks include the interval (how frequently the load balancer performs checks), the timeout (how long the load balancer waits for a response), the unhealthy threshold (the number of consecutive failed checks before an instance is marked as unhealthy), and the healthy threshold (the number of consecutive successful checks before an instance is marked as healthy). These parameters should be carefully configured based on the specific application requirements to accurately reflect the instance’s health status.
Customizing health checks with specific endpoints or probes is a best practice for ensuring accurate health assessments with a classic load balancer aws. For example, instead of simply checking the root URL, a custom endpoint can be created that performs a series of internal application checks (e.g., database connectivity, resource availability) to provide a more comprehensive health status. The health check status, as reported by the classic load balancer aws, indicates whether an instance is considered “InService” (healthy) or “OutOfService” (unhealthy). It’s crucial to regularly monitor health check status and investigate any instances that are consistently marked as unhealthy. By proactively addressing health check failures, you can prevent application outages and ensure high availability when using a classic load balancer aws. Implementing those checks, assures the classic load balancer aws is working at its peak performance and its overall health.
Optimizing Classic Load Balancer Performance: Best Practices
To ensure optimal performance of your classic load balancer aws, several best practices should be implemented. Right-sizing your EC2 instances is crucial. Analyze your application’s resource consumption (CPU, memory, network) under peak load. Choose instance types that can handle the traffic without becoming a bottleneck. Insufficiently sized instances lead to increased latency and potential service disruptions.
Connection draining is another important feature to configure for your classic load balancer aws. This setting allows the load balancer to complete in-flight requests to instances that are being deregistered or are failing health checks. Enabling connection draining prevents abrupt disconnections and ensures a smoother user experience. Consider enabling cross-zone load balancing, if applicable, to distribute traffic evenly across all enabled Availability Zones. This enhances fault tolerance and ensures that your application remains available even if one Availability Zone experiences issues. Regularly monitor performance metrics using CloudWatch. Key metrics include latency, request count, and error rates. High latency or error rates can indicate performance problems or underlying issues with your application or infrastructure. CloudWatch alarms can be configured to notify you of potential problems, allowing you to proactively address them before they impact users. Addressing these issues can greatly improve the classic load balancer aws performance.
Scaling considerations are paramount when handling traffic spikes with your classic load balancer aws. Implement auto scaling for your EC2 instances. Auto scaling automatically adjusts the number of instances based on traffic demand, ensuring that your application can handle sudden increases in traffic without performance degradation. Regularly review and adjust your auto scaling configuration to ensure that it meets your application’s needs. Security is also a vital consideration. Secure your classic load balancer aws by configuring security groups to restrict access to only necessary ports and protocols. Use SSL/TLS certificates to encrypt traffic between clients and the load balancer, protecting sensitive data from eavesdropping. Regularly update security configurations and monitor for suspicious activity to maintain a secure environment. By implementing these best practices, you can significantly improve the performance, scalability, and security of your classic load balancer aws deployment.
Troubleshooting Common Classic Load Balancer Issues
When using the classic load balancer aws, encountering issues is inevitable. This section provides guidance on resolving common problems, ensuring your applications remain available and performant. Connectivity problems, health check failures, and performance bottlenecks are addressed, offering practical solutions for each.
One frequent problem involves connectivity errors. If users cannot access your application through the classic load balancer aws, several factors could be at play. First, verify the security group configurations. The load balancer’s security group must allow traffic on the listener ports. Similarly, the EC2 instances’ security groups must permit traffic from the load balancer. Incorrectly configured security groups are a common source of connectivity issues. Another potential cause is DNS resolution problems. Ensure that the load balancer’s DNS name resolves correctly to its IP addresses. Use tools like nslookup or dig to confirm proper resolution. Misconfigured DNS settings can prevent users from reaching the load balancer.
Health check failures are another common challenge. The classic load balancer aws relies on health checks to determine the availability of backend instances. If instances fail these checks, the load balancer stops routing traffic to them. Start by examining the health check configuration. Verify that the health check path is correct and that the instances are responding as expected. Check the instance’s logs for errors or timeouts that might cause the health check to fail. Network connectivity issues between the load balancer and the instances can also lead to health check failures. Ensure there are no firewall rules or network ACLs blocking communication. Performance bottlenecks can also manifest as health check failures. If instances are overloaded, they may not respond to health checks in a timely manner. Monitor instance CPU utilization, memory usage, and disk I/O to identify performance bottlenecks. Adjust instance sizes or optimize application code to improve performance. When troubleshooting, pay attention to error messages. Common errors include “503 Service Unavailable” and “Connection timed out.” These messages provide valuable clues about the underlying cause of the problem. Address each issue methodically to maintain a healthy and responsive application environment leveraging the classic load balancer aws. Misconfigurations, such as incorrect listener configurations, can also cause issues. Always double-check these settings when troubleshooting.
Classic Load Balancer Security Considerations
Security is paramount when deploying a classic load balancer aws. Configuring security groups is a critical first step. These act as virtual firewalls, controlling inbound and outbound traffic. Restrict access to the classic load balancer aws by only allowing traffic from known and trusted sources. For example, allow HTTP (port 80) and HTTPS (port 443) traffic from specific IP address ranges or security groups. Ensure that backend EC2 instances only accept traffic from the classic load balancer aws security group, further limiting the attack surface.
SSL/TLS certificates are crucial for encrypting traffic between clients and the classic load balancer aws. This protects sensitive data transmitted over the internet. AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) simplifies the process of provisioning, managing, and deploying SSL/TLS certificates. Configure the classic load balancer aws to use an SSL/TLS certificate. This enables HTTPS listeners. Regularly rotate SSL/TLS certificates to maintain a strong security posture. Access logging is another vital security measure. Enable access logging on the classic load balancer aws to record detailed information about each request. This includes the source IP address, request path, response code, and user agent. Store these logs securely in Amazon S3. Use them for auditing, security analysis, and troubleshooting. Analyze access logs regularly to identify suspicious activity or potential security breaches related to your classic load balancer aws.
Regularly review and update security configurations for the classic load balancer aws. Stay informed about the latest security best practices and vulnerabilities. Apply security patches and updates promptly. Implement a web application firewall (WAF) to protect against common web exploits, such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). AWS WAF integrates seamlessly with the classic load balancer aws. It provides an additional layer of security. Consider using AWS Shield to protect against Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. AWS Shield provides always-on detection and automatic inline mitigations. By implementing these security best practices, you can ensure the classic load balancer aws. You can also secure applications remain protected from potential threats in the AWS environment. Remember that a layered security approach is essential for comprehensive protection of your classic load balancer aws and the applications it supports.
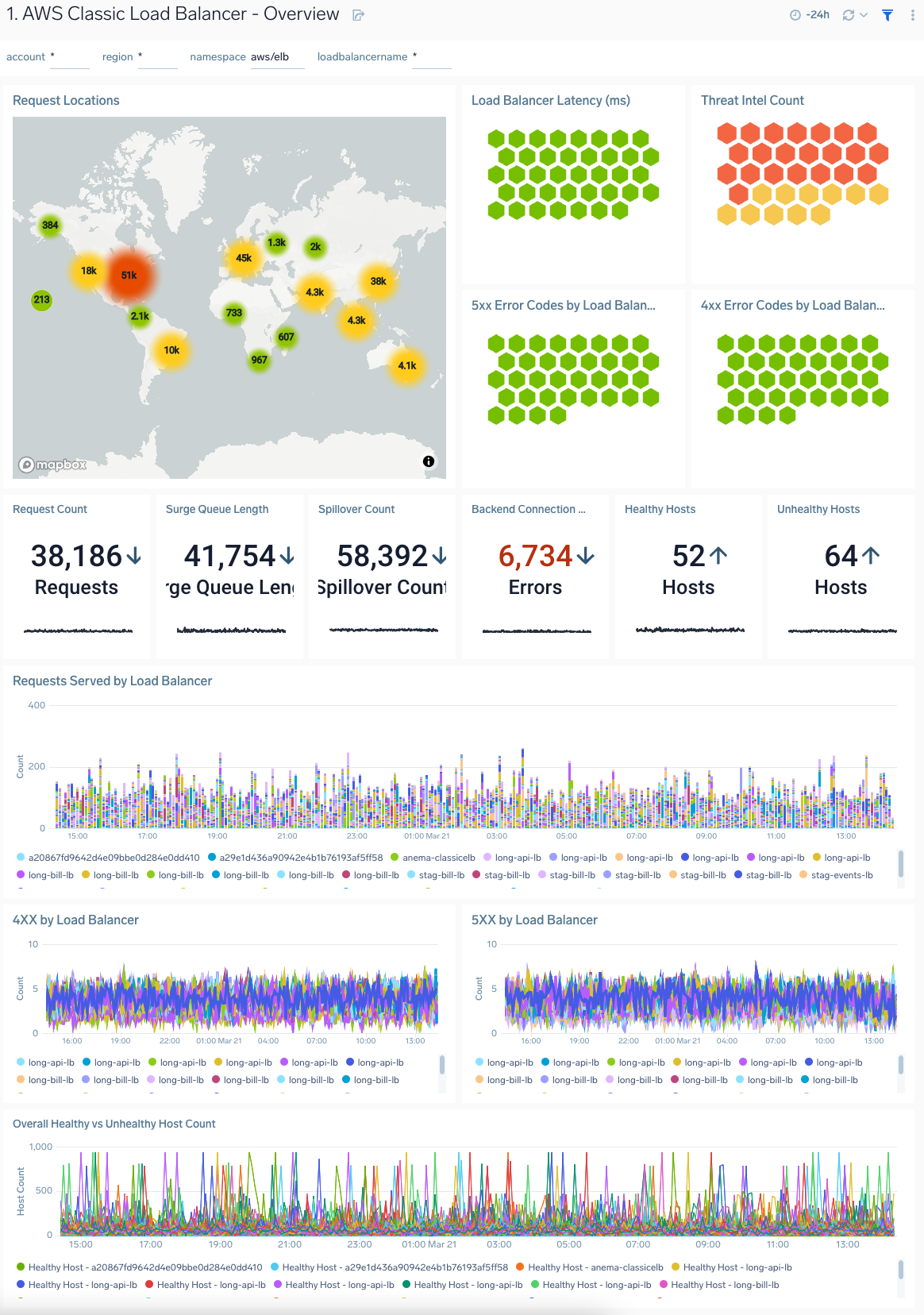
Monitoring Classic Load Balancer: Leveraging CloudWatch Metrics
Monitoring your classic load balancer aws is critical for maintaining optimal application performance and quickly identifying potential issues. Amazon CloudWatch provides a robust suite of metrics that offer valuable insights into the health and performance of your classic load balancer aws. By leveraging these metrics, you can proactively address problems and ensure a seamless user experience.
Key metrics to monitor for your classic load balancer aws include: Request Count, which indicates the total number of requests received by the load balancer. A sudden spike or drop in request count can signal traffic anomalies or application issues. Latency measures the time it takes for the load balancer to process and forward requests. High latency can indicate network congestion, overloaded backend instances, or inefficient application code. Error Rates, specifically HTTP error codes (e.g., 5XX errors), reveal problems with the backend instances or the application itself. Monitoring the Healthy Host Count provides a real-time view of the number of healthy instances behind the load balancer. A decrease in this number suggests potential issues with individual instances. CloudWatch alarms can be configured to trigger notifications when these metrics exceed predefined thresholds. For example, you can set up an alarm to notify you if the latency exceeds a certain value or if the healthy host count falls below a critical level. These alarms enable you to respond quickly to potential problems before they impact users.
CloudWatch logs provide even more detailed information about the operation of your classic load balancer aws. These logs capture information about each request, including the source IP address, the request URL, the response code, and the latency. By analyzing these logs, you can identify patterns and trends that can help you troubleshoot performance problems. For example, you can use CloudWatch logs to identify specific URLs that are experiencing high latency or to track the number of requests from a particular IP address. These metrics can also be used to diagnose performance problems and ensure optimal application performance. Regularly reviewing CloudWatch metrics and logs allows for proactive identification of potential issues, optimization of classic load balancer aws configurations, and ultimately, ensuring a reliable and performant application environment. The classic load balancer aws is a key component and should be properly monitored to ensure everything is working as expected.