What is Backup and Disaster Recovery (BDR) and Why is it Important for Cloud Computing?
Backup and Disaster Recovery (BDR) is a set of strategies, tools, and policies that help organizations protect their data and applications from disruptions, failures, and disasters. BDR involves creating and maintaining copies of data and systems in a secure and remote location, so that they can be quickly restored in case of outages, cyberattacks, or other incidents. Cloud computing has become a popular and convenient platform for BDR, as it offers scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
Having a reliable BDR strategy is crucial for cloud computing, as it ensures data protection, business continuity, and regulatory compliance. Data protection means preventing data loss, corruption, or theft, which can have severe consequences for businesses, such as financial losses, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. Business continuity means maintaining the operations and services of an organization, even in the face of unexpected events, such as natural disasters, power outages, or cyberattacks. Regulatory compliance means adhering to the laws and regulations that apply to an industry or a region, such as HIPAA for healthcare, GDPR for Europe, or PCI-DSS for payments.
By implementing a cloud-based BDR solution, organizations can enjoy several benefits, such as reducing the cost and complexity of managing their own backup infrastructure, improving the speed and efficiency of recovery, enhancing the security and privacy of their data, and meeting the regulatory and compliance requirements. However, choosing the right cloud BDR provider and implementing and managing the solution correctly are also important factors to consider, as they can affect the performance, reliability, and cost of the BDR service.

Key Components of a Cloud-Based BDR Solution
A cloud-based BDR solution is a set of services and tools that help organizations protect and recover their data and applications in the cloud. A reliable and effective cloud BDR solution should include the following essential components:
- Backup and Recovery Services: The primary function of a cloud BDR solution is to create and maintain copies of data and systems in a secure and remote location. This involves backing up data and applications regularly and automatically, according to a schedule and a policy that suit the needs and requirements of the organization. The solution should also provide recovery services that allow organizations to restore their data and systems quickly and easily, in case of outages, cyberattacks, or other incidents. The recovery services should support different scenarios, such as bare-metal recovery, granular recovery, and recovery to dissimilar hardware or cloud environments.
- Replication and Synchronization: To ensure the availability and consistency of data and applications, a cloud BDR solution should provide replication and synchronization services that keep the backup copies up-to-date and consistent with the production copies. Replication means copying data and applications from the primary site to the backup site in real-time or near real-time, depending on the recovery point objective (RPO) and the recovery time objective (RTO) of the organization. Synchronization means ensuring that the backup copies are consistent with each other and with the production copies, by resolving any conflicts or discrepancies that may arise due to concurrent changes or updates.
- Automation and Orchestration: A cloud BDR solution should provide automation and orchestration services that simplify and streamline the backup and recovery processes, by reducing the manual intervention and the human error. Automation means automating the repetitive tasks, such as scheduling backups, monitoring the backup status, and sending alerts or notifications. Orchestration means defining and executing the recovery workflows, such as failover, failback, and testing, in a consistent and predictable manner. The solution should also provide APIs and integrations that allow organizations to integrate the BDR solution with other cloud services and tools, such as cloud storage, cloud computing, and cloud networking.
- Monitoring and Reporting: A cloud BDR solution should provide monitoring and reporting services that allow organizations to track and measure the performance, efficiency, and effectiveness of the BDR solution, by collecting and analyzing the relevant metrics and data. Monitoring means monitoring the backup and recovery operations, such as the backup size, the backup duration, the recovery time, and the network latency. Reporting means generating and delivering the reports and the dashboards that provide insights and visibility into the BDR solution, such as the backup and recovery trends, the capacity planning, and the compliance status.
By choosing a cloud BDR solution that includes these key components, organizations can ensure that they have a robust, reliable, and scalable BDR strategy that protects their data and applications, ensures business continuity, and meets regulatory compliance.

How to Choose the Right Cloud BDR Provider
When selecting a cloud BDR provider, organizations should consider several factors that can impact their data protection, business continuity, and regulatory compliance. Here are some tips and criteria for choosing a reputable and trustworthy cloud BDR provider:
- Data Security and Privacy: The cloud BDR provider should have robust and reliable security measures in place to protect the data and applications of the organization from unauthorized access, theft, loss, or damage. The provider should also comply with the relevant data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and provide the necessary certifications and attestations, such as SOC 2 or ISO 27001.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): The cloud BDR provider should offer clear and concise SLAs that define the level of service, availability, performance, and support that the organization can expect from the provider. The SLAs should cover the backup and recovery objectives, the replication and synchronization frequency, the recovery time and point, and the uptime and downtime. The SLAs should also specify the remedies and penalties in case of any breach or violation.
- Pricing and Billing: The cloud BDR provider should have transparent and flexible pricing and billing models that align with the budget and needs of the organization. The provider should charge based on the amount and type of data, the frequency and duration of the backup and recovery, the number and complexity of the workflows, and the level of support and service. The provider should also offer a free trial or a proof of concept to test the solution before committing to it.
- Customer Support and Service: The cloud BDR provider should provide excellent and responsive customer support and service that help the organization to resolve any issue or query in a timely and effective manner. The provider should offer multiple channels of communication, such as phone, email, chat, or ticket, and provide 24/7/365 availability and coverage. The provider should also have a dedicated team of experts and specialists who can assist the organization with the implementation, configuration, optimization, and troubleshooting of the solution.
By considering these factors and criteria, organizations can choose the right cloud BDR provider that meets their needs and expectations, and ensures their data protection, business continuity, and regulatory compliance.
Real-World Examples of Cloud BDR in Action
Cloud backup and disaster recovery (BDR) solutions have become increasingly popular among businesses of all sizes and industries, as they offer a reliable and cost-effective way to protect and recover their data and applications. Here are some successful and inspiring use cases of cloud BDR in different scenarios and contexts:
- Healthcare: A hospital chain uses a cloud BDR solution to back up and recover its electronic health records (EHRs) and medical images, ensuring the continuity of care and the compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). The solution enables the hospital to restore its data in minutes, reducing the downtime and the impact on the patients and the staff.
- Finance: A bank uses a cloud BDR solution to protect its financial transactions and customer data, ensuring the security and the availability of its services. The solution allows the bank to replicate its data across multiple regions and clouds, preventing the loss and the theft of its data, and meeting the regulatory requirements, such as the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC) guidelines.
- E-commerce: An online retailer uses a cloud BDR solution to safeguard its website and its database, ensuring the business continuity and the customer satisfaction. The solution enables the retailer to failover its website to a secondary cloud in case of any disruption or disaster, minimizing the revenue loss and the reputation damage.
- Remote Work: A company with a distributed workforce uses a cloud BDR solution to secure and manage its remote devices and applications, ensuring the productivity and the flexibility of its employees. The solution allows the company to backup and recover its data from any location and device, enhancing the collaboration and the resilience of its workforce.
These examples demonstrate the versatility and the effectiveness of cloud BDR solutions in various industries and scenarios. By adopting a cloud BDR solution, businesses can benefit from the data protection, the business continuity, and the regulatory compliance, while also improving the user experience and the operational efficiency.

Best Practices for Implementing and Managing Cloud BDR
Implementing and managing a cloud backup and disaster recovery (BDR) solution can be a complex and challenging task, but it can also be a rewarding and beneficial one. By following some best practices and guidelines, businesses can ensure the success and the effectiveness of their cloud BDR strategy, and avoid some common pitfalls and mistakes. Here are some practical and actionable advice for implementing and managing a cloud BDR solution:
- Set up backup schedules and retention policies: One of the first steps in implementing a cloud BDR solution is to determine the frequency and the duration of the backups. Businesses should consider their recovery time objective (RTO) and their recovery point objective (RPO) when setting up the backup schedules and retention policies. The RTO is the maximum acceptable length of time that a system can be down, while the RPO is the maximum acceptable amount of data loss. By aligning the backup schedules and retention policies with the RTO and RPO, businesses can ensure the timely and efficient recovery of their data and applications in case of any disruption or disaster.
- Test and validate recovery procedures: Another important step in implementing a cloud BDR solution is to test and validate the recovery procedures. Businesses should regularly test their backups and their recovery plans to ensure their functionality and their accuracy. By testing and validating the recovery procedures, businesses can identify and address any issues and gaps, and improve their confidence and their readiness in case of any emergency or disaster.
- Integrate with other cloud services and tools: A cloud BDR solution should not be a standalone or isolated solution, but a part of a broader and more comprehensive cloud strategy. Businesses should integrate their cloud BDR solution with other cloud services and tools, such as cloud monitoring, cloud automation, and cloud orchestration. By integrating the cloud BDR solution with other cloud services and tools, businesses can enhance the visibility, the control, and the automation of their cloud operations, and improve the overall efficiency and the effectiveness of their cloud strategy.
- Monitor and report on the cloud BDR performance: A cloud BDR solution should not be a set-and-forget or a fire-and-forget solution, but a continuously monitored and reported solution. Businesses should monitor and report on the cloud BDR performance, such as the backup and recovery times, the backup and recovery sizes, and the backup and recovery success rates. By monitoring and reporting on the cloud BDR performance, businesses can detect and troubleshoot any issues and anomalies, and optimize and improve the cloud BDR strategy.
By following these best practices and guidelines, businesses can ensure the success and the effectiveness of their cloud BDR strategy, and benefit from the data protection, the business continuity, and the regulatory compliance. However, businesses should also be aware of the potential challenges and limitations of cloud BDR, such as data transfer costs, network latency, and vendor lock-in, and seek some workarounds and solutions to mitigate and overcome them.
Challenges and Limitations of Cloud BDR
While cloud backup and disaster recovery (BDR) solutions offer numerous benefits and advantages, they also come with some potential issues and constraints. By being aware of these challenges and limitations, businesses can make informed decisions and seek some workarounds and solutions to mitigate and overcome them. Here are some of the most common challenges and limitations of cloud BDR:
- Data transfer costs: One of the challenges of cloud BDR is the cost of transferring data to and from the cloud. Depending on the amount and the frequency of the data, the data transfer costs can add up and become a significant expense for businesses. To address this challenge, businesses can use data compression, data deduplication, and data tiering to reduce the data transfer volume and the data transfer frequency. They can also use cloud providers that offer flat-rate or reduced-rate data transfer fees, or negotiate a customized data transfer agreement with their cloud provider.
- Network latency: Another challenge of cloud BDR is the time it takes to transmit and receive data over the network. Depending on the distance and the quality of the network, the network latency can affect the performance and the efficiency of the cloud BDR solution. To address this challenge, businesses can use network optimization techniques, such as caching, buffering, and load balancing, to reduce the network latency and the network congestion. They can also use cloud providers that have a presence in multiple regions or locations, or use a hybrid cloud model that combines the public cloud and the private cloud.
- Vendor lock-in: A challenge of cloud BDR is the dependency and the loyalty to a specific cloud provider. Depending on the cloud provider’s features, functions, and services, the cloud BDR solution may not be compatible or interoperable with other cloud providers or solutions. To address this challenge, businesses can use open standards, open interfaces, and open APIs to ensure the portability and the flexibility of the cloud BDR solution. They can also use multi-cloud or hybrid cloud models that allow them to switch or migrate between different cloud providers or solutions, or use a cloud broker or a cloud manager that can manage and orchestrate multiple cloud providers or solutions.
By being aware of these challenges and limitations, businesses can make informed decisions and seek some workarounds and solutions to mitigate and overcome them. By doing so, they can ensure the success and the effectiveness of their cloud BDR strategy, and benefit from the data protection, the business continuity, and the regulatory compliance.
The Future of Cloud BDR: Trends and Innovations
As cloud backup and disaster recovery (BDR) solutions continue to evolve and mature, businesses can expect to see some emerging and promising trends and innovations that can enhance their data protection, business continuity, and regulatory compliance. Here are some of the most exciting and inspiring trends and innovations in cloud BDR:
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML): AI and ML can help cloud BDR solutions to become more intelligent, adaptive, and predictive. By analyzing the data patterns, behaviors, and trends, AI and ML can automatically adjust the backup schedules, retention policies, and recovery procedures to optimize the performance, efficiency, and effectiveness of the cloud BDR solution. They can also detect and prevent potential threats, attacks, and anomalies that can compromise the data integrity, confidentiality, and availability. For example, AI and ML can identify and block ransomware attacks that can encrypt or delete the data, or detect and alert the administrators of unusual data access, modification, or deletion that can indicate insider threats or external breaches.
- Blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT): Blockchain and DLT can help cloud BDR solutions to become more secure, transparent, and immutable. By using a decentralized and distributed network of nodes, blockchain and DLT can ensure the integrity, authenticity, and non-repudiation of the data. They can also enable the data to be audited, verified, and traced by multiple parties, without the need for a central authority or a trusted third party. For example, blockchain and DLT can be used to create an immutable and tamper-proof log of all the backup and recovery activities, or to facilitate the multi-party data sharing and collaboration in a secure and compliant manner.
- Hybrid cloud and multi-cloud solutions: Hybrid cloud and multi-cloud solutions can help cloud BDR solutions to become more flexible, scalable, and resilient. By using a combination of public cloud, private cloud, and edge cloud, businesses can leverage the strengths and advantages of each cloud model, and mitigate the weaknesses and limitations. They can also ensure the data sovereignty, data locality, and data compliance, by storing and processing the data in the appropriate cloud environment. For example, businesses can use the public cloud for the backup and archival storage, the private cloud for the disaster recovery, and the edge cloud for the real-time replication and synchronization.
By adopting these trends and innovations, businesses can take advantage of the full potential and value of cloud BDR solutions, and achieve their data protection, business continuity, and regulatory compliance objectives. They can also stay ahead of the competition and the market demands, and provide the best possible user experience and satisfaction.
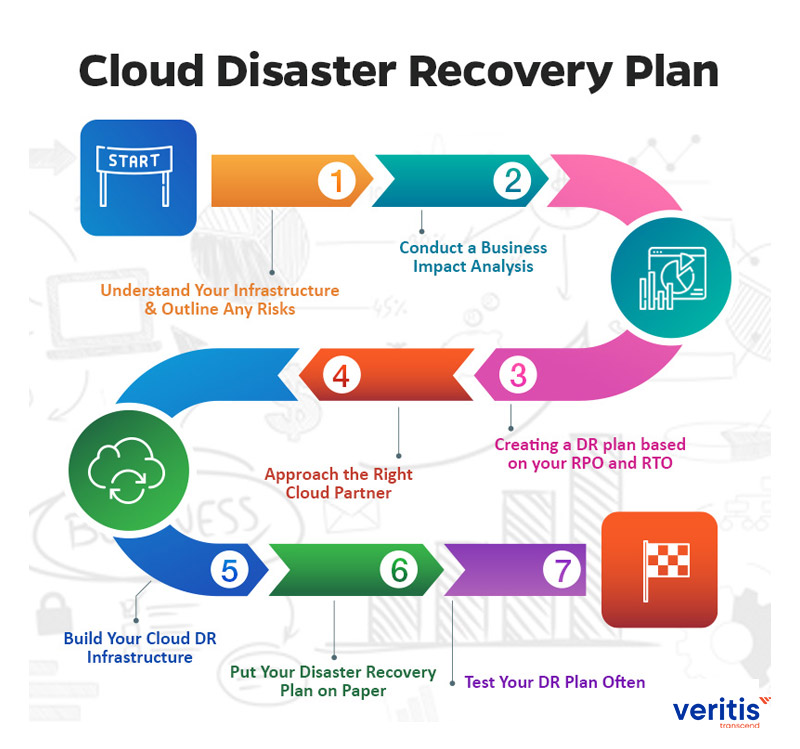
Conclusion: Making the Most of Cloud BDR for Your Business
In conclusion, Backup and disaster recovery (BDR) in cloud solutions is a critical aspect of any business’s IT strategy, ensuring data protection, business continuity, and regulatory compliance. A reliable cloud BDR solution can help businesses to minimize the risk and impact of data loss, downtime, and disruption, and maximize the value and benefits of cloud computing. By choosing the right cloud BDR provider, implementing and managing the solution effectively, and staying updated with the latest trends and innovations, businesses can take advantage of the full potential and value of cloud BDR solutions, and achieve their strategic objectives and goals.
Therefore, we encourage you to take action and adopt a cloud BDR solution for your business, if you haven’t done so already. By doing so, you can protect your data, maintain your operations, and comply with the regulations, and gain a competitive edge and a peace of mind. We hope that this comprehensive guide has provided you with the necessary knowledge, insights, and best practices to make an informed and confident decision, and to make the most of cloud BDR for your business.
