Azure File Storage Pricing Models
Azure File Storage pricing is a complex system influenced by multiple factors. Understanding the different pricing models is crucial for managing cloud costs effectively. The core pricing elements include storage type, access patterns, and data transfer. Different storage types have varying performance and cost implications. Access patterns, such as the frequency of file access, also significantly affect the final cost of azure file pricing. Data transfer, both inbound and outbound, incurs additional charges. Analyzing these factors allows for informed decision-making in selecting the most cost-effective approach for specific workloads.
For example, a frequently accessed file stored in a premium storage tier will likely cost more than a rarely accessed file in a standard storage tier. High-performance storage options often come with premium pricing but offer faster retrieval speeds. Data transfer costs can vary greatly depending on the volume and location. This variability in costs within different azure file pricing models makes it vital to meticulously evaluate these factors before finalizing deployment decisions.
Careful consideration of data transfer patterns and storage tiers is critical for optimizing overall costs. Analyzing historical data access patterns can assist in forecasting costs and determining the most cost-effective azure file pricing options. This in-depth approach ensures proper resource allocation while reducing unnecessary expenditures. Storage tiers, data transfer, and access frequency all significantly affect the total cost of storage. Implementing strategies to optimize these factors reduces financial burdens while maintaining required functionality.
Storage Tier Options and Cost Implications
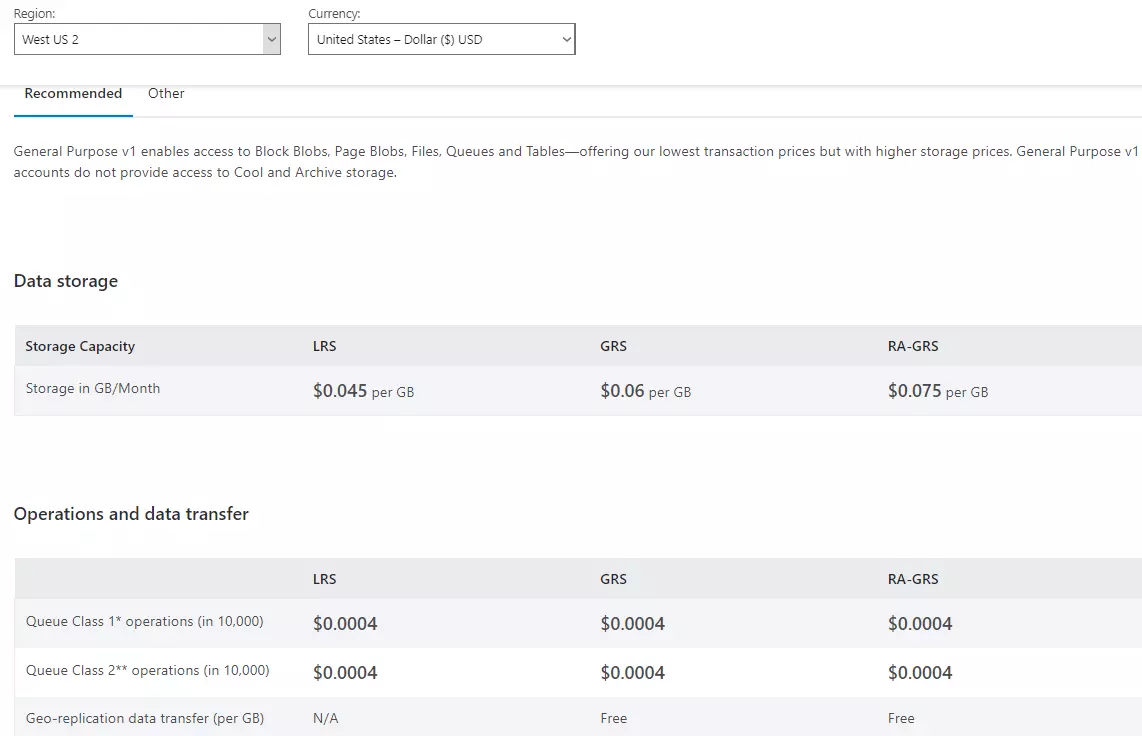
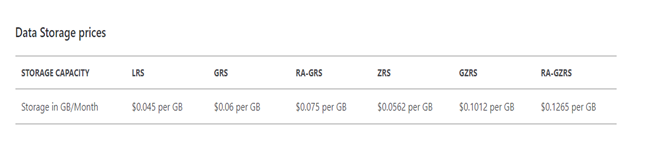
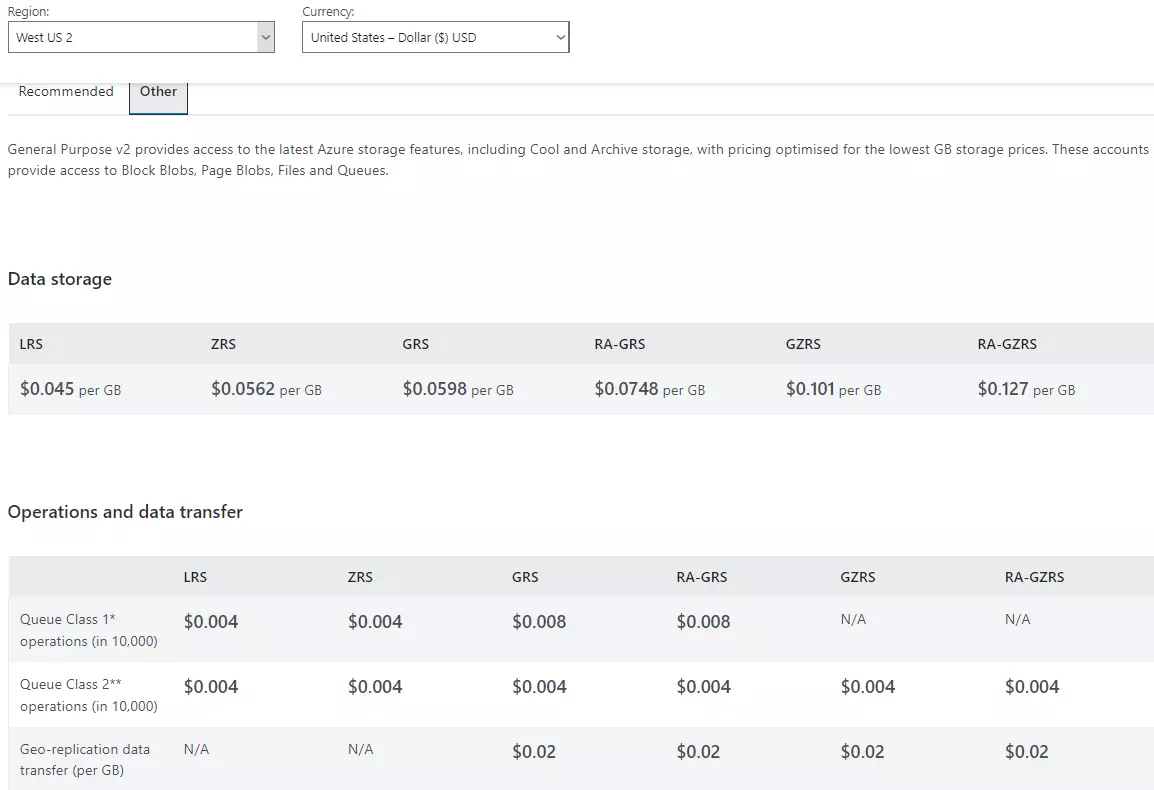
Azure File Storage offers various storage tiers, each balancing performance and cost. Understanding these tiers is crucial for effective azure file pricing management. Hot, Cool, and Archive tiers provide different access speeds and storage durations. Hot storage, designed for frequent access, is the most expensive. Ideal for actively accessed files, it’s optimized for fast retrieval. Cool storage is less expensive but has slower retrieval times. Suitable for less frequently accessed data, it offers a cost-effective balance for workloads with intermediate access needs. Archive storage, the most economical option, stores data for infrequent access, suitable for backup or archival data that rarely needs retrieval. The cost-benefit analysis hinges on your access patterns. Frequent retrieval justifies the expense of Hot storage. Less frequent access might make Cool or Archive tiers more suitable for reducing azure file pricing. Choosing the right tier directly impacts overall storage expenditures. Data migrating between tiers requires consideration for transfer costs.
Storage tiers directly influence the cost of storing your data in Azure File Storage. Choosing the right tier is crucial in optimizing your azure file pricing strategy. Different use cases necessitate different approaches. For frequently accessed data, high-performance Hot storage is often the most cost-effective option. The cost trade-offs must be evaluated carefully. The benefits of fast access may outweigh the higher storage costs. For data accessed less frequently, Cool or Archive tiers offer substantial savings. The cost-effectiveness of these tiers depends on your specific access patterns. Evaluate your file access patterns to determine the ideal azure file pricing strategy.
Consider the trade-offs between cost and performance. Optimizing storage tiers is essential for minimizing Azure File Storage expenses. The selection of the appropriate storage tier directly impacts the total cost of storing data. A thorough analysis of access patterns is vital to effective azure file pricing optimization. Evaluating your data access patterns is key to successful Azure File Storage cost optimization. This allows you to select the appropriate storage tier for your specific needs, ensuring your costs are aligned with your usage patterns. Careful consideration is key to successfully managing your azure file pricing.
Analyzing Data Transfer Costs: Inbound and Outbound
Data transfer costs play a crucial role in overall azure file pricing. Understanding how data moves into and out of Azure File Storage is vital for effective cost management. Factors like geographic location and network bandwidth significantly affect these costs. Transfer frequency also impacts the overall expense. Data transfer costs often vary substantially based on these factors.
Transferring data into Azure File Storage, often referred to as inbound data transfer, may incur charges based on the amount of data moved and the distance between the source and Azure location. For example, transferring data from a location in Europe to an Azure region in North America may incur higher costs compared to transferring data within the same region. Outbound transfer costs, similarly, depend on data volume and distance. This cost can quickly add up for large file transfers or frequent data movements. The cost of transferring data between various Azure regions also should be considered for effective budgeting. Careful consideration of data transfer patterns and optimization strategies can help businesses manage transfer costs effectively.
Optimizing data transfer strategies is crucial for managing azure file pricing. Strategies can include leveraging Azure’s global network and optimizing storage tier selection to minimize data movement. For instance, moving frequently accessed data to a tier with lower latency can decrease the cost of outbound data transfers. Careful planning and diligent monitoring of transfer patterns will allow businesses to effectively control their data transfer costs within Azure file storage.
Analyzing File Operation Costs in Azure File Storage
Understanding the costs associated with file operations like reading, writing, and deleting files is crucial for effective Azure file pricing management. Frequent operations can significantly impact overall expenses. Optimizing access patterns is key to mitigating these costs within specific workloads. Careful consideration of access frequency and methods can minimize the impact on the azure file pricing structure.
Azure File Storage charges for file operations based on the volume and nature of these activities. Reading files incurs charges that are directly proportional to the amount of data retrieved. Writing operations are similarly priced, reflecting the data volume committed to the storage system. Deleting files also incurs charges, though the rate is typically lower compared to read or write operations. Frequent read, write, and delete operations can accumulate significant costs, especially for demanding applications or high-traffic scenarios. Identifying and addressing potential bottlenecks in access patterns can help to reduce overall costs for these operations.
Optimizing access patterns is critical for managing these costs effectively. Employing caching strategies can reduce the frequency of read operations by storing frequently accessed data locally. Implementing efficient data transfer techniques, like using larger file uploads or optimizing write operations, can reduce the overall impact of frequent operations on Azure file pricing. Monitoring file operation patterns allows administrators to identify areas for optimization, helping to proactively control and reduce costs within the azure file storage environment. Implementing strategies for efficiently managing these operations will help to keep azure file pricing under control. Data compression can also significantly decrease the volume of data being written or read, reducing charges.
How to Estimate Azure File Storage Costs Effectively
Estimating Azure file storage costs involves a methodical approach, considering various factors. A robust cost estimation process relies on accurate data projections and a clear understanding of individual pricing components. This includes anticipating storage needs, access patterns, and data transfer volumes. Accurate forecasting helps avoid unforeseen expenses related to azure file pricing.
Begin by meticulously documenting expected file sizes and volumes. Projecting future data growth is crucial. Detailed analysis of access patterns, including frequency and types of access (read, write, delete), aids in forecasting operational costs. Factor in potential data transfer needs, including both inbound and outbound transfers. Consider geographic locations, as this significantly influences transfer costs. Utilize Azure’s pricing calculators to gain insights into precise cost breakdowns. Realistic projections account for potential peaks and troughs in activity levels. This forecasting approach facilitates informed budgeting and resource allocation for Azure file storage needs.
Employing historical data, if available, is highly beneficial. Analyze past storage usage to identify patterns and trends. This allows for more accurate predictions of future storage needs. Utilize Azure’s cost management tools for detailed insights into pricing structures. These tools often provide flexible reporting options. Consider the different storage tiers and their respective costs. Using these insights and appropriate tools, develop a cost model. This cost model provides a comprehensive view of estimated expenses, facilitating informed budgeting and resource allocation. Thorough planning minimizes surprises and enables cost-effective management of Azure file pricing strategies.
Comparing Azure File Storage with Alternatives
Evaluating the cost-effectiveness of Azure File Storage necessitates a comparison with other cloud storage solutions and on-premises alternatives. Key factors to consider include scalability, reliability, and security. Azure File Storage offers robust scalability, enabling effortless accommodation of growing data volumes. Its reliability is ensured through redundant storage mechanisms, safeguarding data integrity. Further, Azure’s comprehensive security features protect data and maintain compliance with industry standards. Weighing these benefits against potential cost savings from alternative solutions is crucial. Consider the specific demands of your workload; Azure’s flexibility in pricing models makes it a compelling option for many scenarios. For instance, its pay-as-you-go model aligns with agile development practices. Alternative solutions might offer cheaper initial investments, but their long-term costs could exceed the expenditure with Azure file pricing, given the significant benefits and scalability offered by the cloud-based solution. Comparing on-premises storage solutions to Azure File Storage typically highlights Azure’s superior scalability and reduced maintenance requirements. Azure File Storage is a cost-effective choice when considering long-term expenses.
Comparing Azure File Storage’s pricing against other cloud storage options depends on your specific requirements. If your primary concern is minimizing initial costs, on-premises solutions might seem attractive. However, the long-term operational costs associated with on-premises solutions – maintenance, upgrades, and personnel – can frequently exceed those for cloud-based storage solutions. Alternative cloud storage solutions may offer comparable functionalities but vary in storage options and associated costs. Evaluating these differences carefully is crucial. Comprehensive comparison demands considering factors such as data transfer rates, security protocols, and support options, each influencing the total expenditure. Careful attention to these aspects will lead to a better understanding of how these different models affect the ultimate azure file pricing.
Evaluating the cost-effectiveness of Azure File Storage against competitors requires a deep dive into each solution’s strengths and weaknesses. Azure offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model, offering flexibility, while alternatives might impose upfront costs or usage-based fees. Assess the scalability and reliability requirements of your use case. Evaluate the security protocols and compliance standards offered by each option. In comparing azure file pricing across solutions, consider factors such as data transfer costs, storage tier options, and performance characteristics. Comprehensive assessment considering the specific requirements of your application and infrastructure is key to a comprehensive analysis. Selecting the optimal solution depends on specific needs and potential use cases.
Optimizing Your Azure File Storage Costs: Best Practices
Optimizing azure file pricing involves strategic approaches to minimize costs associated with data storage and management. Implementing these best practices can significantly reduce storage expenses. Selecting the appropriate storage tier is crucial for controlling costs. Infrequent access data may benefit from the less expensive archive tier, while frequently accessed files might be better served by a premium tier for performance.
Minimizing data transfer is another key aspect. Analyze and optimize data transfer patterns. Employing efficient transfer methods and transferring data during off-peak hours can greatly reduce costs. Transferring data in bulk or using optimized network connections can minimize the associated expenses. Strategically plan and execute data transfers to take advantage of lower costs associated with these optimal procedures.
Managing file access efficiently is paramount. Designating specific permissions and access controls prevents unauthorized access to files and eliminates unnecessary read or write operations. Implementing efficient access controls within Azure File Storage can significantly reduce unwarranted access. Regularly reviewing and adjusting access policies optimizes storage use and prevents unnecessary costs. Employing proper access controls and policies minimizes the potential for unauthorized access and associated operational expenses. Consistent monitoring of access patterns and adjusting storage tier and access policies helps sustain cost optimization strategies. Thoroughly understanding the Azure File Storage pricing model helps organizations implement best practices for optimal cost management.
Managing Azure File Storage Costs: Tools and Techniques
Effective management of Azure file pricing is crucial for optimizing cloud storage expenditures. Understanding and leveraging available tools and techniques provides control over costs. Detailed cost reporting and analysis tools are essential. Microsoft provides robust resources for monitoring Azure storage spending.
Monitoring and tracking Azure file storage expenses are vital for proactive cost control. Utilize built-in Azure cost management tools to track and analyze spending. These tools provide detailed insights into resource utilization and costs associated with various Azure services, including Azure file storage. Regular reporting and analysis facilitate identification of areas for cost optimization and potential overspending. Analyzing spending trends and identifying anomalies allows for proactive adjustments to minimize unexpected costs. Key performance indicators (KPIs) concerning Azure file pricing can aid in identifying areas for improvement, such as inefficient storage tiers or excessive data transfers.
Implementing cost optimization strategies tailored to specific use cases is critical. Implementing alerts for exceeding predefined cost thresholds allows for prompt action and prevention of escalating expenditures. Employing cost allocation methods ensures accurate tracking of costs and efficient resource allocation. Detailed cost breakdowns of Azure file storage services provide a clear picture of individual component costs. Regular reviews of storage usage patterns and access frequency offer insight into potential cost reduction areas in Azure file pricing. This systematic approach ensures efficient management of Azure file pricing, enabling businesses to effectively control costs and maximize return on investment.