Understanding Azure Regions: An Overview
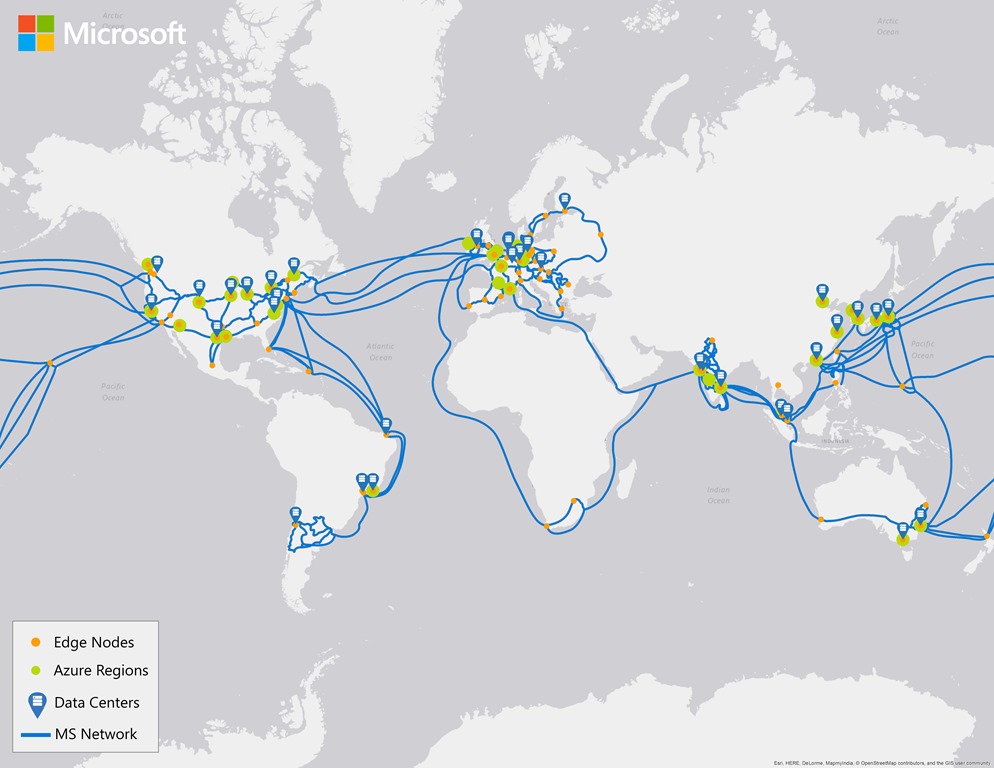
Azure regions are a critical component of Microsoft’s cloud infrastructure, providing a global network of datacenters that offer a wide range of Azure services. These regions are strategically located around the world, enabling businesses and organizations to deploy their applications and services close to their users, reducing latency and improving performance.
Azure regions consist of multiple datacenters, each with its own set of compute, storage, and network resources. These regions are grouped into pairs, with each pair consisting of a primary and secondary region located in close proximity to each other. This setup, known as region pairs, ensures data redundancy and disaster recovery capabilities, minimizing downtime in the event of a disaster.
Availability zones are also a key part of Azure regions. These are physically separate datacenters within an Azure region, each with its own power, cooling, and networking infrastructure. Availability zones provide additional redundancy and high availability for mission-critical applications, ensuring that they remain operational even in the event of a datacenter failure.
In summary, Azure regions are a vital part of Microsoft’s cloud infrastructure, providing a global network of datacenters that offer a wide range of Azure services. With region pairs and availability zones, Azure regions ensure data redundancy, disaster recovery, and high availability, making them an essential tool for businesses and organizations using Azure services.
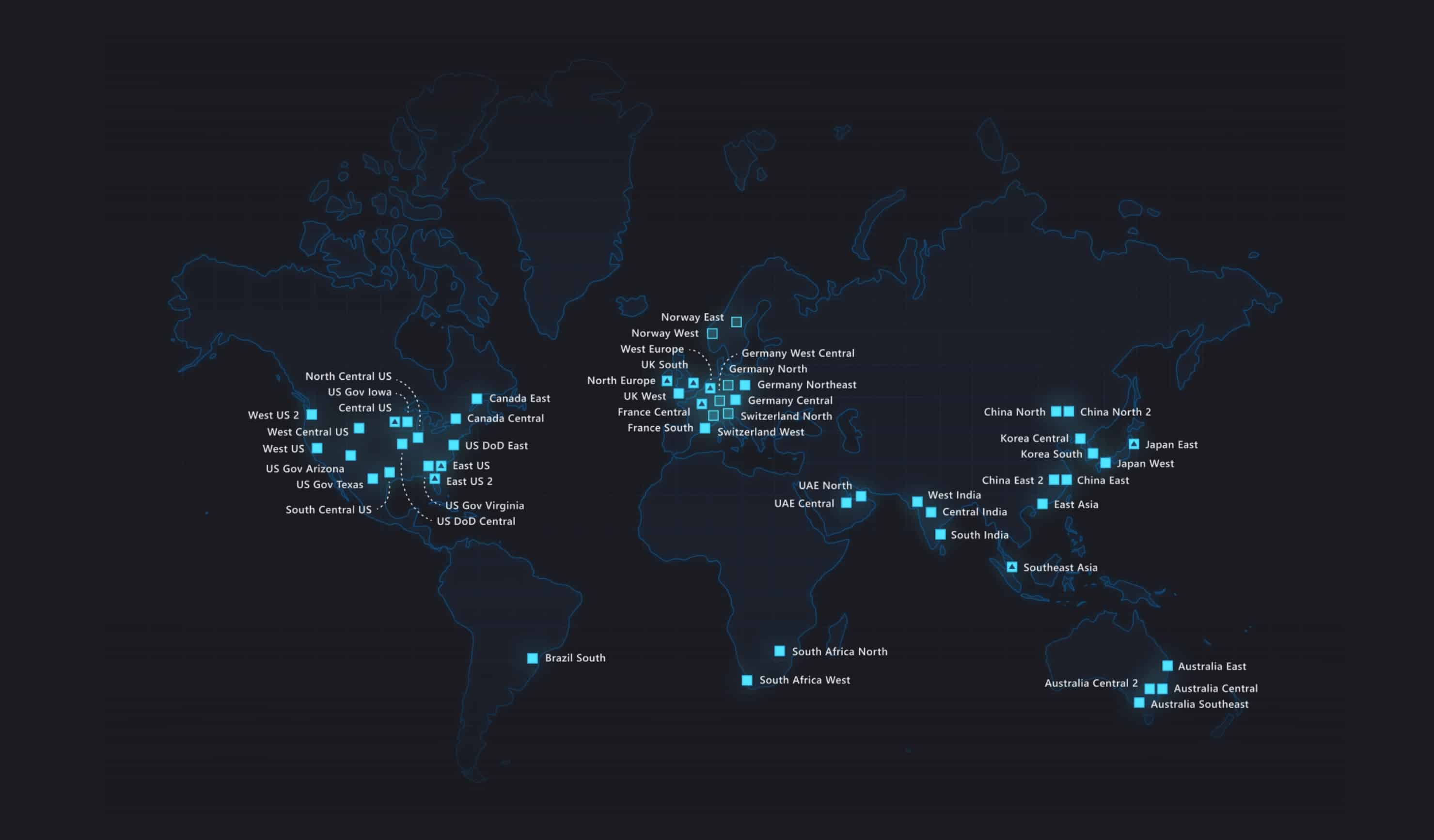
The Azure region map is a visual representation of the global distribution of Azure regions, highlighting the various regions and their locations. By understanding the Azure region map, businesses and organizations can make informed decisions about where to deploy their applications and services, taking into account factors such as proximity to users, data sovereignty, and compliance requirements.
Exploring the Azure Region Map: A Detailed Look
The Azure region map is a comprehensive visual representation of the global distribution of Azure regions. With regions located in every major continent, Azure provides a truly global infrastructure that enables businesses and organizations to deploy their applications and services close to their users, reducing latency and improving performance.
The Azure region map highlights the various regions and their locations, with a focus on regions with high demand and growth potential. For example, the Europe West region, located in the Netherlands, is one of the most popular Azure regions in Europe, serving a wide range of industries, including finance, healthcare, and gaming. Similarly, the East Asia region, located in Hong Kong, is a popular choice for businesses and organizations operating in the Asia-Pacific region, providing low-latency access to users in China, Japan, and South Korea.
The Azure region map also provides a visual representation of the distribution of Azure regions across the globe. For example, the United States has the highest concentration of Azure regions, with a total of 14 regions located in various parts of the country. This distribution ensures that businesses and organizations operating in the US can deploy their applications and services close to their users, reducing latency and improving performance.
In addition to the visual representation of the Azure region map, the Azure portal provides a comprehensive list of all Azure regions, along with detailed information about each region, including its location, availability zones, and compliance certifications. This information is essential for businesses and organizations when choosing the right Azure region for their applications and services, taking into account factors such as proximity to users, data sovereignty, and compliance requirements.
In conclusion, the Azure region map is a valuable tool for businesses and organizations using Azure services. By providing a visual representation of the global distribution of Azure regions, the Azure region map enables businesses and organizations to make informed decisions about where to deploy their applications and services, taking into account factors such as proximity to users, data sovereignty, and compliance requirements. With a wide range of Azure regions located in every major continent, Azure provides a truly global infrastructure that enables businesses and organizations to deploy their applications and services close to their users, reducing latency and improving performance.
How to Utilize the Azure Region Map for Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Azure regions play a critical role in ensuring business continuity and disaster recovery for businesses and organizations using Azure services. By understanding the concept of region pairs and how they can be used to ensure data redundancy and minimize downtime in the event of a disaster, businesses and organizations can build a robust and reliable Azure infrastructure.
Region pairs are a fundamental concept in Azure’s business continuity and disaster recovery strategy. A region pair consists of two Azure regions located close to each other, with one region serving as the primary region and the other as the secondary region. By replicating data and services across region pairs, businesses and organizations can ensure that their applications and services remain available and operational even in the event of a disaster.
For example, if a business is using Azure services in the US East region, it can replicate its data and services to the US East 2 region, which is located in the same geographical area. In the event of a disaster in the US East region, the business can failover to the US East 2 region, ensuring that its applications and services remain available and operational.
The Azure region map is a valuable tool for businesses and organizations when planning for business continuity and disaster recovery. By visualizing the distribution of Azure regions across the globe, businesses and organizations can choose the right region pairs for their applications and services, taking into account factors such as proximity to users, data sovereignty, and compliance requirements.
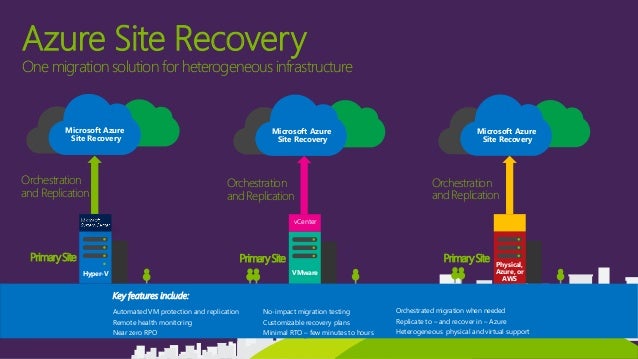
When planning for business continuity and disaster recovery, businesses and organizations should also consider Azure’s Site Recovery and Backup services. Site Recovery enables businesses and organizations to replicate their applications and services to a secondary region, while Backup provides a simple and cost-effective way to protect and recover data.
In conclusion, Azure regions play a critical role in ensuring business continuity and disaster recovery for businesses and organizations using Azure services. By understanding the concept of region pairs and how they can be used to ensure data redundancy and minimize downtime in the event of a disaster, businesses and organizations can build a robust and reliable Azure infrastructure. The Azure region map is a valuable tool for businesses and organizations when planning for business continuity and disaster recovery, enabling them to choose the right region pairs for their applications and services and ensuring that their applications and services remain available and operational even in the event of a disaster.
Comparing Azure Regions: Performance, Pricing, and Features
When it comes to choosing the right Azure region for your business, there are several factors to consider, including performance, pricing, and features. By comparing different Azure regions, you can make an informed decision that meets your business needs and ensures the success of your cloud computing strategy.
Performance is a critical factor when choosing an Azure region. Different regions offer different levels of performance, depending on factors such as network latency, processing power, and storage capacity. For example, the West US region offers high-performance computing capabilities, making it an ideal choice for businesses that require powerful processing capabilities, such as scientific simulations or machine learning applications.
Pricing is another important factor to consider when comparing Azure regions. Different regions offer different pricing models, depending on factors such as local taxes, market demand, and infrastructure costs. For example, the Central US region offers competitive pricing for virtual machines, making it an attractive choice for businesses looking to reduce their cloud computing costs.
Features are also an important consideration when comparing Azure regions. Different regions offer different features, depending on factors such as compliance certifications, data regulations, and availability zones. For example, the Europe North region offers compliance certifications for GDPR and HIPAA, making it an ideal choice for businesses operating in Europe or in the healthcare industry.
When comparing Azure regions, it’s important to consider factors such as proximity to users, data sovereignty, and compliance requirements. For example, if your business operates in Europe, you may want to choose an Azure region in Europe to ensure compliance with EU data regulations. Similarly, if your business requires low-latency connectivity to users in Asia, you may want to choose an Azure region in Asia to ensure optimal performance.
In conclusion, comparing Azure regions is a critical step in choosing the right Azure region for your business. By considering factors such as performance, pricing, and features, you can make an informed decision that meets your business needs and ensures the success of your cloud computing strategy. The Azure region map is a valuable tool for comparing Azure regions, enabling you to visualize the distribution of regions across the globe and choose the right region for your applications and services.
Azure Region Expansion: Future Plans and Predictions
Microsoft is continuously expanding its Azure regions to meet the growing demand for cloud computing services. By adding new regions and investing in existing ones, Microsoft is ensuring that businesses and organizations around the world have access to reliable and high-performance Azure services.
One region that is expected to see significant growth in the coming years is the Asia Pacific region. With a rapidly growing economy and a large population, the Asia Pacific region is an important market for Microsoft. In response to this demand, Microsoft has announced plans to open several new Azure regions in the region, including in Australia, New Zealand, and Indonesia.
Another region that is expected to see growth is the European region. With strict data regulations and a growing demand for cloud computing services, the European region is an important market for Microsoft. In response to this demand, Microsoft has announced plans to open several new Azure regions in the region, including in Germany, Switzerland, and Norway.
In addition to these new regions, Microsoft is also investing in existing Azure regions. For example, the US East region is one of the most popular Azure regions, and Microsoft is continuously investing in this region to ensure that it can meet the growing demand for Azure services. Similarly, the Europe North region is an important region for Microsoft, and the company is investing in this region to ensure that it can meet the compliance requirements of businesses operating in Europe.
The expansion of Azure regions is not only beneficial for businesses and organizations, but it also has a positive impact on the cloud computing market. By expanding its presence in different regions, Microsoft is increasing competition in the cloud computing market, which can lead to lower prices and better services for businesses and organizations.
In conclusion, Microsoft’s plans for expanding Azure regions are an important factor to consider when choosing an Azure region for your business. By understanding the regions that are expected to see growth and investment, you can make an informed decision that meets your business needs and ensures the success of your cloud computing strategy. The Azure region map is a valuable tool for visualizing the distribution of Azure regions and planning for the future of your Azure infrastructure.
Best Practices for Working with Azure Regions
To get the most out of Azure regions and ensure the success of your cloud computing strategy, it’s important to follow best practices for working with Azure regions. Here are some best practices to consider:
Monitor and Manage Region Health
It’s important to continuously monitor and manage the health of Azure regions to ensure that they are running smoothly and meeting your business needs. Azure Monitor and Azure Advisor are two tools that can help you monitor and manage Azure region health. These tools provide real-time insights into the performance and availability of Azure services, enabling you to quickly identify and resolve any issues.
Optimize Network Connectivity
Network connectivity is a critical factor in the performance and reliability of Azure services. To ensure optimal network connectivity, it’s important to choose the right Azure region for your applications and services, and to optimize network connectivity using tools such as Azure ExpressRoute and Azure Virtual WAN.
Ensure Compliance with Data Regulations
Data regulations are an important consideration when working with Azure regions. To ensure compliance with data regulations, it’s important to choose an Azure region that meets your compliance requirements, and to use tools such as Azure Policy and Azure Security Center to monitor and enforce compliance.
Plan for Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Business continuity and disaster recovery are critical considerations when working with Azure regions. To ensure data redundancy and minimize downtime in the event of a disaster, it’s important to use region pairs and to have a well-defined business continuity and disaster recovery plan in place.
Stay Up-to-Date with Azure Region Expansion
Microsoft is continuously expanding its Azure regions to meet the growing demand for cloud computing services. To ensure that you are taking advantage of the latest Azure regions and features, it’s important to stay up-to-date with Azure region expansion and to plan for the future of your Azure infrastructure.
By following these best practices, you can ensure the success of your cloud computing strategy and take full advantage of the power and potential of Azure regions. The Azure region map is a valuable tool for visualizing the distribution of Azure regions and planning for the future of your Azure infrastructure.
Real-World Examples of Azure Regions in Action
Azure regions are being used by businesses and organizations of all sizes and industries to support their operations and achieve their goals. Here are some real-world examples of Azure regions in action:
Global Retailer
A global retailer with operations in over 30 countries uses Azure regions to support its e-commerce platform. By using Azure regions located close to its customers, the retailer is able to provide a fast and reliable online shopping experience, even during peak shopping seasons. The retailer also uses Azure regions for business continuity and disaster recovery, ensuring that its e-commerce platform remains available in the event of a disaster.
Healthcare Provider
A healthcare provider with sensitive patient data uses Azure regions to ensure data sovereignty and compliance with healthcare regulations. By using Azure regions located in the same country as its patients, the healthcare provider is able to keep patient data within national borders and comply with data privacy regulations. The healthcare provider also uses Azure regions for data backup and disaster recovery, ensuring the availability and integrity of patient data in the event of a disaster.
Manufacturing Company
A manufacturing company with operations in multiple countries uses Azure regions to support its supply chain management system. By using Azure regions located close to its manufacturing facilities, the company is able to provide real-time visibility into its supply chain and make data-driven decisions to optimize operations. The company also uses Azure regions for business continuity and disaster recovery, ensuring that its supply chain management system remains available in the event of a disaster.
These real-world examples demonstrate the power and potential of Azure regions to support the operations and growth of businesses and organizations. By using Azure regions, businesses and organizations can ensure the availability, reliability, and performance of their applications and services, while also meeting data sovereignty and compliance requirements.
Conclusion: The Power and Potential of Azure Regions
Azure regions are a critical component of Microsoft’s cloud infrastructure, providing a global network of datacenters that enable businesses and organizations to deploy their applications and services with high availability, low latency, and data sovereignty. By using Azure regions, businesses and organizations can ensure the reliability and performance of their applications and services, while also meeting data compliance requirements.
The Azure region map is a valuable tool for visualizing the distribution of Azure regions and planning for the deployment and management of applications and services. By understanding the various Azure regions and their locations, businesses and organizations can make informed decisions about where to deploy their applications and services, taking into account factors such as proximity to users, data sovereignty, and compliance requirements.
Azure regions also play a critical role in business continuity and disaster recovery planning. By using region pairs and availability zones, businesses and organizations can ensure data redundancy and minimize downtime in the event of a disaster. By following best practices for working with Azure regions, such as monitoring and managing region health, optimizing network connectivity, and ensuring compliance with data regulations, businesses and organizations can ensure the availability and reliability of their applications and services.
As the cloud computing market continues to grow and evolve, Microsoft is investing in the expansion of Azure regions to meet the increasing demand for cloud services. By understanding and utilizing Azure regions, businesses and organizations can take advantage of the power and potential of cloud computing to support their growth and success.