Exploring AWS Lambda’s Versatile Language Support
AWS Lambda offers extensive aws lambda language support, empowering developers with a diverse range of programming languages to build serverless applications. Popular choices include Node.js, Python, Java, C#, Go, and Ruby. Each language brings unique strengths to the table. Node.js, known for its asynchronous nature and vast library ecosystem, excels in handling I/O-bound operations. Python’s readability and extensive libraries make it ideal for data processing and machine learning tasks. Java’s robustness and scalability are beneficial for large-scale enterprise applications. C# provides seamless integration with .NET environments. Go offers performance advantages for CPU-intensive workloads, while Ruby’s flexibility is suited to various application types. Understanding these nuances is key to selecting the optimal language for a given project. The choice significantly impacts development speed, performance, and maintainability.
The selection of the right language depends heavily on the specific project requirements. Factors such as existing infrastructure, team expertise, and library availability all play crucial roles. For instance, a project leveraging existing .NET infrastructure might benefit from C#, while a data-intensive project could favor Python’s rich data science libraries. Similarly, projects requiring high performance and concurrency might find Go a suitable choice, leveraging its efficient runtime. AWS Lambda’s aws lambda language support ensures developers have ample options to align their technology stack with project demands. Careful consideration of these factors ensures efficient development and optimal application performance.
Beyond the primary choices, several other languages further broaden AWS Lambda’s capabilities. This robust aws lambda language support caters to diverse needs and development preferences. Developers can leverage the strengths of each language to optimize their serverless functions. The wide selection allows for flexibility and tailored solutions. Choosing the right language hinges on the specific demands of the project and the developer’s familiarity with a particular language. This combination of factors ultimately determines the optimal choice for a particular project within the AWS Lambda environment.
Node.js: A JavaScript Powerhouse for Serverless
Node.js enjoys significant popularity within the serverless computing landscape, and for good reason. Its asynchronous, event-driven architecture aligns perfectly with the AWS Lambda execution model. This allows for efficient handling of concurrent requests, maximizing resource utilization. A vast and active community provides extensive support, readily available libraries, and numerous readily-available solutions for common tasks. The wide adoption of JavaScript further enhances Node.js’s appeal, making it a familiar choice for many developers. This widespread use contributes to the readily-available resources and expertise surrounding Node.js for AWS Lambda, making it a powerful option for building scalable and efficient serverless applications. The rich ecosystem of JavaScript libraries significantly expands Node.js’s capabilities for AWS Lambda, further enhancing its utility.
However, the asynchronous nature of Node.js, while advantageous, can also lead to complexities if not managed carefully. The infamous “callback hell” can emerge if not addressed through structured approaches like promises or async/await. While Node.js excels at I/O-bound operations, its performance might suffer for CPU-intensive tasks compared to compiled languages. Despite these potential drawbacks, its strengths in handling concurrent requests and its widespread adoption in the AWS Lambda ecosystem firmly establish Node.js as a leading choice for numerous serverless applications. API gateways often leverage Node.js for its ability to efficiently process numerous incoming requests, showcasing its strengths in event-driven architectures. Microservices built using Node.js benefit from its scalability and ease of deployment within the AWS Lambda environment, showcasing its suitability for modern application architectures. Node.js’s capabilities make it a valuable tool within the aws lambda language support ecosystem.
Real-world applications frequently utilize Node.js within AWS Lambda functions. Consider the development of RESTful APIs using API Gateway; Node.js excels in this domain, handling requests efficiently and effectively. Another common use case is the creation of microservices, where Node.js’s lightweight nature and scalability make it a perfect fit. These examples highlight Node.js’s versatility and power in the context of serverless architecture. The aws lambda language support for Node.js is robust and well-documented, simplifying development and deployment. This combination of strong community support, a wealth of readily available libraries, and inherent suitability to the AWS Lambda model ensures the continued popularity of Node.js within serverless application development.
Python: Elegance and Simplicity for AWS Lambda
Python’s readability and ease of use make it a popular choice for AWS Lambda functions. Its extensive standard library and vast ecosystem of third-party packages offer solutions for diverse tasks. Data scientists frequently leverage Python’s powerful libraries like Pandas and NumPy for data manipulation and analysis within Lambda, enabling efficient data processing and machine learning workflows. This makes Python a strong contender in the aws lambda language support arena. Python’s simple syntax reduces development time, leading to faster iteration cycles. The large and active Python community provides ample support and resources, ensuring developers can quickly find solutions to common problems. This ease of use contributes significantly to Python’s appeal for AWS Lambda projects, particularly for those with less extensive programming experience. This makes it a highly accessible option within the aws lambda language support range.
However, Python’s interpreted nature can lead to performance limitations compared to compiled languages like Java or Go, especially for computationally intensive tasks. Cold starts, a common issue with serverless functions, can be more pronounced with Python due to its initialization overhead. Despite this, Python’s versatility and extensive library support often outweigh these performance considerations, particularly for tasks involving data analysis, ETL processes, or microservices where ease of development is prioritized. Consider using optimization techniques like Lambda layers to minimize the deployment package size and reduce cold start times. For tasks like data transformations and batch processing, Python shines within the aws lambda language support environment. Its ability to handle large datasets efficiently and seamlessly integrate with other AWS services makes it a compelling choice.
Examples of Python in AWS Lambda include ETL processes that move and transform data between various AWS services, such as S3 and Redshift. Python is also frequently used for building APIs, handling asynchronous tasks, and creating custom backend logic for web applications. Python’s strength lies in its readability, ease of use, and extensive libraries, making it an excellent option for a wide range of AWS Lambda use cases. This contributes greatly to Python’s position within the spectrum of aws lambda language support. The balance between ease of use and functionality makes Python a practical and efficient language for many serverless applications, offering substantial value within the broader landscape of aws lambda language support.
Java: Robustness and Scalability for Enterprise Applications
Java, a stalwart in the enterprise world, brings its strengths to AWS Lambda functions. Its renowned robustness and scalability make it an ideal choice for large-scale applications. A mature ecosystem surrounds Java, offering a wealth of libraries and frameworks to streamline development. This robust support translates to reliable and maintainable Lambda functions, even within complex enterprise architectures. The extensive Java community ensures readily available support and resources, minimizing development hurdles. Java’s suitability for AWS Lambda extends to a wide range of enterprise use cases, from backend processing and complex business logic to integrations with legacy systems. Choosing Java leverages existing investments in enterprise infrastructure and skillsets, fostering efficient development workflows. This choice aligns seamlessly with an organization’s existing Java expertise, further strengthening its place within many AWS Lambda deployments.
However, Java’s benefits come with considerations. Compared to lighter languages like Node.js or Python, Java applications generally have larger deployment sizes. This increased size can impact cold start times, potentially affecting initial response latency. The increased complexity associated with Java development also requires a higher level of expertise. Development teams must carefully manage dependencies and optimize the application to mitigate the performance impact of larger deployments. For example, careful attention to dependency management using tools like Maven is crucial for minimizing deployment size and reducing cold start latency. This balance between leveraging Java’s power and managing deployment characteristics is key to successful implementation within the AWS Lambda environment. Understanding AWS Lambda language support, particularly for Java, is paramount in such deployments.
Despite these challenges, Java remains a powerful option for specific AWS Lambda use cases. Enterprise integrations often benefit from Java’s robust capabilities and mature ecosystem. Applications requiring high levels of security and reliability find Java’s extensive security features and stability advantageous. When dealing with complex business logic or large datasets, Java’s performance characteristics shine, making it a viable, even preferred, choice. The decision to use Java for AWS Lambda should consider the project’s scale and complexity, along with the existing team’s Java expertise and the potential trade-offs in deployment size and cold start times. The ability to manage dependencies efficiently becomes a critical factor in achieving optimal performance within the constraints of the AWS Lambda environment. Ultimately, Java’s power and enterprise-grade features continue to make it a strong contender in the landscape of AWS Lambda language support.
How to Select the Best Language for Your AWS Lambda Project
Choosing the right AWS Lambda language significantly impacts project success. A systematic approach ensures optimal performance and maintainability. Begin by clearly defining project requirements. Consider performance needs. Will the function handle computationally intensive tasks? High-performance demands may favor compiled languages like Go or Java. Less demanding projects might benefit from the rapid development capabilities of Node.js or Python. The availability of relevant libraries also plays a crucial role. Data processing tasks might benefit from Python’s extensive scientific computing libraries. Meanwhile, Node.js offers a rich ecosystem for web development. Evaluate the existing infrastructure and its compatibility with your chosen language. This integration can simplify deployment and maintenance.
Team expertise is another vital factor in AWS Lambda language support. Selecting a language familiar to your team reduces development time and maintenance costs. A skilled team can effectively overcome potential language limitations. Prioritize maintainability. Consider long-term support and the language’s community size. A large, active community provides ample resources, tutorials, and readily available solutions to common issues. Furthermore, assess scalability requirements. Will the function need to handle significant increases in traffic? Languages like Java are known for their ability to scale effectively to meet increased demand. The decision-making process should prioritize aligning language choices with project demands and the team’s capabilities. This strategic approach ensures efficiency and sustainable project growth.
A structured decision tree can aid in this process. Start by assessing performance needs. High-performance requirements lead to Go or Java. Lower demands suggest Node.js or Python. Next, evaluate library availability. Specific libraries might dictate language choice. Consider team expertise. Choose a language the team is proficient in. Finally, examine scalability needs. Java’s scalability is a key advantage for large applications. This decision tree framework simplifies the selection process for optimal AWS Lambda language support, ensuring alignment between project needs and technical capabilities. This systematic approach enhances the chances of a successful project outcome.
Beyond the Big Four: Exploring Other AWS Lambda Languages
While Node.js, Python, Java, and other popular languages dominate AWS Lambda development, several other options offer unique advantages. C#, for instance, benefits developers already invested in the .NET ecosystem. Its robust libraries and familiarity make it a seamless choice for integrating with existing .NET applications. However, C#’s larger deployment size compared to languages like Node.js can impact cold start performance. This makes it less ideal for applications requiring extremely rapid response times. Choosing the right aws lambda language support depends on the project’s specific needs.
Go, known for its performance and concurrency features, provides a compelling alternative for applications demanding high throughput and low latency. Go’s efficiency makes it suitable for microservices and compute-intensive tasks where speed is paramount. Its smaller runtime environment also contributes to faster cold starts. However, Go’s relatively smaller community compared to Python or Node.js might mean fewer readily available libraries and less extensive community support. Developers should weigh this trade-off when considering Go within their aws lambda language support strategy. The choice of language significantly affects application performance and operational efficiency.
Ruby, with its elegant syntax and developer-friendly nature, finds its niche in applications valuing rapid development and prototyping. Its flexibility makes it a good choice for specific tasks or projects where development speed outweighs performance concerns. However, Ruby’s performance often lags behind compiled languages like Go or Java. This makes it less appropriate for applications with stringent performance requirements. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each language within the context of aws lambda language support is crucial for successful Lambda function development. The best language choice always depends on a project’s specific goals and constraints.
Understanding Runtime Environments and Dependencies in AWS Lambda
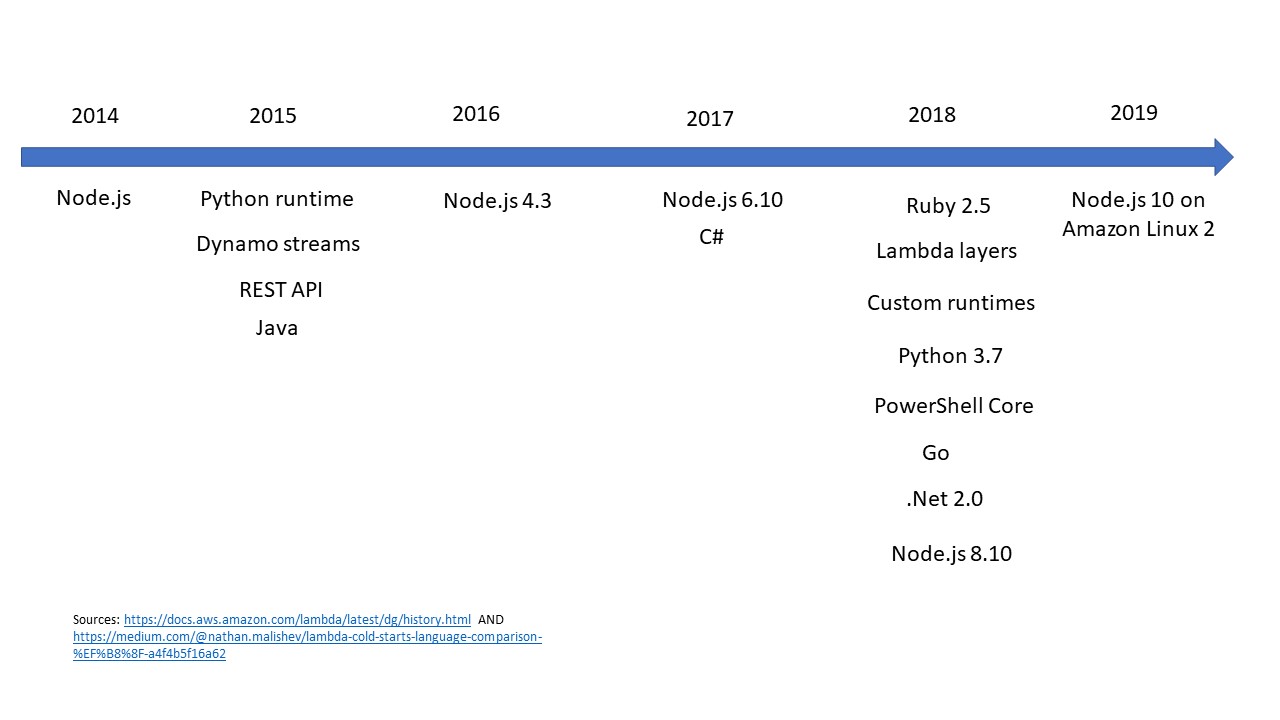
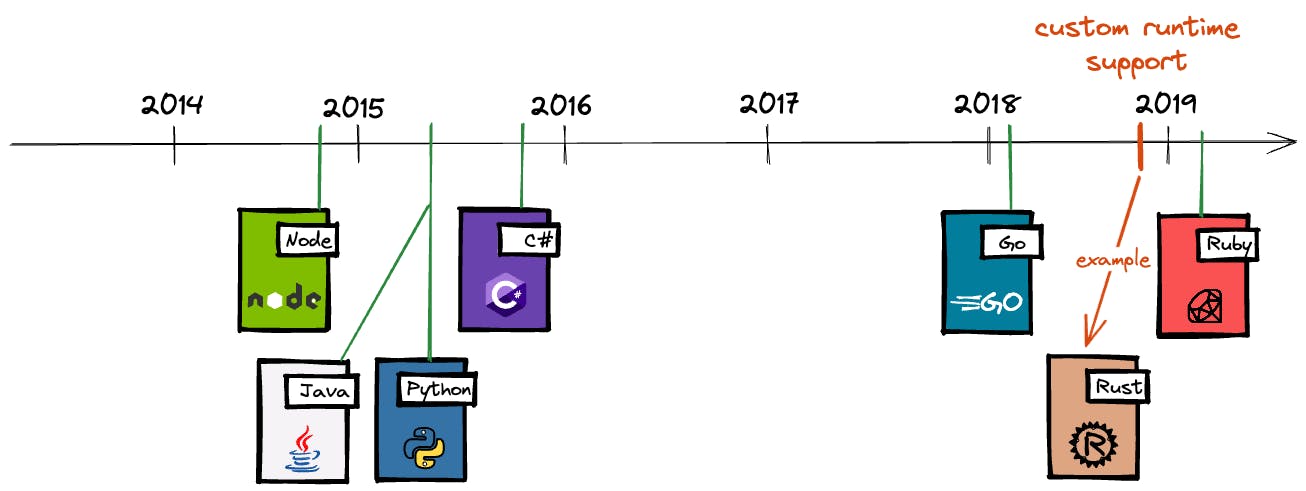
AWS Lambda provides specific runtime environments for each supported aws lambda language support. Understanding these environments is crucial for successful deployment. Each language has its own nuances. For example, Node.js relies on npm for package management, while Python uses pip and Java leverages Maven or Gradle. Choosing the right package manager is essential for efficient dependency management within the aws lambda language support ecosystem.
Managing dependencies directly impacts deployment size and cold start performance. Larger deployment packages lead to slower cold starts, as Lambda needs more time to initialize the function. Careful selection and optimization of dependencies are therefore vital. Techniques like minimizing package size, using smaller libraries and bundling only necessary code, are essential. AWS Lambda layers provide a mechanism to share dependencies across multiple functions, reducing overall deployment size and improving cold start times. This reusable component approach is a best practice for optimizing aws lambda language support projects.
The impact of dependencies extends beyond cold starts. Efficient dependency management is vital for maintaining application stability and security. Regular updates and rigorous dependency checks help to mitigate vulnerabilities and ensure optimal performance. Developers should use tools and practices that aid in dependency analysis and ensure only necessary packages are included. This focus on efficiency, security, and the specific runtime environment provided by aws lambda language support is a key factor in creating reliable and scalable serverless applications. By understanding these runtime environments and dependencies, developers can significantly improve the overall performance and stability of their AWS Lambda functions.
Future Trends and Emerging Languages in AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda’s commitment to expanding its aws lambda language support ensures its continued relevance in the serverless landscape. The platform’s evolution reflects the broader trends in programming languages and developer preferences. We can expect to see continued refinement of existing language runtimes, with optimizations for improved performance and reduced cold starts. AWS will likely prioritize languages popular for serverless architectures and cloud-native development. The emphasis will likely remain on providing a robust and efficient execution environment, fostering innovation across various application domains. This focus on developer experience and language diversity underpins AWS Lambda’s position as a leading serverless platform.
While predicting the future with certainty is impossible, several factors suggest potential directions for aws lambda language support. Increased adoption of WebAssembly (Wasm) presents a compelling possibility. Wasm’s portability and performance characteristics make it an attractive option for a variety of programming languages. Its potential to compile code from multiple languages into a single, efficient runtime could significantly impact AWS Lambda’s capabilities. Similarly, languages gaining popularity in the broader serverless ecosystem, like Rust, with its focus on memory safety and performance, may see increased integration into AWS Lambda. The platform’s evolution will likely depend on community demand, technological advancements, and the need to cater to a wider range of application requirements. Staying current with these trends will be essential for developers leveraging AWS Lambda.
Monitoring the evolution of aws lambda language support is crucial for developers. Regularly reviewing AWS’s announcements and updates will help developers adapt to new offerings and optimize their application development strategies. The platform’s commitment to providing a diverse set of language options allows developers to choose the best tool for each project, ensuring efficiency and optimized performance. The evolution of aws lambda language support directly influences the technology stack choices developers make, impacting their ability to build scalable and efficient applications.