Embarking on Your Azure Development Journey
The world is rapidly transitioning towards cloud computing, marking a significant shift in how applications are developed, deployed, and managed. Cloud platforms offer unprecedented scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making them indispensable for modern software development. Microsoft Azure stands as a leading cloud service provider, presenting a vast array of tools and services tailored for developers. Understanding what Azure is and why it’s crucial for developers in today’s landscape is the first step towards mastering cloud development. Azure essentially provides a platform where developers can build, test, deploy, and manage applications and services through Microsoft’s global network of data centers. For developers, Azure cloud programming represents a substantial opportunity to enhance skills, build more sophisticated applications, and remain competitive in the tech industry. It is important to grasp the foundational concepts of cloud computing and understand Azure’s specific offerings. The transition to Azure is not just a trend, but a strategic move that empowers developers to innovate faster and reach a global audience with ease.
The demand for cloud expertise, particularly in azure cloud programming, is soaring across all industries. Companies are increasingly relying on cloud-based solutions to streamline operations, enhance user experiences, and scale their businesses effectively. This translates into significant career benefits for developers proficient in Azure technologies. The ability to design, implement, and manage applications on Azure is not only a highly sought-after skill, but also a pathway to diverse roles, from cloud architects and developers to DevOps engineers and data scientists. Learning azure cloud programming equips professionals with the skills necessary to lead the digital transformation initiatives driving business today. The versatility of Azure allows developers to work across various types of projects, offering experiences in areas like web development, data analytics, and artificial intelligence, ultimately leading to rewarding and challenging careers. Azure provides a versatile and innovative platform, thus securing a high demand for professional in azure cloud programming.
Furthermore, embracing azure cloud programming allows developers to shift their focus from infrastructure management to application innovation. By using Azure, developers can offload the complexities of hardware maintenance, operating system updates, and other infrastructure-related tasks, allowing them to concentrate on writing code that drives business value. This freedom fosters a more agile development cycle and enables faster time-to-market for new products and services. Whether creating web applications, deploying mobile backends, or building complex AI-powered solutions, Azure provides the necessary tools and services to accelerate the development process. Therefore, acquiring azure cloud programming skills represents not just career advancement, but also a strategic move towards a more productive and future-focused approach to software development, hence solidifying the importance of this journey.
Essential Azure Services for Developers
Azure provides a wide array of services catering to diverse development needs, understanding these is fundamental for effective azure cloud programming. These services are generally categorized into Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS provides the basic building blocks of computing infrastructure, like virtual machines, offering maximum control over resources. PaaS provides a complete environment for developing, running, and managing applications, without managing the underlying infrastructure, with services such as Azure App Service. SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on demand. Developers focusing on azure cloud programming can greatly benefit from selecting the right service model and specific services that best fit project requirements. Key services for developers include Virtual Machines, which offer customizable computing environments for running various operating systems and applications. Azure App Service facilitates the hosting of web applications and APIs with minimal infrastructure management, and it scales automatically based on traffic, ensuring the application’s performance remains consistent. Azure Functions enables serverless computing, allowing developers to execute code without managing servers, perfect for event-driven architectures. Azure Container Instances and Azure Kubernetes Service provide platforms for deploying and managing containerized applications, offering enhanced portability and scalability. Additionally, Azure Storage provides options for storing various types of data such as blobs, files, and queues. These services form the core of azure cloud programming, supporting the building of scalable, robust, and reliable applications.
The choice of specific Azure service depends heavily on the project’s requirements, especially when looking at robust azure cloud programming solutions. For example, Virtual Machines are ideal when there is a need for full control over the operating system and infrastructure, or when running legacy applications. Azure App Service is best suited for web applications that require automatic scaling and simplified management, offering a faster time-to-market and less operational overhead for azure cloud programming projects. Azure Functions is an exceptional option for applications with event-driven architectures, like processing uploaded files or scheduling tasks, and they are ideal for microservices based on azure cloud programming. Container services, such as Azure Container Instances and Kubernetes Service, are perfect for modern applications based on microservices and for applications that require scalability and portability across different environments. Azure Storage provides options for storing various types of data with robust security measures and various access tiers. By leveraging these services, developers engaging in azure cloud programming can build and deploy applications that are not only robust and scalable, but also cost-effective and maintainable. These services provide capabilities to build applications from simple web pages to complex microservices architecture. Understanding the intricacies of each service is the key to efficient azure cloud programming and successful deployment strategies.
How to Build Your First Azure Web App
Embarking on your journey into azure cloud programming begins with practical application, and creating a web app on Azure App Service is an excellent starting point. This process demystifies cloud deployment and provides hands-on experience with essential Azure resources. The Azure portal serves as the central hub for managing Azure services, and navigating it is the first step in bringing your web application to life. To begin, access the portal and search for “App Services”. Select “Create” to initiate the process of provisioning a new web app resource. You’ll be prompted to choose a resource group, which is a container that holds related resources for an Azure solution. If you don’t have a resource group already, create a new one and assign a unique name for your web app. This name will also form part of your application’s URL. Next, select your preferred runtime stack like .NET, Python, Node.js, etc. After choosing the runtime you can proceed with configuring your app service plan. This plan determines the underlying infrastructure of your app and you can chose different pricing tiers based on your needs. Once these configurations are done, review and create the application.
Once the app service is created, deploying code becomes the next task. For a simple demonstration, assume that you have a basic HTML file with a hello world message. A popular method for deploying your application code is through Git. Azure App Service integrates directly with repositories like GitHub, Azure Repos, or Bitbucket. You can establish a connection to your Git repository by navigating to the “Deployment Center” under the “Deployment” settings of your web app and selecting your source. Once configured, any changes committed to your chosen branch will trigger an automatic deployment to your Azure App Service. For this example, let’s create a basic `index.html` file: `
Hello, Azure Cloud Programming World!
`. This file, along with required code and configuration files, can be pushed to a Git repository. After configuring deployment, any push to the configured branch will reflect the changes to the web application. This process allows you to experience a simple continuous deployment and see first hand the practical results of azure cloud programming.
This hands-on approach provides a great insight into the capabilities of Azure App Service, while also familiarizing you with the basics of azure cloud programming. You’ve now successfully created a basic web application in the cloud with minimal complexity, setting the stage for more complex and scalable application developments. This initial step is crucial, building the foundational skills needed to explore the extensive suite of services that Azure offers. Remember, consistency and practice are key to mastering Azure Cloud Programming.
Leveraging Azure Serverless Computing
Azure Functions represents a pivotal shift in application development, allowing developers to execute code without managing server infrastructure, which is a key aspect of efficient azure cloud programming. This serverless approach contrasts sharply with traditional server-based web applications, where developers must provision and maintain virtual machines or containers. With Azure Functions, the focus is solely on writing code that responds to specific events, such as HTTP requests, database changes, or messages from queues, making it exceptionally well-suited for event-driven architectures. This model is particularly beneficial in scenarios requiring rapid scalability and cost-efficiency, as the function automatically scales to meet demand and only incurs costs when code is actively running. For example, processing incoming data streams, handling webhook calls, and performing scheduled tasks are perfect use cases for Azure Functions, which minimizes resource waste and reduces operational burden. The ease of deployment and the pay-per-use model makes serverless a compelling choice for modern application development where agility and cost control are critical.
The core of Azure Functions lies in its event-driven model. An event triggers the execution of a function, which then performs a specific task. This could involve a database trigger, an HTTP endpoint call, or a message from a message queue. To illustrate, consider a function designed to resize uploaded images. This function could be triggered by the addition of a new blob to Azure Blob Storage, a crucial step in many media-rich applications built with azure cloud programming. The function reads the new image blob, resizes it, and then writes the new resized image to a different storage location. Developers would define the trigger (new blob created), implement the function code (image resizing logic), and configure the output location, without the need for server administration. Another example could involve implementing business logic: a function can be triggered by a user request, which could process data, call external APIs, and return a response. This flexible execution model of Azure Functions enables developers to focus on the application’s logic rather than the intricacies of infrastructure management, thus accelerating development cycles and promoting a more efficient approach to development.
Furthermore, the abstraction provided by serverless reduces operational overhead. Unlike server based apps, where maintenance, updates, and scaling are the developers or operators responsibilities, Azure Functions handles these automatically. This means that developers can quickly deploy code, iterate on features, and scale their applications based on actual usage without significant management challenges. This agility is a major advantage for fast-paced environments where getting new features to market quickly is essential. Using the pay-as-you-go model, resources are only consumed when code is running, which makes Azure Functions a very cost-effective option for applications with fluctuating demands. In summary, Azure Functions provides a compelling approach for modern azure cloud programming, enhancing agility, reducing operational overhead, and increasing cost efficiency by embracing a true serverless execution model.
Data Storage and Management in Azure
Effective data storage and management are crucial aspects of successful applications developed with azure cloud programming. Azure provides a variety of storage options tailored to different needs and data types. Azure Blob Storage is a highly scalable and cost-effective solution for storing unstructured data such as images, videos, and documents. It’s designed to handle massive amounts of data, making it ideal for scenarios like media hosting or backup and recovery. In contrast, Azure SQL Database is a fully managed relational database service built for structured data. It supports features like automatic backups, high availability, and scalability, ensuring robust performance for transactional applications. This is frequently used in applications needing the power of a traditional database system within the azure cloud programming ecosystem. Azure Cosmos DB is a globally distributed, multi-model database service designed for modern application development. It’s known for its flexible data models (document, key-value, graph, and column-family), low latency, and high availability. These features make it suitable for applications that require geographically distributed access, fast data retrieval, and the ability to handle diverse data types. Each storage option is designed with specific performance and cost considerations. Understanding the differences between these services is key for any development in azure cloud programming to maximize efficiency and minimize cost. The optimal choice will depend on specific data requirements, such as the structure of the data, read and write speeds needed, and expected scalability needs.
Selecting the appropriate storage solution involves careful evaluation. For instance, if an application primarily stores and retrieves large files, Azure Blob Storage is the logical choice due to its high capacity and cost-effectiveness. However, if the application relies on relational data and needs the full capabilities of SQL, Azure SQL Database is more suitable. Similarly, applications that demand high availability, fast global access, and the flexibility to store data in different formats might find Azure Cosmos DB as the best option. Azure’s storage solutions also incorporate advanced security features. Data encryption at rest and in transit, access control via role-based access, and network isolation are some of the key security features. These provide developers robust capabilities to implement data security and governance policies. This is essential in building applications that are not only functional but also protected. Furthermore, Azure’s scalability features across the different storage options ensure the application can handle a growing workload. Each service provides automatic or on-demand scaling to accommodate increases in data or traffic. By leveraging the various features within Azure, developers are capable of building robust, scalable, and secure data-driven applications for any use case in the azure cloud programming context.
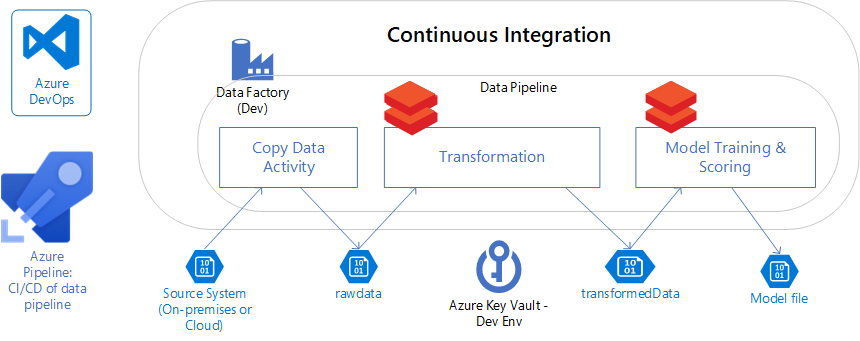
Implementing CI/CD Pipelines with Azure DevOps
The implementation of Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines stands as a cornerstone of modern software development, significantly accelerating the development lifecycle and enhancing the reliability of applications. Azure DevOps provides a robust platform to establish these pipelines, facilitating the automation of code integration, testing, and deployment to Azure. This process begins with integrating version control systems, such as Git, where developers commit their code changes. Once code is pushed to the repository, a CI pipeline is triggered. This pipeline typically involves compiling the code, running automated tests (unit, integration, etc.) to ensure code quality and prevent regressions, and packaging the application into a deployable artifact. Azure DevOps streamlines this process by providing built-in tasks and integrations, enabling the creation of complex CI pipelines with relative ease. The value of these pipelines lies in their ability to rapidly detect issues through automated testing and provide timely feedback to developers, which can save crucial development time. For effective azure cloud programming, incorporating CI/CD pipelines is essential for agility.
Once the CI pipeline completes successfully and generates deployable artifacts, the CD pipeline takes over, orchestrating the deployment of these artifacts to the target Azure environment. This deployment can range from updating web applications on Azure App Service to deploying containerized applications to Azure Kubernetes Service or Azure Container Instances. The CD pipeline automates the steps needed to release new application versions, reducing human error and minimizing downtime during deployments. This automation often involves defining deployment strategies, such as blue/green deployments or canary deployments, to gradually roll out changes while minimizing the risk of breaking the application. Azure DevOps provides flexibility in how these deployment pipelines are designed and executed, enabling developers to choose from a variety of deployment methods that align with their application’s needs. Furthermore, through the use of infrastructure as code (IaC), deployment configurations can also be version-controlled, making the entire process auditable and reproducible. For developers engaged in azure cloud programming, adopting CI/CD pipelines in Azure DevOps is a crucial step in achieving rapid and reliable deployments. Azure DevOps contributes to more efficient azure cloud programming by reducing manual work and increasing focus on code development and quality assurance.
Best Practices for Azure Cloud Programming
Effective azure cloud programming requires adherence to established best practices to ensure applications are secure, efficient, and scalable. One fundamental principle is adopting Infrastructure as Code (IaC) using tools like Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates or Bicep. This approach enables developers to manage and provision infrastructure through code, allowing for consistent and repeatable deployments. IaC facilitates version control of infrastructure configurations, just like application code, enabling teams to track changes and revert to previous states as necessary. Security should be a paramount concern during azure cloud programming. Employing best practices like using Azure Key Vault to manage secrets, implementing robust authentication and authorization mechanisms, and continuously monitoring for vulnerabilities are crucial for protecting sensitive data and resources. It is also important to adopt a “security by design” approach where security is integrated throughout the application development lifecycle, rather than being treated as an afterthought.
Another critical aspect of efficient azure cloud programming involves cost optimization. Carefully select the appropriate Azure services and resource sizes to match application needs and avoid unnecessary costs. Azure provides tools to monitor resource consumption and identify opportunities for cost savings. Implementing auto-scaling to dynamically adjust resources based on demand and leveraging reserved instances for steady-state workloads are valuable techniques for reducing overall expenditure. Performance monitoring is essential for proactively identifying and addressing performance issues before they impact users. Azure Monitor offers comprehensive monitoring capabilities, allowing developers to track application performance, resource utilization, and system health. It is crucial to implement logging and alerting mechanisms that promptly notify teams of any anomalies. Designing applications for failure is a key aspect of creating resilient and dependable cloud solutions. Incorporating practices like redundancy, fault tolerance, and implementing appropriate retry mechanisms are essential for ensuring that the application remains operational despite potential disruptions. The principles of graceful degradation should be followed to ensure some functionality of the application is still available during outages. Thorough testing of the failover procedures is critical to validate the resiliency of the system.
Finally, always prioritize the performance and scalability of the azure cloud programming. This entails optimizing queries, leveraging caching mechanisms, and implementing load balancing. As applications evolve, scalability is paramount to cater to increasing user base or data volume. Developers need to plan for growth and incorporate features that enable their applications to automatically adjust as required. Adopting these best practices not only leads to better azure cloud programming outcomes but also ensures that applications are secure, reliable, and well-performing. By combining IaC, security first design, cost management, proper monitoring, fault tolerance, and an emphasis on performance and scalability, development teams can deliver high-quality cloud applications that meet the needs of the end users and provide long-term benefits.
The Future of Azure Cloud Development
The landscape of azure cloud programming is in constant evolution, driven by rapid technological advancements and the increasing demands of modern applications. One of the most significant trends is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into Azure services. Developers are now empowered to build intelligent applications with ease, leveraging pre-trained models and cognitive services available within the Azure ecosystem. This trend not only simplifies the development process but also enables the creation of sophisticated, data-driven solutions that were previously difficult to achieve. The future of azure cloud programming will see more emphasis on serverless architectures, allowing developers to focus on code without the burden of infrastructure management. Furthermore, innovations like low-code and no-code platforms are democratizing software development, making it more accessible to a broader range of individuals and businesses. These platforms will likely play a vital role in accelerating application development cycles, allowing teams to prototype and deploy solutions faster than ever before.
Another vital aspect of the future involves the expansion of cloud-native technologies. Containerization with Docker and Kubernetes will continue to dominate application deployments, emphasizing the need for developers to master these tools within the Azure environment. Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) offers a robust platform for managing containerized applications, and its adoption will rise as businesses seek to achieve greater scalability and agility. The growing sophistication of DevOps practices will also shape the future of azure cloud programming, with more automation and streamlined workflows. Tools within Azure DevOps will become even more refined, offering better capabilities for continuous integration, continuous delivery, and infrastructure as code. This emphasis on automation will ensure that development teams can release new features quickly while maintaining high levels of reliability and security. The continued growth of cloud computing suggests that the opportunities in azure cloud programming will be numerous, offering promising career paths for skilled developers.
Looking ahead, the focus of azure cloud programming will increasingly shift towards building resilient, secure, and cost-effective solutions. Developers will need to embrace best practices such as infrastructure as code to automate deployments, implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data, and monitor application performance to ensure optimal efficiency. The emphasis on sustainability and green IT will also influence development practices, with developers seeking ways to reduce the environmental impact of their applications. The integration of new and innovative technologies, such as quantum computing, will potentially lead to new frontiers in azure cloud programming, requiring developers to adapt and learn new paradigms. Therefore, continuous learning and exploration of Azure’s ever-evolving capabilities are essential for those who seek to remain at the forefront of this dynamic field. The future of azure cloud programming is bright, brimming with endless possibilities for those willing to innovate and explore.