What is Azure Resource Governance and Why Does it Matter?
Azure resource governance is the framework that guides how organizations manage their cloud resources within the Azure environment. It is essential for maintaining security, ensuring compliance, and controlling costs. Effective governance allows businesses to operate efficiently and securely in the cloud. By implementing governance policies, organizations can mitigate risks and optimize their cloud investments. This involves establishing clear guidelines and controls over resource deployment, configuration, and access. Without proper governance, Azure environments can become complex and difficult to manage, leading to potential security breaches, compliance violations, and uncontrolled spending. Management groups are a crucial component of Azure governance, providing a way to organize and manage subscriptions hierarchically. They allow for the application of policies and access controls at scale, ensuring consistent governance across multiple subscriptions. A well-defined azure initiative improves resource management, reduces administrative overhead, and ensures that cloud resources align with business objectives. Azure initiative helps organizations maintain a secure and compliant cloud environment while optimizing cost efficiency. Adopting a strong azure initiative is critical for organizations looking to leverage the benefits of Azure while mitigating potential risks.
A key aspect of azure initiative is the ability to enforce policies across multiple subscriptions. This ensures that all resources within the organization adhere to predefined standards and regulations. For example, policies can be implemented to require specific resource tags, restrict allowed resource types, or enforce location restrictions. These policies are inherited through the management group hierarchy, ensuring consistency across all subscriptions within a given management group. This hierarchical structure simplifies the management of policies and access controls, making it easier to maintain a secure and compliant cloud environment. Azure initiative also provides visibility into resource usage and costs, enabling organizations to track spending and optimize their cloud investments. By organizing subscriptions into management groups, businesses can allocate costs to different departments or projects, providing a clear understanding of cloud spending. Furthermore, governance helps ensure that resources are deployed and configured in a way that aligns with business requirements, improving efficiency and reducing waste.
In summary, Azure resource governance is a critical aspect of cloud management that should not be overlooked. It provides the framework for maintaining security, ensuring compliance, and controlling costs across Azure environments. Management groups are a key component of azure initiative, allowing organizations to organize and manage subscriptions hierarchically, apply policies at scale, and track resource usage and costs. By implementing a robust azure initiative, businesses can leverage the benefits of Azure while mitigating potential risks and optimizing their cloud investments. The use of azure initiative allows businesses to gain full control over their environment. A proper azure initiative lets businesses succeed with their cloud solutions.
How to Implement a Robust Azure Governance Strategy
Developing a comprehensive Azure governance strategy is crucial for organizations seeking to manage their cloud resources effectively. This involves establishing a clear set of policies that dictate how resources are created, configured, and managed. These policies should address key areas such as security, compliance, and cost control. Naming conventions are essential for maintaining order and clarity within your Azure environment. Consistent naming helps identify resources and their purpose, simplifying management and troubleshooting. Implementing role-based access control (RBAC) is fundamental to securing your Azure resources. RBAC allows you to grant specific permissions to users and groups, limiting their access to only the resources they need. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and accidental misconfigurations. Establishing robust monitoring and alerting mechanisms is vital for proactive management. Monitoring helps you track the performance and health of your resources, while alerts notify you of any issues or anomalies that require attention. Consider leveraging Azure Monitor and Azure Advisor to gain insights into your environment and identify potential problems. The strategic deployment of azure initiative is vital to make the process successful.
Azure management groups play a pivotal role in enforcing these policies across multiple subscriptions. They provide a hierarchical structure that allows you to group subscriptions together and apply policies at the management group level. This ensures that all subscriptions within a management group inherit the same policies, promoting consistency and compliance. For example, you can create a management group for your development environment and apply policies that restrict the types of resources that can be created, or a security baseline. Consider using azure initiative to implement consistent security controls, ensuring consistent application of organizational policies across different environments and subscriptions, by applying specific policy sets to resource groups.
When defining policies, it’s important to consider the specific needs and requirements of your organization. Policies should be clear, concise, and easy to understand. They should also be regularly reviewed and updated to ensure they remain relevant and effective. Furthermore, policies should be communicated effectively to all stakeholders to ensure everyone is aware of their responsibilities. Thorough planning and documentation are also key components of an effective Azure governance strategy. Documenting your policies, naming conventions, and RBAC assignments will help ensure consistency and facilitate knowledge sharing within your organization. A well-defined azure initiative, documented and readily available, will increase awareness and compliance. This approach promotes collaboration and ensures that everyone is working towards the same goals, creating a sustainable and well-managed Azure environment. By following these guidelines, organizations can create a robust Azure governance strategy that supports their business objectives and minimizes risk.
Understanding Azure Management Groups: The Foundation of Organizational Structure
Azure management groups serve as a foundational element for organizing and governing Azure subscriptions. They establish a hierarchical structure that enables unified policy and access management across multiple subscriptions. Think of management groups as containers above subscriptions, allowing organizations to group these subscriptions based on various criteria, such as business units, departments, or geographical regions. This grouping facilitates the application of consistent policies and access controls, ensuring compliance and security across the entire Azure environment. Azure initiative is crucial for implementing and optimizing your Azure environment.
The hierarchical structure of management groups allows for inheritance of policies and access controls. Policies and roles assigned at a higher level management group automatically cascade down to all child management groups and subscriptions. This inheritance model simplifies management and ensures consistent governance throughout the organization. For example, a policy requiring specific resource tags can be applied at the root management group, ensuring that all resources in all subscriptions adhere to the tagging standard. This concept of inheritance is a cornerstone of effective Azure governance. Every Azure initiative will benefit from this inheritance.
When working with Azure management groups, it’s crucial to consider certain limits and considerations. Each Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant can support up to six levels of management group hierarchy, excluding the root level. Subscriptions can only be direct children of a management group. Each management group can have multiple child management groups or subscriptions. There are also limitations on the number of management group deployments. Proper planning and documentation are essential before implementing a management group structure to ensure it aligns with the organization’s needs and complies with these limits. Understanding these constraints helps organizations avoid potential issues and create a scalable and maintainable governance model. Properly implemented azure initiative is important. The root management group is created automatically when the first management group is created.
How to Create and Manage Management Groups in Azure Portal
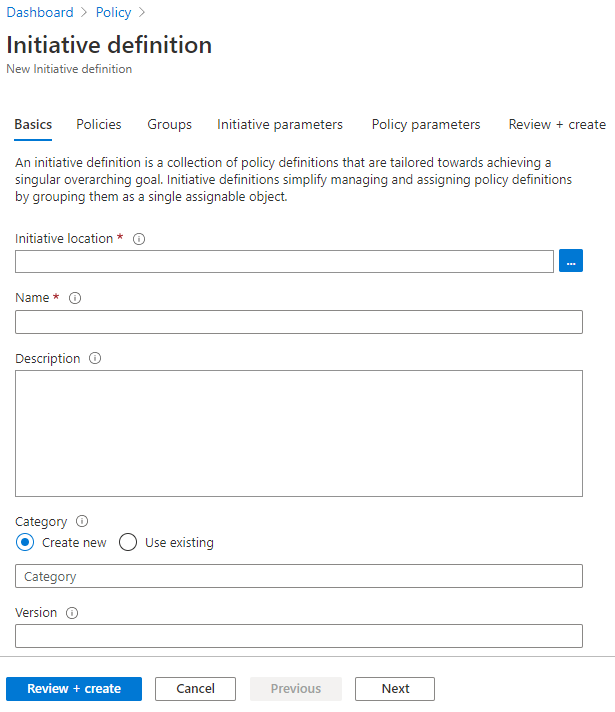
Managing Azure resources effectively requires a structured approach, and Azure Management Groups provide the foundation for organizing your subscriptions. This section provides a step-by-step guide on how to create and manage these groups using the Azure portal. The Azure portal offers a user-friendly interface for creating, modifying, and assigning policies to management groups, ensuring consistent governance across your Azure environment. Implementing an azure initiative involves first understanding how to set up the management group structure itself.
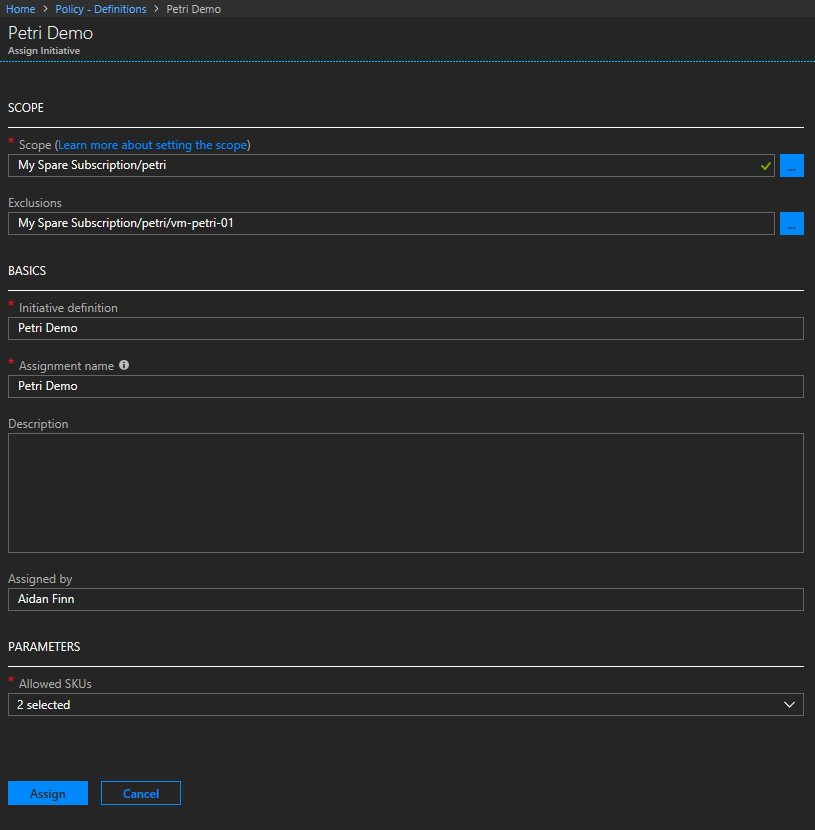
To begin, log in to the Azure portal. Navigate to the “Management Groups” service by searching for it in the search bar. To create a new management group, click on the “+ Create” button. Provide a unique ID and display name for the new group. The ID is used for programmatic access, while the display name is what you see in the portal. Choose the parent management group under which this new group will reside. This establishes the hierarchical structure. Once the management group is created, you can move subscriptions into it. Locate the subscription you want to move, and under the “Overview” section, click on “Change management group”. Select the target management group from the dropdown list. Keep in mind that you need appropriate permissions to move subscriptions. With subscriptions assigned, the focus shifts to governance through the azure initiative approach.
Assigning policies and roles at the management group level is a key aspect of Azure governance. To assign a policy, navigate to the desired management group and select “Policies”. Click “Assign policy” and choose a policy definition from the available list. You can filter policies by category or search for specific policies. Configure the policy parameters as needed and create the assignment. Similarly, to assign roles, go to “Access control (IAM)” within the management group. Click “+ Add role assignment” and select the desired role and the users, groups, or service principals to whom you want to grant access. Role assignments at the management group level are inherited by all subscriptions within that group, simplifying access management. Through these steps, the Azure portal offers a centralized location to manage the hierarchical structure and policies that define your azure initiative.
Leveraging Azure Policy for Consistent Resource Configuration
Azure Policy is a crucial service that, when combined with management groups, enforces consistent resource configuration across an entire organization. It functions as a guardrail, ensuring that resources adhere to defined standards and comply with both internal policies and external regulations. By assigning policies at the management group level, organizations can propagate these rules down the hierarchy, affecting all subscriptions and resources within those groups. This inheritance model simplifies governance and reduces the risk of configuration drift.
Consider several examples of common policies applicable at the management group level. One might require specific resource tags, such as “Department” or “CostCenter,” to be present on all resources. This enables better cost tracking and accountability. Another policy could restrict the allowed resource types, preventing the deployment of unauthorized or unsupported services. Furthermore, location restrictions can be enforced, ensuring that resources are only deployed to approved Azure regions for compliance or data sovereignty reasons. The power of Azure Policy lies in its ability to automatically audit resource configurations and, if necessary, remediate non-compliant resources or prevent their creation altogether. Defining an azure initiative that encompasses several policies is possible, simplifying policy management. The azure initiative makes the configuration easier to implement and maintain.
The benefits of policy inheritance through the management group hierarchy are significant. It eliminates the need to configure the same policies repeatedly across multiple subscriptions, saving time and reducing errors. As an organization grows and its Azure environment becomes more complex, management groups and Azure Policy provide a scalable and effective way to maintain control and consistency. Moreover, Azure Policy assignments at the management group level contribute to a more secure and compliant environment, minimizing the risk of costly misconfigurations or violations. Understanding the interaction of azure initiative and management groups is key to designing a sound governance strategy. Using the azure initiative simplifies reporting on compliance since it becomes a single compliance status. The azure initiative is a critical component to managing complex environments that require various policies.
Cost Management and Optimization with Management Groups
Azure management groups are useful for cost management and optimization. They allow organizations to track and allocate cloud spending. Azure Cost Management + Billing allows to monitor expenditures at the management group level, giving a consolidated view of costs. This helps identify areas where costs can be reduced or optimized. By using management groups, organizations can assign costs to specific departments, projects, or business units. This enhances accountability and promotes cost-conscious decision-making. Tagging strategies are also crucial for granular cost analysis. Resources should be tagged consistently to filter and categorize costs accurately. This enables organizations to gain insights into the cost drivers within each management group.
Effective cost allocation is achieved by aligning management groups with the organizational structure. Each department or project can have its own management group. This setup facilitates the monitoring of costs associated with each entity. Azure Cost Management provides features to create budgets, set spending alerts, and analyze cost trends. These tools help in controlling costs and preventing overspending. Furthermore, the use of reserved instances and Azure Hybrid Benefit can be optimized at the management group level. Organizations can maximize cost savings by centrally managing these benefits. The **azure initiative** framework can be applied to implement consistent cost management policies across all subscriptions within a management group.
To improve cost optimization, organizations should regularly review cost data at the management group level. Identify underutilized resources and implement right-sizing strategies. Consider using Azure Advisor to get recommendations on optimizing resource utilization and reducing costs. Management groups also aid in enforcing cost-related policies, such as restricting the deployment of expensive resource types. By combining management groups with Azure Policy, organizations can ensure that all resources comply with cost optimization guidelines. For example, a policy can be created to automatically shut down virtual machines during off-peak hours. Effective cost management is a continuous process that requires ongoing monitoring, analysis, and optimization. The **azure initiative** provides a structured way to achieve this within the Azure environment. Consistently applying **azure initiative** across different management groups ensures uniformity and cost efficiency. Leveraging management groups along with consistent tagging strategies will enhance an organization’s cost visibility. By implementing **azure initiative** and strategically utilizing management groups, enterprises can achieve significant savings. Moreover, understanding how to leverage the **azure initiative** framework can lead to better governance.
Best Practices for Structuring Your Azure Environment with Management Groups
Designing an effective Azure environment using management groups requires careful planning and a clear understanding of your organization’s structure and needs. The goal is to create a hierarchy that simplifies management, enforces policies consistently, and aligns with your business units, geographical regions, or other relevant criteria. Before implementing any structure, thorough planning and comprehensive documentation are essential for long-term success. This approach ensures that the management group hierarchy remains relevant and adaptable as your organization evolves. Consider starting with a simple structure and iteratively refining it as your Azure footprint grows.
One common approach is to align the management group hierarchy with your organization’s business units. Each business unit can have its own management group, allowing for independent management and cost tracking. Another strategy is to organize by geographical region, which is particularly useful for organizations with a global presence. This allows you to enforce region-specific policies and optimize resource placement. Furthermore, you may group by environment such as production, development, and testing. This is especially relevant for enforcing policies that are appropriate for each environment. Consider implementing naming conventions to enhance clarity and organization within the hierarchy. A well-defined naming strategy makes it easier to identify and manage management groups. Azure Initiative plays a key role in standardizing resources. Azure Initiative helps enforce consistent resource configuration across different areas of operations. Azure Initiative is designed to maintain consistency and manage all your cloud resources.
When designing your management group structure, it’s crucial to consider policy inheritance. Policies assigned at a higher level in the hierarchy are automatically inherited by all child management groups and subscriptions. Leveraging this inheritance mechanism can significantly reduce administrative overhead and ensure consistent policy enforcement. Thoroughly test your management group structure in a non-production environment before implementing it in production. This allows you to identify and address any potential issues or conflicts before they impact your production workloads. Regular reviews of your management group structure are essential to ensure it remains aligned with your organization’s evolving needs. Be ready to adapt as your business grows and changes. Azure Initiative is very relevant in creating an efficient and compliant cloud environment. Azure Initiative is also key in ensuring costs are optimized. By using management groups and Azure Initiative effectively, organizations can achieve the best results.
Troubleshooting Common Management Group Issues
Navigating Azure management groups can sometimes present challenges. Issues such as policy conflicts, inheritance complexities, and access control errors may arise. When troubleshooting, a systematic approach is essential. One frequent problem involves policy conflicts. These occur when multiple policies, potentially inherited from different levels of the management group hierarchy, contradict each other. To resolve this, carefully examine the policy definitions and assignments. Identify the conflicting policies and adjust their configurations to align with the desired outcome. Utilizing the “azure initiative” feature within Azure Policy can help streamline policy management and reduce conflicts by grouping related policies together. Another common problem is inheritance issues. Policies and role assignments applied at a higher level in the management group hierarchy should propagate down to lower levels. If this inheritance is not functioning as expected, verify that the “Do not apply this policy to child scopes” setting is not enabled on the policy assignment. Additionally, ensure that there are no explicit denials configured at lower levels that might be blocking the inheritance. The effective access rights are also crucial. Incorrect role assignments at the management group level can lead to access control errors. If users are unable to perform certain actions, confirm that they have the necessary roles assigned at the appropriate scope. Use Azure’s built-in role definitions or create custom roles to grant granular permissions. Remember that the “azure initiative” also streamlines Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) at scale.
Certain error messages frequently appear when working with management groups. “The resource write operation is not allowed” usually indicates an RBAC issue. Double-check the user’s permissions and the scope of their assignment. “Policy conflict detected” signals overlapping or contradictory policy definitions. Review the policies and adjust their configurations to resolve the conflict. “Subscription is not in a valid state for this operation” suggests that the subscription might be undergoing maintenance or have an active deployment. Wait for the operation to complete or contact Azure support for assistance. When troubleshooting, leverage Azure Monitor to track activity logs and identify potential issues. Examine the audit logs for management group operations to gain insights into changes and errors. Use Azure Resource Graph to query and analyze your management group hierarchy and resource configurations. Consistent naming conventions can significantly improve the ease of troubleshooting. Standardized naming makes it easier to identify the purpose and scope of each management group and resource, therefore, consistent naming is part of the “azure initiative”.
To proactively prevent issues, adhere to best practices for structuring your Azure environment. Design a well-defined management group hierarchy that aligns with your organization’s business units or functional areas. Implement clear policies and role assignments at each level of the hierarchy. Regularly review and update your governance strategy to adapt to changing business requirements. Consider using “azure initiative” features for complex scenarios. Thoroughly document your management group structure and governance policies to ensure transparency and consistency. Proper planning and documentation are very important and should not be overlooked. By taking a proactive approach and addressing issues promptly, you can effectively manage your Azure environment and maintain a secure, compliant, and cost-optimized cloud infrastructure.