The ‘As-a-Service’ Model: A Modern Business Approach
The ‘as-a-service’ model has become increasingly popular in the modern business world, offering flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. This innovative approach enables organizations to access and utilize various services, such as software, platforms, and infrastructure, on a subscription or demand basis. By embracing the ‘as-a-service’ model, businesses can streamline operations, reduce upfront costs, and enhance their ability to adapt to changing market conditions.
Key ‘As-a-Service’ Offerings in Today’s Digital Landscape
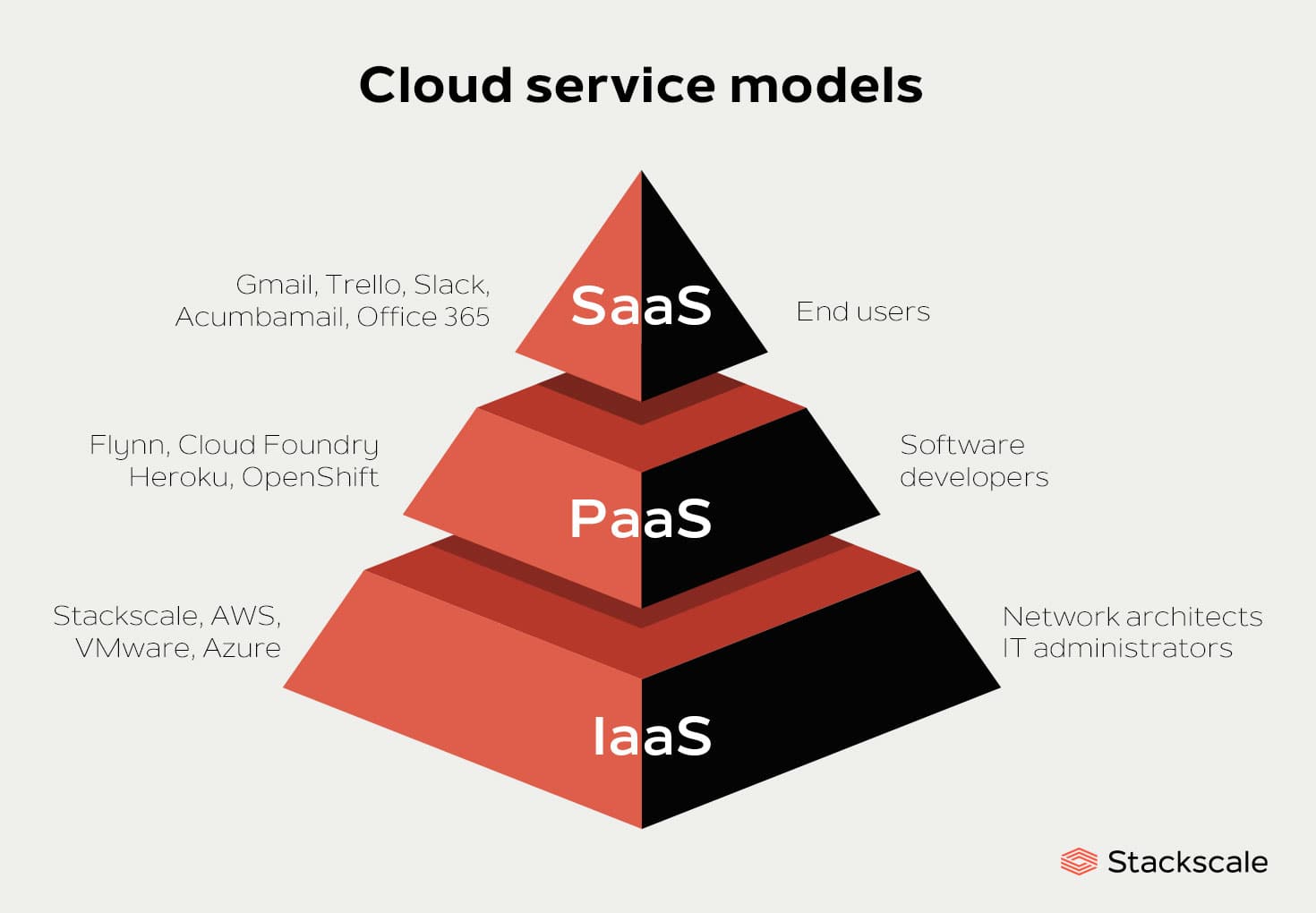
The ‘as-a-service’ model encompasses a wide range of offerings designed to meet the diverse needs of modern businesses. Among the most popular ‘as-a-service’ models are Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS).
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) refers to cloud-based software applications that users can access via the internet. SaaS offerings include productivity tools, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and human resources management (HRM) solutions. Examples of successful SaaS companies include Salesforce, Microsoft 365, and Slack.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) provides a cloud-based platform for developers to build, test, and deploy applications. PaaS offerings simplify the development process by handling infrastructure management, allowing developers to focus on creating innovative solutions. Notable PaaS providers include Google App Engine, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, and Microsoft Azure.
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) delivers cloud-based computing resources, such as virtual machines, storage, and networking, on-demand. IaaS enables businesses to scale their infrastructure according to their needs, reducing capital expenditures and improving operational efficiency. Leading IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
How to Implement the ‘As-a-Service’ Model in Your Organization
Transitioning to an ‘as-a-service’ model requires careful planning and execution. By following these steps, businesses can successfully implement the ‘as-a-service’ model and enjoy its numerous benefits:
1. Assess Business Needs
Begin by evaluating your organization’s requirements, including current infrastructure, software, and platform capabilities. Identify areas where the ‘as-a-service’ model can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer experiences.
2. Select the Right Model
Choose the most suitable ‘as-a-service’ model based on your business needs. Consider factors such as cost, scalability, and security when selecting between SaaS, PaaS, or IaaS offerings.
3. Develop an Implementation Strategy
Create a detailed implementation plan, outlining the steps required to transition to the ‘as-a-service’ model. This may include training staff, configuring new systems, and integrating existing infrastructure with the new model.
4. Manage the Implementation Process
Appoint a dedicated project manager to oversee the implementation process. This individual should be responsible for monitoring progress, addressing issues, and ensuring that the transition is completed on time and within budget.
5. Evaluate and Optimize
After implementing the ‘as-a-service’ model, regularly assess its performance and make adjustments as needed. Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and utilize analytics tools to measure the success of your implementation and identify areas for improvement.
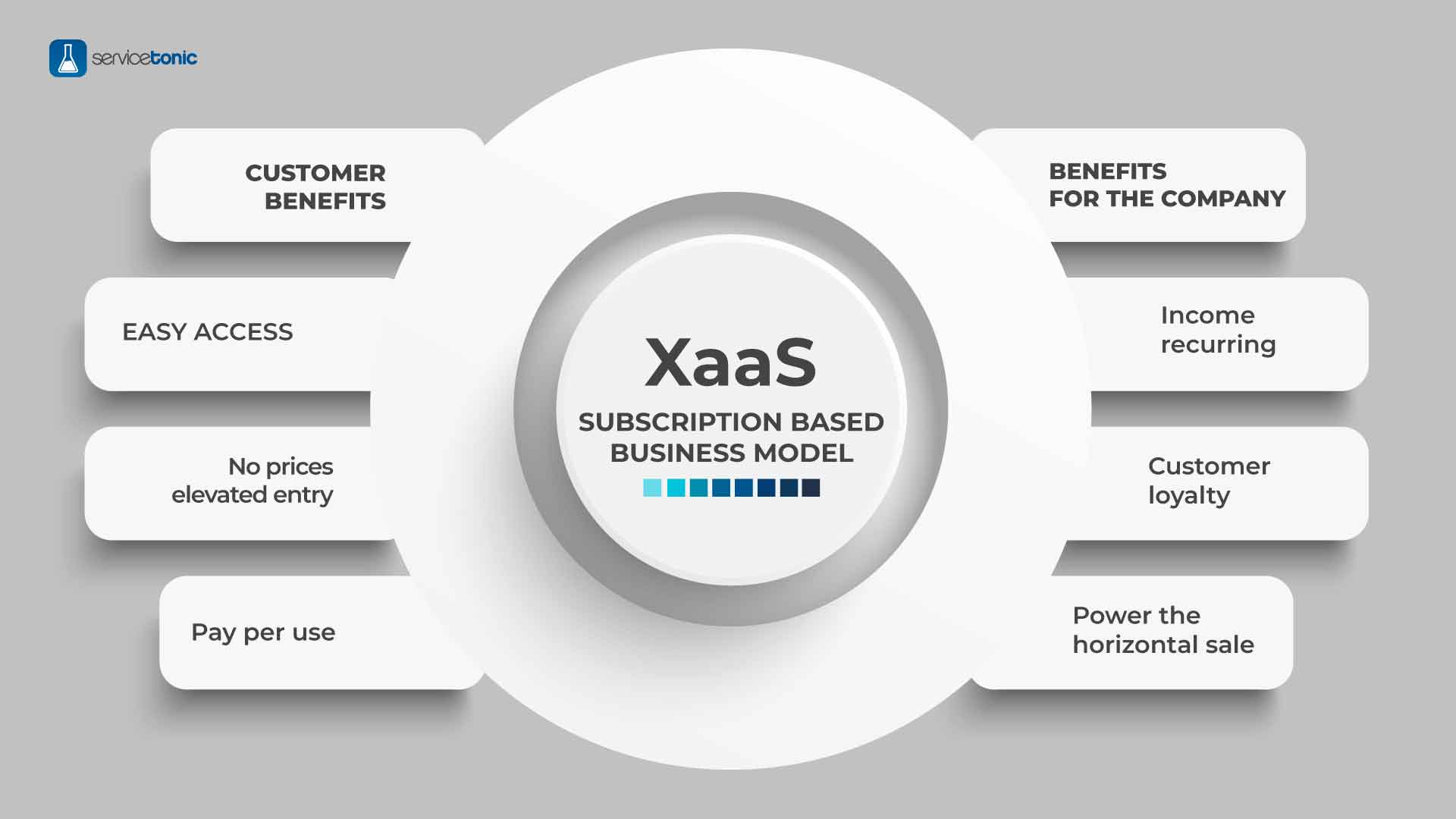
Benefits of Adopting the ‘As-a-Service’ Model
Transitioning to an ‘as-a-service’ model can bring numerous advantages to modern businesses. By embracing this approach, organizations can enhance their operations, reduce costs, and improve customer experiences. Some of the key benefits of the ‘as-a-service’ model include:
1. Increased Efficiency
The ‘as-a-service’ model enables businesses to streamline their processes and reduce the time spent on managing infrastructure, software, and platforms. This increased efficiency allows organizations to focus on their core competencies and deliver better services to their customers.
2. Reduced Costs
By utilizing the ‘as-a-service’ model, businesses can lower their capital and operational expenses. Instead of investing in expensive hardware, software, and maintenance, organizations can pay for only the resources they need, reducing overall costs and improving their bottom line.
3. Improved Customer Experiences
The ‘as-a-service’ model allows businesses to provide their customers with more personalized, responsive, and reliable services. By leveraging the power of cloud-based solutions, organizations can quickly adapt to changing customer needs and preferences, ensuring a positive user experience.
4. Scalability and Flexibility
The ‘as-a-service’ model offers businesses the ability to scale their resources up or down according to demand. This flexibility enables organizations to respond quickly to market changes, seize new opportunities, and maintain a competitive edge in their industry.
5. Enhanced Security
Reputable ‘as-a-service’ providers invest heavily in security measures to protect their customers’ data and systems. By partnering with these providers, businesses can benefit from advanced security features, reducing the risk of data breaches and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing the ‘As-a-Service’ Model
While the ‘as-a-service’ model offers numerous benefits, organizations may face certain challenges during implementation. Addressing these challenges proactively can help ensure a smooth transition and maximize the value of the ‘as-a-service’ model. Some common obstacles and solutions include:
1. Data Security Concerns
Businesses may worry about the security of their data when transitioning to an ‘as-a-service’ model. To mitigate this concern, organizations should carefully evaluate potential providers, ensuring they have robust security measures in place and are compliant with relevant data protection regulations.
2. Integration Issues
Integrating ‘as-a-service’ solutions with existing systems can be challenging. To overcome this hurdle, businesses should work closely with their service providers to develop a customized integration plan that addresses their unique needs and requirements.
3. Staff Training and Adaptation
Employees may require training to effectively use ‘as-a-service’ solutions. Providing comprehensive training programs and ensuring staff understand the benefits of the ‘as-a-service’ model can help ease the transition and improve user adoption.
4. Vendor Lock-In
Organizations may become overly dependent on a single ‘as-a-service’ provider, making it difficult to switch to a different vendor in the future. To avoid vendor lock-in, businesses should ensure they have the flexibility to migrate to alternative providers if needed and maintain a competitive landscape when negotiating contracts.
5. Cost Management
Managing costs can be challenging when transitioning to an ‘as-a-service’ model, as businesses may incur unexpected expenses. To prevent this, organizations should develop a detailed cost management plan, outlining potential expenses and establishing budgetary guidelines.
The Future of the ‘As-a-Service’ Model
The ‘as-a-service’ model is continuously evolving, with new trends and advancements shaping its future. Some of the most exciting developments in the ‘as-a-service’ landscape include:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML technologies are increasingly being integrated into ‘as-a-service’ offerings, enabling businesses to automate processes, analyze data more effectively, and make more informed decisions. AI-powered SaaS solutions can help organizations improve customer support, sales, and marketing efforts, while ML-driven PaaS and IaaS platforms can enhance data analytics and predictive modeling capabilities.
2. Internet of Things (IoT)
The proliferation of IoT devices is driving the demand for ‘as-a-service’ models capable of managing and analyzing the vast amounts of data generated by these devices. IoT-focused ‘as-a-service’ solutions can help businesses optimize their operations, improve asset management, and create new revenue streams.
3. Edge Computing
As IoT devices become more prevalent, the need for edge computing is growing. Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving performance. ‘As-a-service’ providers are beginning to offer edge computing solutions, enabling businesses to take full advantage of IoT technologies and improve their overall efficiency.
4. Blockchain
Blockchain technology is gaining traction in various industries, and ‘as-a-service’ providers are starting to explore its potential. Blockchain-based ‘as-a-service’ solutions can help organizations enhance security, improve transparency, and streamline processes, particularly in sectors such as finance, supply chain management, and healthcare.
5. Serverless Computing
Serverless computing is an emerging ‘as-a-service’ trend that enables businesses to build and run applications without managing servers. This approach allows organizations to focus on application development, reduce costs, and improve scalability.
Assessing the Success of Your ‘As-a-Service’ Model Implementation
Measuring the success of your ‘as-a-service’ model implementation is crucial for ensuring that your organization is reaping the benefits of this modern business approach. By monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) and utilizing analytics tools, you can evaluate the effectiveness of your ‘as-a-service’ strategy and make data-driven decisions to optimize performance. Here are some steps to help you assess the success of your ‘as-a-service’ model implementation:
1. Define Success Metrics
Begin by establishing clear success metrics that align with your business objectives. These KPIs may include increased efficiency, reduced costs, improved customer experiences, or enhanced security. Ensuring that your success metrics are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) will help you accurately track your progress and identify areas for improvement.
2. Utilize Analytics Tools
Leverage analytics tools to monitor your ‘as-a-service’ model implementation’s performance. These tools can help you track KPIs, identify trends, and gain insights into user behavior. By analyzing this data, you can make informed decisions to optimize your ‘as-a-service’ strategy and maximize its benefits.
3. Regularly Review and Adjust
Periodically review your KPIs and adjust your ‘as-a-service’ strategy as needed. This iterative approach will help you stay agile and responsive to changing business needs and market conditions. Regularly evaluating your success metrics will also enable you to identify potential issues early and address them proactively, ensuring the long-term success of your ‘as-a-service’ model implementation.
4. Seek Feedback
Solicit feedback from stakeholders, including employees, customers, and partners, to gain a holistic view of your ‘as-a-service’ model implementation’s success. This feedback can help you identify areas for improvement, refine your strategy, and ensure that your ‘as-a-service’ model is meeting the needs of all involved parties.
Case Studies: Successful ‘As-a-Service’ Model Implementations
Exploring real-life examples of successful ‘as-a-service’ model implementations can provide valuable insights and best practices for organizations considering this modern business approach. Here, we share two case studies that highlight the benefits and successes of transitioning to an ‘as-a-service’ model.
1. Company A: Streamlining Operations with SaaS
Company A, a mid-sized manufacturing firm, adopted a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model to manage its human resources and finance operations. By implementing a cloud-based SaaS solution, Company A was able to streamline its processes, reduce manual data entry, and improve data accuracy. The SaaS model also offered greater scalability and flexibility, enabling the company to easily add or remove users as needed. As a result, Company A experienced a 20% increase in operational efficiency and a 15% reduction in costs associated with HR and finance management.
2. Company B: Enhancing Customer Experiences with PaaS
Company B, a large e-commerce retailer, utilized a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) model to develop and deploy a custom mobile application. The PaaS solution allowed Company B to quickly and easily create a user-friendly mobile experience, which led to a 30% increase in customer engagement and a 25% boost in sales. Additionally, the PaaS model provided Company B with the tools and resources needed to continuously update and improve the application, ensuring a positive and seamless customer experience.
These case studies demonstrate the potential benefits and successes of adopting an ‘as-a-service’ model. By carefully assessing business needs, selecting the right model, and managing the implementation process, organizations can reap the rewards of increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved customer experiences. Furthermore, monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) and utilizing analytics tools can help organizations measure the success of their ‘as-a-service’ model implementation and make data-driven decisions to optimize performance.