Understanding Azure Autoscaling Groups: The Fundamentals
Azure Autoscaling Groups (ASGs) automatically adjust the number of virtual machines (VMs) in response to changing demands. This ensures optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. Imagine a restaurant needing more waiters during peak hours and fewer during slower times; azure ASG works similarly for cloud resources. The core benefit is resource optimization. Azure ASGs constantly monitor predefined metrics. These metrics could be CPU utilization, memory usage, or custom metrics defined by the user. Based on these metrics, the azure ASG scales up or down the number of VMs. This ensures that applications always have the necessary resources while minimizing costs.
Key terms include scaling policies, which define the rules for scaling; metrics, which are the data points used to trigger scaling; and cooldown periods, which prevent rapid and unnecessary scaling fluctuations. The azure ASG employs these to manage resources effectively. A well-configured azure ASG scales efficiently. It reacts quickly to demand changes. The system avoids over-provisioning resources, resulting in cost savings. It also prevents under-provisioning, ensuring optimal application performance. Understanding these concepts is crucial for effective azure ASG management. Properly setting scaling policies, choosing relevant metrics, and defining appropriate cooldown periods are all critical steps in successfully implementing and utilizing an azure ASG.
Azure ASGs provide several advantages. They improve application responsiveness by ensuring sufficient resources are always available. They minimize costs by scaling down during periods of low demand. High availability is also enhanced, as the azure ASG ensures that enough VMs are running to handle traffic spikes. The azure ASG increases operational efficiency, allowing administrators to focus on other tasks rather than manually managing VM counts. Moreover, the scalability and flexibility offered by the azure ASG are invaluable for handling unpredictable workloads and ensuring business continuity. The automation features of azure ASG reduce manual intervention, leading to fewer operational errors and greater efficiency.
How to Create and Configure Your First Azure Autoscaling Group
Creating an azure ASG involves several steps. First, navigate to the Azure portal and select “Create a resource.” Search for “Autoscale” and select the Autoscale option. The creation process begins with defining the target resource. This usually involves selecting an existing virtual machine scale set. Azure provides a user-friendly interface to guide you through this process. You will specify the resource group, choose a region for optimal performance, and select an appropriate name for your azure ASG. Ensure the selected resource group aligns with your organizational structure for efficient management. Careful consideration of the region impacts latency and availability. A descriptive name improves organization.
Next, configure the scaling rules. This is where you define how your azure ASG will respond to changing demands. The Azure portal allows you to set rules based on various metrics, such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and custom metrics from your applications. For instance, you might set a rule to increase the number of VMs when CPU utilization exceeds 80% and decrease them when it falls below 50%. The scaling rules define the scaling logic for your azure ASG. You can choose between different scaling types, including instance count scaling and capacity scaling, to suit your application needs. Adjusting these parameters directly influences the responsiveness and efficiency of your azure ASG. Remember to set appropriate cooldown periods to prevent over-reaction to temporary spikes in demand.
Finally, you’ll configure health probes. These probes regularly check the health of your VMs. Azure uses these probes to ensure only healthy VMs are included in the scale set. Unhealthy VMs are automatically replaced, ensuring high availability. You’ll define how frequently the probes check, what constitutes a healthy response and how to react when failures occur. This critical step maintains the reliability of your azure ASG. Proper configuration of health probes is essential for maintaining the stability and performance of your application. Thorough testing of your health probes after implementing them is recommended to ensure proper function and prevent unexpected issues with your azure ASG.
Scaling Policies: Fine-tuning Your Azure ASG Strategy
Azure ASGs offer versatile scaling policies to optimize resource allocation. Instance count scaling adjusts the total number of VMs in the group. Capacity scaling, on the other hand, modifies the VM size, impacting compute power. Choosing the right approach depends on application needs. For instance, scaling instance count is ideal for handling fluctuating demand, while capacity scaling might be preferred for handling specific resource-intensive tasks. Azure ASG automatically adjusts VM numbers based on pre-defined metrics. These metrics can include CPU utilization, memory usage, network traffic, or even custom metrics tailored to specific application needs. The configuration allows precise control over scaling behavior. Properly configuring these metrics ensures responsiveness to demand fluctuations.
Effective scaling relies on understanding cooldown periods. This is a crucial setting in azure ASG configurations. The cooldown period prevents the ASG from overreacting to temporary spikes in demand. It introduces a delay before the ASG initiates another scaling action. A poorly chosen cooldown can lead to inefficient resource use or insufficient scaling. Short cooldown periods increase responsiveness but may lead to instability. Longer periods stabilize the system but reduce agility. Finding the optimal balance requires careful consideration of application characteristics and anticipated demand patterns. This is an important consideration when optimizing azure ASG performance. Experimentation and monitoring are key to identifying the ideal cooldown duration for your specific azure ASG deployment.
Beyond basic metrics, advanced techniques enhance azure ASG management. Predictive scaling leverages historical data and machine learning to anticipate future demand. This proactive approach minimizes response times and ensures sufficient resources are available before demand peaks. Auto-adjusting scaling, based on historical data analysis via tools like Azure Monitor, further refines the scaling strategy. It continuously learns and adapts to changing demand patterns, continuously improving the resource allocation efficiency of the azure ASG. This automated approach minimizes manual intervention and reduces operational overhead. However, it’s crucial to carefully monitor these advanced features to ensure they remain aligned with overall performance and cost objectives within the azure ASG. Consider factors like the tradeoffs between achieving peak performance, minimizing costs, and maintaining optimal resource utilization in the context of your azure ASG setup.
Advanced Autoscaling Techniques: Optimizing for Performance and Cost
Predictive scaling significantly enhances Azure ASG capabilities. This feature leverages historical data and machine learning to anticipate future demand. Azure Monitor plays a crucial role, collecting metrics like CPU utilization, memory consumption, and network traffic. By analyzing trends, predictive scaling proactively adjusts the number of VMs, preventing performance bottlenecks and ensuring optimal resource allocation. The azure asg system uses this data to scale resources before demand surges, enhancing user experience and reducing latency. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of scaling delays and ensures smooth operation even during peak periods. Proper configuration of predictive scaling requires careful consideration of historical data accuracy and prediction intervals.
Auto-adjusting scaling based on historical data offers another layer of optimization for azure asg. This approach automatically refines scaling policies over time, learning from past performance. The system continuously analyzes data from Azure Monitor and other monitoring tools. It then uses this information to adjust scaling parameters, such as the target CPU utilization threshold or the cooldown period. This iterative process fine-tunes the scaling strategy to achieve the optimal balance between performance, cost, and resource utilization. Regular review of auto-adjusted scaling parameters is recommended to ensure the azure asg remains aligned with changing demands and operational goals. Over time, the system continuously improves scaling efficiency, reducing costs and improving performance.
Efficiently managing an azure asg requires understanding the trade-offs between performance, cost, and resource utilization. Over-provisioning resources leads to increased costs, while under-provisioning risks performance degradation. Effective resource management depends on accurately predicting demand and configuring appropriate scaling policies. Azure provides tools and guidance to help users strike the optimal balance. Using these tools helps ensure efficient resource allocation and minimizes unnecessary expenses. Regular monitoring and analysis help identify opportunities to further optimize the azure asg configuration. By carefully analyzing performance data and cost metrics, users can continually refine their scaling strategies to achieve significant improvements in both cost and performance.
Integrating Azure ASGs with Other Azure Services
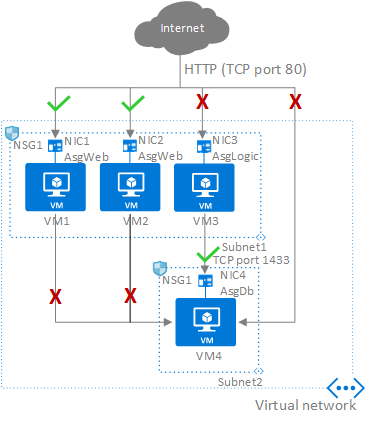
Azure Autoscaling Groups (ASGs) work synergistically with other Azure services to create robust and scalable applications. Integrating an azure asg with Azure Load Balancers distributes incoming traffic across multiple VMs within the ASG, ensuring high availability and preventing single points of failure. This setup automatically distributes traffic to healthy VMs as the azure asg scales up or down, maintaining consistent application performance. Azure Load Balancers also simplify the management of IP addresses and DNS records, further streamlining the deployment process. The integration enhances the overall reliability and efficiency of the application.
Azure Application Gateway provides advanced traffic management capabilities for web applications integrated with an azure asg. It acts as a reverse proxy, offering features like SSL termination, web application firewall (WAF), and URL path-based routing. By integrating with an azure asg, the Application Gateway automatically adapts to changes in the number of VMs, ensuring that traffic is always routed to healthy instances. This dynamic scaling enables the application to handle fluctuating traffic demands effectively, preventing performance bottlenecks and enhancing user experience. The combined power of azure asg and Application Gateway provides a scalable and secure solution for web applications.
Azure Monitor plays a crucial role in providing insights into the performance and health of your azure asg. It collects and analyzes various metrics, such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and network traffic, allowing you to make informed decisions about scaling policies. Integrating Azure Monitor with your azure asg enables proactive monitoring and alerts, helping to identify potential issues before they impact users. By visualizing metrics and setting up alerts based on predefined thresholds, you can quickly respond to unexpected changes, preventing performance degradation and ensuring optimal resource utilization. This close integration between Azure Monitor and the azure asg is fundamental for maintaining a healthy and efficient application.
Troubleshooting Common Azure ASG Issues
Azure ASG deployments occasionally encounter challenges. Scaling delays, for instance, can stem from insufficient resources or network bottlenecks. Investigate resource limits and network configurations to identify and rectify constraints. Azure Monitor provides valuable insights into resource utilization and potential bottlenecks. Carefully review scaling policies and ensure they are appropriately configured for the anticipated workload. Incorrectly configured health probes can also lead to unexpected scaling behavior. Verify that health probes accurately reflect the application’s health status. Azure ASG’s health probes should be adjusted to properly assess the application’s health, preventing unnecessary scaling actions. Use the Azure portal’s diagnostic tools for detailed analysis. The azure asg documentation offers further guidance on troubleshooting these issues.
Unexpected scaling behavior in an azure asg might result from improperly configured scaling rules or erratic metrics. Thoroughly review scaling rules, ensuring they accurately reflect desired scaling patterns. Check for anomalies in the metrics triggering scaling events. External factors, such as spikes in network traffic or database performance issues, can impact scaling behavior. Investigate these external dependencies and address any performance bottlenecks. Use Azure Monitor to identify trends and patterns in metric data. This proactive approach can prevent future scaling problems within your azure asg. Analyzing these metrics helps pinpoint the root cause and implement corrective actions, improving overall stability.
Health probe failures frequently disrupt the functioning of an azure asg. Incorrectly configured probes might fail to accurately assess application health, leading to unnecessary scaling events. Adjust probe settings to reflect the application’s actual health. Network issues can also cause probe failures. Investigate network connectivity and ensure the probes can reach the application instances. The azure asg health probes should correctly identify healthy and unhealthy instances, and promptly handle unhealthy instances. Review application logs for any errors that might be triggering health probe failures. Addressing these issues will enhance the stability and reliability of your azure asg. Regularly testing health probes is crucial for maintaining an optimal azure asg configuration.
Real-World Azure ASG Use Cases and Examples
E-commerce platforms leverage Azure ASGs to handle fluctuating customer demand during peak seasons like holidays. Azure ASG dynamically scales resources up or down, ensuring website responsiveness and preventing outages. This allows for efficient resource allocation and cost optimization. The ability to rapidly respond to traffic surges is critical for maintaining a positive customer experience. This is a prime example of how Azure ASG improves operational efficiency.
Gaming companies utilize Azure ASGs to manage game servers. Azure ASG scales the number of servers based on the number of active players. This ensures low latency and a smooth gaming experience for all users. The dynamic scaling capabilities of Azure ASG are essential for maintaining a high-quality gaming environment. Efficient scaling prevents server overload and ensures consistent performance. This showcases the versatility of Azure ASG in diverse applications.
In the financial services industry, Azure ASG helps manage high-volume transaction processing. During peak trading hours, Azure ASG automatically increases the number of servers to handle the increased load. This ensures the stability and responsiveness of crucial financial systems. Reliable and scalable infrastructure is critical in this sector, and Azure ASG provides the necessary flexibility. The automated scaling minimizes downtime and enhances the reliability of trading platforms. Using Azure ASG in this context reduces operational expenses by only using the resources needed at any given moment. This highlights the importance of Azure ASG for mission-critical applications.
Best Practices for Azure Autoscaling Group Management
Efficiently managing Azure ASGs requires a proactive approach encompassing monitoring, optimization, and security. Regularly monitor your azure asg’s performance using Azure Monitor. Set up alerts for critical metrics like CPU utilization, memory usage, and network traffic. These alerts provide immediate notification of potential issues, enabling timely intervention and preventing performance degradation. Proactive monitoring minimizes downtime and ensures optimal resource utilization within the azure asg environment. This preventative approach is crucial for maintaining a stable and responsive application. Implement robust logging practices to track scaling events and diagnose issues effectively.
Cost optimization is paramount when utilizing azure asg resources. Analyze scaling patterns to identify periods of low demand. Adjust scaling policies to reduce the number of instances during these periods. Consider using spot instances for less critical workloads to significantly lower costs. Regularly review instance sizes and choose the most cost-effective options that still meet performance requirements. Azure’s cost management tools provide detailed insights into resource consumption, empowering data-driven decisions for optimization. This strategic approach balances performance with cost efficiency within the azure asg infrastructure.
Security best practices are essential for protecting your azure asg resources. Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to restrict access to your ASGs. Regularly update the operating system and applications on your VMs. Use Azure Security Center to monitor for threats and vulnerabilities. Regularly review and update your scaling policies to account for changing security requirements. By addressing these security considerations, organizations ensure the protection of their applications and data within the azure asg environment. A secure azure asg configuration safeguards against potential breaches and maintains the integrity of the infrastructure. Remember to adhere to the principle of least privilege to minimize the risk of unauthorized access. This comprehensive approach ensures that your azure asg is not just efficient and cost-effective, but also robust and secure.